Abstract
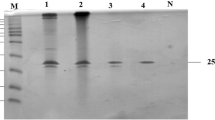
A haloalkalitolerant xylanase-producing Bacillus pumilus strain, GESF1 was isolated from an experimental salt farm of CSMCRI. Birch wood xylan and xylose induced maximum xylanase production with considerable activity seen in wheat straw and no activity at all with caboxymethyl cellulose (CMC). A three step purification yielded 21.21-fold purification with a specific activity of 112.42 U/mg protein (unit expressed as μmole of xylose released per min). Xylanase produced showed an optimum activity at pH 8.0, with approximately 50 and 30% relative activity at a pH 6.0 and 10.0, respectively. The temperature optimum was 40°C and kinetic properties such as Km and Vmax were 5.3 mg/mL and 0.42 μmol/min/mL (6593.4 μmol/min/mg protein). Xylanase activity (160∼ 120%) was considerably enhanced in 2.5 to 7.5% NaCl with 87 and 73% retention of activity in 10 and 15% of NaCl. Enzyme activity was enhanced by Ca2+, Mn2+, Mg2+, and Na+ but strongly inhibited by heavy metals such as Hg2+, Fe3+, Cu2+, Cd2+, and Zn2+. Organic reagents such as β-Mercaptoethanol enhanced xylanase activity whereas EDTA strongly inhibited its activity. Xylanase, purified from the Bacillus pumilus strain, GESF1 could have potential biotechnological applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Collins, T., C. Gerday, and G. Feller (2005) Xylanases, xylanase families and extremophilic xylanases. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 29: 3–23.
Shallom, D. and Y. Shoham (2003) Microbial hemicellulases. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 6: 219–228.
Singh, S., A. M. Madlala, and B. A. Prior (2003) Thermomyces lanuginosus: properties of strains and their hemicellulases. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 27: 3–16.
Lee, S. F., C. W. Forsberg, and L. N. Gibbins (1985) Xylanolytic activity of Clostridium acetobutylicum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 50: 1068–1076.
Marques, S., L. Alves, S. Ribeiro, F. M. Gírio, and M. T. Amaral- Collaco (1998) Characterization of a thermotolerant and alkalotolerant xylanase from a Bacillus sp. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 73: 159–172.
Shao, W. and J. Wiegel (1992) Purification and characterization of a thermostable β-xylosidase from Thermoanaerobacter ethanolicus. J. Bacteriol. 174: 5848–5853.
Bhat, M. K. (2000) Cellulases and related enzymes in biotechnology. Biotechnol. Adv. 18: 355–383.
Kulkarni, N., A. Shendye, and M. Rao (1999) Molecular and biotechnological aspects of xylanases. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 23: 411–456.
Mohandass, C. and C. Raghukumar (2005) Biological deinking of inkjet-printed paper using Vibrio alginolyticus and its enzymes. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 32: 424–429.
Mørkbak, A. L. and W. Zimmermann (1998) Deinking of mixed office paper, old newspaper and vegetable oil-based ink printed paper using cellulases, xylanases and lipases. Prog. Pap. Recycl. 7: 14–21.
Beg, Q. K., M. Kapoor, L. Mahajan, and G. S. Hoondal (2001) Microbial xylanases and their industrial applications: A review. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 56: 326–338.
Kiddinamoorthy, J., A. J. Anceno, G. D. Haki, and S. K. Rakshit (2008) Production, purification and characterization of Bacillus sp. GRE7 xylanase and its application in eucalyptus kraft pulp biobleaching. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 24: 605–612.
Subramaniyan, S. and P. Prema (2002) Biotechnology of microbial xylanases: Enzymology, molecular biology and application. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 22: 33–46.
Haki, G. D. and S. K. Rakshit (2003) Developments in industrially important thermostable enzymes: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 89: 17–34.
Holt, J. D. (1994) Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology. 9th ed., pp. 559–564. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore.
Sambrook, J. and D. W. Russel (2001) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. 3rd ed., p. 1.72–1.73. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Sambrook, J. and D. W. Russel (2001) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. 3rd ed., p. 5.77 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
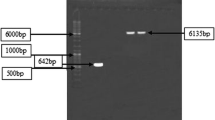
Weisburg, W. G., S. M. Barns, D. A. Pelletier, and D. J. Lane (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J. Bacteriol. 173: 697–703.
Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215: 403–410.
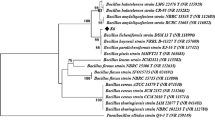
Tamura, K., J. Dudley, M. Nei, and S. Kumar (2007) MEGA4: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 24: 1596–1599.
Saitou, N. and M. Nei (1987) The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4: 406–425.
Roy, N. (2004) Characterization and identification of xylanase producing bacterial strains isolated from soil and water. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 7: 711–716.
Miller, G. L. (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal. Chem. 31: 426–428.
Lowry, O. H., N. J. Rosebrough, A. C. Farr, and R. J. Randall (1951) Protein measurement with folin phenol reagent. J. Bio. Chem. 193: 265–275.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685.
Wejse, P. L., K. Ingvorsen, and K. K. Mortensen (2003) Purification and characterisation of two extremely halotolerant xylanases from a novel halophilic bacterium. Extremophiles 7: 423–431.
Dimitrov, P. L., M. S. Kambourova, R. D. Mandeva, and E. I. Emanuilova (1997) Isolation and characterization of xylandegrading alkali-tolerant thermophiles. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 157: 27–30.
Gessesse, A. and G. Mamo (1998) Purification and characterization of an alkaline xylanase from alkaliphilic Micrococcus sp. AR-135. J. Ind. Microbiol. 20: 210–214.
Honda, H., T. Kudo, and K. Horikoshi (1985) Purification and partial characterization of alkaline xylanase from Escherichia coli carrying pCX311. Agric. Biol. Chem. 49: 3165–3169.
Khandeparkar, R. and N. B. Bhosle (2006) Purification and characterization of thermoalkalophilic xylanase isolated from the Enterobacter sp. MTCC 5112. Res. Microbiol. 157: 315–325.
Kuhad, R. C., P. Chopra, B. Battan, M. Kapoor, and S. Kuhar (2006) Production, partial purification and characterization of a thermo-alkali stable xylanase from Bacillus sp. RPP-1. Ind. J. Microbiol. 46: 13–23.
Mamo. G., R. H. Kaul, and B. Mattiasson (2006) A thermostable alkaline active endo-β-1-4-xylanase from Bacillus halodurans S7: Purification and characterization. Enz. Microb. Technol. 39: 1492–1498.
Tseng, M. J., M. N. Yap, K. Ratanakhanokchai, K. L. Kyu, and S. T. Chen (2002) Purification and characterization of two cellulase free xylanases from an alkaliphilic Bacillus firmus. Enz. Microb. Technol. 30: 590–595.
Uchino, F. and T. Nakane (1981) A thermostable xylanase from a thermophilic acidophilic Bacillus sp. Agric. Biol. Chem. 45: 1121–1127.
Kiyohara, M., K. Sakaguchi, K. Yamaguchi, T. Araki, T. Nakamura, and M. Ito (2005) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel β-1,3-xylanase possessing two putative carbohydratebinding modules from a marine bacterium Vibrio sp. Strain AX-44. Biochem. J. 388: 949–957.
Wainø, M. and K. Ingvorsen (2003) Production of b-xylanase and b-xylosidase by the extremely halophilic archaeon Halorhabdus utahensis. Extremophiles 7: 87–93.
Bocchini, D. A., E. Gomes, and R. Da Silva (2008) Xylanase production by Bacillus circulans D1 using maltose as carbon source. Appl. Biochem. Biotecnol. 146: 29–37.
Lindner, C., J. Stulke, and M. Hecker (1994) Regulation of xylanolytic enzymes in Bacillus subtilis. Microbiol. 140:753–757.
Gessesse, A. and B. A. Gashe (1997) Production of alkaline xylanase by an alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. isolated from an alkaline soda lake. J. Appl. Microbiol. 83: 402–406.
Gupta, S., B. Bushan, and G. S. Hoondal (2000) Isolation, purification and characterization of xylanase from Staphylococcus sp. SG-13 and its application in biobleaching of kraft pulp. J. Appl. Microbiol. 88: 325–334.
Battan, B., J. Sharma, S. S. Dhiman, and R. C. Kuhad (2007) Enhanced production of cellulase-free thermostable xylanase by Bacillus pumilus ASH and its potential application in paper industry. Enz. Microb. Technol. 41: 733–739.
Ratanakhanokchai, K., K. L. Kyu, and M. Tanticharoen (1999) Purification and properties of a xylan-binding endoxylanase from alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. strain K-1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65: 694–697.
Cordeiro, C. A. M., M. L. L. Martins, A. B. Luciano, and R. F. Da silva (2002) Production and properties of xylanase from thermophilic Bacillus sp. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 45: 413–418.
Anuradha, P., K. Vijayalakshmi, N. D. Prasanna, and K. Sridevi (2007) Production and properties of alkaline xylanases from Bacillus sp. Isolated from sugarcane fields. Curr. Sci. 92: 1283–1286.
Amani, M. D., E. Ahwany, and S. Y. Amany (2007) Xylanase production by Bacillus pumilus: optimization by statistical and immobilization methods. Res. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 3: 727–732.
Duarte, M. C. T., E. C. Silva, I. M. B. Gomes, A. N. Ponezi, E. P. Portugal, J. R. Vicente, and E. Davanzo (2003) Xylan-hydrolyzing enzyme system from Bacillus pumilus CBMAI 0008 and its effects on Eucalyptus grandis kraft pulp for pulp bleaching improvement. Bioresour. Technol. 88: 9–15.
Nuyens, F., W. H. Zyl, D. I. H. Verachtert, and C. Michiels (2001) Heterologous expression of the Bacillus pumilus endo-β-xylanase( xynA) gene in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 56: 431–434.
Courtin, C. M., A. Roelants, and J. A. Delcour (1999) Fractionation-reconstitution experiments provide insight into the role of endoxylanases in bread-making. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 47: 1870–1877.
Popper, L. (1997) Simple approaches for identification of baking active xylanases. pp. 110–120. In: Angelino SAGF et al. (eds.). The first European symposium on enzymes and grain processing. TNO Nutrition and Food Research Institute, Zeist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Menon, G., Mody, K., Keshri, J. et al. Isolation, purification, and characterization of haloalkaline xylanase from a marine Bacillus pumilus strain, GESF-1. Biotechnol Bioproc E 15, 998–1005 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-010-0116-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-010-0116-x