Abstract
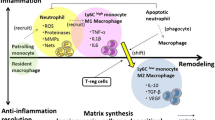
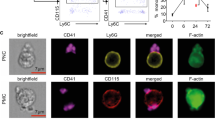
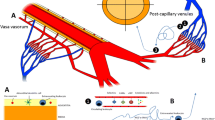
Polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) play a prominent role in the tissue injury associated with ischemia and reperfusion of a number of organs [4]. The adhesion of PMNs to the vascular endothelium is a critical step in PMN-mediated reperfusion injury [4, 5]. Furthermore, recent experimental evidence suggests that a number of adhesion molecules expressed on the surface of the PMNs and the endothelial cell (EC) regulate PMN-EC interactions [1, 17]. PMN-EC interactions occur in a highly orchestrated manner with the expression of distinct families of PMN and EC adhesion molecules at various times during the inflammatory response [17].
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bevilacqua MP, Nelson RM (1993) Selectins. J Clin Invest 91: 379–387
Buerke M, Weyrich AS, Zheng Z, Gaeta FCA, Forrest MJ, Lefer AM (1994) Sialyl Lewisx-containing oligosaccharide attenuates myocardial reperfusion injury in cats. J Clin Invest 93: 1140–1148
Buerke M, Weyrich AS, Murohara T, Queen C, Klingbeil CK, Co MS, Lefer AM (1994) Humanized monoclonal antibody DREG-200 directed against L-selectin protects in feline myocardial reperfusion injury. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 271: 134–142
Harlan JM, Winn RK, Vedder NB, Doerschuk CM, Rice CL (1991) In vivo models of leukocyte adherence to endothelium. In: Harlan JM, Liu DY (eds) Adhesion: its role in inflammatory disease. Freeman, New York, pp 117–150
Hansen PR (1995) Role of neutrophils in myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Circulation 91: 1872–1885
Ikeda H, Takajo Y, Ichiki K, Ueno T, Maki S, Noda T, Sugi K, Imaizumi T (1995) Increased soluble form of P-selectin in patients with unstable angina. Circulation 92: 1693–1696
Kaikita K, Ogawa H, Yasue H, Sakamoto T, Suefuji H, Sumida H, Okumura K (1995) Soluble P-selectin is released into the coronary circulation after coronary spasm. Circulation 92: 1726–1730
Lawrence MB, Springer TA (1991) Leukocytes roll on a selectin at physiologic flow rates: distinction from and prerequisite for adhesion through integrins. Cell 65: 859–873
Lasky LA (1992) Selectins: interpreters of cell-specific carbohydrate information during inflammation. Science 258: 964–969
Lefer DJ, Flynn DM, Buda AJ (1996) Effects of a monoclonal antibody directed against P-selectin after myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Am J Physiol (Heart and Circ Physiol 39) 270: H88–H98
Lefer DJ, Flynn DM, Phillips ML, Ratcliffe M, Buda AJ (1994) A novel sialyl Lewisx analog attenuates neutrophil accumulation and myocardial necrosis following ischemia and re-perfusion. Circulation 90: 2390–2401
Ma X-L, Weyrich AS, Lefer DJ, Buerke M, Albertine KH, Kishimoto TK, Lefer AM (1993) Monoclonal antibody to L-selectin attenuates neutrophil accumulation and protects ischemic reperfused cat myocardium. Circulation 88: 649–658
McEver RP (1991) Leukocyte interactions mediated by selectins. Thromb Haemost 66: 80–87
Muller WA, Weigel SA, Deng X, Phillips DM (1993) PECAM-1 is required for transendothelial migration of leukocytes. J Exp Med 178: 449–460
Paulson JC Selectin/carbohydrate-mediated adhesion of leukocytes. In: Harlan JM, Liu DY (eds) Adhesion: its role in inflammatory disease. Freeman, New York, pp 19–38
Picker LJ, Warnock RA, Burns AR, Doerschuk CM, Berg EL, Butcher EC (1991) The neutrophil selectin LECAM-1 presents carbohydrate ligands for the vascular selectins ELAM-1 and GMP-140. Cell 66: 921–933
Springer TA (1994) Traffic signals for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration: the multistep paradigm. Cell 76: 301–314
Tenaglia AN, Buda AJ, Wilkins RG, Barron MK, Jeffords PR, Vo KD, Jordan MO, Kusnick BA, Lefer DJ (1995) Increased expression of P-selectin in coronary atherectomy specimens from patients with unstable angina: evidence for leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions in unstable angina. Circulation 92 [Suppl I]: I–341
Weyrich AS, Ma X-L, Lefer DJ, Albertine KH, Lefer AM (1993) In vivo neutralization of P-selectin protects feline heart and endothelium in myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury. J Clin Invest 91: 2620–2629
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1997 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lefer, D.J. (1997). Immunological Mechanisms in Myocardial Reperfusion Injury. In: Schultheiss, HP., Schwimmbeck, P. (eds) The Role of Immune Mechanisms in Cardiovascular Disease. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-60463-8_20
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-60463-8_20
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-61358-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-60463-8
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive