Abstract
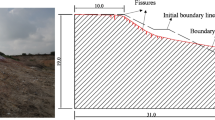
The major problem of unsaturated slope is the variation of their volumetric water content which is an important factor in the variation of mechanical parameters of soils into the subsurface. It can also influence the soil shear strength; consequently several methods were proposed to improve the unsaturated slope stability including the concrete lozenges technique. It is a new technique used to protect slopes. It constituted a non-continuous mesh mask on the slop, having the effect of collecting and transporting runoff water on the slope. Using the finite element method, the objective of this paper was to study both how the value of soil volumetric water content and the safety factor changed by the use of this new technique. Indeed, the safety factor is <1 for the shallow soil and increases with depth. Simulation and calculation results demonstrated that the proposed technique is capable of making the amount of soil masse affected, less than 1 m.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lam, L., Fredlunda, D.G., Barbou, N.D.S.L.: Transient seepage model for saturated-unsaturated soil systems: a geotechnical engineering approach. Can. Geotech. J. 24, 565–580 (1987)
Elbouanani, L., Baba, K. et al.: Concrete lozenges impact on the slope erodibility. In: MATEC Web Conference, 2nd International Congress on Materials & Structural Stability (CMSS-2017), vol.149, p. 02073 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/201814902073
Alavi, G.: Estimation of soil hydraulic parameters to simulate water flux in volcanic soils. N. Z. J. For. Sci. 31(1), 51–65 (2001)
Tjie-Liong, G.: Common mistakes on the application of plaxis 2D in analyzing excavation problems. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 9(21), 8291–8311 ISSN 0973–4562 (2014)
Irmay, S.: On the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Trans. Am. Geophys. Un. 35(3), 463–467 (1954)
Van Genuchten, M.T.: A closed form for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soils Sci. Am. Soc. 44, 892–898 (1980)
Casulli, V., Zanolli, P.: A nested newton-type algorithm for finite volume methods solving richards’ equation in mixed form SIAM J. Sci. Comput. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, vol. 32, No. 4, pp. 2255–2273 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
El Bouanani, L., Baba, K., Ouadif, L. (2019). Use of the Method of Concrete Lozenges to Strengthening the Slopes Stability: Assessment of the Safety Factor by the Finite Element Method. In: Hemeda, S., Bouassida, M. (eds) Contemporary Issues in Soil Mechanics. GeoMEast 2018. Sustainable Civil Infrastructures. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01941-9_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01941-9_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-01940-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-01941-9
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)