Abstract
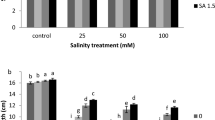
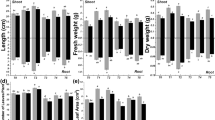
Transpiration rate, stomatal frequency, growth, contents of pigments, saccharides, total nitrogen, proteins and some nutritive elements (K, Ca, Mg, P) of radish plants were significantly lowere dwith the rise in salinization levels using NaCl. Spraying radish shoots with proline solution (200 g m-3) counteracted the above adverse effects, especially at low and moderate salinity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, A. M. Heikal, M. M., Zidan, M. A.: Effects of salinization treatments on growth and some related physiological activities of some leguminous plants. - Can. J. Plant Sci.60: 713–720. 1980.
Barnett, N. M., Naylor, A. W.: Amino acids and protein metabolism in Bermuda grass during water stress. - Plant Physiol.41: 1222–1230, 1966.
Bar-Nun, N., Poljakoff-Mayber, A.: Salinity stress and the content of proline in root ofPisum sativum andTamarix retragyna. - Ann. Bot. 41: 173–179, 1977.
Bates, L. S., Waldren, R. P., Teare, I. D.: Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Short communication. - Plant Soil39: 205–207, 1973.
Bozcuk, S.: Effect of sodium chloride upon growth and transpiration inStatice sp. andPisum sativum L. - Proc. Third Meeting (Izmir): 37–42, 1975.
Fales, F. W.: The assimilation and degradation of carbohydrates of yeast cells. - J. biol. Chem.193:113–118, 1951.
Handa, S., Bressan, R. A., Handa, A. K., Carpita, N. S., Husegawa, P. M.: Solutes contributing to osmotic adjustment in cultured plant cells adapted to water stress.-Plant Physiol.73: 834–843, 1983.
Hedge, B. A., Joshi, G. C.: Mineral salt absorption in saline rice variety Kala rata. - Plant Soil41: 421–424, 1974.
Heikal, M. M., Shaddad, M. A.: Alleviation of osmotic stress on seed germination and seedling growth of cotton, pea and wheat by proline. - Phyton (Aust.)22: 275–287, 1982.
Huang, A. H. S., Cavalieri, A. J.: Proline oxidase and water stress-induced proline accumulation in spinach leaves. - Plant Physiol.63: 531–535, 1979.
Janardan, K. V., Murtay, K., Girira, J., Panchaksharais, S.: Salt tolerance of cotton and potential use of saline water for irrigation. - Curr. Sci.45: 334–336, 1976.
LaHaye, P. A., Epstein, E.: Calcium and salt tolerance by bean plants. - Physiol. Plant.25:213–218, 1971.
Lowry, C. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., Randall, R. J.: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. - J. biol. Chem.193: 265–275, 1951.
Meiri, A., Poljakoff-Mayber, A.: Effects of various salinity regions on growth, leaf expansion and transpiration rate of bean plants. - Soil Sci.109: 26–36, 1970.
Metzner, H., Rau, H. Senger, H.: Untersuchungen zur Synchronisierbarkeit einzelner Pigment-Mangel Mutanten von Chlorella. - Planta65: 186–194, 1965.
Moore, S., Stein, W. H.: Photometric ninhydrin method for use in the chromatography of amino acids. - J. biol. Chem.176: 367–388, 1948.
Munns, R., Greenway, H., Delane, R., Gibbs, J.: Ion concentration and carbohydrate status of the elongating leaf tissue ofHordeum vulgare growing at high external NaCl. II. Cause of the growth reduction. - J. exp. Bot.33: 574–583, 1982.
Palfi, G., Juhasz, J.: The theoretical basis and practical application of a new method of selection for determining water deficiency. - Plant Soil34: 503–507, 1971.
Schwarzenbach, G., Biederman, W.: Komplexone X. Erdalkalikomplexe von 0, 6-Dioxy-azo-Farbstoffen. - Helv. chim. Acta31: 678–687, 1948.
Singh, T. N., Aspinall, D., Paleg, L. G.: Stress metabolism 1. Nitrogen metabolism and growth in the barley plant during water stress. - Aust. J. biol. Sci.26: 45–56, 1973.
Stewart, C. R., Lee, J. A.: The role of proline accumulation in halophytes. - Planta120: 279–289, 1974.
Stewart, C. R., Morris, C. J., Thompson, J. F.: Changes in amino acid content of excised leaves during incubation. II-Role of sugar in the accumulation of proline in wilted leaves. - Planta120: 279–289, 1974.
Thakur, P. S., Rai, V. K.: Exogenously supplied amino acids and water deficits in Zea mays cultivars. - Biol. plant.27: 458–461, 1985.
Watson, D. J., Watson, M. A.: Studies in potatoes agronomy. 1. Effect of variety seed size and spacing on growth, development and yield. - J. agr. Sci.66: 241–249, 1933.
Williams, V., Twine, S.: Flame photometric method for sodium, potassium and calcium. - In:Paech, K., Tracey, M. V. (ed.): Modern Methods of Plant Analysis. Vol. V. Pp. 3–5. Springer-Verlag, Berlin 1960.
Woods, J. T., Mellon, M. G.: Chlorostannous-reduced molybdophosphoric blue color in sulfuric acid system. - In:Jackson, M. L. (ed.): Soil Chemical Analysis. Pp. 141–144. Prentice-Hall International, London 1941.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shaddad, M.A. The effect of proline application on the physiology ofraphanus sativus plants grown under salinity stress. Biol Plant 32, 104–112 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02897548
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02897548