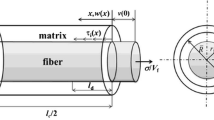
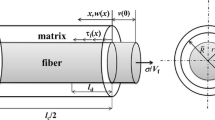
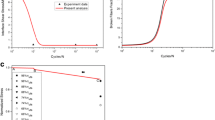
Abstract
A life prediction model is being developed by the authors for application to metal matrix composites (MMC’s). The systems under study are continuous silicon carbide fibers imbedded in titanium matrix. The model utilizes a computationally based framework based on thermodynamics and continuum mechanics, and accounts for matrix inelasticity, damage evolution, and environmental degradation due to oxidation. The computational model utilizes the finite element method, and an evolutionary analysis of a unit cell is accomplished via a time stepping algorithm. The computational scheme accounts for damage growth such as fiber-matrix debonding, surface cracking, and matrix cracking via the inclusion of cohesive zone elements in the unit cell. These elements are located based on experimental evidence also obtained by the authors.
The current paper outlines the formulation utilized by the authors to solve this problem, and recent results are discussed. Specifically, results are given for a four-ply unidirectional composite subjected to cyclic fatigue loading at 650°C both in air and inert gas. The effects of oxidation on the life of the composite are predicted with the model, and the results are compared to limited experimental results.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Ashley, Boeing 777 Gets a Boost from Titanium, Mech. Eng., (July 1993), pp. 60–65.
E.V. Zaretsky, Modeling the Future with Metal-Matrix Composites, Mach. Des., (Mar. 7, 1994 ), pp. 124–126.
J.M. Larsen, S.M. Russ, and J.W. Jones, Possibilities and Pitfalls in Aerospace Applications of Titanium Matrix Composites, in the proceedings of the NATO AGARD Conference on Characterization of Fibre Reinforced Titanium Metal Matrix Composites, Bordeaux, France, Sep. 1993.
S.M. Arnold, V.K. Arya, and M.E. Melis, Reduction of Thermal Residual Stresses in Advanced Metallic Composites Based Upon a Compensation/Compliant Layer Concept, J. Compos. Mater., Vol. 26, No. 9 (1992), pp. 1287–1309.
J. Aboudi, Thermoelastic Response of Metal Matrix Composites with Large-Diameter Fibers Subjected to Thermal Gradients, NASA Technical Memorandum 106344 (1993).
I. Doghri, S. Jansson, and F.A. Leckie, Optimization of Coating Layers in the Design of Ceramic Fiber Reinforced Metal Matrix Composites, J. Compos. Mater., Vol. 28, No. 2 (1994), pp. 167–187.
S. Jansson and F. A. Leckie, Reduction of Thermal Stresses in Continuous Fiber Reinforced Metal Matrix Composites with Interface Layers, J. Compos. Mater., Vol. 26, No. 10 (1992), pp. 1474–1486.
M.P. Thomas and J.E. King, Effect of Thermal and Mechanical Processing on Tensile Properties of Powder Formed 2124 Aluminum and 2124 Al-SiCp Metal Matrix Composite, Mater. Sci. Technol., (Sep. 1993), pp. 742–753.
A. Assar and M. Al-Nimr, Fabrication of Metal Matrix Composite by Infiltration Process: Modeling of Hydrodynamic and Thermal Behavior, J. Compos. Mater., Vol. 28, No. 15 (1994), pp. 1480–1490.
G.S. Jeong, D.H. Allen, and D.C. Lagoudas, Residual Stress Evolution Due to Cool Down in Viscoplastic Metal Matrix Composites, Int. J. Solids Struct., Vol. 31, No. 19 (1994), pp. 2653–2677.
D.B. Marshall, W.L. Morris, B.N. Cox, J. Graves, J.R. Porter, D. Kouris, and R.K. Everett, Transverse Strengths and Failure Mechanisms in Ti3Al Matrix Composites, Acta Metall. Mater., Vol. 42, No. 8 (1994), pp. 2657–2673.
R.H. Dauskardt, R.O. Ritchie, and B.N. Cox, Fatigue of Advanced Materials, Adv. Mater. Processes, (July 1993), pp. 26–31.
J.R. Ellis, M.G. Castelli, T.P. Gabb, and J. Gayda, Isothermal, Nonisothermal, and Thermomechanical Fatigue Damage/Failure Mechanisms in Titanium Matrix Composites, NASP Government Work Package 85d/e, NASA Lewis Research Center, Cleveland, Ohio, Nov. 1–3, 1993.
T.P. Gabb, J. Gayda, P.A. Bartolotta, M.G. Castelli, A Review of Thermomechanical Fatigue Damage Mechanisms in Two Titanium and Titanium Aluminide Matrix Composites, Int. J. Fatigue, (Sep. 1993), pp. 413–422.
G.M. Newaz, B.S. Majumdar, and F.W. Brust, Thermal Cycling Response of Quasi-Isotropic Metal Matrix Composites, J. Eng. Mater. Technol. Trans. ASME, (Apr. 1992), pp. 156–161.
J.G. Bakuckas, W.S. Johnson, and C.A. Bigelow, Fatigue Damage in Cross-Ply Titanium Metal Matrix Composites Containing Center Holes, J. Eng. Mater. Technol. Trans. ASME, Vol. 115 (Oct. 1993), pp. 404–410.
W.S. Johnson, Damage Development in Titanium Metal Matrix Composites Subjected to Cyclic Loading, NASA Technical Memorandum 107597 (1992).
C.R. Saff, D.M. Harmon, and W.S. Johnson, Damage Initiation and Growth in Fiber-Reinforced MMC’s, J. Metals, (Nov. 1988), pp. 58–63.
KS. Kim, A Finite Element Analysis of Crack Bridging in Metal Matrix Composites, J. Compos. Mater., Vol. 28, No. 15 (1994), pp. 1413–1431.
N. Heh and E. Krempl, A Numerical Simulation of the Effects of Volume Fraction, Creep, and Thermal Cycling on the Behavior of Fibrous Metal-Matrix Composites, J. Compos. Mater., Vol. 26, No. 6 (1992), pp. 900–915.
D. Zheng and H. Ghonem, High Temperature/High Frequency Bridging Fatigue Crack Growth Damage Mechanisms in Titanium Metal Matrix Composites, submitted to the J. Compos. Mater., (1994).
M.N. Tamin, D. Zheng, and H. Ghonem, Evolution of Bridging Fiber Stress in Titanium Metal Matrix Composites at Elevated Temperature, in the proceedings of ASTM 3rd Symposium on Advances in Fatigue Lifetime Predictive Techniques, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, May 16–17, 1994.
I.W. Hall, J.L. Lirn, and Y. Lepetitcorps, Microstructural Analysis of Isothermally Exposed Ti/SiC Metal Matrix Composites, J. Mater. Sci., (July 15, 1992 ), pp. 3835–3842.
S. Aksoy, Stiffness Degradation in Metal Matrix Composites Caused by Thermomechanical Fatigue Loading, J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power Trans. ASME, Vol. 116 (July 1994), pp. 616–621.
P.K. Gotsis, Combined Thermal and Bending Fatigue of High- Temperature Metal-Matrix Composites, NASA Technical Memorandum 104354 (1991).
J. Aboudi, M.-J. Pindera, and S.M. Arnold, Elastic Response of Metal Matrix Composites with Tailored Microstructures to Thermal Gradients, Int. J. Solids Struct., Vol. 31, No. 10 (1994), pp. 1393–1428.
M.-J. Pindera, A.D. Freed, and S.M. Arnold, Effects of Fiber and Interfacial Layer Morphologies on the Thermoplastic Response of Metal Matrix Composites, Int. J. Solids Struct., Vol. 30, No. 9 (1993), pp. 1213–1238.
Z.Z. Du and R.M. McMeeking, Creep Models for Metal Matrix Composites with Long Brittle Fibers, submitted to J. Mech. Physics Solids, (1994).
Z.Z. Du, R.M. McMeeking, and S. Schmauder, Transverse Yielding and Matrix Flow Past the Fibers in Metal Matrix Composites, submitted to Mech. Mater., (1994).
T.E. Wilt, A Coupled/Uncoupled Deformation and Fatigue Damage Algorithm Utilizing the Finite Element Method, NASA Technical Memorandum 106526 (1994).
S.M. Arnold, A Differential CDM Model for Fatigue of Unidirectional Metal Matrix Composites, NASA Technical Memorandum 105726 (1992).
S.M. Arnold, Differential Continuum Damage Mechanics Models for Creep and Fatigue of Unidirectional Metal Matrix Composites, NASA Technical Memorandum 105213 (1991).
D.C. Lagoudas, X. Ma, D.A. Miller, and D.H. Allen, Modelling of Oxidation in Metal Matrix Composites, accepted for publication in Int. J. Eng. Sci., (1995).
S. Xu, D.C. Lagoudas, and D.H. Allen, Impact of Surface Oxidation on Damage Evolution in Metal Matrix Composites, to appear in the proceedings of the ASME Winter Annual Meeting, 1995.
D.C. Lagoudas, D.H. Allen, and X. Ma, Modeling of Surface Oxidation and Oxidation Induced Damage in Metal Matrix Composites, Computational Material Modeling, AD-Vol.42, PVP-Vol.294, A. K. Noor and A. Needleman, Eds., American Society of Mechanical Engineers, New York (1994), pp. 245–264.
F.W. Zok, S.J. Connell,and Z.Z. Du, Fatigue Maps for Titanium Matrix Composites, to be published in ASTM Special Technical Publication on Life Prediction Methodology for Titanium Matrix Composites (Mar. 1994).
M.N. Tamin, D. Zheng, and H. Ghonem, Time-Dependent Behavior of Continuous-Fiber-Reinforced Metal Matrix Composites: Modelling and Applications, submitted to J. Compos. Technol. Res., (Feb. 1994).
D.H. Allen, R.H. Jones, and J.G. Boyd, Micromechanical Analysis of a Continuous Fiber Metal Matrix Composite Including the Effects of Matrix Viscoplasticity and Evolving Damage, J. Mech. Physics Solids, Vol. 42, No. 3 (1994), pp. 502–529.
G.R. Halford, Proposed Framework for Thermomechanical Life Modeling of Metal Matrix Composites, NASA Technical Paper 3320 (1993).
R.W. Neu, A Mechanistic-Based Thermomechanical Fatigue Life Prediction Model for Metal Matrix Composites, Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct., Vol. 16, No. 8 (1993), pp. 811–828.
J.L. Kroupa, R.W. Neu, T. Nicholas, D. Coker, D.D. Robertson, and S. Mall, A Comparison of Analysis Tools for Predicting the Inelastic Cyclic Response of Cross-Ply Titanium Matrix Composites, in the proceedings of the ASTM Symposium on Life Prediction Methodology for Titanium Matrix Composites, Hilton Head, South Carolina, Mar. 22–24, 1994.
T. Nicholas, J. Zuiker, and J. Pernot, Characterization of Titanium Matrix Composites, NASP Technical Memorandum 1199, Vol. I (Apr. 1995).
M.R. Eggleston and E. Krempl, The Transverse Creep and Tensile Behaviour of SCS-6/Ti-6Al-4V Metal Matrix Composites at 482°C, Mech. Compos. Mater. Struct., Vol. 1 (1994), pp. 53–73.
W.O. Soboyejo, Investigation of the Effects of Matrix Microstructure and Interfacial Properties on the Fatigue and Fracture Behavior of a Ti-15V-3Cr- 3Al-3Sn/SCS9 Composite, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 183 (1994), pp. 49–58.
R.A. Naik, W.D. Pollock, and W.S. Johnson, Effect of a High-Temperature Cycle on the Mechanical Properties of Silicon Carbide/Titanium Metal Matrix Composites, J. Mater. Sci., (June 1, 1991 ), pp. 2913–2920.
W.C. Revelos and P.R. Smith, Effect of Environment on the Thermal Fatigue Response of an SCS-6/Ti-24Al-llNb Composite, Metall. Trans., (Feb. 1993), pp. 587–595.
R.W. Schutz, Environmental Behavior of Beta Titanium Alloys, J. Mech., (July 1994), pp. 24–29.
J.V. Tesha, D.J. Stephenson, and P. Hancock, A New Criterion for Determining the Failure of Ti/SiC Metal-Matrix Composites, J. Mater. Sci., (Nov. 15, 1994 ), pp. 5787–5793.
J.J. Pernot, S. Mall, and T. Nicholas, Crack Growth Rate Behavior of a Titanium-Aluminde Alloy during Isothermal and Nonisothermal Conditions, J. Eng. Mater. Technol. Trans. ASME, (Jan. 1995), pp. 118–126.
D. Kouris and D. Marshall, Damage Mechanisms in Ti3Al Matrix Composites, J. Eng. Mater. Technol. Trans. ASME, (July 1994), pp. 319–324.
S.J. Connell, F.W. Zok, Z.Z. Du, and Z. Suo, On the Tensile Properties of a Fiber Reinforced Titanium Matrix Composite — II. Influence of Notches and Holes, submitted to Acta Metall. Mater., (1994).
T.B. Nguyen, S.M. Jeng, and J.M. Yang, The Effect of Fiber Orientation on Fatigue Crack Propagation in SCS-6/Ti-15-3 Composites, Mater. Sci. Eng., A183 (1994), pp. 1–9.
B.S. Majumdar and G.M. Newaz, Inelastic Deformation of MMC’s: Thermo-Mechanical Fatigue (TMF), HITEMP Review 1993, NASA Conference Publication 19117, (1993).
G.M. Newaz and B.S. Majumdar, Inelastic Deformation Mechanisms in SCS-6/Ti-15-3 MMC Lamina Under Compression, NASA Contractor Report 191170, (Sep. 1993).
N. Bonora, M. Constanzi, G. Newaz, and M. Marchetti, Microdamage Effects on the Overall Response of Long Fibre/Metal-Matrix Composites, Composites, Vol. 25, No. 7 (1994), pp. 575–582.
S. Mall, and B. Portner, Characterization of Fatigue Behavior in Cross- Ply Laminate SCS-6/Ti-15-3 Metal Matrix Composite at Elevated Temperature, J. Eng. Mater. Technol. Trans. ASME, (Oct. 1992), pp. 409–415.
S. Mall and P.G. Ermer, Thermal Fatigue Behavior of Unidirectional SCS-6/Ti-15-3 Metal Matrix Composite, J. Compos. Mater., Vol. 25 (Dec. 1991), pp. 1668–1686.
K.A. Hart and S. Mall, Thermomechanical Fatigue Behavior of a Quasi-Isotropie SCS6-Ti-15-3 Metal Matrix Composite, J. Eng. Mater. Technol. Trans. ASME, (Jan. 1995), pp. 109–117.
L.A. Wittig and D.H. Allen, Modeling the Effect of Oxidation on Damage in SiC/Ti-15-3 Metal Matrix Composites, J. Eng. Mater. Technol. Trans. ASME, Vol. 116 (July 1994), pp. 421–427.
L.D. Hurtado and D.H. Allen, Effect of Oxidation on Damage Evolution in Titanium Matrix MMC’s, in the proceedings of the Symposium on Inelasticity and Micromechanics in Metal Matrix Composites, Twelfth U.S. National Congress of Applied Mechanics, Seattle, June 26–July 1, 1994.
Timetal 21S Data Sheet, TIMET, Denver, May 1993.
J.C. Fanning, Timetal 21S Property Data, unpublished TIMET Henderson Technical Lab Report, (1993).
R.W. Neu, Nonisothermal Material Parameters for the Bodner-Partom Model, in the proceedings of the ASME Winter Annual Meeting, New Orleans, November 28 - December 3, 1993.
B. Bavarian, V. Wahi, G. Canzona, and M. Zamanzadeh, in the proceedings of the AEROMAT 93: Advanced Aerospace Materials/Process Conference, 1993.
B. Bavarian, G. Canzona, and M. Zamanzadeh, in the proceedings of the CORROSION 93: NACE Annual Conference and Corrosion Show, 1993, pp.243/1–243/9.
B. Bavarian and M. Zamanzadeh, in the proceedings of the CORROSION 93: NACE Annual Conference and Corrosion Show, 1993, pp.284/1–284/10.
J.S. Grauman, Corrosion Behavior of TIMETAL®21S for Non-Aerospace Applications, in the proceedings of the 7th World Conference on Titanium, San Diego, June 1992.
J.S. Grauman and E.E. Mild, in the proceedings of the OMAE Conference, Edmonton, June 1992.
W.M. Parris and P.J. Bania, Oxygen Effects on the Mechanical Properties of TIMETAL®21S, in the proceedings of the 7th World Conference on Titanium, San Diego, June 1992.
T.A. Wallace, K.E. Wiedemann, and R.K. Clark, Oxidation Characteristics of Beta-21S in Air in the Temperature Range 600 to 800°C, NASA Technical Memorandum 104217, (1992).
P.S. Liu, K.H. Hou, W.A. Baeslack, and J. Hurley, Laser Welding of an Oxidation Resistant, Metastable-Beta Titanium Alloy-ß-21S, in the proceedings of the 7th World Conference on Titanium, San Diego, June 1992.
R.R. Cervay, SCS-6 /ß21S and SCS-9/ß21S Mechanical Property Evaluation, NASP Contractor Report 1165, (Apr. 1994).
R.R. Cervay, σ/ß21S Physical and Mechanical Property Evaluation, NASP Contractor Report 1169, (Sep. 1994).
P.J. Bania and W.M. Parris, Cß-21S: A High Temperature Metastable Beta Titanium Alloy, in the proceedings of the Titanium 90 - Products and Applications Conference, Titanium Development Association, Dayton, Ohio, 1990.
R.W. Neu and T. Nicholas, Thermomechanical Fatigue of SCS-6/Timetal 2 IS Under Out-of-Phase Loading, in the proceedings of the 1993 ASME Winter Annual Meeting, New Orleans, November 28 - December 3, 1993.
H. Ghonem, Y. Wen, and D. Zheng, An Interactive Simulation Technique to Determine the Internal Stress States in Fiber Reinforced Metal Matrix Composites, Mater. Sci. Eng., A177 (1994), pp. 125–134.
H. Ghonem, Y. Wen, and D. Zheng, Effects of Temperature and Frequency on Fatigue Crack Growth in Ti-ß21S Monolithic Laminate, Mater. Sci. Eng., A161 (1993), pp. 45–53.
M.G. Castelli, Isothermal Damage and Fatigue Behavior of SCS- 6/Timetal 21S [0/90] s Composite at 650°C, NASA Contractor Report 195345, (June 1994).
M.G. Castelli, Thermomechanical Fatigue Damage/Failure Mechanisms in SCS-6/Timetal 21S [0/90]s Composite, submitted to Compos. Eng., (1994).
M.G. Castelli, An Advanced Test Technique to Quantify Thermomechanical Fatigue Damage Accumulation in Composite Materials, J. Compos. Technol. Res., (Oct. 1994).
R.W. Neu and I. Roman, Acoustic Emission Monitoring Damage in Metal-Matrix Composites Subjected to Thermomechanical Fatigue, Compos. Sci. Technol., Vol. 52 (1994), pp. 1–8.
D. Coker, N.E. Ashbaugh, and T. Nicholas, Analysis of the Thermomechanical Behavior of [0] and [0/90] SCS-6/Timetal®21S Composites, in the proceedings of the ASME Winter Annual Meeting, 1993.
R.W. Neu, and T. Nicholas, Effect of Laminate Orientation on the Thermomechanical Fatigue Behavior of a Titanium Matrix Composite, J. Compos. Technol. Res., (July 1994), pp. 214–224.
G. Newaz, Evaluation and Modeling of Mechanical Response and Strength of MMC in Compression, unpublished report, (1994).
R.W. Neu, D. Coker, and T. Nicholas, Cyclic Behavior of Unidirectional and Cross-Ply Titanium Matrix Composites, submitted to Int. J. Plast., (1994).
T. Nicholas and S.M. Buss, Response of a [0/90] SCS-6/Timetal 21S Composite to Isothermal and Thermomechanical Fatigue, in the proceedings of the Structural Testing Technology at High Temperature - II, the Society for Experimental Mechanics, November 1993, pp. 155–164.
S. Mall, D.G. Hanson, T. Nicholas, and S.M. Russ, Thermomechanical Fatigue Behavior of a Cross-Ply SCS-6/ß21-S Metal Matrix Composite, in the proceedings of the ASME Winter Annual Meeting, 1992.
D. Coker, R.W. Neu, and T. Nicholas, Analysis of the Thermoviscoplastic Behavior of [0/90] SCS-6/Timetal®21S Composites, in the proceedings of the Second Symposium on Thermomechanical Fatigue Behavior of Materials ASTM, Phoenix, November 14–15, 1994.
R.W. Neu, Thermomechanical Fatigue Damage Mechanism Maps for Metal Matrix Composites, Thermo-Mechanical Fatigue Behavior of Materials: 2nd Volume, ASTM STP 1263, M. J. Verrilli and M. G. Castelli, Eds., American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, (1995).
D.H. Allen, A Review of the Theory of Thermomechanical Coupling in Inelastic Solids, Appl. Mech. Rev., American Society of Mechanical Engineers, Vol. 44, No. 8 (1991), pp. 361–373.
KS. Chan, S.R. Bodner, and U.S. Lindholm, Phenomenolgical Modeling of Hardening and Thermal Recovery in Metals, J. Eng. Mater. Technol. Trans. ASME, (Jan. 1988), pp. 1–8.
L.A. Wittig, A Micromechanical Model of Oxidation Effects in SiC/Ti Metal Matrix Composites, Master’s Thesis, Texas A and M University, College Station, Texas, (1993).
A. Needleman, A Continuum Model for Void Nucleation by Inclusion Debonding, J. Appl. Mech. Trans. ASME, Vol. 54 (1987), pp. 525–531.
V. Tvergaard, Micromechanical Modeling of Fibre Debonding in a Metal Reinforced by Short Fibres, in the proceedings of the IUTAM Symposium on Inelastic Deformation of Composite Materials, G. J. Dvorak, Ed., Springer-Verlag, 1990, pp. 99–111.
V. Tvergaard and J.W. Hutchinson, The Influence of Plasticity on Mixed Mode Interface Toughness, J. Mech. Physics Solids, Vol. 41, No. 6 (1993), pp. 1119–1135.
D.H. Allen, M.R. Eggleston, and L.D. Hurtado, Recent Research on Damage Development in SiC/Ti Continuous Fiber Metal Matrix Composites, to appear in Fracture of Composites, E. A. Armanios, Ed., in Key Engineering Materials, Trans Tech Publications, (1995).
D.C. Lo and D.H. Allen, Modeling of Delamination Damage Evolution in Laminated Composites Subjected to Low Velocity Impact, Int. J. Damage Mech., Vol. 3, No. 4 (Oct. 1994), pp. 378–407.
F. Costanzo and D.H. Allen, D. H., A Continuum Mechanics Approach to Some Problems in Subcritical Crack Propagation, Int. J. Fract., Vol. 63, No. 1 (1993), pp. 27–57.
F. Costanzo and D.H. Allen, A Continuum Thermodynamics Analysis of Cohesive Zone Models, accepted for publication in the Int. J. Eng. Sci., (1995).
D.A. Miller, Damage Evolution of a SiC/Ti-15-3 Metal Matrix Composite with Different Heat Treatments, Master’s Thesis, Texas Aamp;M University, College Station, Texas, (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1995 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Allen, D., Helms, K., Hurtado, L., Lagoudas, D. (1995). Prediction of Damage Evolution in Continuous Fiber Metal Matrix Composites Subjected to Fatigue Loading. In: Batra, R.C. (eds) Contemporary Research in Engineering Science. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-80001-6_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-80001-6_1
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-80003-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-80001-6
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive