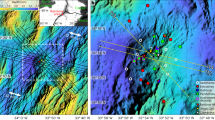
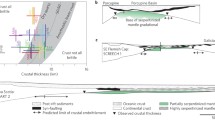
Abstract
Abundant oceanic gabbros created in slow-spreading ridges have been collected by dredging, drilling or with submersibles (Atlantic ocean crust, Mid-Cayman Rise, South West Indian Ridge). A review of published studies as well as work in progress show that these gabbros may be extensively metamorphosed and more or less deformed. Structural and petrological investigations suggest that shearing starts in the lower crust at very high temperature, before the complete solidification of the magma chamber. Continuing shearing allows seawater penetration and formation of synkinematic amphibole as temperature decreases. In the absence of ductile deformation, metamorphic reactions result from interaction between gabbros and a seawater-derived fluid phase circulating through a crack network.
We propose a model to explain the metamorphic and deformational characteristics of oceanic gabbros. We suggest that early lithospheric stretching beneath the ridge allows seawater penetration in the lower crust when it is still very hot, through permeability created by shear zones and associated synkinematic cracks. Therefore, hydration of the lower crust starts at high temperature (750°C), in contrast with a simple cracking front model in which hydration starts at temperature below 500°C. The amount of stretching may be related to the spreading rate through the magma budget.
Gabbroic series from ophiolite complexes may show either this early stretching and high temperature metamorphism associated with ductile shear zones (Western Alps ophiolites) or a crack network related to the cracking front and moderate temperature metamorphism (Haylayn massif, Oman ophiolite).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonatti, E., Honnorez, J., Kirst, P. and Radicati, F., 1975. Metagabbros from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge at 06°N: contact hydrothermal dynamic metamorphism beneath the axial valley., J. Geol., 83: 61–78.
Bowen, A.N. and White, S., 1986. Deep-tow seimic profiles from the Vema transform and ridge/transform intersection, J. Geol. Soc. London, 143: 807–817.
Bower, T.S. and Taylor, H.P. Jr, 1985. An integrated chemical and stable isotope model of the origin of mid-ocean ridge hot spring system, J. Geophys. Res., 90, B14: 12583–12606.
Cannat, M., 1991. Plastic deformation at an oceanic spreading ridge: a microstructural study of the site 735 gabbros (Southwest Indian ocean). Proceedings of the ODP, Leg 118.
Cannat, M., Mével, C. and Stakes, D., 1991. Normal ductile shear zones at an oceanic spreading ridge: tectonic evolution of the site 735 gabbros, SW Indian Ocean, Proceedings of the ODP, Leg 118, part B.
Cannat, M., Mével, C. and Stakes, D., 1991. Stretching of the deep crust at the slow-spreading SW Indian Ridge. Tectonophysics.
CAYTROUGH, 1979. Geological and geophysical investigation of the Mid-Cayman Rise spreading center: intitial results and observations. In: Taiwan, M., Harrison, C.G. and Hayes, D.E. (eds), Maurice Ewing series 2, Washington D.C, AGU, pp. 66–95.
CYAGOR II Group, 1984. Intraoceanic tectonism on the Gorringe Bank. In: I.G. Gan, S.J. Lippard and A.W. Shelton (eds), Opiolites and oceanic lithosphere, Blackwell, London, 113–120.
Delaney, J.R., Mogk, D.W. and Mottl, M.J., 1987. Quartz-cemented breccias from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge: samples of high salinity hydrothermal upflow zone J. Geophys. Res., 92: 9175–9192.
Dick, H.J.B., Thompson, G. and Bryan, W.B., 1981. Low-angle faulting and steady state emplacement of plutonic rocks at ridge-transform intersections, Eos, 62: 406.
Dick, H.J.B., Meyer, P.S., Bloomer, S., Kirby, S., Stakes, D.S. and Mawver, C., 1991. Lithostratigraphic evolution of an in-situ section of oceanic layer 3. Proceedings of ODP, vol. 118.
DSDP Leg 37 Scientific Party, 1977. Site 334, Initial Reports of the DSDP, 37: 201–238.
DSDP Leg 82 Scientific Party, 1985. Site 556. Initial Report of the DSDP, 82: 61–244.
Engel, C.G. and Fisher, R.L., 1975. Granitic to ultramafic rock complexes of the Indian ocean ridge system, western Indian ocean, Geol. Soc. Amer. Built., 86: 1553–1578.
Fehn, U., Green, K.E., Von Herzen, R.P. and Catthles, L.M., 1983. Numerical models for the hydrothermal field at the Galapagos spreading center, J. Geophys. Res., 88: 1033–1048.
Francheteau, J., Armijo, R., Cheminée, J.L., Hekinian, R., Lonsdale, P. and Blum, N., 1990. 1 Ma East Pacific Rise oceanic crust and uppermost mantle exposed in Hess Deep. Earth Plan. Sci. Letters, 101: 281–295.
Francis, T.J.G., 1981. Serpentinization faults and their role in the tectonics of slow-spreading ridges, J. Geophys. Res., 86(11): 616–622.
Gente, P., Auzende, J.M., Renard, V., Fouquet, Y. and Bideau, D., 1986. Detailed geological mapping by submersible of the East Pacific Rise axial graben near 13°N, Earth Planet. Sci. Letters, 78: 224–236.
Helmstaedt, H. and Allen, J.M., 1977. Metagabbronorites from DSDP Hole 334. An example of high temperature deformation and recrystallization near the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, Can. J. Earth Sci., 14: 886–898.
Honnorez, J. and Fox, P.J., 1972. Petrography of the Gorringe bank “basement”. In: Ryan, W.B.F. and Hsü, H.J., Initial Reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project, vol XIII: 747–752.
Ito, E. and Anderson, A.T. Jr, 1983. Submarine metamorphism of gabbros from the Mid-Cayman Rise: petrographic and mineialogic constraints on hydrothermal processes at slow-spreading ridges, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 82: 371–388.
Ito, E. and Clayton, R., 1983. Submarine metamorphism of gabbros from the mid-Cayman Rise: an oxygen isotopic study, J Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 47: 535–546.
Kappel, E.S. and Ryan, W,F.B., 1986. Volcanic episodicity and a non-steady state rift valley along northeast Pacific spreading centers: evidence from Sea MARC I, J. Geophy. Res., 91: 13925–13940.
Karson, J.A., 1991. Seafloor spreading on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge: implication for the structure of ophiolite and oceanic lithosphere produced in slow-spreading environments. In: J. Malpas, E.M. Moores, A. Panayiotou and C. Xenophontos (eds), Ophiolites: oceanic crust analogues, Geological Survey, Nicosia, Cyprus, 547–556.
Karson, J.A. and Dick, H.J.B., 1983. Tectonics of ridge-transform intersections at the Kane fracture zone., Mar. Geophys. Res., 6: 51–91.
Karson, J.A., Thompson, G., Humphris, S.E., Edmond, J.M., Bryan, W.B., Brown, J.R., Winters, A.T., Pockalny, R.A., Casey, J.F., Campbell, A.C., Klinkhammer, C., Palmer, M.R., Kinzler, R.J., and Sulanowska, M.M., 1987. Along axis variations in seafloor spreading in the MARK area Nature, 328: 681–685.
Kelley, D.S. and Delaney, J.R., 1987. Two phase separation and fracturing in mid-oceanic ridge gabbros at temperatures greater than 700°C, Earth Planet. Sci. Letters, 83: 53–66.
Lachenbruch, A.H., 1973. A simple mechanical model for oceanic spreading centers, J. Geo-phys. Res., 78: 3395–3417.
Lagabrielle, Y. and Cannat, M., 1990. Ancient alpine jurassic ocean floor resembles the modern central Atlantic basement. Geology, 18: 319–322.
Lister, C.R.B., 1974. On the penetration of water into hot rocks. Geophys, J.R. Astr. Soc., 39 465–509.
Malcolm, F.L., 1981. Microstructures of the Cayman trough gabbros, J. Geol., 89: 675–688.
Mével, C., 1987. Evolution of oceanic gabbros from DSDP leg 82: influence of the fluid phase on metamorphic crystallizations, Earth Planet. Sci. Letters, 83: 67–79.
Mével, 1988. Metamorphism of oceanic layer 3, Gorringe bank, Eastern Atlantic, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 100: 496–509.
Mével, C., Caby, R. and Kienast, J.R., 1978. Amphibolite facies conditions in the oceanic crust: example of amphibolitized flaser-gabbros and amphibolites from the Chenaillet ophiolite massif (Hautes Alpes, France), Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 39: 98–108.
Mével, C., Cannat, M., Gente, P., Marion, E., Auzende, J.M. and Karson, J.A., 1991. Emplacement of deep crustal and mantle rocks on the west median valley wall of the MARK area (M.A.R., 23°N). Tectonophysics.
Meyer, P.S., Dick, H.J.B. and Thompson, G., 1989. Cumulate gabbros from the Southwest Indian Ridge, 54°S-7°16’E: implications for magmatic processes at a slow-spreading ridge.
Nicolas, A., Boudier, F. and Ceuleneer, G., 1988. Mantle flow patterns and magma chambers at ocean ridges. Evidence from the Oman ophiolite, Marine Geophys. Res., 9: 293–310.
Mottl, M.J., 1983. Metabasalts, hot springs and the structure of hydrothermal systems at mid-ocean ridges. Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull., 94: 161–180.
Nehlig, P. and Juteau, T., 1988. Flow porosities, permeabilities and preliminary data on fluid inclusions and fossil geothermal gradients in the crustal sequence of the Sumail ophiolite, Oman. Tectonophysics, 151, 199–221.
ODP Leg 118 Scientific Party, 1989. Proceedings of the ODP, volume 118.
Phipps-Morgan, J., Parmentier, E.M. and Lin, J., 1987. Mechanisms for the origin of Mid-Ocean Ridge axial topography: implication for the thermal and mechanical structure of accreting plate boundaries, J. Geophy. Res., 92: 12823–12836.
Prichard, H.M. and Cann, J.R., 1982. Petrology and mineralogy of dredged gabbros from Gettysburg bank, North Atlantic ocean., Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 79: 46–55.
Sleep, N.H., 1969. Sensitivity of heat flow and gravity to the mechanism of seafloor spreading, J. Geophys. Res., 74: 542–549.
Stakes, D.S. and Vanko, D.A., 1986. Multistage alteration of gabbroic rocks from the failed Mathematician Ridge, Earth Planet. Sci. Letter, 79: 75–92.
Stakes, D.S., Mével, C., Cannat, M. and Chaput, T., 1991. Metamorphic stratigraphy of site 735B gabbros. Proceedings of ODP, Volume 118.
Stroup, J. and Fox, P.J., 1981. Geologic investigation in the Cayman trough: evidence for thin crust along the Mid-Cayman Rise, J. Geol., 89: 395–420.
Tapponnier, P. and Francheteau, J, 1978. Necking of the lithosphere and the mechanics of slowly accreting plate boundaries, J. Geophys. Res., 83(B8): 3955–3970.
Toomey, D.R., Solomon, S.C. and Purdy, G.M., 1988. Microearthquakes beneath the median valley of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge near 23°N: tomography and tectonics, J. Geophys. Res., 93 (B8): 9093–9112.
Vanko, D.A. and Batiza, R., 1982. Gabbroïc rock from the Mathematician Ridge failed rift, Nature, 300: 742–744.
Vanko, D.A. and Stake, D.S., 1991. Fluids in oceanic layer 3: evidence from veined rock, Hole 735B, South West Indian Ridge. Proceeding of the ODP, Volume 118.
Wolery, T.J. and Sleep, N.H., 1976. Hydrothermal circulation and geochemical flux at Mid-Ocean Ridges, J. Geol., 84: 249–275.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1991 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mével, C., Cannat, M. (1991). Lithospheric Stretching and Hydrothermal Processes in Oceanic Gabbros from Slow-Spreading Ridges. In: Peters, T., Nicolas, A., Coleman, R.G. (eds) Ophiolite Genesis and Evolution of the Oceanic Lithosphere. Petrology and Structural Geology, vol 5. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-3358-6_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-3358-6_16
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-010-5484-3
Online ISBN: 978-94-011-3358-6
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive