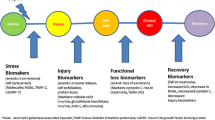
Abstract
Both sepsis and renal dysfunction are common in critically ill patients. A consensus definition for sepsis has existed for over 20 years, and more recently renal dysfunction has also been categorized by consensus into progressive grades and termed acute kidney injury (AKI). Of patients in the intensive care unit (ICU) who develop AKI, sepsis and septic shock have been estimated to be the likely cause in 11–50% of cases (Bagshaw et al. 2007a; Oh et al. 1993; Metnitz et al. 2002; Schwilk et al. 1997; Douma et al. 1997; Uchino et al. 2005). The incidence of AKI increases with the severity of sepsis, from approximately 19% in patients with moderate sepsis, to 23% in patients with severe sepsis, and 51% in patients with septic shock (Riedemann et al. 2003; Rangel-Frausto et al. 1995). AKI in septic patients, or septic AKI, is frequently associated with other organ failures. A retrospective analysis of over 120,000 patients in Australia and New Zealand, demonstrated that patients with septic AKI had greater physiological derangements with higher simplified acute physiology score II (SAPS II) and sequential organ failure (SOFA) scores, and a greater requirement for mechanical ventilation and infusion of vasoactive drugs, than non-septic AKI patients (Bagshaw et al. 2008). In this study septic AKI was associated with significantly higher covariate adjusted mortality in ICU (OR 1.60, 95% CI 1.5–1.7) and hospital mortality (OR 1.53, 95% CI 1.46–1.60) compared with non-septic AKI (Bagshaw et al. 2008).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagshaw SM, Langenberg C, Bellomo R (2006) Urinary biochemistry and microscopy in septic acute renal failure: a systematic review. Am J Kidney Dis 48:695–705
Bagshaw SM, Uchino S, Bellomo R et al (2007a) Septic acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: clinical characteristics and outcomes. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2:431–439
Bagshaw SM, Langenberg C, Haase M et al (2007b) Urinary biomarkers in septic acute kidney injury. Intensive Care Med 33:1285–1296
Bagshaw SM, George C, Bellomo R et al (2008a) A comparison of the RIFLE and AKIN criteria for acute kidney injury in critically ill patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:1569–1574
Bagshaw SM, George C, Bellomo R et al (2008b) Early acute kidney injury and sepsis: a multicentre evaluation. Crit Care 12:R47
Bagshaw SM, Bennett M, Haase M et al (2010) Plasma and urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in septic versus non-septic acute kidney injury in critical illness. Intensive Care Med 36:452–461
Bellomo R, Kellum JA, Ronco C (2004a) Defining acute renal failure: physiological principles. Intensive Care Med 30:33–37
Bellomo R, Ronco C, Kellum JA et al (2004b) Acute renal failure – definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: the Second International Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Group. Crit Care 8:R204–R212
Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB et al (1992) Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference Committee. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine. Chest 101:1644–1655
Brändström E, Grzegorczyk A, Jacobsson L et al (1998) GFR measurement with iohexol and 51Cr-EDTA. A comparison of the two favoured GFR markers in Europe. Nephrol Dial Transplant 13:1176–1182
Brealey D, Singer M (2003) Mitochondrial dysfunction in sepsis. Curr Infect Dis Rep 5:365–371
Cohen J (2002) The immunopathogenesis of sepsis. Nature 420:885–891
Coresh J, Astor BC, McQuillan G et al (2002) Calibration and random variation of the serum creatinine assay as critical elements of using equations to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Am J Kidney Dis 39:920–929
Delanaye P, Lambermont B, Chapelle JP et al (2004) Plasmatic cystatin C for the estimation of glomerular filtration rate in intensive care units. Intensive Care Med 30:980–983
Delanghe J (2002) Standardization of creatinine determination and its consequences for the clinician. Acta Clin Belg 57:172–175
Di Giantomasso D, May CN, Bellomo R (2003a) Norepinephrine and vital organ blood flow during experimental hyperdynamic sepsis. Intensive Care Med 29:1774–1781
Di Giantomasso D, May CN, Bellomo R (2003b) Vital organ blood flow during hyperdynamic sepsis. Chest 124:1053–1059
Douma CE, Redekop WK, van der Meulen JH et al (1997) Predicting mortality in intensive care patients with acute renal failure treated with dialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 8:111–117
El-Achkar TM, Huang X, Plotkin Z et al (2006) Sepsis induces changes in the expression and distribution of Toll-like receptor 4 in the rat kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290:F1034–F1043
Filep JG (2000) Role for endogenous endothelin in the regulation of plasma volume and albumin escape during endotoxin shock in conscious rats. Br J Pharmacol 129:975–983
Herrera-Gutiérrez ME, Seller-Pérez G, Banderas-Bravo E et al (2007) Replacement of 24-h creatinine clearance by 2-h creatinine clearance in intensive care unit patients: a single-center study. Intensive Care Med 33:1900–1906
Hoste EA, Lameire NH, Vanholder RC et al (2003) Acute renal failure in patients with sepsis in a surgical ICU: predictive factors, incidence, comorbidity, and outcome. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:1022–1030
Jo SK, Cha DR, Cho WY et al (2002) Inflammatory cytokines and lipopolysaccharide induce Fas-mediated apoptosis in renal tubular cells. Nephron 91:406–415
Joannidis M, Metnitz B, Bauer P et al (2009) Acute kidney injury in critically ill patients classified by AKIN versus RIFLE using the SAPS 3 database. Intensive Care Med 35:1692–1702
Kang YH, Falk MC, Bentley TB et al (1995) Distribution and role of lipopolysaccharide in the pathogenesis of acute renal proximal tubule injury. Shock 4:441–449
Kellum JA (2008) Acute kidney injury. Crit Care Med 36:S141–S145
Kim KE, Onesti G, Ramirez O et al (1969) Creatinine clearance in renal disease. A reappraisal. Br Med J 4:11–14
Kohl BA, Deutschman CS (2006) The inflammatory response to surgery and trauma. Curr Opin Crit Care 12:325–332
Kon V, Badr KF (1991) Biological actions and pathophysiologic significance of endothelin in the kidney. Kidney Int 40:1–12
Koo DJ, Zhou M, Chaudry IH et al (2001) The role of adrenomedullin in producing differential hemodynamic responses during sepsis. J Surg Res 95:207–218
Kümpers P, Hafer C, Lukasz A et al (2010) Serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin at inception of renal replacement therapy predicts survival in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. Crit Care 14:R9
Lam M, Kaufman CE (1985) Fractional excretion of sodium as a guide to volume depletion during recovery from acute renal failure. Am J Kidney Dis 6:18–21
Lameire N, Van Biesen W, Vanholder R (2005) Acute renal failure. Lancet 365:417–430
Lameire N, Van Biesen W, Vanholder R (2008) Acute kidney injury. Lancet 372:1863–1865
Landry DW, Oliver JA (2001) The pathogenesis of vasodilatory shock. N Engl J Med 345:588–595
Langenberg C, Bellomo R, May C et al (2005) Renal blood flow in sepsis. Crit Care 9:R363–R374
Langenberg C, Bellomo R, May CN et al (2006a) Renal vascular resistance in sepsis. Nephron Physiol 104:1–11
Langenberg C, Wan L, Egi M et al (2006b) Renal blood flow in experimental septic acute renal failure. Kidney Int 69:1996–2002
Langenberg C, Bagshaw SM, May CN et al (2008) The histopathology of septic acute kidney injury: a systematic review. Crit Care 12:R38
Le Dorze M, Legrand M, Payen D et al (2009) The role of the microcirculation in acute kidney injury. Curr Opin Crit Care 15:503–508
Lerolle N, Nochy D, Guérot E et al (2010) Histopathology of septic shock induced acute kidney injury: apoptosis and leukocytic infiltration. Intensive Care Med 36:471–478
Leverve XM (2007) Mitochondrial function and substrate availability. Crit Care Med 35:S454–S460
Levey AS (1990) Measurement of renal function in chronic renal disease. Kidney Int 38:167–184
Levy MM, Fink MP, Marshall JC et al (2003) 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference. Crit Care Med 31:1250–1256
Levy MM, Dellinger RP, Townsend SR et al (2010) The Surviving Sepsis Campaign: results of an international guideline-based performance improvement program targeting severe sepsis. Intensive Care Med 36:222–231
Liangos O, Perianayagam MC, Vaidya VS et al (2007) Urinary N-acetyl-beta-(D)-glucosaminidase activity and kidney injury molecule-1 level are associated with adverse outcomes in acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:904–912
Lopes JA, Fernandes P, Jorge S et al (2008) Acute kidney injury in intensive care unit patients: a comparison between the RIFLE and the Acute Kidney Injury Network classifications. Crit Care 12:R110
Mårtensson J, Bell M, Oldner A et al (2010) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in adult septic patients with and without acute kidney injury. Intensive Care Med 36(8):1333–1340, Epub 2010 Apr 16
Mathiak G, Szewczyk D, Abdullah F et al (2000) An improved clinically relevant sepsis model in the conscious rat. Crit Care Med 28:1947–1952
Mehta RL, Kellum JA, Shah SV et al (2007) Acute Kidney Injury Network: report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury. Crit Care 11:R31
Messaris E, Memos N, Chatzigianni E et al (2008) Apoptotic death of renal tubular cells in experimental sepsis. Surg Infect (Larchmt) 9:377–388
Messmer UK, Briner VA, Pfeilschifter J (1999) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and lipopolysaccharide induce apoptotic cell death in bovine glomerular endothelial cells. Kidney Int 55:2322–2337
Metnitz PG, Krenn CG, Steltzer H et al (2002) Effect of acute renal failure requiring renal replacement therapy on outcome in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med 30:2051–2058
Mori K, Nakao K (2007) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as the real-time indicator of active kidney damage. Kidney Int 71:967–970
Musson RA, Morrison DC, Ulevitch RJ (1978) Distribution of endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide) in the tissues of lipopolysaccharide-responsive and -unresponsive mice. Infect Immun 21:448–457
Nejat M, Pickering JW, Walker RJ et al (2010) Urinary cystatin C is diagnostic of acute kidney injury and sepsis, and predicts mortality in the intensive care unit. Crit Care 14:R85
Neveu H, Kleinknecht D, Brivet F et al (1996) Prognostic factors in acute renal failure due to sepsis. Results of a prospective multicentre study. The French Study Group on Acute Renal Failure. Nephrol Dial Transplant 11:293–299
Oh TE, Hutchinson R, Short S et al (1993) Verification of the Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation scoring system in a Hong Kong intensive care unit. Crit Care Med 21:698–705
Ostermann M, Chang R, Riyadh ICU, Group PU (2008) Correlation between the AKI classification and outcome. Crit Care 12:R144
Parikh CR, Devarajan P (2008) New biomarkers of acute kidney injury. Crit Care Med 36:S159–S165
Parikh CR, Abraham E, Ancukiewicz M et al (2005) Urine IL-18 is an early diagnostic marker for acute kidney injury and predicts mortality in the intensive care unit. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:3046–3052
Parrillo JE, Parker MM, Natanson C et al (1990) Septic shock in humans. Advances in the understanding of pathogenesis, cardiovascular dysfunction, and therapy. Ann Intern Med 113:227–242
Rangel-Frausto MS, Pittet D, Costigan M et al (1995) The natural history of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). A prospective study. JAMA 273:117–123
Reinhart K, Bayer O, Brunkhorst F et al (2002) Markers of endothelial damage in organ dysfunction and sepsis. Crit Care Med 30:S302–S312
Ricci Z, Cruz D, Ronco C (2008) The RIFLE criteria and mortality in acute kidney injury: a systematic review. Kidney Int 73:538–546
Riedemann NC, Guo RF, Ward PA (2003) The enigma of sepsis. J Clin Invest 112:460–467
Rivers E, Nguyen B, Havstad S et al (2001) Early goal-directed therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med 345:1368–1377
Ronco C, Bellomo R (1998) Critical care nephrology. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht
Schrier RW, Wang W (2004) Acute renal failure and sepsis. N Engl J Med 351:159–169
Schwilk B, Wiedeck H, Stein B et al (1997) Epidemiology of acute renal failure and outcome of haemodiafiltration in intensive care. Intensive Care Med 23:1204–1211
Shemesh O, Golbetz H, Kriss JP et al (1985) Limitations of creatinine as a filtration marker in glomerulopathic patients. Kidney Int 28:830–838
Sladen RN, Endo E, Harrison T (1987) Two-hour versus 22-hour creatinine clearance in critically ill patients. Anesthesiology 67:1013–1016
Stevens LA, Levey AS (2005) Measurement of kidney function. Med Clin North Am 89:457–473
Stevens LA, Levey AS (2009) Measured GFR as a confirmatory test for estimated GFR. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:2305–2313
Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R et al (2005) Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. JAMA 294:813–818
Udy AA, Roberts JA, Boots RJ et al (2010) Augmented renal clearance: implications for antibacterial dosing in the critically ill. Clin Pharmacokinet 49:1–16
Vaidya VS, Ramirez V, Ichimura T et al (2006) Urinary kidney injury molecule-1: a sensitive quantitative biomarker for early detection of kidney tubular injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290:F517–F529
Vaz AJ (1983) Low fractional excretion of urine sodium in acute renal failure due to sepsis. Arch Intern Med 143:738–739
Villa P, Jiménez M, Soriano MC et al (2005) Serum cystatin C concentration as a marker of acute renal dysfunction in critically ill patients. Crit Care 9:R139–R143
Villazón SA, Sierra UA, López SF et al (1975) Hemodynamic patterns in shock and critically ill patients. Crit Care Med 3:215–221
Waikar SS, Bonventre JV (2007) Biomarkers for the diagnosis of acute kidney injury. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 16:557–564
Wan L, Bellomo R, May CN (2006) The effect of normal saline resuscitation on vital organ blood flow in septic sheep. Intensive Care Med 32:1238–1242
Wan L, Bagshaw SM, Langenberg C et al (2008) Pathophysiology of septic acute kidney injury: what do we really know? Crit Care Med 36:S198–S203
Wang W, Jittikanont S, Falk SA et al (2003) Interaction among nitric oxide, reactive oxygen species, and antioxidants during endotoxemia-related acute renal failure. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 284:F532–F537
Wells M, Lipman J (1997a) Measurements of glomerular filtration in the intensive care unit are only a rough guide to renal function. S Afr J Surg 35:20–23
Wells M, Lipman J (1997b) Pitfalls in the prediction of renal function in the intensive care unit. A review. S Afr J Surg 35:16–19
Wheeler DS, Devarajan P, Ma Q et al (2008) Serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a marker of acute kidney injury in critically ill children with septic shock. Crit Care Med 36:1297–1303
Xu S, Venge P (2000) Lipocalins as biochemical markers of disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1482:298–307
Yegenaga I, Hoste E, Van Biesen W et al (2004) Clinical characteristics of patients developing ARF due to sepsis/systemic inflammatory response syndrome: results of a prospective study. Am J Kidney Dis 43:817–824
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Choi, G.Y.S., Joynt, G.M., Gomersall, C.D. (2012). Assessing Renal Dysfunction in Septic Patients. In: Rello, J., Lipman, J., Lisboa, T. (eds) Sepsis Management. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-03519-7_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-03519-7_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-03518-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-03519-7
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)