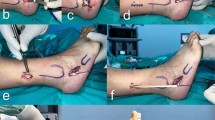
Abstract
Tearing of the peroneus brevis and/or peroneus longus can be a cause of lateral ankle pain and dysfunction. In cases of chronic, attritional injuries where nonoperative management has failed, intercalary allograft reconstruction is a viable option. Cadaveric and clinical investigations, along with anecdotal experience, have resulted in restoration of the muscle-tendon unit and patient function. Utilization of allograft reconstruction is safe and effective, while limiting donor site morbidity and decreased functionality that may accompany other treatment options, such as tenodesis and autograft tendon transfers. The authors provide step-by-step instruction of their preferred allograft reconstruction technique using peroneal or semitendinosus allograft.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brodsky JW, Zide JR, Kane JM. Acute peroneal injury. [cited 2018 Sep 15]; Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcl.2017.07.013.
Dombek MF, Lamm BM, Saltrick K, Mendicino RW, Catanzariti AR. Peroneal tendon tears: a retrospective review. J Foot Ankle Surg [Internet]. [cited 2018 Sep 16];42(5):250–8. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14566716.
Petersen W, Bobka T, Stein V, Tillmann B. Blood supply of the peroneal tendons: Injection and immunohistochemical studies of cadaver tendons. Acta Orthop Scand [Internet]. 2000 [cited 2018 Sep 15];71(2):168–74. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10852323.
Lamm BM, Myers DT, Dombek M, Mendicino RW, Catanzariti AR, Saltrick K. Magnetic resonance imaging and surgical correlation of peroneus brevis tears. J Foot Ankle Surg [Internet]. 2004 [cited 2018 Sep 16];43(1):30–6. Available from: http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1067251603004186.
Mirmiran R, Squire C, Wassell D. Prevalence and role of a low-lying peroneus Brevis uscle belly in patients with peroneal tendon pathologic features: a potential source of tendon subluxation. J Foot Ankle Surg [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2018 Sep 15];54(5):872–5. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25998478.
Housley SN, Lewis JE, Thompson DL, Warren G. A proximal fibularis brevis muscle is associated with longitudinal split tendons: a cadaveric study. J Foot Ankle Surg [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2018 Sep 16];56(1):34–6. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27989344.
Gökhan Bilgili M, Kaynak G, Botanlıog H, Serdar ·, Basaran H. Peroneus quartus: prevalance and clinical importance. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2018 Sep 16];134:481–7. Available from: https//link-springer-com.proxy.lib.duke.edu/content/pdf/10.1007%2Fs00402-014-1937-4.pdf.
Sobel M, Pavlov H, Geppert MJ, Thompson FM, DiCarlo EF, Davis WH. Painful Os peroneum syndrome: a spectrum of conditions responsible for plantar lateral foot pain. Foot Ankle Int [Internet]. 1994 [cited 2018 Sep 16];15(3):112–24. Available from: http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/107110079401500306.
Stockton KG, Brodsky JW. Peroneus Longus Tears Associated With Pathology of the Os Peroneum. Foot Ankle Int [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2018 Sep 16];35(4):346–52. Available from: http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1071100714522026.
Sobel M, Geppert MJ, Olson EJ, O Bohne WH, Arnoczky SP. The dynamics of peroneus brevis tendon splits: a proposed mechanism technique of diagnosis, and classification of injury [Internet]. 1992 [cited 2018 Sep 9]. Available from: http://journals.sagepub.com.proxy.lib.duke.edu/doi/pdf/10.1177/107110079201300710.
Molini L, Bianchi S. US in peroneal tendon tear. J Ultrasound [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2018 Sep 14];17(2):125–34. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24883136.
Res LCS, Dixon T, Lubberts B, Vicentini JRT, van Dijk PA, Hosseini A, et al. Peroneal Tendon Tears. J Am Acad Orthop Surg [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2018 Sep 15];1. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30138295.
Wang X-T, Rosenberg ZS, Mechlin MB, Schweitzer ME. Normal variants and diseases of the peroneal tendons and superior peroneal retinaculum: MR imaging features. RadioGraphics [Internet]. 2005 [cited 2018 Sep 16];25(3):587–602. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15888611.
Working Together for Life [Internet]. [cited 2018 Sep 14]. Available from: https://www.aatb.org/sites/default/files/sites/default/files/private/AATB2017AnnualReport.pdf.
Xu X, Hu M, Liu J, Zhu Y, Wang B. Minimally invasive reconstruction of the lateral ankle ligaments using semitendinosus autograft or tendon allograft. Foot Ankle Int [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2018 Sep 14];35(10):1015–21. Available from: http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1071100714540145.
CEnters for Disease Control and Prevention, Food and Drug Administration, and Health Resources and Services Administration, Department of Health and Human Services convene the Workshop on Preventing Organ and Tissue Allograft-Transmitted Infection: Priori [Internet]. [cited 2018 Sep 14]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/transplantsafety/pdfs/BOOTS-Workshop-2005-final-report.pdf.
Hinsenkamp M, Muylle L, Eastlund T, Fehily D, Noël L, Strong DM. Adverse reactions and events related to musculoskeletal allografts: reviewed by the World Health Organisation Project NOTIFY. Int Orthop [Internet]. 2012 [cited 2018 Sep 14];36(3):633–41. Available from: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00264-011-1391-7.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Update: allograft-associated bacterial infections--United States, 2002. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep [Internet]. 2002 [cited 2018 Sep 16];51(10):207–10. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11922189.
Yu A, Prentice HA, Burfeind WE, Funahashi T, Maletis GB. Risk of infection after allograft anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: are nonprocessed allografts more likely to get infected? A cohort study of over 10,000 allografts. Am J Sports Med [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2018 Sep 16];46(4):846–51. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29298084.
Mook WR, Parekh SG, Nunley JA. Allograft reconstruction of peroneal tendons: operative technique and clinical outcomes. Foot Ankle Int [Internet]. [cited 2018 Sep 3];34(9):1212–20. Available from: http://journals.sagepub.com.proxy.lib.duke.edu/doi/pdf/10.1177/1071100713487527.
2016 IFFAS Award for Excellence Winner. [cited 2018. Sep 9]; Available from: http://journals.sagepub.com.proxy.lib.duke.edu/doi/pdf/10.1177/1071100716658469.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Hanselman, A.E., Nunley, J.A. (2020). Attritional Rupture of Peroneus Brevis and Peroneus Longus Tendons: Allograft Reconstruction. In: Sobel, M. (eds) The Peroneal Tendons. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-46646-6_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-46646-6_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-46645-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-46646-6
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)