Abstract
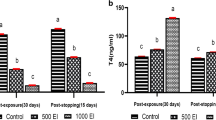
The effect of hexachlorobenzene (HCB) (1 g/kg bw) administration for 4 weeks, on thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) metabolism was studied in Wistar rats. The effect on serum binding of T4 has also been studied. Animals were injected with a tracer dose of either labeled hormone and by examining serum L-125I-T4 and L-125-I-T3, kinetics of radiolabeled hormones metabolism were calculated. The T4 metabolic clearance (MCI) as well as the distribution space, were increased by 6 fold. Decreased serum T4 levels result from an increase both in deiodinative and fecal disposal in HCB-treated rats. 125I-T3 metabolism was slightly affected. The enhanced peripheral disposition of thyroxine appears to lead to increased thyroid function, as measured by augmented TSH serum levels and 125I-thyroidal uptake. Serum binding of T4 was not affected.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barsano C.P. Environmental factors altering thyroid function and their assessment. Environ. Health Perspect. 38: 71, 1981.
Cavalieri R.R., Pitt-Rivers R. The effects of drugs on the distribution and metabolism of thyroid hormones. Pharmacol. Rev. 33: 55, 1981.
United States Environmental Protection Agency Health Assessment Document for chlorinated benzenes, EPA/600/8-84/015F, 1985.
Cabrai J.R.P., Shubik P. Carcinogenic activity of hexachlorobenzene in mice and hamsters. In: Morris, C.R. and Cabrai, J.R.P. (Eds.), Hexachlorobenzene: Proceedings of an international symposium. IARC Scientific Publications, Lyon, 1986, No 77, p. 411.
Cabrai J.R., Shubik P., Moller T., Ractano F. Carcinogenic activity of hexachlorobenzene in hamsters. Nature 269: 510, 1977.
Cripps D.J., Peters H.A., Gocmen A., Doqramaci I. Porphyria Turcica due to hexachlorobenzene: a 20 to 30 year follow-up study on 204 patients. Br. J. Dermatol. 111: 413, 1984.
Collins W.T., Capen C.C., Kasza L., Carter C., Dailey R.E. Effect of polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) on the thyroid gland of rats. Am. J. Pathol. 89: 119, 1977.
Rozman K., Gorski J.R., Rozman P., Parkinson A. Reduced serum thyroid hormone levels in hexacloro-benzene induced porphyria. Toxicology Lett. 30: 71, 1986.
Grupta B.N., Mc Connell E.E., Goldstein J.A., Harris M.W., Moore J.A. Effect of a polybrominated biphenyl mixture in the rat and mouse. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 68: 1, 1983.
Rall J.E., Robbins J., Lewallen C.G. The thyroid. In: Pincus G., Thimann K.V., Astwood E.B. (Eds.), The Hormones. Academic Press Inc., New York, 1964, vol. 5, p. 159.
Oppenheimer J.H., Schwartz H.C., Shapiro H.G., Bernstein G., Surks M.I. Differences in primary cellular factors influencing the metabolism and distribution of 3,5,3′-L-triiodothyronine and L-thyroxine. J. Clin. Invest. 49: 1016, 1970.
Boado R., Ulloa E., Zaninovich A.A. Reciprocal effects of an acute load of thyroxine or triiodothyronine on their peripheral metabolism and deiodination in the cold-acclimated rat. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 5: 217, 1982.
Oppenheimer J.H., Bernstein G., Surks M.I. Increased thyroxine turnover and thyroidal function after stimulation of hepto-cellular binding of thyroxine by phenobarbital. J. Clin. Invest. 47: 1399, 1968.
Rozman K., Gorski J.R., Rozman P., Parkinson A. Reduced serum thyroid hormone levels in hexachlorobenzene induced porphyria. Toxicology Lett. 30: 71, 1986.
San Martín de Viale L.C., Tomio J.M., Ferramola de Sancovich A.M., Sancovich H.A., Tigier H.A. Experimental porphyria induced in rats by hexachlorobenzene. Studies on enzymes associated with haem pathway. Effect of 17 ß oestradiol. In: Doss M., Marburg A.D. Lahn, Karger S. (Eds.), Porphyrins in Human Diseases. 1st Int. Porphyrin Meet, 1975 Basel, München, Paris-London. New York. Sydney, 1976, p. 453.
Newman W.C., Fernández R.C., Slayden R.M., Moon R.C. Accelerated biliary thyroxine secretion in rats treated with 3-methylcholantrene (36015). Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 138: 899, 1971.
Newman W.C., Moon R.C. Altered thyroxine metabolism resulting from the chemical carcinogen 3-methylcholantrene. Endocrinology 80: 896, 1967.
Bastomsky C.H. Enhanced thyroxine metabolism and high uptake goiters in rats after a single dose of 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Endocrinology 101: 292, 1977.
Lucier G.W., McDaniel O.C., Hook G.E.R. Nature of the enhancement of hepatic uridine diphosphate glucuronyltransferase activity by 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in rats. Biochem. Pharmacol. 24: 325, 1975.
Bastomsky C.H., Murthy P.V.N. Enhanced “in vitro” hepatic glucuronidation of T4 in rats following cutaneous application or ingestion of polychlorinated biphenyls. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 54: 23, 1976.
Nikolaev V., Naydenova E., Kerimova M., Dimov S., Ivanov E. Rat liver plasma membrane damage in hexachloro-benzene intoxication and its potentiation by ethanol. Toxicology Lett. 32: 269, 1986.
Cullen J.M., Doherty G.F., Ingbar S.H. The effect of hypothyroidism and thyrotoxicosis on thyroxine metabolism in the rat. Endocrinology 92: 1028, 1973.
Gómez Catalán J., To-Figueras J., Planas J., Rodamilans M., Corbella J. Pentachlorophenol and hexachlorobenzene in serum and urine of the population of Barcelona. Human Toxicol. 6: 397, 1987.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Career Scientific Researchers in CONICET (Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Pisarev, D.L.K., Sancovich, H.A. & de Sancovich, A.M.F. Enhanced thyroxine metabolism in hexachlorobenzene-intoxicated rats. J Endocrinol Invest 12, 767–772 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03350056
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03350056