Abstract
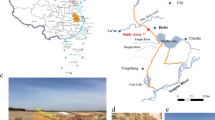
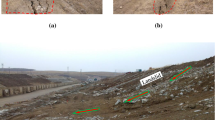
An expansive soil slope of a high-speed railway under construction in Yunnan suffered a local collapse after a heavy rainfall. The expansive soil on this slope surface is prone to slip and collapse under the action of rainfall. The analysis of water sensitivity reveals the attenuation law of the shear strength of the expansive soil. With the increase in the water content, the shear strength of the expansive soil decreases significantly. Wet–dry cycles also significantly lower the shear strength of the expansive soil. In addition, a high-density electrical method test is performed on the expansive soil slope to determine the structural characteristics of the internal soil. The test results indicate that the internal soil of the slope exhibits poor mechanical properties and contains fissures and cracks, which are also the factors that caused the landslide. The finite element software, ABAQUS, is used to analyze the impact of rainfall on the expansive soil slope. The results reveal that the soil at a depth of approximately 2 m below the surface reaches complete saturation after 24 h of rainfall, and the plastic failure zone is mainly distributed on the surface and toe of the slope. Based on the electrical test results, the slope soil material is classified into saturated, fissured, and non-fissured soil zones. The stability analysis results reveal that the sliding surface is circular and in the shallow layer of the slope, and the sliding depth is 2–3 m. Although the depth of the landslide mass is not large, almost the entire slope surface soil undergoes plastic failure, resulting in a large area of slippage.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali A, Huang J, Lyamin AV, Sloan SW, Cassidy MJ (2014) Boundary effects of rainfall-induced landslides. Comput Geotech 61(Sep):341–354
Alonso EE, Gens A, Delahaye CH (2003) Influence of rainfall on the deformation and stability of a slope in overconsolidated clays: a case study. Hydrogeol J 11(1):174–192
Aref A, Alkhafaji RA, Chunjie Y, Akhtar MM (2014) Characteristics, modification and environmental application of Yemen’s natural bentonite. Arab J Geosci 7(3):841–853
Aubeny C, Lytton R (2004) Shallow slides in compacted high plasticity clay slopes. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 130(7):717–727
Azanon JM (2010) Regional-scale high-plasticity clay-bearing formation as controlling factor on landslides in Southeast Spain. Geomorphology 120(1-2):26–37
Bachouche S, Boutaleb A (2013) Geology, mineralogy, and chemistry of the M’zila bentonitic clay deposit (Mostaganem, NW Algeria). Arab J Geosci 6(6):2165–2172
Cai F, Ugai K, Wakai A, Li Q (1998) Effects of horizontal drains on slope stability under rainfall by three-dimensional finite element analysis. Comput Geotech 23(4):255–275
Calabresi G (2013) Research study of the hydraulic behaviour of the Po River embankments. Can Geotech J 50(9):947–960
Chen HX, Zhang LM (2014) A physically-based distributed cell model for predicting regional rainfall-induced shallow slope failures. Eng Geol 176(Jun):79–92
Chen WZ, Jiang GL, Wang ZM, Li AH (2014) Physical-mechanical parameters and consolidation characteristics of undisturbed expansive soil in Mile. J Cent South Univ (Sci Tech) 45(6):1908–1915
Cho SE, Lee SR (2001) Instability of unsaturated soil slopes due to infiltration. Comput Geotech 28(3):185–208
Dai Z, Chen S, Li J (2018) The failure characteristics and evolution mechanism of the expansive soil trench slope (conference paper). Geotech Spec Publ:196–205
Day R (1994) Surficial stability of compacted clay: case study. J Geotech Eng 120(11):1980–1990
Dooradarshi C, Murali Krishna A (2019) Effect of slope angle on the stability of a slope under rainfall infiltration. Indian Geotech J 49(6):708–717
Fouzan AF, Dafalla MA (2014) Study of cracks and fissures phenomenon in Central Saudi Arabia by applying geotechnical and geophysical techniques. Arab J Geosci 7(3):1157–1164
Fukue M, Minatoa T, Horibe H, Taya N (1999) The microstructure of clay given by resistivity measurements. Eng Geol 54:43–53
George AM, Chakraborty S, Das JT (2017) Understanding shallow slope failures on expansive soil embankments in North Texas using unsaturated soil property framework (conference paper). Geotech Spec Publ 206-216
Gofar N, Rahardjo H (2017) Saturated and unsaturated stability analysis of slope subjected to rainfall infiltration. MATEC Web Conf 101:5004
Griffiths DV, Lane PA (1999) Slope stability analysis by finite elements. Geotechnique 49(3):387–403
Hamdhan I, Schweiger H (2013) Finite element method–based analysis of an unsaturated soil slope subjected to rainfall infiltration. Int J Geomech 13:653–658
Hou TS, Xu GL, Shen YJ, Wu ZZ, Zhang NN, Wang R (2013) Formation mechanism and stability analysis of the Houba expansive soil landslide. Eng Geol 161:34–43
Kong LW, Zeng ZX, Bai W, Wang M (2018) Engineering geological properties of weathered swelling mudstones and their effects on the landslides occurrence in the Yanji section of the Jilin-Hunchun high-speed railway. Bull Eng Geol Environ 77(4):1491–1503
Krisnanto S, Rahardjo H, Fredlund D, Leong EC (2014) Mapping of cracked soils and lateral water flow characteristics through a network of cracks. Eng Geol 172:12–25
Krisnanto S, Rahardjo H, Fredlund D, Leong EC (2016) Water content of soil matrix during lateral water flow through cracked soil. Eng Geol 210:168–179
Li JH, Zhang LM (2011) Study of desiccation crack initiation and development at ground surface. Eng Geol 123(4):347–358
Liu GH, Wang ZY, Hang JP (2004) Research on electrical resistivity feature of soil and its application. Chin J Geotech Eng 26(1):83–87
McCarter WJ (1984) The electrical resistivity characteristics of compacted clays. Geotechnique 34:263–267
Michot D, Benderitter Y, Dorigny A, Nicoullaud B, King D, Tabbagh A (2003) Spatial and temporal monitoring of soil water content with an irrigated corn crop cover using electrical resistivity tomography. Water Resour Res 39:1138
Morgenstern and Price (1966) The analysis of the stability of general slip surfaces. JTerramechanics 3(1):74
Ng CW, Wang B, Tung YK (2001) Three-dimensional numerical investigations of groundwater responses in an unsaturated slope subjected to various rainfall patterns. Can Geotech J 38(5):1049–1062
Ni P, Wang S, Zhang S, Mei L (2016) Response of heterogeneous slopes to increased surcharge load. Comput Geotech 78:99–109
Pei P, Zhao YL, Ni P, Mei G. (2020). A protective measure for expansive soil slopes based on moisture content control. Eng Geol 269.
Qi S, Vanapalli SK (2015a) Hydro-mechanical coupling effect on surficial layer stability of unsaturated expansive soil slopes. Comput Geotech 70(Oct):68–82
Qi S, Vanapalli SK (2015b) Stability analysis of an expansive clay slope: A case study of infiltration-induced shallow failure of an embankment in Regina Canada. Int J Georesour Environ 1(1):1–1
Qi S, Vanapalli SK (2018) Simulating hydraulic and mechanical responses of unsaturated expansive soil slope to rainfall: case study. Int J Geomech 18(6)
Rouainia M, Davies O, O’Brien T, Glendinning S (2009) Numerical modelling of climate effects on slope stability. Proc Inst Civ Eng Eng Sustainability 162(2):81–89
Shi B, Jiang H, Liu Z, Fang H (2002) Engineering geological characteristics of expansive soils in China. Eng Geol 67(1):63–71
Stianson JR, Fredlund DG, Chan D (2011) Three-dimensional slope stability based on stresses from a stress-deformation analysis. Can Geotech J 48(6):891–904
Sun DM, Zang YG, Semprich S (2015) Effects of airflow induced by rainfall infiltration on unsaturated soil slope stability. Transp Porous Media 107(3):821–841
Sun DM, Li XM, Feng P (2016) Stability analysis of unsaturated soil slope during rainfall infiltration using coupled liquid-gas-solid three-phase model. Water Sci Eng 9(3):183–194
Tommasi P, Boldini D, Caldarini G, Coli N (2013) Influence of infiltration on the periodic re-activation of slow movements in an over-consolidated clay slope. Can Geotech J 50(1):54–67
Tsai TL, Chen HE, Yang JC (2008) Numerical modeling of rainstorm-induced shallow landslides in saturated and unsaturated soils. Environ Geol 55(6):1269–1277
Wang S, Ni P (2014) Application of block theory modeling on spatial block topological identification to rock slope stability analysis. Int J Comput Methods 11(1):7–49
Wang S, Ni P, Yang H, Xu Y (2011) Modeling on spatial block topological identification and their progressive failure analysis of slope and cavern rock mass. Procedia Eng 10:1509–1514
Wang S, Huang R, Ni P, Jeon S (2017) Advanced discretization of rock slope using block theory within the framework of discontinuous deformation analysis. Geomech Eng 12(4):723–738
Widger RA, Fredlund DG (1979) Stability of swelling clay embankments. Can GeotechJ 16(1):140–151
Xiao J, Tong C, Yang HP (2017) Causes of shallow landslides of expansive soil slopes. J Highway Transp Res Develop (English Ed) 11(1):1–6
Yan YJ, Yan YS, Zhao GZ (2019) Study on moisture migration in natural slope using high-density electrical resistivity tomography method. Rock Soil Mech 40(7):2807–2814
Zhan L. (2003). Field and laboratory study of an unsaturated expansive soil associated with rain-induced slope instability. Ph.D. thesis, Hong Kong Univ. of Science and Technology, Kowloon, Hong Kong.
Zhang LL, Fredlund DG, Fredlund MD, Wilson GW (2014) Modeling the unsaturated soil zone in slope stability analysis 1. Can Geotech J 51(12):1384–1398
Zhou JW, Cui P, Hao MH (2016a) Comprehensive analyses of the initiation and entrainment processes of the 2000 Yigong catastrophic landslide in Tibet, China. Landslides 13(1):39–54
Zhou JW, Xu FG, Yang XG, Yang YC, Lu PY (2016b) Comprehensive analyses of the initiation and landslide-generated wave processes of the 24 June 2015 Hongyanzi landslide at the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Landslides 13(3):589–601
Funding
This study is financial supported by the National Earthquake Science Joint Foundation of China (No. U1939209), the Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research (STEP) Program (Grant No. 2019QZKK0905), the Key Project of Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41630636), and the Scientific Research Foundation for Introducing Talent of Nanjing Tech University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Editorial Responsibility: Zeynal Abiddin Erguler
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, C., Wu, Z., Liu, X. et al. Analysis of shallow landslide mechanism of expansive soil slope under rainfall: a case study. Arab J Geosci 14, 584 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-06829-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-06829-6