Abstract
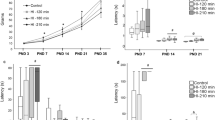
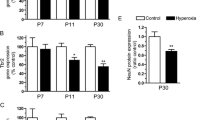
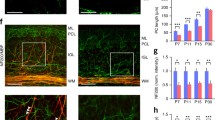
Hypoxic-ischemic (HI) injury is an important cause of death and disabilities. Despite all improvements in neonatal care, the number of children who suffer some kind of injury during birth has remained stable in the last decade. A great number of studies have shown alterations in neural cells and many animal models have been proposed in the last 5 decades. Robinson et al. (2005) proposed an HI model in which the uterine arteries are temporarily clamped on the 18th gestation day. The findings were quite similar to the ones observed in postmortem studies. The white matter is clearly damaged, and a great amount of astrogliosis takes place both in the gray and white matters. Motor changes were also found but no data regarding the cerebellum, an important structure related to motor performance, was presented. Using this model, we have shown an increased level of iNOS at P0 and microgliosis and astrogliosis at P9, and astrogliosis at P23 (up to 4 weeks from the insult). NO is important in migration, maturation, and synaptic plasticity, but in exacerbated levels it may also contribute to cellular and tissue damage. We have also evaluated oligodendroglia development in the cerebellum. At P9 in HI animals, we found a decrease in the number of PDGFRα+ cells and an apparent delay in myelination, suggesting a failure in oligodendroglial progenitors migration/maturation and/or in the myelination process. These results point to an injury in cerebellar development that might help to explain the motor problems in HI.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CP:
-
Cerebral palsy
- CREB:
-
cAMP response element-binding protein
- ED1:
-
Antibody that labels macrophage/microglia
- GFAP:
-
Glial fibrillary acid protein
- HI:
-
Hypoxia ischemia
- MBP:
-
Myelin basic protein
- NADPH-d:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate reduced diaphorase
- NADPH-d+:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate reduced diaphorase positive
- NM:
-
Non-manipulated
- NMDA:
-
N-methyl-d-aspartate
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- NOS:
-
Nitric oxide synthase
- nNOS:
-
Neuronal nitric oxide synthase
- iNOS:
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
- PDGFRα:
-
Platelet derived growth factor receptor alpha
- P0:
-
Postnatal day 0, here considered as the day of birth
- P2, 7, 9, 23:
-
Postnatal day 2, 7, 9, and 23
- SHAM:
-
Surgical control
- SMV:
-
Superior Medullary Vellum
- uANOVA:
-
Univariate analises of variance
- WHO:
-
World health organization
References
Adlinolfi M (1993) Infectious diseases in pregnancy, cytokines and neurological impairment: an hypothesis. Dev Med Child Neurol 35:549–553
Back SA, Han BH, Luo NL et al (2002a) Selective vulnerability of late oligodendrocyte progenitors to hypoxia-ischemia. J Neurosci 22:455–463
Back SA, Luo NL, Borenstein NS et al (2002b) Arrested oligodendrocyte lineage progression during human cerebral white matter development: dissociation between the timing of progenitor differentiation and myelinogenesis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61:197–211
Back SA, Craig A, Kayton RJ et al (2007) Hypoxia-ischemia preferentially triggers glutamate depletion from oligodendroglia and axons in perinatal cerebral white matter. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:334–347. doi:10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600344
Baumann N, Pham-Dinh D (2001) Biology of oligodendrocyte and myelin in the mammalian central nervous system. Physiol Rev 81:871–927
Chanez C, Rabin O, Heroux M, Giguere JF (1993) Cerebral amino acid changes in an animal model of intrauterine growth retardation. Metab Brain Dis 8:61–72
Cummins SK, Nelson KB, Grether JK, Velie EM (1993) Cerebral palsy in four northern California counties, births 1983 through 1985. J Pediatr 123:230–237
Dieni S, Rees S (2003) Dendritic morphology is altered in hippocampal neurons following prenatal compromise. J Neurobiol 55:41–52. doi:10.1002/neu.10194
Folkerth RD, Haynes RL, Borenstein NS et al (2004) Developmental lag in superoxide dismutases relative to other antioxidant enzymes in premyelinated human telencephalic white matter. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 63:990–999
Gottlieb M, Matute C (1997) Expression of ionotropic glutamate receptor subunits in glial cells of the hippocampal CA1 area following transient forebrain ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 17:290–300. doi:10.1097/00004647-199703000-00006
Grojean S, Schroeder H, Pourié G et al (2003) Histopathological alterations and functional brain deficits after transient hypoxia in the newborn rat pup: a long term follow-up. Neurobiol Dis 14:265–278. doi:10.1016/S0969-9961(03)00082-2
Haynes V, Elfering SL, Squires RJ et al (2003) Mitochondrial nitric-oxide synthase: role in pathophysiology. IUBMB Life 55:599–603. doi:10.1080/15216540310001628681
Jensen A, Klönne HJ, Detmer A, Carter AM (1996) Catecholamine and serotonin concentrations in fetal guinea-pig brain: relation to regional cerebral blood flow and oxygen delivery in the growth-restricted fetus. Reprod Fertil Dev 8:355–364
Kashiwagi K, Iizuka Y, Mochizuki S et al (2003) Differences in nitric oxide production: a comparison of retinal ganglion cells and retinal glial cells cultured under hypoxic conditions. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 112:126–134
Kaur C, Sivakumar V, Foulds WS (2006) Early response of neurons and glial cells to hypoxia in the retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47:1126–1141. doi:10.1167/iovs.05-0518
Kuban KC, Leviton A (1994) Cerebral palsy. N Engl J Med 330:188–195. doi:10.1056/NEJM199401203300308
Lawn J, Shibuya K, Stein C (2005) No cry at birth: global estimates of intrapartum stillbirths and intrapartum-related neonatal deaths. Bull World Health Organ 83:409–417
Le Mellédo J-MM, Mahil N, Baker GB (2004) Nitric oxide: a key player in the relation between cardiovascular disease and major depressive disorder? J Psychiatry Neurosci 29:414–416
Levine S (1960) Anoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in rats. Am J Pathol 36:1–17
Loeliger M, Watson CS, Reynolds JD et al (2003) Extracellular glutamate levels and neuropathology in cerebral white matter following repeated umbilical cord occlusion in the near term fetal sheep. Neuroscience 116:705–714
Marín-Padilla M (1997) Developmental neuropathology and impact of perinatal brain damage. II: white matter lesions of the neocortex. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 56:219–235
Marín-Padilla M (1999) Developmental neuropathology and impact of perinatal brain damage. III: gray matter lesions of the neocortex. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 58:407–429
Mazur M, Miller RH, Robinson S (2010) Postnatal erythropoietin treatment mitigates neural cell loss after systemic prenatal hypoxic-ischemic injury. J Neurosurg Pediatr 6:206–221. doi:10.3171/2010.5.PEDS1032
Minkowski A, Chanez C, Priam M et al (1981) Long lasting effects of intrauterine malnutrition on neurotransmitters metabolism in the brain of developing rats. Prog Clin Biol Res 77:643–660
Mishra O, Mishra R, Ashraf Q, Delivoria-Papadopoulos M (2006) Nitric oxide-mediated mechanism of neuronal nitric oxide synthase and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression during hypoxia in the cerebral cortex of newborn piglets. Neuroscience 140:857863. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.02.060
Morand O, Chanez C, Masson M et al (1982) Alteration in fatty acid composition of neurons, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, myelin and synaptosomes in intrauterine malnutrition in rat. Ann Nutr Metab 26:111–120
Nelson KB, Grether JK, Dambrosia JM et al (2003) Neonatal cytokines and cerebral palsy in very preterm infants. Pediatr Res 53:600–607. doi:10.1203/01.PDR.0000056802.22454.AB
Olivier P, Baud O, Evrard P et al (2005) Prenatal ischemia and white matter damage in rats. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64:998–1006
Park SY, Lee H, Hur J et al (2002) Hypoxia induces nitric oxide production in mouse microglia via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 107:9–16
Perlman JM, Risser R, Broyles RS (1996) Bilateral cystic periventricular leukomalacia in the premature infant: associated risk factors. Pediatrics 97:822–827
Pfeiffer SE, Warrington AE, Bansal R (1993) The oligodendrocyte and its many cellular processes. Trends Cell Biol 3:191–197
Reynolds R, Wilkin GP (1988) Development of macroglial cells in rat cerebellum. II. An in situ immunohistochemical study of oligodendroglial lineage from precursor to mature myelinating cell. Development 102:409–425
Rice JE, Vannucci RC, Brierley JB (1981) The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann Neurol 9:131–141. doi:10.1002/ana.410090206
Robinson S, Petelenz K, Li Q et al (2005) Developmental changes induced by graded prenatal systemic hypoxic-ischemic insults in rats. Neurobiol Dis 18:568–581. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2004.10.024
Sadiq HF, Das UG, Tracy TF, Devaskar SU (1999) Intra-uterine growth restriction differentially regulates perinatal brain and skeletal muscle glucose transporters. Brain Res 823:96–103
Savignon T, Costa E, Tenorio F et al (2012) Prenatal hypoxic-ischemic insult changes the distribution and number of NADPH-diaphorase cells in the cerebellum. PLoS ONE 7:e35786. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0035786
Spinillo A, Capuzzo E, Stronati M et al (1998) Obstetric risk factors for periventricular leukomalacia among preterm infants. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 105:865–871
Tashima L, Nakata M, Anno K et al (2001) Prenatal influence of ischemia-hypoxia-induced intrauterine growth retardation on brain development and behavioral activity in rats. Biol Neonate 80:81–87
Terzidou V, Bennett P (2001) Maternal risk factors for fetal and neonatal brain damage. Biol Neonate 79:157–162
Thorburne SK, Juurlink BH (1996) Low glutathione and high iron govern the susceptibility of oligodendroglial precursors to oxidative stress. J Neurochem 67:1014–1022
Vannucci RC, Vannucci SJ (2005) Perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage: evolution of an animal model. Dev Neurosci 27:81–86. doi:10.1159/000085978
Verma U, Tejani N, Klein S et al (1997) Obstetric antecedents of intraventricular hemorrhage and periventricular leukomalacia in the low-birth-weight neonate. Am J Obstet Gynecol 176:275–281
Vexler ZS, Yenari MA (2009) Does inflammation after stroke affect the developing brain differently than adult brain? Dev Neurosci 31:378–393. doi:10.1159/000232556
Volpe JJ (2001) Neurobiology of periventricular leukomalacia in the premature infant. Pediatr Res 50:553–562. doi:10.1203/00006450-200111000-00003
Volpe JJ (2003) Cerebral white matter injury of the premature infant-more common than you think. Pediatrics 112:176–180
Volpe J (2009) Cerebellum of the premature infant: rapidly developing, vulnerable, clinically important. J Child Neurol 24:10851104. doi:10.1177/0883073809338067
Wigglesworth (1964) Experimental growth retardation in the foetal rat. J Pathol Bacteriol 88:1–13
Wu YW, Colford JM (2000) Chorioamnionitis as a risk factor for cerebral palsy: A meta-analysis. JAMA 284:1417–1424
You Y, Kaur C (2000) Expression of induced nitric oxide synthase in amoeboid microglia in postnatal rats following an exposure to hypoxia. Neurosci Lett 279:101–104
Zubrow AB, Delivoria-Papadopoulos M, Ashraf QM et al (2002a) Nitric oxide-mediated expression of Bax protein and DNA fragmentation during hypoxia in neuronal nuclei from newborn piglets. Brain Res 954:60–67
Zubrow AB, Delivoria-Papadopoulos M, Ashraf QM et al (2002b) Nitric oxide-mediated Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV activity during hypoxia in neuronal nuclei from newborn piglets. Neurosci Lett 335:5–8
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Jorge Pereira das Neves for technical assistance and Mariana Soares Magalhães for animal care.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Barradas, P.C. et al. (2016). Prenatal Systemic Hypoxia-Ischemia and Oligodendroglia Loss in Cerebellum. In: von Bernhardi, R. (eds) Glial Cells in Health and Disease of the CNS. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 949. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-40764-7_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-40764-7_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-40762-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-40764-7
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)