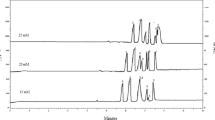
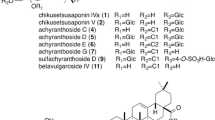
Abstract
The analysis of saponins in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) is important for their identification and quantification in plant material, as these substances are of great interest with respect to their biological and nutritional aspects. Indeed, the chemical, physical and physiological effects saponins have been known for a long time and have been widely studied.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jurzysta, M. (1979) Haemolytic micromethod for rapid estimation of toxic alfalfa saponins. Acta Agrobot. 32, 5–11.
Pracros, P. (1988) Mesure de l’activité des saponins de la lucerne par les larves du ver de la farine: Tenebrio molitor L. (Colèoptére, Tenebrionidae). I. - Comparaison avec les résultats de divers tests biologiques. Agronomie 8, 275–263.
Zimmer, D.E., Pederson, M.W. and McGuire, C.F. (1967) A bioassay for alfalfa saponins using the fungus Trichoderma viride Pers. Crop Sci. 7, 223–224.
Oleszek, W. (1996) Alfalfa saponins: structure, biological activity, and chemotaxonomy, in G.R. Waller and K. Yamasaki (eds.), Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Volume 405. Saponins Used in Food and Agriculture,Plenum Press, New York, pp. 155–170.
Oleszek, W., Jurzysta, M., Price, K.R. and Fenwick, G.R. (1990) High performance liquid chromatography of alfalfa root saponins. J. Chromatogr. 519, 109–116.
Nowacka, J. and Oleszek, W. (1992) High performance liquid chromatography of zanhic acid glycoside in alfalfa (Medicago sativa). Phytochem. Anal. 3, 227–230.
Nowacka, J. and Oleszek, W. (1994) Determination of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) saponins by high performance liquid chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 42, 727–729.
Jurzysta, M. and Jurzysta, A. (1978) Gas-liquid chromatography of trimethylsilyl ethers of soyasapogenols and medicagenic acid. J. Chromatogr. 148, 517–520.
Brawn, P.R., Lindner, N. M., Miller, J. M. and Telling, G. M. (1981) A gas chromatographic method for the determination of medicagenic acid in lucerne (alfalfa) leaf protein concentrate. J. Sci. Food Agric. 32, 1157–1162.
Rao, D. and Boris, G. (1987) Simple gas chromatographic method for the determination of medicagenic acid in alfalfa (Medicago sativa). J. Chromatogr. 410, 169–175.
Tava, A., Oleszek, W., Jurzysta, M., Berardo, N. and Odoardi, M. (1993) Alfalfa saponins and sapogenins: isolation and quantification in two different cultivars. Phytochem. Anal. 4, 269–274.
Jurzysta, M. and Waller, G.R. (1996) Antifungal and hemolytic activity of aerial parts of alfalfa (Medicago) species in relation to saponin composition, in G.R. Waller and K. Yamasaki (eds.), Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Volume 404. Saponins Used in Traditional and Modern Medicine,Plenum Press, New York, pp. 565–574.
Kitagawa, I., Taniyama, T., Marukami, T., Yoshihara, M. and Yoshikawa, M. (1988) Saponin and sapogenol. XLVI. On the constituents in aerial parts of American alfalfa, Medicago sativa L. The structure of dehydrosoyasaponin I. Yakugaku Zasshi 108, 547-.
Timbekova, A.E. and Abubakirov, N.K. (1984) Triterpene glycosides of alfalfa. I. Medicoside G–a novel bidesmoside from Medicago sativa. Khim. Prir. Soed. 4, 451–458.
Levy, M., Zehavi, U., Naim, M. and Polacheck, J. (1986) An improved procedure for the isolation of medicagenic acid 3–0-glucopyranoside from alfalfa roots and its antifungal activity on plant pathogens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 34, 960–963.
Massiot, G., Lavaud, C., Le Men-Olivier, L., Van Binst, G., Miller, S.F. and Fales, H.M. (1988) Structure elucidation of alfalfa root saponins by mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance analysis. J. Chem. Soc. Perkun Trans. I, 3071–3079.
Oleszek, W. (1988) Solid-phase extraction-fractionation of alfalfa saponins. J. Sci. Food Agric. 44, 4349.
Oleszek, W., Price, K.R., Colquhoun, I.J., Jurzysta, M., Ploszynski, M. and Fenwick, R.G. (1990) Isolation and identification of alfalfa (Medicago sativa) root saponins: their activity in relation to a fungal bioassay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 38, 1810–1817.
Massiot, G., Lavaud, C., Besson, V., Le Men-Olivier, L. and Van Binst, G. (1991) Saponins from aerial parts of alfalfa (Medicago sativa). J. Agric. Food Chem. 39, 78–82.
Oleszek, W., Jurzysta, M., Ploszynski, M., Colquhoun, I.J., Price, K.R. and Fenwick, R.G. (1992) Zanhic acid tridesmoside and other dominant saponin from alfalfa (Medicago sativa) aerial parts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 40, 191–196.
Massiot, G., Lavaud, C., Benkhaled, M. and Le Men-Olivier, L. (1992) Soyasaponin VI, a new maltol conjugate from alfalfa and soybean. J. Nat. Prod. 55, 1339–1342.
Timbekova, A.E. and Abubakirov, N.K. (1985) Triterpene glycosides of alfalfa. II. Medicoside C. Khim. Prir. Soed. 6, 805–808.
Timbekova, A.E. and Abubakirov, N.K. (1986) Triterpene glycosides of alfalfa. IV. Medicoside J. Khim. Prir. Soed. 5, 610–613.
Cheeke, P.R. (1996) Biological effects of feed and forage saponins and their impact on animal nutrition, in G.R. Waller and K. Yamasaki (eds.), Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Volume 405. Saponins Used in Food and Agriculture,Plenum Press, New York, pp. 377–385.
Sen, S., Makkar, H.P.S. and Becker, (1998) Alfalfa saponins and their implication in animal nutrition. J. Agric. Food Chem. 46, 131–140.
Cheeke, P.R. (1983) Biological properties and nutritional significance of legume saponins, in L. Telek and H.D. Graham (eds.), Leaf Protein Concentrates, AVI Publ.Co., Wesport, CT, pp. 396–412.
Price, K.R., Johnson, I.T. and Fenwick, G.R. (1987) The chemistry and biological significance of saponins in foods and feedingstuffs. CRC Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 26, 27–135.
Fenwick, G.R., Price, K.R. Tsukamoto, C. and Okubo, K. (1991) Saponins, in J.P.F. D’Mello, C.M. Duffus and J.H. Duffus (eds.), Toxic Substances in Crop Plants, The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, UK, pp. 285–327.
Lu, C.D. and Jorgensen, N.A. (1987) Alfalfa saponins affect site and extent of nutrient digestion in ruminants. Am. Inst. Nutr. 117, 919–927.
Lu, C.D., Tsai, L.S., Schafer, D.M. and Jorgensen, N.A. (1987) Alteration of fermentation in continuous culture of mixed rumen bacteria by isolated alfalfa saponins. J. Dairy Sci. 70, 799–805.
Oleszek, W., Nowacka, J., Gee, J. M., Wartley, G. M. and Johnson, I. T. (1994) Effects of some purified alfalfa (Medicago sativa) saponins on transmural potential difference in mammalian small intestine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 65, 35–39.
Oleszek, W., Nowacka-Zaborska, J., Minta, M. and Zmudzki, J. (1995) Effect of alfalfa saponin-zanhic acid tridesmoside on hamsters (Mesocricetus auratus), in: C. Garcia-Viguera et al. (eds.), Current Trends in Fruit and Vegetable Phytochemistry, Cons. Sup. Invest. Cient., Madrid, pp. 293–297.
Applebaum, S.W. and Birk, Y. (1979) Saponins, in: G.A. Rosenthal and D.H. Janzen (eds.), Herbivores–Their Interaction with Secondary Plant Metabolites, Academic Press Inc., New York, pp. 539–566.
Applebaum, S.W., Marco, S. and Birk, Y. (1969) Saponins as a possible factor of resistance of legume seeds to attack of insects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 17, 618–622.
Puszkar, L., Jastrzebski, A., Jurzysta, M. and Bialy, Z. (1994) Alfalfa saponins as a chance in the integrated hop protection. Proc. XXXIVIOR, vol. II, Poznan, 255–259.
Waligora, D. and Krzymanska, J. (1994) The influence of secondary plant substances: glucosinolates, alkaloids and saponins on the feeding of Colorado potato beetle (Lepidoptera decemlineata Say) Proc. XXXIV Session IOR, vol II, Poznan, 9–12.
Tava, A. and Odoardi, M. (1996) Saponins from Medicago spp.: chemical characterization and biological activity against insects, in G.R. Waller and K. Yamasaki (eds.), Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Volume 405. Saponins Used in Food and Agriculture,Plenum Press, New York, pp. 97–109.
Tava, A. and Pecetti, L. (1998) Hemolytic activity and saponin content in lucerne (Medicago sativa complex) genotypes. J. Genet. and Breed. 52, 33–37.
Oleszek, W. (1998) Composition and quantification of saponins in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) seedlings. J. Agric. Food Chem. 46, 960–962.
Pedersen, M. W., Zimmer, D. E., Anderson, J. O. and McGuire, C. F. (1966) A comparison of saponins from Du Puits, Ranger and Quinta alfalfas. Proc. 10 6 ’ Int. Grassland Congress, Helsinky, pp. 693–698.
Pedersen, M. W., Zimmer, D. E., McAllister, D. R., Anderson, J. O., Wilding, M. D., Taylor, G. A. and McGuire, C. F. (1967) Comparative studies of saponins of several alfalfa varieties using chemical and biochemical assay. Crop Sci. 7, 349–352.
Burda, S., Jurzysta, M. and Oleszek, W. (1994) Biologically active saponin content in eight cultivars of alfalfa (Medicago saliva), in: Management and Breeding of Perennial Lucerne for Diversification Purposes. REUR Technical Series 36, FAO, Rome, pp. 128–130.
Oleszek, W., Tava, A. and Odoardi, M. (1995) Zanhic acid glucosides in alfalfa-seasonal changes in alfalfa varieties. Proc. Symp. “Resistence of Plant to Diseases, Pests and to Unfavorable Environmental Conditions” Radzikow, Poland.
Tava, A., Odoardi, M. and Oleszek. W. (1999) Seasonal changes of saponin content in five alfalfa (Medicago sativa) cultivars. Agricoltura Mediterranea, 129, 1–6.
Tava, A., Corsi, P., Annicchiarico, P. and Pecetti, L. (1999) Evolution over the growing season of sapogenin content in lucerne varieties. Proc. 13 * Eucarpia Medicago spp. Group Meeting,Perugia, in press.
Grossman, P. D. and Colbum, J. C. (1992) Capillary Electrophoresis. Theory and Practice, Academic Press, San Diego.
Li, S. F. Y. (1992) Capillary Electrophoresis - Principles, Practice and Applications, Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Chiari, M. (1998) Enhancement of selectivity in capillary electophoretic separation of metal and ligand through complex formation. J. Chromatogr. A 805, 1–15.
Stefannson, M. and Novotny, M. (1994) Separation of complex oligosaccharide mixtures by capillary electrophoresis in the open-tibular format. Anal. Chem. 66, 1134–1140.
Plocek, J. and Chmelik, J. (1997) Separation of oligosaccharides as their borate complexes by capillary electrophoresis with indirect detection in visible range. Electrophoresis 18, 1148–1152.
Yamaguchi, H., Matsuura, H., Kasai, R., Mizutani, K., Fujino, H., Ohtani, K., Fuwa„ T. and Tanaka, O. (1986) Application of borate ion-exchange mode high-performance liquid chromatography to separation of glycosides: saponins of ginseng, Sapindus mukurossi Gaertn. and Anemone rivularis Buch.-Ham. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 34, 2859–2867.
The Perkin-Elmer Corporation (1994) Free Solution Capillary Electrophoresis Methods Development Strategies. The Perkin Elmer Corporation, Norwalk, CT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2000 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Tava, A., Chiari, M., Oleszek, W. (2000). Separation of Alfalfa (Medicago Sativa L.) Saponins as Their Borate Complexes by Capillary Electrophoresis. In: Oleszek, W., Marston, A. (eds) Saponins in Food, Feedstuffs and Medicinal Plants. Proceedings of the Phythochemical Society of Europe, vol 45. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-015-9339-7_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-015-9339-7_5
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-90-481-5341-1
Online ISBN: 978-94-015-9339-7
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive