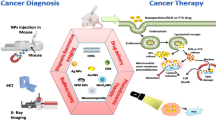
Abstract
Hybrid nanoparticles, composed of both inorganic and organic components, have been exploited as promising platforms for cancer imaging and therapy. This class of nanoparticles can not only retain the beneficial features of both inorganic and organic materials, but also allow systematic fine-tuning of their properties through the judicious combination of functional components. This chapter summarizes recent advances in the design and synthesis of hybrid nanomaterials, with particular emphasis on two main categories of hybrid nanoparticles: Nanoscale metal-organic frameworks (also known as nanoscale coordination polymers) and polysilsesquioxane nanoparticles. Preliminary applications of these hybrid nanoparticles in cancer imaging and therapy are described.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vander Heiden MG (2011) Targeting cancer metabolism: a therapeutic window opens. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10(9):671–684. doi:10.1038/Nrd3504
Dobbelstein M, Moll U (2014) Targeting tumour-supportive cellular machineries in anticancer drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 13(3):179–196. doi:10.1038/Nrd4201
Davis ME, Chen Z, Shin DM (2008) Nanoparticle therapeutics: an emerging treatment modality for cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7(9):771–782. doi:10.1038/Nrd2614
Kim CS, Duncan B, Creran B, Rotello VM (2013) Triggered nanoparticles as therapeutics. Nano Today 8(4):439–447. doi:10.1016/j.nantod.2013.07.004
Thorek DL, Ulmert D, Diop NF, Lupu ME, Doran MG, Huang R et al (2014) Non-invasive mapping of deep-tissue lymph nodes in live animals using a multimodal PET/MRI nanoparticle. Nat Commun 5:3097. doi:10.1038/ncomms4097
Lee N, Cho HR, Oh MH, Lee SH, Kim K, Kim BH et al (2012) Multifunctional Fe3O4/TaOx core/shell nanoparticles for simultaneous magnetic resonance imaging and X-ray computed tomography. J Am Chem Soc 134(25):10309–10312. doi:10.1021/Ja3016582
Rolfe BE, Blakey I, Squires O, Peng H, Boase NRB, Alexander C et al (2014) Multimodal polymer nanoparticles with combined F-19 magnetic resonance and optical detection for tunable, targeted, multimodal imaging in vivo. J Am Chem Soc 136(6):2413–2419. doi:10.1021/Ja410351h
Zhao YF, Sultan D, Detering L, Cho SH, Sun GR, Pierce R et al (2014) Copper-64-alloyed gold nanoparticles for cancer imaging: improved radiolabel stability and diagnostic accuracy. Angew Chem Int Edit 53(1):156–159. doi:10.1002/anie.201308494
Lee SB, Kim HL, Jeong HJ, Lim ST, Sohn MH, Kim DW (2013) Mesoporous silica nanoparticle pretargeting for PET imaging based on a rapid bioorthogonal reaction in a living body. Angew Chem Int Edit 52(40):10549–10552. doi:10.1002/anie.201304026
Nahrendorf M, Keliher E, Marinelli B, Waterman P, Feruglio PF, Fexon L et al (2010) Hybrid PET-optical imaging using targeted probes. Pro Nat Acad Sci USA 107(17):7910–7915. doi:10.1073/pnas.0915163107
Petros RA, DeSimone JM (2010) Strategies in the design of nanoparticles for therapeutic applications. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9(8):615–627. doi:10.1038/Nrd2591
Bardhan R, Lal S, Joshi A, Halas NJ (2011) Theranostic nanoshells: from probe design to imaging and treatment of cancer. Acc Chem Res 44(10):936–946. doi:10.1021/Ar200023x
Master A, Livingston M, Sen Gupta A (2013) Photodynamic nanomedicine in the treatment of solid tumors: perspectives and challenges. J Control Release 168(1):88–102. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.02.020
Szakacs G, Paterson JK, Ludwig JA, Booth-Genthe C, Gottesman MM (2006) Targeting multidrug resistance in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5(3):219–234. doi:10.1038/Nrd1984
Bock C, Lengauer T (2012) Managing drug resistance in cancer: lessons from HIV therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 12(7):494–501. doi:10.1038/Nrc3297
Pasparakis G, Manouras T, Vamvakaki M, Argitis P (2014) Harnessing photochemical internalization with dual degradable nanoparticles for combinatorial photo-chemotherapy. Nat Commun 5:3623. doi:10.1038/ncomms4623
Gao XH, Cui YY, Levenson RM, Chung LWK, Nie SM (2004) In vivo cancer targeting and imaging with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol 22(8):969–976. doi:10.1038/Nbt994
Huang XH, El-Sayed IH, Qian W, El-Sayed MA (2006) Cancer cell imaging and photothermal therapy in the near-infrared region by using gold nanorods. J Am Chem Soc 128(6):2115–2120. doi:10.1021/Ja057254a
Gupta AK, Gupta M (2005) Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 26(18):3995–4021. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.10.012
Shen J, Zhao L, Han G (2013) Lanthanide-doped upconverting luminescent nanoparticle platforms for optical imaging-guided drug delivery and therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65(5):744–755. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2012.05.007
Li Z, Huve J, Krampe C, Luppi G, Tsotsalas M, Klingauf J et al (2013) Internalization pathways of anisotropic disc-shaped Zeolite L nanocrystals with different surface properties in HeLa cancer cells. Small 9(9–10):1809–1820. doi:10.1002/smll.201201702
Torchilin VP (2005) Recent advances with liposomes as pharmaceutical carriers. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4(2):145–160. doi:10.1038/Nrd1632
Lee CC, MacKay JA, Frechet JMJ, Szoka FC (2005) Designing dendrimers for biological applications. Nat Biotechnol 23(12):1517–1526. doi:10.1038/Nbt1171
Kataoka K, Harada A, Nagasaki Y (2012) Block copolymer micelles for drug delivery: design, characterization and biological significance. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 64:37–48. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2012.09.013
Hamidi M, Azadi A, Rafiei P (2008) Hydrogel nanoparticles in drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 60(15):1638–1649. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2008.08.002
Taylor-Pashow KML, Della Rocca J, Huxford RC, Lin W (2010) Hybrid nanomaterials for biomedical applications. Chem Commun 46(32):5832–5849. doi:10.1039/C002073g
Della Rocca J, Liu D, Lin W (2011) Nanoscale metal-organic frameworks for biomedical imaging and drug delivery. Acc Chem Res 44(10):957–968. doi:10.1021/Ar200028a
Kitagawa S, Kitaura R, Noro S (2004) Functional porous coordination polymers. Angew Chem Int Edit 43(18):2334–2375. doi:10.1002/anie.200300610
Férey G (2008) Hybrid porous solids: past, present, future. Chem Soc Rev 37(1):191–214. doi:10.1039/B618320b
Yaghi OM, Li HL, Davis C, Richardson D, Groy TL (1998) Synthetic strategies, structure patterns, and emerging properties in the chemistry of modular porous solids. Acc Chem Res 31(8):474–484. doi:10.1021/Ar970151f
Taylor-Pashow KML, Della Rocca J, Xie Z, Tran S, Lin W (2009) Postsynthetic Modifications of iron-carboxylate nanoscale metal-organic frameworks for imaging and drug delivery. J Am Chem Soc 131(40):14261–14263. doi:10.1021/Ja906198y
Della Rocca J, Lin W (2010) Nanoscale metal-organic frameworks: magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents and beyond. Eur J Inorg Chem (24):3725-3734. doi:10.1002/ejic.201000496
Horcajada P, Chalati T, Serre C, Gillet B, Sebrie C, Baati T et al (2010) Porous metal-organic-framework nanoscale carriers as a potential platform for drug delivery and imaging. Nat Mater 9(2):172–178. doi:10.1038/Nmat2608
Della Rocca J, Huxford RC, Comstock-Duggan E, Lin W (2011) Polysilsesquioxane nanoparticles for targeted platin-based cancer chemotherapy by triggered release. Angew Chem Int Edit 50(44):10330–10334. doi:10.1002/anie.201104510
Vivero-Escoto JL, Rieter WJ, Lau H, Huxford-Phillips RC, Lin W (2013) Biodegradable polysilsesquioxane nanoparticles as efficient contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Small 9(20):3523–3531. doi:10.1002/smll.201300198
Zhang T, Lin W (2014) Metal-organic frameworks for artificial photosynthesis and photocatalysis. Chem Soc Rev 43(16):5982–5993. doi:10.1039/c4cs00103f
Jiang HL, Feng DW, Wang KC, Gu ZY, Wei ZW, Chen YP et al (2013) An exceptionally stable, porphyrinic Zr metal-organic framework exhibiting pH-dependent fluorescence. J Am Chem Soc 135(37):13934–13938. doi:10.1021/Ja406844r
Liu D, Lu K, Poon C, Lin W (2014) Metal-organic frameworks as sensory materials and imaging agents. Inorg Chem 53(4):1916–1924. doi:10.1021/Ic402194c
Rao XT, Song T, Gao JK, Cui YJ, Yang Y, Wu CD et al (2013) A highly sensitive mixed Lanthanide metal-organic framework self-calibrated luminescent thermometer. J Am Chem Soc 135(41):15559–15564. doi:10.1021/Ja407219k
Rieter WJ, Taylor KML, Lin W (2007) Surface modification and functionalization of nanoscale metal-organic frameworks for controlled release and luminescence sensing. J Am Chem Soc 129(32):9852–9853. doi:10.1021/Ja073506r
Xie Z, Ma L, deKrafft KE, Jin A, Lin W (2010) Porous phosphorescent coordination polymers for oxygen sensing. J Am Chem Soc 132(3):922–923. doi:10.1021/Ja909629f
Wanderley MM, Wang C, Wu C, Lin W (2012) A chiral porous metal-organic framework for highly sensitive and enantioselective fluorescence sensing of amino alcohols. J Am Chem Soc 134(22):9050–9053. doi:10.1021/Ja302110d
Harbuzaru BV, Corma A, Rey F, Jorda JL, Ananias D, Carlos LD et al (2009) A miniaturized linear pH sensor based on a highly photoluminescent self-assembled Europium(III) metal-organic framework. Angew Chem Int Edit 48(35):6476–6479. doi:10.1002/anie.200902045
Hirai K, Sumida K, Meilikhov M, Louvain N, Nakahama M, Uehara H et al (2014) Impact of crystal orientation on the adsorption kinetics of a porous coordination polymer-quartz crystal microbalance hybrid sensor. J Mater Chem C 2(17):3336–3344. doi:10.1039/C3tc32101k
Beauvais LG, Shores MP, Long JR (2000) Cyano-bridged Re(6)Q(8) (Q = S, Se) Cluster-Cobalt(II) framework materials: versatile solid chemical sensors. J Am Chem Soc 122(12):2763–2772. doi:10.1021/Ja994186h
Lu G, Farha OK, Kreno LE, Schoenecker PM, Walton KS, Van Duyne RP et al (2011) Fabrication of metal-organic framework-containing silica-colloidal crystals for vapor sensing. Adv Mater 23(38):4449–4452. doi:10.1002/adma.201102116
Yoon M, Srirambalaji R, Kim K (2012) Homochiral metal-organic frameworks for asymmetric heterogeneous catalysis. Chem Rev 112(2):1196–1231. doi:10.1021/Cr2003147
Rieter WJ, Pott KM, Taylor KML, Lin W (2008) Nanoscale coordination polymers for platinum-based anticancer drug delivery. J Am Chem Soc 130(35):11584–11585. doi:10.1021/Ja803383k
Huxford-Phillips RC, Russell SR, Liu D, Lin W (2013) Lipid-coated nanoscale coordination polymers for targeted cisplatin delivery. Rsc Adv 3(34):14438–14443. doi:10.1039/C3ra42033g
Liu D, Kramer SA, Huxford-Phillips RC, Wang S, Della Rocca J, Lin W (2012) Coercing bisphosphonates to kill cancer cells with nanoscale coordination polymers. Chem Commun. 48(21):2668–2670. doi:10.1039/C2cc17635a
He C, Lu K, Liu D, Lin W (2014) Nanoscale metal-organic frameworks for the co-delivery of cisplatin and pooled siRNAs to enhance therapeutic efficacy in drug-resistant ovarian cancer cells. J Am Chem Soc 136(14):5181–5184. doi:10.1021/Ja4098862
Rieter WJ, Taylor KML, An HY, Lin W, Lin W (2006) Nanoscale metal-organic frameworks as potential multimodal contrast enhancing agents. J Am Chem Soc 128(28):9024–9025. doi:10.1021/Ja0627444
Taylor KML, Jin A, Lin W (2008) Surfactant-assisted synthesis of nanoscale gadolinium metal-organic frameworks for potential multimodal imaging. Angew Chem Int Edit 47(40):7722–7725. doi:10.1002/anie.200802911
Huxford RC, deKrafft KE, Boyle WS, Liu D, Lin W (2012) Lipid-coated nanoscale coordination polymers for targeted delivery of antifolates to cancer cells. Chem Sci 3(1):198–204. doi:10.1039/C1sc00499a
Liu D, Poon C, Lu K, He C, Lin W (2014) Self-assembled nanoscale coordination polymers with trigger release properties for effective anticancer therapy. Nat Commun 5:4182. doi:10.1038/ncomms5182
Dekrafft KE, Xie ZG, Cao GH, Tran S, Ma L, Zhou OZ et al (2009) Iodinated nanoscale coordination polymers as potential contrast agents for computed tomography. Angew Chem Int Edit 48(52):9901–9904. doi:10.1002/anie.200904958
Miller SR, Heurtaux D, Baati T, Horcajada P, Greneche JM, Serre C (2010) Biodegradable therapeutic MOFs for the delivery of bioactive molecules. Chem Commun 46(25):4526–4528. doi:10.1039/C001181a
Nguyen JG, Tanabe KK, Cohen SM (2010) Postsynthetic diazeniumdiolate formation and NO release from MOFs. CrystEngComm 12(8):2335–2338. doi:10.1039/C000154f
Vivero-Escoto JL, Huxford-Phillips RC, Lin W (2012) Silica-based nanoprobes for biomedical imaging and theranostic applications. Chem Soc Rev 41(7):2673–2685. doi:10.1039/C2cs15229k
Lee GH, Chang Y, Kim TJ (2012) Blood-pool and targeting MRI contrast agents: from Gd-chelates to Gd-nanoparticles. Eur J Inorg Chem 12:1924–1933. doi:10.1002/ejic.201101137
Perrier M, Kenouche S, Long J, Thangavel K, Larionova J, Goze-Bac C et al (2013) Investigation on NMR relaxivity of nano-sized cyano-bridged coordination polymers. Inorg Chem 52(23):13402–13414. doi:10.1021/Ic401710j
Rowe MD, Chang CC, Thamm DH, Kraft SL, Harmon JF, Vogt AP et al (2009) Tuning the magnetic resonance imaging properties of positive contrast agent nanoparticles by surface modification with RAFT polymers. Langmuir 25(16):9487–9499. doi:10.1021/La900730b
Rowe MD, Thamm DH, Kraft SL, Boyes SG (2009) Polymer-modified gadolinium metal-organic framework nanoparticles used as multifunctional nanomedicines for the targeted imaging and treatment of cancer. Biomacromolecules 10(4):983–993. doi:10.1021/Bm900043e
Caravan P, Ellison JJ, McMurry TJ, Lauffer RB (1999) Gadolinium(III) chelates as MRI contrast agents: structure, dynamics, and applications. Chem Rev 99(9):2293–2352. doi:10.1021/Cr980440x
Taylor KML, Rieter WJ, Lin W (2008) Manganese-based nanoscale metal-organic frameworks for magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Chem Soc 130(44):14358–14359. doi:10.1021/Ja803777x
Paul G, Prado Y, Dia N, Riviere E, Laurent S, Roch M et al (2014) Mn-II-containing coordination nanoparticles as highly efficient T-1 contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Chem Commun 50(51):6740–6743. doi:10.1039/C4cc01251h
Brenner DJ, Hall EJ (2007) Current concepts—computed tomography—an increasing source of radiation exposure. New Engl J Med 357(22):2277–2284. doi:10.1056/Nejmra072149
deKrafft KE, Boyle WS, Burk LM, Zhou OZ, Lin W (2012) Zr- and Hf-based nanoscale metal-organic frameworks as contrast agents for computed tomography. J Mater Chem 22(35):18139–18144. doi:10.1039/C2jm32299d
Liu D, Huxford RC, Lin W (2011) Phosphorescent nanoscale coordination polymers as contrast agents for optical imaging. Angew Chem Int Edit 50(16):3696–3700. doi:10.1002/anie.201008277
Nishiyabu R, Aime C, Gondo R, Kaneko K, Kimizuka N (2010) Selective inclusion of anionic quantum dots in coordination network shells of nucleotides and lanthanide ions. Chem Commun 46(24):4333–4335. doi:10.1039/C001012j
Aime C, Nishiyahu R, Gondo R, Kimizuka N (2010) Switching on luminescence in nucleotide/lanthanide coordination nanoparticles via synergistic interactions with a cofactor ligand. Chem-Eur J 16(12):3604–3607. doi:10.1002/chem.201090007
Nishiyabu R, Hashimoto N, Cho T, Watanabe K, Yasunaga T, Endo A et al (2009) Nanoparticles of adaptive supramolecular networks self-assembled from nucleotides and lanthanide ions. J Am Chem Soc 131(6):2151–2158. doi:10.1021/Ja8058843
Aime C, Nishiyabu R, Gondo R, Kaneko K, Kimizuka N (2008) Controlled self-assembly of nucleotide-lanthanide complexes: specific formation of nanofibers from dimeric guanine nucleotides. Chem Commun 48:6534–6536. doi:10.1039/B815779k
He C, Lu K, Lin W (2014) Nanoscale metal-organic frameworks for real-time intracellular pH sensing in live cells. J Am Chem Soc 136(35):12253–12256. doi:10.1021/ja507333c
Duncan R (2006) Polymer conjugates as anticancer nanomedicines. Nat Rev Cancer 6(9):688–701. doi:10.1038/Nrc1958
Allen TM (2002) Ligand-targeted therapeutics in anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2(10):750–763. doi:10.1038/Nrc903
Harley CB (2008) Telomerase and cancer therapeutics. Nat Rev Cancer 8(3):167–179. doi:10.1038/Nrc2275
Li SD, Huang L (2008) Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of nanoparticles. Mol Pharm 5(4):496–504. doi:10.1021/mp800049w
Imaz I, Rubio-Martinez M, Garcia-Fernandez L, Garcia F, Ruiz-Molina D, Hernando J et al (2010) Coordination polymer particles as potential drug delivery systems. Chem Commun 46(26):4737–4739. doi:10.1039/C003084h
Gao PF, Zheng LL, Liang LJ, Yang XX, Li YF, Huang CZ (2013) A new type of pH-responsive coordination polymer sphere as a vehicle for targeted anticancer drug delivery and sustained release. J Mater Chem B 1(25):3202–3208. doi:10.1039/C3tb00026e
McKinlay AC, Xiao B, Wragg DS, Wheatley PS, Megson IL, Morris RE (2008) Exceptional behavior over the whole adsorption-storage-delivery cycle for NO in porous metal organic frameworks. J Am Chem Soc 130(31):10440–10444. doi:10.1021/Ja801997r
Morris W, Briley WE, Auyeung E, Cabezas MD, Mirkin CA (2014) Nucleic acid-metal organic framework (MOF) nanoparticle conjugates. J Am Chem Soc 136(20):7261–7264. doi:10.1021/Ja503215w
Della Rocca J, Werner ME, Kramer SA, Huxford-Phillips RC, Sukumar R, Cummings ND, Vivero-Escoto JL, Wang AZ, Lin W (2014) Polysilsesquioxane nanoparticles for triggered release of cisplatin and effective cancer chemoradiotherapy. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med 11(1):31–38. doi:10.1016/j.nano.2014.07.004
Tang L, Fan TM, Borst LB, Cheng JJ (2012) Synthesis and biological response of size-specific, monodisperse drug-silica nanoconjugates. Acs Nano 6(5):3954–3966. doi:10.1021/Nn300149c
Tang L, Gabrielson NP, Uckun FM, Fan TM, Cheng JJ (2013) Size-dependent tumor penetration and in vivo efficacy of monodisperse drug-silica nanoconjugates. Mol Pharmaceut 10(3):883–892. doi:10.1021/Mp300684a
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
He, C., Lin, W. (2015). Hybrid Nanoparticles for Cancer Imaging and Therapy. In: Mirkin, C., Meade, T., Petrosko, S., Stegh, A. (eds) Nanotechnology-Based Precision Tools for the Detection and Treatment of Cancer. Cancer Treatment and Research, vol 166. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16555-4_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16555-4_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-16554-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-16555-4
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)