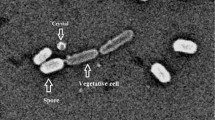
Abstract
Mosquitoes are great threat to human health as they transmit various dreadful diseases. Many strategies have been employed to control these mosquito vectors of public health importance. Synthetic chemical insecticides have been purposely used for several years for the eradication of such mosquito vectors. However, these synthetic chemicals detrimentally create many serious conditions like development of insecticide resistance in mosquito population, environmental pollution, cellular toxicity in mammals, adverse effects on beneficial insects, and other non-target organisms. Hence, use of biological agents has attracted attention as an alternative to chemical insecticides for the control of mosquito vectors. Among these, Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) seems to be the most important and successful microbiocontrol agent. Bacillus thuringiensis is a natural occurring, soil-borne bacteria that produces insecticidal proteins as parasporal crystals during its sporulation phase. These crystals are mainly comprised of one or more proteins, also called δ-endotoxins (Cry and Cyt toxins) which are very specific to the target insect but are safe to other non-target organisms. Upon ingestion by insect, δ-endotoxin gets cleaved, binds to the gut epithelium, and forms cation channels causing cell lysis and death. After the discovery of Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis, these bacteria are extensively used as biocontrol agents for the management of mosquito vector populations due to their distinctive evolutionary characteristics like synergism, combinational working mechanism, and counter-resistance effects. The present chapter emphasizes on Bt, its origin, classification, details of its active mosquitocidal compound (composition, structure, and function), factors affecting larvicidal activity, development of resistance in mosquitoes, effects on non-target organisms and the environment in general.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah MAF, Alzate O, Mohammad M, McNall RJ, Adang MJ, Dean DH (2003) Introduction of Culex toxicity into Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba by protein engineering. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:5343–5353
Afrane YA, Mweresa NG, Wanjala CL, Gilbreath TM III, Zhou G, Lee MC, Yan G (2016) Evaluation of long-lasting microbial larvicide for malaria vector control in Kenya. Malar J 15:577
Akiba Y (1991) Assessment of rainwater-mediated dispersion of field-sprayed Bacillus thuringiensis in soil. Jpn J Appl Entomol Z 26:477–483
Ali A (1981) Bacillus thuringiensis serovar israelensis (ABG-6108) against chironomids and some nontarget aquatic invertebrates. J Invertebr Pathol 38:264–272
Ali A, Sauerman DM, Nayar JK (1984) Pathogenicity of industrial formulations of Bacillus thuringiensis serovar. israelensis to larvae of some Culicine mosquitoes in the laboratory. Florida Entomol 67:193–197
Aly C (1988) Filter feeding of mosquito larvae (Diptera: Culicidae) in the presence of the bacterial pathogen Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis. J Appl Entomol 105:160–166
Aly C, Mulla MS, Bo-Zhao X, Schnetter W (1988) Rate of ingestion by mosquito larvae (Diptera: Culicidae) as a factor in the effectiveness of a bacterial stomach toxin. Med Entomol 25:191–196
Amer A, Mehlhorn H (2006a) Larvicidal effects of various essential oils against Aedes, Anopheles, and Culex larvae (Diptera, Culicidae). Parasitol Res 99:466–472
Amer A, Mehlhorn H (2006b) Persistency of larvicidal effects of plant oil extracts under different storage conditions. Parasitol Res 99:473–477
Angsuthanasombat C, Crickmore N, Ellar DJ (1992) Comparison of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis CryIVA and CryIVB cloned toxins reveals synergism in vivo. FEMS Microbiol Lett 94:63–68
Angsuthanasombat C, Uawithya P, Leetachewa S, Pornwiroon W, Ounjai P, Kerdcharoen T, Katzenmeier G, Panyim S (2004) Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4A and Cry4B mosquito-larvicidal proteins: Homology-based 3D model and implications for toxin activity. J Biochem Mol Biol 37:304–313
Aronson AI, Shai Y (2001) Why Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal toxins are so effective: Unique features of their mode of action. FEMS Microbiol Lett 195:1–8
Baumann L, Okamoto K, Unterman BM, Lynch MJ, Bauman P (1984) Phenotypic characterization of Bacillus thuringiensis and Bacillus cereus. J Invertebr Pathol 44:329–341
Becker N, Margalit J (1993) Use of Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis against mosquitoes and blackflies. In: Entwistle PF, Cory JS, Bailey MJ, Higgs S (eds) Bacillus thuringiensis, an environmental biopesticide: Theory and practice. John Wiley & Sons, New York, pp 147–170
Becker N, Zgomba M, Ludwig M, Petric D, Rettich F (1992) Factors influencing the activity of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis treatments. J Am Mosq Control Assoc 8:285–289
Beltrao HBM, Silva-Filha MHNL (2007) Interaction of Bacillus thuringiensis svar. israelensis cry toxins with binding sites from Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) larvae midgut. FEMS Microbiol Lett 266:163–169
Ben-Dov E (2014) Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis and its dipteran-specific toxins. Toxins 6:1222–1243
Ben-Dov E, Boussiba S, Zaritsky A (1995) Mosquito larvicidal activity of Escherichia coli with combinations of genes from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. J Bacteriol 177:2851–2857
Benelli G (2015) Plant-borne ovicides in the fight against mosquito vectors of medical and veterinary importance: A systematic review. Parasitol Res 114:3201–3212
Benelli G, Jeffries CL, Walker T (2016) Biological control of mosquito vectors: past, present, and future. Insects 7:52
Berry J, O’Neil S, Ben-Dov E, Jones AF, Murphy L, Quail MA, Holden MTG, Harris D, Zaritsky A, Parkhill J (2002) Complete sequence and organization of pBtoxis, the toxin-coding plasmid of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5082–5095
Blaustein L, Margalit J (1991) Indirect effects of the fairy shrimp, Branchipus schaefferi and two ostracod species on Bacillus thuringiensis var israelensis induced mortality in mosquito larvae. Hydrobiologia 212:67–73
Boisvert M, Boisvert J (1999) Persistence of toxic activity and recycling of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis in cold water: Field experiments using diffusion chambers in a pond. Biocontrol Sci Technol 9:507–522
Boisvert M, Boisvert J (2000) Effects of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis on target and nontarget organisms: A review of laboratory and field experiments. Biocontrol Sci Technol 10:517–561
Boisvert J, Lacoursière JO (2004) Le Bacillus thuringiensis et le contrôle des insectes piqueurs au Québec. ENV/2004/0278. Ministère de l’Environnement Québéquois, Québec, 101p
Boonserm P, Ellar DJ, Li J (2003) Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction studies of a mosquito larvicidal toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Acta Cryst D 59:591–594
Boonserm P, Davis P, Ellar DJ, Li J (2005) Crystal structure of the mosquito-larvicidal toxin Cry4Ba and its biological implications. J Mol Biol 348:363–382
Boonserm P, Mo M, Angsuthanasombat C, Lescar J (2006) Structure of the functional form of the mosquito larvicidal Cry4Aa toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis at a 2.8-angstrom resolution. J Bacteriol 188:3391–3401
Bourgouin C, Klier A, Rapoport G (1986) Characterization of the genes encoding the haemolytic toxin and mosquitocidal δ-endotoxin of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis. Mol Gen Genet 205:390–397
Brady OJ, Gething PW, Bhatt S, Messina JP, Brownstein JS, Hoen AG (2012) Refining the global spatial limits of dengue virus transmission by evidence-based consensus. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 6:e1760
Bravo A, Gill SS, Soberón M (2005) Comprehensive molecular insect science. In: Bacillus thuringiensis mechanisms and use. Elsevier BV, Amsterdam, pp 175–206
Bravo A, Gill SS, Soberón M (2007) Mode of action of Bacillus thuringiensis cry and Cyt toxins and their potential for insect control. Toxicon 49:423–435
Burges HD (1981) Safety, safety testing and quality control of microbial pesticides. Microbial control of pests and plant diseases. Academic Press Inc, London, pp 738–768
Burke WF Jr, McDonald KO, Davidson EW (1983) Effect of UV light on spore viability and mosquito larvicidal activity of Bacillus sphaericus 1593. Appl Environ Microbiol 46:954–956
Butko P (2003) Cytolytic toxin Cyt1A and its mechanism of membrane damage: Data and hypotheses. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:2415–2422
Butko P, Huang F, Pusztai-Carey M, Surewicz WK (1996) Membrane permeabilization induced by cytolytic δ-endotoxin CytA from Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis. Biochemistry 35:11355–11360
Butko P, Huang F, Pusztai-Carey M, Surewicz WJ (1997) Interaction of the delta-endotoxin CytA from Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis with lipid membranes. Biochem 36:12862–12868
Buzdin AA, Revina LP, Kostina LI, Zalunin IA, Chestukhina GG (2002) Interaction of 65- and 62-kD proteins from the apical membranes of the Aedes aegypti larvae midgut epithelium with Cry4B and Cry11A endotoxins of Bacillus thuringiensis. Biochemistry 67:540–546
Canton PE, Lopez-Diaz JA, Gill SS, Bravo A, Soberon M (2014) Membrane binding and oligomer membrane insertion are necessary but insufficient for Bacillus thuringiensis Cyt1Aa toxicity. Peptides 53:286–291
Carlson CR, Kolsto AB (1993) A complete physical map of a Bacillus thuringiensis chromosome. J Bacteriol 175:1053–1060
Chang C, Yu YM, Dai SM, Law SK, Gill SS (1993) High-level cryIVD and cytA gene expression in Bacillus thuringiensis does not require the 20-kilodalton protein, and the coexpressed gene products are synergistic in their toxicity to mosquitoes. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:815–821
Chayaratanasin P, Moonsom S, Sakdee S, Chaisri U, Katzenmeier G, Angsuthanasombat C (2007) High level of soluble expression in Escherichia coli and characterisation of the cloned Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba domain III fragment. J Biochem Mol Biol 40:58–64
Chen SF, Xiao TC, Lu JF (1984) A study of the toxicity of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis to mosquito larvae and factors affecting it. Nat Enemies Insects Kunchong Tiandi 6:115–117
Chen J, Aimanova KG, Fernandez LE, Bravo A, Soberon M, Gill SS (2009a) Aedes aegypti cadherin serves as a putative receptor of the Cry11Aa toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Biochem J 424:191–200
Chen J, Aimanova KG, Pan S, Gill SS (2009b) Identification and characterization of Aedes aegypti aminopeptidase N as a putative receptor of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry11A toxin. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 39:688–699
Chen J, Likitvivatanavong S, Aimanova KG, Gill SS (2013) A 104 kDa Aedes aegypti aminopeptidase N is a putative receptor for the Cry11Aa toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Insect Biochem. Molec Biol 43:1201–1208
Christiansen JA, McAbee RD, Stanich MA, DeChant P, Boronda D, Cornel J (2004) Influence of temperature and concentration of VectoBacH on control of the salt-marsh mosquito, Ochlerotatus squamiger, in Monterey County, California. J Am Mosq Control Assoc 20:165–170
Claus D, Berkeley RCW (1986) Genus bacillus Cohn 1872. In: Sneath PHA, Mair NS, Sharp ME, Holt JG (eds) Beghey's manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 2. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 1105–1139
Cohen S, Dym O, Albeck S, Ben-Dov E, Cahan R, Firer M, Zaritsky A (2008) High-resolution crystal structure of activated Cyt2Ba monomer from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. J Mol Biol 380:820–827
Cohen S, Albeck S, Ben-Dov E, Cahan R, Firer M, Zaritsky A, Dym O (2011) Cyt1Aa toxin: Crystal structure reveals implications for its membrane-perforating function. J Mol Biol 413:804–814
Crickmore N (2005) Using worms to better understand how Bacillus thuringiensis kills insects. Trends Microbiol 13:347–350
Crickmore N, Bone EJ, Williams JA, Ellar DJ (1995) Contribution of the individual components of the δ-endotoxin crystal to the mosquitocidal activity of Bacillus thuringiensissubsp. israelensis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 131:249–254
Crickmore N, Zeigler DR, Feitelson J, Schnepf E, Van Rie J, Lereclus D, Baum J, Dean DH (1998) Revision of the nomenclature for the Bacillus thuringiensis pesticidal crystal proteins. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:807–813
Crickmore N, Baum J, Bravo A, Lereclus D, Narva K, Sampson K, Schnepf E, Sun M, Zeigler D (2017) Bacillus thuringiensis toxin nomenclature. [online] Available at: Accessed 20 Jan 2017
Chowanadisai L (1998) Factors influencing the larvicidal activity of bacterial toxin. Indian J. Malariol. 35:117–122
Dai SM, Gill SS (1993) In vitro and in vivo proteolysis of the Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis CryIVD protein by Culex quinquefasciatus larval midgut proteases. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 23:273–283
Davidson EW (1981) A review of the pathology of bacilli infecting mosquitoes, including an ultrastructural study of larvae fed Bacillus sphaericus 1593 spores. Dev Ind Microbiol 22:69–81
de Barjac H, Bonnefoi A (1962) Essai de classification biochimique et sérologique de 24 souches de Bacillus de type thuringiensis. Entomophaga 7:5–31
de Maagd RA, Bravo A, Berry C, Crickmore N, Schnepf HE (2003) Structure, diversity and evolution of protein toxins from spore-forming entomopathogenic bacteria. Annu Rev Genet 37:409–433
de Respinis S, Demarta A, Patocchi N, Luthy P, Peduzzi R (2006) Molecular identification of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis to trace its fate after application as a biological insecticide in wetland ecosystems. Lett Appl Microbiol 43:495–501
Delecluse A, Bourgouin C, Klier A, Rapoport G (1988) Specificity of action on mosquito larvae of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis toxins encoded by two different genes. Mol Gen Genet 214:42–47
Delecluse A, Poncet S, Klier A, Rapoport G (1993) Expression of cryIVA and cryIVB genes, independently or in combination, in a crystal-negative strain of Bacillus thuringiensis subs. israelensis. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:3922–3927
DeLucca AJ II, Simonson JG, Larson AD (1981) Bacillus thuringiensis distribution in soils of the United States. Can J Microbiol 27:865–870
DeMelo-Santos MAV, Sanches EG, de Jesus FJ, Regis L (2001) Evaluation of a new tablet formulation based on Bacillus thuringiensis serovar israelensis for larvicidal control of Aedes aegypti. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 96:859–860
Derbyshire DJ, Ellar DJ, Li J (2001) Crystallization of the Bacillus thuringiensis toxin Cry1Ac and its complex with the receptor ligand N-acetyl-d-galactosamine. Acta Crystallogr Sect D 57:1938–1944
Faust RM (1975) Toxins of Bacillus thuringiensis: Mode of action. In: Biological regulation of vectors - a conference report. U.S. Govt. Printing Office, Washington, D.C, pp 31–48
Federici AB (1995) The future of microbial insecticides as vector control agents. J Am Mosq Control Assoc 11:260–269
Federici BA, Ibarra JE, Padua LE, Gallart NJ, Sivasubramanian N (1987) Parasporal body of mosquitocidal subspecies of Bacillus thuringiensis. In: Maramorosch K (ed) Biotechnology in invertebrate pathology and cell culture. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, pp 115–131
Federici BA, Park HW, Bideshi DK, Wirth MC, Johnson JJ (2003) Recombinant bacteria for mosquito control. J Exp Biol 206:3877–3885
Federici BA, Park HW, Bideshi DK (2010) Overview of the basic biology of Bacillus thuringiensis with emphasis on genetic engineering of bacterial larvicides for mosquito control. Open Toxinol J 3:83–100
Feldmann F, Dullemans A, Waalwijk C (1995) Binding of the CryIVD toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis to larval dipteran midgut proteins. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:2601–2605
Fernandez LE, Perez C, Segovia L, Rodriguez MH, Gill SS, Bravo A, Soberon M (2005) Cry11Aa toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis binds its receptor in Aedes aegypti mosquito larvae through loop α-8 of domain II. FEBS Lett 579:3508–3514
Fernandez LE, Aimanova KG, Gill SS, Bravo A, Soberón M (2006) A GPI-anchored alkaline phosphatase is a functional midgut receptor of Cry11Aa toxin in Aedes aegypti larvae. Biochem J 394:77–84
Fernandez-Luna MT, Lanz-Mendoza H, Gill SS, Bravo A, Soberon M, Miranda-Rios J (2010) An α-amylase is a novel receptor for Bacillus thuringiensis ssp. israelensis Cry4Ba and Cry11Aa toxins in the malaria vector mosquito Anopheles albimanus (Diptera: Culicidae). Environ Microbiol 12:746–757
Frutos R, Rang C, Royer M (1999) Managing insect resistance to plants producing Bacillus thuringiensis toxins. Critical Rev Biotech 19:227–276
Galitsky N, Cody V, Wojtczak A, Ghosh D, Luft JR, Pangborn W, English L (2001) Structure of the insecticidal bacterial δ-endotoxin Cry3Bb1 of Bacillus thuringiensis. Acta Crystallogr Sect D 57:1101–1109
Garcia R, Desrochers B, Tozer W (1981) Studies on Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis against mosquito larvae and other organisms. UNDP/World Bank/WHO, New York/Washington, D.C/Geneva. 16 pp. #790197
Garguno F, Thorne L, Walfield AM, Pollock TJ (1988) Structural relatedness between mosquitocidal endotoxins of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:277–279
Georghiou GP, Wirth MC (1997) Influence of exposure to single versus multiple toxins of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis on development of resistance in the mosquito Culex quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae). Appl Environ Microbiol 63:1095–1101
Gill SS, Singh GJ, Hornung JM (1987) Cell membrane interaction of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis cytolytic toxins. Infect Immun 55:1300–1308
Goldberg LJ (1979) Mosquito larvae control using a bacterial larvicide. US Patent 4:112
Goldberg LJ, Margalit J (1977) A bacterial spore demonstrating rapid larvicidal activity against Anopheles sergentii, Uranotaenia unguiculata, Culex univitattus, Aedes aegypti and Culex pipiens. Mosq News 37:355–358
Grochulski P, Masson L, Borisova S, Pusztai-Carey M, Schwartz JL, Brousseau R, Cygler M (1995) Bacillus thuringiensis CryIA(a) insecticidal toxin: Crystal structure and channel formation. J Mol Biol 254:447–464
Guerchicoff A, Ugalde R, Rubinstein CP (1997) Identification and characterization of a previously undescribed cyt gene in Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:2716–2721
Guo SY, Ye S, Liu YF, Wei L, Xue J, Wu HF, Song FP, Zhang J, Wu XA, Huang DF, Rao Z (2009) Crystal structure of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry8Ea1: An insecticidal toxin toxic to underground pests, the larvae of Holotrichia parallela. J Struct Biol 168:259–266
Habib MEM, Andrade CFS (1998) Bactérias entomopatogênicas. In: Alves SB (ed) Controle microbiano de insetos. FEALQ, Piracicaba, pp 383–446
Hannay CL (1953) Crystalline inclusion in aerobic spore forming bacteria. Nature 172:1004
Hannay CL, Fitz-James P (1955) The protein crystals of Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner. Can J Microbiol 1:694–710
Hansen BM, Salamitou S (2000) Virulence of Bacillus thuringiensis. In: Charles JF, Delecluse A, Nielsen-Le Roux C (eds) Entomopathogenic bacteria: From laboratory to field application. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 41–44
Hansen BM, Damgaard PH, Eilenberg J, Pedersen JC (1998) Molecular and phenotypic characterization of Bacillus thuringiensis isolated from leaves and insects. J Invertebr Pathol 71:106–114
He LS, Ong KH (2000) Effects of Bacillus thuringiensis H-14 on bloodworms (Diptera: Chironomidae). Singap J Prim Ind 28:7–12
Helgason E, Caugant DA, Lecadet M-M, Chen Y, Mahillon J, Lovgren A, Hegna I, Kvaloy K, Kolsto AB (1998) Genetic diversity of Bacillus cereus, B. thuringiensis isolates from natural sources. Curr Microbiol 37:80–87
Hemingway J, Ranson H (2000) Insecticide resistance in insect vectors of human disease. Ann Rev Entomol 45:371–391
Hernandez-Soto A, Del Rincon-Castro MC, Espinoza AM, Ibarra JE (2009) Parasporal body formation via overexpression of the Cry10Aa toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis, and Cry10Aa-Cyt1Aa synergism. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:4661–4667
Hilmy NM, Merdan AI (1985) Larvicidal activity of Bacillus thuringiensis serotype H-14 on certain Egyptian mosquito species. J Egypt Soc Parasitol l5:263–27l
Hofte H, Whiteley HR (1989) Insecticidal crystal proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis. Microbiol Rev 53:242–255
Howlader MTH, Kagawa Y, Sakai H, Hayakawa T (2009) Biological properties of loop-replaced mutants of Bacillus thuringiensis mosquitocidal Cry4Aa. J Biosci Bioeng 108:179–183
Howlader MTH, Kagawa Y, Miyakawa A, Yamamoto A, Taniguchi T, Hayakawa T, Sakai H (2010) Alanine scanning analyses of the three major loops in domain II of Bacillus thuringiensis mosquitocidal toxin Cry4Aa. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:860–865
Hui F, Scheib U, Hu Y, Sommer RJ, Aroian RV, Ghosh P (2012) Structure and glycolipid binding properties of the nematicidal protein Cry5B. Biochemistry 51:9911–9921
Ibrahim AM, Griko N, Junker M, Lee A (2010) Bacillus thuringiensis a genomics and proteomics perspective. Bulla Bioeng Bugs 1:31–50
Ishiwata S (1901) On a kind of severe flacherie (sotto disease). Dainihon Sanshi Kaiho 114:1–5
Jacobs SE (1950) Bacteriological control of the flour moth Ephestia kuehniella. Proc Soc Apply Bacteriol 13:83–91
Jouzani GS, Seifinejad A, Saeedizadeh A (2008) Molecular detection of nematicidal crystalliferous Bacillus thuringiensis strains of Iran and evaluation of their toxicity on free-living and plant-parasitic nematodes. Can J Microbiol 54:812–822
Juarez-Perez GA, Rubinstein C, Delécluse A (2002) Characterization of Cyt2Bc toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. medellin. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1228–1231
Khasdan V, Ben-Dov E, Manasherob R, Boussiba S, Zaritsky A (2001) Toxicity and synergism in transgenic Escherichia coli expressing four genes from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Environ Microbiol 3:798–806
Knowles BH (1994) Mechanism of action of Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal δ-endotoxins. Adv Insect Physiol 24:275–308
Knowles BH, Ellar DJ (1987) Colloid-osmotic lysis is a general feature of the mechanism of action of Bacillus thuringiensis δ-endotoxins with different insect specificities. Biochim Biophys Acta 924:509–518
Knowles BH, Blatt MR, Tester M, Horsnell JM, Carroll MG, Ellar J (1989) A cytolytic δ-endotoxin from Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis forms cation-selective channels in planar lipid bilayers. FEBS Lett 244:259–262
Komano T, Yamigawa M, Nishimoto T, Yoshisue H, Tanabe K, Sen K, Sakai H (1998) Activation process of the insecticidal proteins CryIVA and CryIVB produced by Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Isr J Entomol 32:185–198
Koni PA, Ellar DJ (1993) Cloning and characterization of novel Bacillus thuringiensis cytolytic delta-endotoxin. J Mol Biol 229:319–327
Kramer VL (1990) Efficacy and persistence of Bacillus sphaericus, Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis, and methoprene against Culiseta incidens (Diptera: Culicidae) in tires. J Econ Entomol 83:1280–1285
Kramer VL, Garcia R, Colwell AE (1988) An evaluation of Gambusia affinis and Bacillus thuringiensis var. biorational control of mosquitoes 155 israelensis as mosquito control agents in California wild rice. J Am Mosq Control Assoc 4:470–478
Krieg A, Huger AM, Langenbruch GA, Schnetter W (1983) Bacillus thuringiensis var. tenebrionis, a new pathotype effective against larvae of Coleoptera. Z Angew Entomol 96:500–508
Lacey LA, Oldacre SL (1983) The effect of temperature, larval age, and species of mosquito on the activity of an isolate of Bacillus thuringiensis var. darmstadiensis toxic for mosquito larvae. Mosq News 43:176–180
Lacey LA, Undeen AH (1986) Microbial control of black flies and mosquitoes. Ann Rev Entomol 31:265–296
Lee HL, Cheong WH (1985) Laboratory evaluation of the potential efficacy of Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis for the control of mosquitoes in Malaysia. Trop Biomed 2:133–137
Lee SG, Eckblad W, Bulla A Jr (1985) Diversity of protein inclusion bodies and identification of mosquitocidal protein in Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 126:953–960
Leong KL, Cano RJ, Kubinski AM (1980) Factors affecting Bacillus thuringiensis total field persistence. Environ Entomol 9:593–599
Li J, Carroll J, Ellar DJ (1991) Crystal structure of insecticidal delta-endotoxin from Bacillus thuringiensis at 2.5 Å resolution. Nature 353:815–821
Li J, Koni PA, Ellar DJ (1996) Structure of the mosquitocidal δ-endotoxin CytB from Bacillus thuringiensis sp. kyushuensis and implications for membrane pore formation. J Mol Biol 257:129–152
Li J, Derbyshire DJ, Promdonkoy B, Ellar DJ (2001) Structural implications for the transformation of the Bacillus thuringiensis δ-endotoxins from water-soluble to membrane-inserted forms. Biochem Soc Trans 29:571–577
Likitvivatanavong S, Katzenmeier G, Angsuthanasombat C (2006) Asn183 in α5 is essential for oligomerisation and toxicity of the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba toxin. Arch Biochem Biophys 445:46–55
Lord JC, Undeen AH (1990) Inhibition of the Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis toxin by dissolved tannins. Environ Entomol 19:1547–1551
Manasherob R, Itsko M, Sela-Baranes N, Ben-Dov E, Berry C, Cohen S, Zaritsky A (2006) Cyt1Ca from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis: Production in Escherichia coli and comparison of its biological activities with those of other Cyt-like proteins. Microbiology 152:2651–2659
Manceva SD, Pusztai-Carey M, Russo PS, Butko P (2005) A detergent-like mechanism of action of the cytolytic toxin Cyt1A from Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis. Biochemistry 44:589–597
Margalith Y, Ben-Dov E (2000) Biological control by Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. In: Rechcigl JE, Rechcigl NA (eds) Insect Pest Management: Techniques for Environmental Protection. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 243–301
Martin WF, Reichelderfer CF (1989) Bacillus thuringiensis: Persistence and movement in field crops; 20–24 august, 1989. University of Maryland, College Park
Martin PAW, Travers RS (1989) Worldwide abundance and distribution of Bacillus thuringiensis isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:2437–2442
McGuirre MR, Shasha BS, Eastman CE, Sagedchi HO (1996) Starch and fluor-based sprayable formulations: Effect on rainfastness and solar stability of Bacillus thuringiensis. J Econ Entomol 89:863–869
Merritt RW, Walker ED, Wilzbach MA, Cummins KW, Morgan WT (1989) A broad evaluation of B.t.i. for blackfly (Diptera: Simuliidae) control in a Michigan river: Efficacy, carry and nontarget effects on invertebrates and fish. J Am Mosq Control Assoc 5:397–415
Morris ON (1983) Protection of Bacillus thuringiensis from inactivation from sunlight. Can Entomol 115:1215–1227
Morse RJ, Yamamoto T, Stroud RM (2001) Structure of Cry2Aa suggests an unexpected receptor binding epitope. Structure (Cambridge) 9:409–417
Mulla MS, Federici BA, Darwazeh HA (1982) Larvicidal efficacy of Bacillus thuringiensis serotype H-14 against stagnant-water mosquitoes and its effects on non-target organisms. Environ Entomol 11:788–795
Mulla MS, Darwazeh HA, Zgomba M (1990) Effect of some environmental factors on the efficacy of Bacillus sphaericus 2362 and Bacillus thuringiensis (H-14) against mosquitoes. Bull Soc Vect Ecol 15:166–175
Mulla MS, Thavara U, Tawatsin A, Chompoosri J (2004) Procedures for the evaluation of field efficacy of slow-release formulations of larvicides against Aedes aegypti in water-storage containers. J Am Mosq Control Assoc 20:64–73
Mulligan FS, Schaefer CH, Wilder WH (1980) Efficacy and persistence of Bacillus sphaericus and B. thuringiensis H. 14 against mosquitoes under laboratory and field conditions. J Econ Entomol 3:684–688
Muthukumar G, Nickerson K (1987) The glycoprotein toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis indicates a Lectinlike receptor in the larval mosquito gut. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:2650–2655
Narva KE, Payne JM, Schwab GE, Hickle LA, Galasan T, Sick AJ (1991) Novel Bacillus thuringiensis microbes active against nematodes, and genes encoding novel nematode active toxins cloned from Bacillus thuringiensis isolates: European patent application EP0462 721A2. European Patent Office, Munich
Nayar JK, Knight JW, Ali A, Carlson DB, O’Bryan PD (1999) Laboratory evaluation of biotic and abiotic factors that may influence larvicidal activity of Bacillus thuringiensis serovar. israelensis against two Florida mosquito species. J Am Mosq Control Assoc 15:32–42
Nguyen TT, Su T, Mulla MS (1999) Mosquito control and bacterial flora in water enriched with organic matter and treated with Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis and Bacillus sphaericus formulations. J Vector Ecol 24:138–153
Nisnevitch M, Cohen S, Ben-Dov E, Zaritsky A, Sofer Y, Cahan R (2006) Cyt2Ba of Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis: Activation by putative endogenous protease Biochem. Biophys Res Commun 344:99–105
Ohana B, Margalit J, Barak Z (1987) Fate of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp israelensis under simulated field conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:828–831
Oppert B, Kramer KJ, Beeman RW, Johnson D, Mc Gaughey WH (1997) Proteinase-mediated insect resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxins. J Biol Chem 272:23473–23476
Otieno-Ayayo ZN, Zaritsky A, Wirth MC, Manasherob R, Khasdan V, Cahan R, Ben-Dov E (2008) Variations in the mosquito larvicidal activities of toxins from Bacillus thuringiensis ssp. israelensis. Environ Microbial 10:2191–2199
Pigott CR, Ellar DJ (2007) Role of receptors in Bacillus thuringiensis crystal toxin activity. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 71:255–281
Poncet S, Delecluse A, Klier A, Rapoport G (1995) Evaluation of synergistic interactions among the CryIVA, CryIVB, and CryIVD toxic components of B. thuringiensis subsp. Israelensis crystals. J Invertebr Pathol 66:131–135
Porcar M, Juárez-Pérez V (2003) PCR-based identification of Bacillus thuringiensis pesticidal crystal genes. FEMS Microbiol Rev 26:419–432
Pozsgay M, Fast P, Kaplan H, Carey PR (1987) The effect of sunlight on the protein crystals from Bacillus thuringiensis var. kurstaki HDl and NRDl2: A Raman spectroscopy study. J Znvertebr Pathol 50:246–253
Promdonkoy B, Ellar DJ (2000) Membrane pore architecture of a cytolytic toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis. Biochem J 350:275–282
Promdonkoy B, Ellar DJ (2003) Investigation of the poreforming mechanism of a cytolytic δ-endotoxin from Bacillus thuringiensis. Biochem J 374:255–259
Purcell M, Ellar DJ (1997) The identification and characterization of novel proteinaceous components of the Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis parasporal inclusion. In: Proceedings of the 30th annual meeting of the Society for Invertebrate Pathology, Banff, Canada. 24–29 p 53
Ramírez-Lepe M, Ramírez-Suero M (2012) In: Perveen F (ed) Biological control of mosquito larvae by Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis, insecticides - Pest engineering. InTech, London, ISBN: 978-953-307-895-3, Available from: http://www.intechopen.com/books/insectic
Ramırez-Suero M, Valerio-Alfaro G, Bernal JS, Ramirez-Lepe M (2011) Synergistic effect of chitinases and Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis spore-toxin complex against Aedes aegypti larvae. Can Entomol 143:157–164
Ravoahangimalala O, Charles JF (1995) In vitro binding of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis individual toxins to midgut cells of Anopheles gambiae (Diptera: Culicidae). FEBS Lett 362:111–115
Rettich F (1983) Effects of Bacillus thuringiensis serotype H-14 on mosquito larvae in the Elbe low land. Acta Entomol Bohemoslov 80:21–28
Revina LP, Kostina LI, Ganushkina LA, Mikhailova AL, Zalunin IA, Chestukhina GG (2004) Reconstruction of Bacillus thuringiensis ssp. israelensis Cry11A endotoxin from fragments corresponding to its N- and C moieties restores its original biological activity. Biochemistry 69:181–187
Rodriguez-Almazan C, Ruiz de Escudero I, Canton PE, Munoz-Garay C, Perez C, Gill SS, Soberón M, Bravo A (2010) The amino- and carboxyl-terminal fragments of the Bacillus thuringiensis Cyt1Aa toxin have differential roles in toxin oligomerization and pore formation. Biochemistry 50:388–396
Rowe GE, Margaritis AM (1987) Bioprocess developments in the production of bioinsecticides by Bacillus thuringiensis. CRC Crit Rev Biotechnol 6:87–127
Rushed SS, Mulla MS (1989) Factors influencing ingestion of particulate materials by mosquito larvae (Diptera: Culicidae). J Med Entomol 26:210–216
Saengwiman S, Aroonkesorn A, Dedvisitsakul P, Sakdee S, Leetachewa S, Angsuthanasombat C, Pootanakit K (2011) In vivo identification of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba toxin receptors by RNA interference knockdown of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-linked aminopeptidase N transcripts in Aedes aegypti larvae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 407:708–713
Saleh MS (1985a) Larvicidal activity of Bacillus thuringiensis H-14 against mosquito larvae. Insect Sci Appl 6:617–620
Saleh MS (1985b) Effects of six insect growth regulators on mosquito larvae of Aedes aegypti. Insect Sci Appl 6:609–611
Sandoski CA, Yates MW, Olson JK, Meisch MV (1985) Evaluation of Beecomist applied Bacillus thuringiensis (H-14) against Anopheles quadrimaculatus larvae. J Am Mosq Control Assoc 1:316–319
Schnepf EN, Crickmore J, Van Rie D, Lereclus J, Baum J, Feitelson DR, Zeigler DR, Dean DH (1998) Bacillus thuringiensis and its pesticidal crystal proteins. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:775–806
Semmler M, Abdel-Ghaffar F, Al-Rasheid K, Mehlhorn H (2009) Nature helps: From research to products against blood-sucking arthropods. Parasitol Res 105:1483–1487
Slepecky RA, Hemphill HE (1992) The genus bacillus-nonmedical. In: Balows A, Truper HG, Dworkin M, Harder W, Schleifer KH (eds) The prokaryotes, vol 2. Springer Verlag, New York, pp 1663–1696
Sokolova EI, Kulieva NM, Chekalina LI, Shatalova LA (1987) Larvicidal activity of the preparation Bacillus thuringiensis H-14 strain BTS-393 after prolonged storage. Med Parazitol Parazitarn Bole 1:17–19
Steinhaus EA (1956) Potentialities for microbial control of insects. Agric Food Chem 4:676–680
Sun C, Georghiou GP, Weiss K (1980) Toxicity of Bacillus thuringiensis var israelensis to mosquito larvac variously resistant to conventional insecticides. Mosq News 10:614–661
Taveecharoenkool T, Angsuthanasombat C, Kantchanawarin C (2010) Combined molecular dynamics and continuum solvent studies of the pre-pore Cry4Aa trimer suggest its stability in solution and how it may form a pore. PMC Biophys 3:1–16
Thammasittirong A, Dechklar M, Leetachewa S, Pootanakit K, Angsuthanasombat C (2011) Aedes aegypti membrane-bound alkaline phosphatase expressed in Escherichia coli retains high-affinity binding for Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba toxin. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:6836–6840
Thiery I, Hamon S (1998) Bacterial control of mosquito larvae: Investigation of stability of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis and Bacillus sphaericus standard powders. J Am Mosq Control Assoc 14:472–476
Thiery I, Delecluse A, Tamayo MC, Orduz S (1997) Identification of a gene for Cyt1A-like hemolysin from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. medellin and expression in a crystal-negative B. thuringiensis strain. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:468–473
Thomas WE, Ellar DJ (1983) Mechanism of action of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis insecticidal delta-endotoxin. FEBS Lett 154:362–368
Tian B, Yang J, Zhang K (2007) Bacteria used in the biological control of plant-parasitic nematodes: Populations, mechanisms of action, and future prospects. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 61:197–213
Tyrell D, Davidson LI, Bulla LA Jr, Ramoska WA (1979) Toxicity of parasporal crystals of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis to mosquitoes. Appl Environ Microbiol 38:656–658
Usta C (2013) Microorganisms in biological pest control — a review (Bacterial toxin application and effect of environmental factors)
Vilarinhos PTR, Monnerat R (2004) Larvicidal persistence of formulations of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis to control larval Aedes aegypti. J Am Mosq Control Assoc 20:311–314
Walker ED (1995) Effect of low temperature on feeding rate of Aedes stimulans larvae and efficacy of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis (H-14). J Am Mosq Control Assoc 11:107–110
Wei J-Z, Hale K, Carta L, Platzer E, Wong C, Fang SC, Arioan RV (2003) Bacillus thuringiensis crystal proteins that target nematodes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:2760–2765
WHO (1999) Microbial pest control agent Bacillus thuringiensis. World Health Organization, Geneva
WHO (2017) Lymphatic Filariasis. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs102/en/
WHO (2019) Vector-borne diseases key facts. https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/vector-borne-diseases
Wirth MC (2010) Mosquito resistance to bacterial larvicidal toxins. Open Toxinol J 3:126–140
Wirth MC, Georghiou GP, Federici BA (1997) CytA enables CryIV endotoxins of Bacillus thuringiensis to overcome high levels of CryIV resistance in the mosquito, Culex quinquefasciatus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:10536–10540
Wirth MC, Park HW, Walton WE, Federici BA (2005) Cyt1A of Bacillus thuringiensis delays evolution of resistance to Cry11A in the mosquito Culex quinquefasciatus. Appl Environ Microbial 71:185–189
Wraight SP, Molloy DP, Singer S (1987) Studies on the culicine mosquito host range of Bacillus sphaericus and Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis with notes on the effects of temperature and instar on bacterial efficacy. J Invertebr Pathol 49:291–302
Xu RM, Chang JS, Lu BL (1986) Susceptibility of eight Chinese mosquitoes to Bacillus thuringiensis H-14. Chin J Biol Control 2:20–22
Yamagiwa M, Esaki M, Otake K, Inagaki M, Komano T, Amachi T, Sakai H (1999) Activation process of dipteran-specific insecticidal protein produced by Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:3464–3469
Yamagiwa M, Ogawa R, Yasuda K, Natsuyama H, Sen K, Sakai H (2002) Active form of dipteran-specific insecticidal protein Cry11A produced by Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 66:516–522
Yamagiwa M, Sakagawa K, Sakai H (2004) Functional analysis of two processed fragments of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry11A toxin. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 68:523–528
Yates MM (1984) A portable system for aerial applications of very low volumes of technical grade concentrates of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis. Mosq News 44:583–587
Yamagiwa M, Kamauchi S, Okegawa T, Esaki M, Otake K, Amachi T, Komano T, Sakai H. (2001) Binding properties of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4A toxin to the apical microvilli of larval midgut of Culex pipiens. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 65:2419–2427
Zakharyan RA, Agabalyan AS, Chil-Akopyan LA, Gasparyan NS, Bakunts KA, Tatevosyan PE, Afrikyan EK (1976) About the possibility of extrachromosomal DNA in creation of the entomocidal endotoxin of B. thuringiensis. Dokl Akad Nauk Arrn SSR 63:42–47. [in Russian]
Zhang YW, Zhang J, Lan JP, Wang JM, Liu JX, Yang MS (2016) Temporal and spatial changes in Bt toxin expression in Bt-transgenic poplar and insect resistance in field tests. J Forest Res 27:1249–1256
Zhou G, Wiseman V, Atieli HE, Lee MC, Githeko AK, Yan G (2016) The impact of long-lasting microbial larvicides in reducing malaria transmission and clinical malaria incidence: Study protocol for a cluster randomized controlled trial. Trials 17:423
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Achari, T.S., Barik, T.K., Acharya, U.R. (2020). Toxins of Bacillus thuringiensis: A Novel Microbial Insecticide for Mosquito Vector Control. In: Barik, T.K. (eds) Molecular Identification of Mosquito Vectors and Their Management. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-9456-4_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-9456-4_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-9455-7
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-9456-4
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)