Abstract
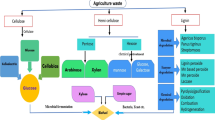
The multifaceted hydrolytic enzyme xylanase has been found to play a pivotal role in the energy and green technology sectors. Extensive research is being carried out with the aim to produce xylanases that would fulfill industrial parameters, in the paper and pulp and fuel industries. Cellulase-free xylanase with good thermal stability finds promising use for biobleaching in paper manufacturing. In current scenario, it has been found that renewable energy is a burgeoning area, where xylanase finds a major role. Xylanase is synergistically involved with other cooperating enzymes for the deconstruction of lignocellulosic raw material, which ultimately paves way for the production of fuel ethanol. In other words, efficient utilization of lignocellulosic raw materials will positively boost the economics of alternate fuel industry.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvira P, Tomás-Pejó E, Ballesteros M, Negro MJ (2010) Pretreatment technologies for an efficient bioethanol production process based on enzymatic hydrolysis: a review. Bioresour Technol 101:4851–4861. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2009.11.093
Balat M (2011) Production of bioethanol from lignocellulosic materials via the biochemical pathway: a review. Energy Convers Manage 52:858–875. doi:10.1016/j.enconman.2010.08.013
Balat M, Balat H (2009) Recent trends in global production and utilization of bioethanol fuel. Appl Energy 86:2273–2282. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2009.03.015
Beg QK, Kapoor M, Mahajan L, Hoondal GS (2001) Microbial xylanases and their industrial applications: a review. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56:326–338. doi:10.1007/s002530100704
Beukes N, Pletschke BI (2011) Effect of alkaline pre-treatment on enzyme synergy for efficient hemicelluloses hydrolysis in sugarcane bagasse. Bioresour Technol 102:5207–5213. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2011.01.090
Bhalla A, Bischoff KM, Sani RK (2015) Highly thermostable xylanase production from a thermophilic Geobacillus sp. strain WSUCF1 utilizing lignocellulosic biomass. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 3:1–8. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2015.00084
Birijlall N, Manimaran A, Kumar KS, Permaul K, Singh S (2011) High level expression of a recombinant xylanase by Pichia pastoris NC38 in a 5 L fermenter and its efficiency in biobleaching of bagasse pulp. Bioresour Technol 102:9723–9729. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2011.07.059
Bungay H (1992) Product opportunities for biomass refining. Enzyme Microb Technol 14:501–507. doi:10.1016/0141-0229(92)90145-E
Chapla D, Divecha J, Madamwar D, Shah A (2010) Utilization of agro-industrial waste for xylanase production by Aspergillus foetidus MTCC 4898 under solid state fermentation and its application in saccharification. Biochem Eng J 49:361–369. doi:10.1016/j.bej.2010.01.012
Collins T, Gerday C, Feller G (2005) Xylanases, xylanase families and extremophilic xylanases. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:3–23. doi:10.1016/j.femsre.2004.06.005
Dale BE, Leong CK, Pham TK, Esquivel VM, Rios L, Latimer VM (1996) Hydrolysis at low enzyme levels: application of the AFEX process. Bioresour Technol 56:111–116. doi:10.1016/0960-8524(95)00183-2
de Freitas Branco R, dos Santos JC, da Silva SS (2011) A novel use for sugarcane bagasse hemicellulosic fraction: xylitol enzymatic production. Biomass Bioenergy 35:3241–3246. doi:10.1016/j.biombioe.2011.02.014
Dodd D, Cann I (2009) Enzymatic deconstruction of xylan for biofuel production. Glob Change Biol Bioenergy 18:2–17. doi:10.1111/j.1757-1707.2009.01004.x
Duarte MCT, Silva EC, Gomes IMB, Ponezi AN, Portugal EP, Vicente JR, Davanzo E (2003) Xylan-hydrolyzing enzyme system from Bacillus pumilus CBMAI 0008 and its effects on Eucalyptus grandis kraft pulp for pulp bleaching improvement. Bioresour Technol 88:9–15. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(02)00270-5
Fernandez-Bolanos J, Felizon B, Heredia A, Rodriguez R, Guillen R, Jimenez A (2001) Steam-explosion of olive stones: hemicellulose solubilization and enhancement of enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose. Bioresour Technol 79:53–61. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(01)00015-3
Fillat U, Roncero MB, Sacón VM, Bassa A (2012) Integrating a xylanase treatment into an industrial-type sequence for eucalyptus kraft pulp bleaching. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:2830–2837. doi:10.1021/ie202863d
Garcia SG, Moreira T, Artal G, Maldonado L, Feijoo G (2010) Environmental impact assessment of non-wood based pulp production by soda-anthraquinone pulping process. J Clean Prod 18:137–145. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2009.10.008
Goldemberg J (2008) Environmental and ecological dimensions of biofuels. In: Proceedings of the conference on the ecological dimensions of biofuels, Washington, DC, 10 March
Gopalakrishnan (2010) Studies on marine microbes of west coast of India for their potential to produce industrially important enzymes. PhD Thesis. http://hdl.handle.net/10603/9199
Heaton EA, Flavell RB, Mascia PN, Thomas SR, Dohleman FG, Long SP (2008) Herbaceous energy crop development: recent progress and future prospects. Curr Opin Biotechnol 19:202–209. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2008.05.001
Heck JX, Flores SH, Hertz PF, Ayub MAZ (2005) Optimization of cellulase-free xylanase activity produced by Bacillus coagulans BL69 in solid-state cultivation. Process Biochem 40:107–112. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2003.11.044
Heo S, Kwak J, Oh H-W, Park D-S, Kyung SB, Dong HS, Park H-Y (2006) Characterization of an extracellular xylanase in Paenibacillus sp. HY-8 isolated from an herbivorous longicorn beetle. J Microbiol Biotechnol 16:1753–1759
Jiang L, Zheng A, Zhao Z, He F, Li H, Liu W (2015) Obtaining fermentable sugars by dilute acid hydrolysis of hemicellulose and fast pyrolysis of cellulose. Bioresour Technol 182:364–367. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2015.01.032
Kaar WE, Holtzaple MT (2000) Using lime pretreatment to facilitate the enzymatic hydrolysis of corn stover. Biomass Bioenergy 18:189–199. doi:10.1016/S0961-9534(99)00091-4
Kiddinamoorthy J, Anceno AJ, Haki GD, Rakshit SK (2008) Production, purification and characterization of Bacillus sp. GRE7 xylanase and its application in eucalyptus kraft pulp biobleaching. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:605–612. doi:10.1007/s11274-007-9516-2
Kim DY, Han MK, Lee JS, Oh H-W, Park D-S, Shin D-H, Bae KS, Son K-H, Park H-Y (2009) Isolation and characterization of a cellulase-free endo-β-1,4-xylanase produced by an invertebrate-symbiotic bacterium, Cellulosimicrobium sp. HY-13. Process Biochem 44:1055–1059. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2009.05.005
Ko C-H, Lin Z-P, Tu J, Tsai C-H, Liu C-C, Chen H-T, Wang T-P (2010) Xylanase production by Paenibacillus campinasensis BL11 and its pretreatment of hardwood kraft pulp bleaching. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 64:13–19. doi:10.1016/j.ibiod.2009.10.001
Kocabaş DS, Güder S, Özben N (2015) Purification strategies and properties of a low-molecular weight xylanase and its application in agricultural waste biomass hydrolysis. J Mol Catal B Enzym 115:66–75. doi:10.1016/j.molcatb.2015.01.012
Kumar V, Satyanarayana T (2012) Thermo-alkali-stable xylanase of a novel polyextremophilic Bacillus haloduransTSEV1 and its application in biobleaching. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 75:138–145. doi:10.1016/j.ibiod.2012.09.007
Laser M, Schulman D, Allen SG, Lichwa J, Antal MJ Jr, Lynd LR (2002) A comparison of liquid hot water and steam pretreatments of sugar cane bagasse for bioconversion to ethanol. Bioresour Technol 81:33–44. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(01)00103-1
Li X, She Y, Sun B, Song H, Zhu Y, Lv Y, Song H (2010) Purification and characterization of a cellulase-free, thermostable xylanase from Streptomyces rameus L2001 and its biobleaching effect on wheat straw pulp. Biochem Eng J 52:71–78. doi:10.1016/j.bej.2010.07.006
Manimaran A, Vatsala TM (2007) Biobleaching of banana fibre pulp using Bacillus subtilis C O1 xylanase produced from wheat bran under solid-state cultivation. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 34:745–749. doi:10.1007/s10295-007-0248-y
McLaughlin SB, Kszos LA (2005) Development of switchgrass (Panicum virgatum) as a bioenergy feedstock in the United States. Biomass Bioenergy 28:515–535. doi:10.1016/j.biombioe.2004.05.006
Menon G, Mody K, Keshri J, Jha B (2010a) Isolation, purification, and characterization of haloalkaline xylanase from a marine Bacillus pumilus strain, GESF-1. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 15:998–1005. doi:10.1007/s12257-010-0116-x
Menon V, Prakash G, Prabhune A, Rao M (2010b) Biocatalytic approach for the utilization of hemicellulose for ethanol production from agricultural residue using thermostable xylanase and thermotolerant yeast. Bioresour Technol 101:5366–5373. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2010.01.150
Mosier N, Wyman CE, Dale BD, Elander RT, Lee YY, Holtzapple M, Ladisch CM (2005) Features of promising technologies for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour Technol 96:673–686. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2004.06.025
Nie S, Wang S, Qin C, Yao S, Ebonka JF, Song X, Li K (2015) Removal of hexenuronic acid by xylanase to reduce adsorbable organic halides formation in chlorine dioxide bleaching of bagasse pulp. Bioresour Technol 196:413–417. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2015.07.115
Oh H-W, Heo S-Y, Kim D-Y, Park D-S, Bae K-S, Park S-Y (2008) Biochemical characterization and sequence analysis of a xylanase produced by an exo-symbiotic bacterium of Gryllotalpa orientalis, Cellulosimicrobium sp. HY-12. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek J Microb 93:437–442. doi:10.1007/s10482-007-9210-2
Parrish DJ, Fike JH (2005) The biology and agronomy of Switch-grass for biofuels. Crit Rev Plant Sci 24:423–459. doi:10.1080/07352680500316433
Passarini KC, Pereira MA, Farias TMB, Calarge FA, Santana CC (2014) Assessment of the viability and sustainability of an integrated waste management system for the city of Campinas (Brazil), by means of ecological cost accounting. J Clean Prod 65:479–488. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.08.037
Pedersen M, Johansen KS, Meyer AS (2011) Low temperature lignocellulose pretreatment: effects and interactions of pretreatment pH are critical for maximizing enzymatic monosaccharide yields from wheat straw. Biotechnol Biofuels 4:1–10. doi:10.1186/1754-6834-4-11
Qing Q, Wyman CE (2011) Supplementation with xylanase and β-xylosidase to reduce xylo-oligomer and xylan inhibition of enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose and pretreated corn stover. Biotechnol Biofuels 4:18. doi:10.1186/1754-6834-4-18
Rémond C, Aubry N, Crônier D, Noël S, Martel F, Roge B, Rakotoarivonina H, Debeire P, Chabbert B (2010) Combination of ammonia and xylanase pretreatments: impact on enzymatic xylan and cellulose recovery from wheat straw. Bioresour Technol 101:6712–6717. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2010.03.115
Sadhasivam S, Savitha S, Swaminathan K (2010) Deployment of Trichoderma harzianum WL1 laccase in pulp bleaching and paper industry effluent treatment. J Clean Prod 18:799–806. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2009.11.014
Saha BC (2003) Hemicellulose bioconversion: a review. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 30:279–291. doi:10.1007/s10295-003-0049-x
Saha BC, Bothast RJ (1997) Enzymes in lignocellulosic biomass conversion. In: Saha BC, Woodward J (eds) Fuels and chemicals from biomass. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp 46–56
Saha BC, Bothast RJ (1999) Pretreatment and enzymatic saccharification of corn fiber. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 76:65–77. doi:10.1385/ABAB:76:2:65
Saleem M, Tabassum MR, Yasmin R, Imran M (2009) Potential of xylanase from thermophilic Bacillus sp. XTR-10 in biobleaching of wood kraft pulp. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 63:1119–1124. doi:10.1016/j.ibiod.2009.09.009
Saleem M, Aslam F, Akhtar MS, Tariq M, Rajoka MI (2012) Characterization of a thermostable and alkaline xylanase from Bacillus sp. and its bleaching impact on wheat straw pulp. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:513–522. doi:10.1007/s11274-011-0842-z
Sasson A (2005) Industrial and environmental biotechnology: achievements, prospects, and perceptions, UNU-IAS Report, pp 1–26
Schmidt AS, Thomsen AB (1998) Optimization of wet oxidation pretreatment of wheat straw. Bioresour Technol 64:139–151. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(97)00164-8
Senthilkumar SR, Dempsey M, Krishnan C, Gunasekaran P (2008) Optimization of biobleaching of paper pulp in an expanded bed bioreactor with immobilized alkali stable xylanase by using response surface methodology. Bioresour Technol 99:7781–7787. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2008.01.058
Shallom D, Shoham Y (2003) Microbial hemicellulases. Curr Opin Microbiol 6:219–228. doi:10.1016/S1369-5274(03)00056-0
Sharma A, Thakur VV, Shrivastava A, Jain RK, Mathur RM, Gupta R, Kuhad RC (2014) Xylanase and laccase based enzymatic kraft pulp bleaching reduces adsorbable organic halogen (AOX) in bleach effluents: a pilot scale study. Bioresour Technol 169:96–102. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2014.06.066
Sharma AK, Anupam K, Swaroop V, Lal PS, Bist V (2015a) Pilot scale soda anthraquinone pulping of palm oil empty fruit bunches and elemental chlorine free bleaching of resulting pulp. J Clean Prod 106:422–429. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.03.095
Sharma P, Sood S, Singh G, Capalash N (2015b) An eco-friendly process for biobleaching of eucalyptus kraft pulp with xylanase producing Bacillus halodurans. J Clean Prod 87:966–970. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.09.083
Somerville C (2007) Biofuels. Curr Biol 17:R115–R119. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2007.01.010
Sun Y, Cheng J (2002) Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials for ethanol production: a review. Bioresour Technol 83:1–11. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(01)00212-7
Thakur VV, Jain RK, Mathur RM (2012) Studies on xylanase and laccase enzymatic prebleaching to reduce chlorine-based chemicals during CEH and ECF bleaching. BioResources 7:2220–2235
Viikari L, Kantelinen A, Sundquist J, Linko M (1994) Xylanases in bleaching: from an idea to the industry. FEMS Microbiol Rev 13:335–350. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.1994.tb00053.x
Wang G, Luo H, Wang Y, Huang H, Shi P, Yang P, Meng K, Bai Y, Yao B (2011) A novel cold-active xylanase gene from the environmental DNA of goat rumen contents: direct cloning, expression and enzyme characterization. Bioresour Technol 102:3330–3336. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2010.11.004
Weil J, Westgate P, Kohlmann K, Ladisch MR (1994) Cellulose pretreatments of lignocellulosic substrates. Enzyme Microb Technol 16:1002–1004. doi:10.1016/0141-0229(94)90012-4
Wyman CE (1994) Ethanol from lignocellulosic biomass: technology, economics, and opportunities. Bioresour Technol 50:3–16. doi:10.1016/0960-8524(94)90214-3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Menon, G., Datta, S. (2017). Xylanases: From Paper to Fuel. In: Kalia, V., Kumar, P. (eds) Microbial Applications Vol.1. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-52666-9_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-52666-9_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-52665-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-52666-9
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)