Abstract
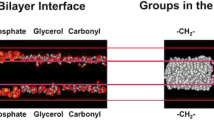
Knowledge of the structure of lipid bilayers in the fluid liquid-crystalline state is important for understanding the permeability and stability of membranes and the insertion and folding of membrane proteins. Quantitative structural models are especially important at the present time for validation of Monte Carlo and molecular dynamics simulations of lipid bilayers (Pastor, 1994). Diffraction studies of phospholipid crystals at low hydrations can provide atomic-resolution images of the phospholipid molecules of membranes (Pascher et al, 1992) but such images are of marginal value for understanding membrane bilayers for the obvious reason that the phospholipids are in a noncrystalline state. Fluid bilayers present special problems to the structural biologist because their inherent thermal motion and disorder exclude entirely the possibility of obtaining three-dimensional structural information. The only kind of structural image that can be obtained by diffraction methods is a one-dimensional one consisting of the time-averaged transbilayer distributions of the multiatom submolecular groups comprising the lipids such as the phosphate, carbonyl groups, double-bonds, etc. (Figure 1). Such projections have become a standard method for describing the results of bilayer simulations (Damodaran and Merz, 1994; Egberts et al, 1994; Fattal and Ben-Shaul, 1994; Heller et al, 1993).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akutsu H, Nagamori T (1991): Conformational analysis of the polar head group in phosphatidylcholine bilayers—A structural change induced by cations. Biochemistry 30:4510–4516
Bevington PR (1969): Data Reduction and Error Analysis for the Physical Sciences. New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company
Blasie JK, Schoenborn BP, Zaccai G (1975): Direct methods for the analysis of lamellar neutron diffraction from oriented multilayers: A difference Patterson deconvolution approach. Brookhaven Symp Biol 27:11158–11167
Blaurock AE (1982): Evidence of bilayer structure and of membrane interactions from X-ray diffraction analysis. Biochim Biophys Acta 650:167–207
Braach-Maksvytis VLB, Cornell BA (1988): Chemical shift anisotropics obtained from aligned egg yolk phosphatidylcholine by solid state 13C nuclear magnetic resonance. Biophys J 53:839–843
Büldt G, Gaily HU, Seelig J, Zaccai G (1979): Neutron diffraction studies on phosphatidylcholine model membranes. I. Head group conformation. J Mol Biol 134:673–691
Büldt G, Gaily HU, Seelig A, Seelig J, Zaccai G (1978): Neutron diffraction studies on selectively deuterated phospholipid bilayers. Nature 271:182–184
Damodaran KV, Merz KM (1994): A comparison of DMPC- and DLPE-based lipid bilayers. Biophys J 66:1076–1087
Egberts E, Marrink S J, Berendsen HJC (1994): Molecular dynamics simulation of a phospholipid membrane. Eur Biophys J 22:423–436
Elder M, Hitchcock PB, Mason R, Shipley GG (1977): A refinement analysis of the crystallography of the phospholipid 1,2-dilauroyl-DL-phosphatidylethanolamine, and some remarks on lipid-lipid and lipid-protein interactions. Proc R Soc Lond 354:157–170
Fattal DR, Ben-Shaul A (1994): Mean-field calculations of chain packing and conformational statistics in lipid bilayers: Comparison with experiments and molecular dynamics studies. Biophys J 67:983–995
Franks NP, Levine YK (1981): Low-angle X-ray diffraction. In: Membrane Spectroscopy, Grell E, ed. Berlin: Springer-Verlag
Franks NP, Lieb WR (1979): The structure of lipid bilayers and the effects of general anesthetics: An X-ray and neutron diffraction study. J Mol Biol 133:469–500
Hauser H, Pascher I, Pearson RH, Sundell S (1981): Preferred conformation and molecular packing of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta 650:21–51
Heller H, Schaefer M, Schulten K (1993): Molecular dynamics simulation of a bilayer of 200 lipids in the gel and in the liquid-crystal phases. J Phys Chem 97:8343–8360
Hitchcock PB, Mason R, Shipley GG (1975): Phospholipid arrangements in multilayers and artificial membranes: Quantitative analysis of the X-ray data from a multilayer of 1,2-dimyristoyl-DL-phosphatiylethanolamine. J Mol Biol 94:297–299
Hosemann R, Bagchi SN (1962): Direct Analysis of Diffraction by Matter. Amsterdam: North-Holland
Inoko Y, Mitsui T (1978): Structural parameters of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine lamellar phases and bilayer phase transitions. J Phys Soc Japan 44:1918–1924
Jacobs RE, White SH (1989): The nature of the hydrophobic binding of small peptides at the bilayer interface: Implications for the insertion of transbilayer helices. Biochemistry 28:3421–3437
Janiak MJ, Small DM, Shipley GG (1979): Temperature and compositional dependence of the structure of hydrated dymyristoyl lecithin. J Biol Chem 254:6068–6078
King GI, White SH (1986): Determining bilayer hydrocarbon thickness from neutron diffraction measurements using strip-function models. Biophys J 49:1047–1054
Kuriyan J, Petsko GA, Levy RM, Karplus M (1986): Effect of anisotropy and anharmonicity on protein crystallographic refinement. An evaluation by molecular dynamics. J Mol Biol 190:227–254
Levine YK, Wilkins MHF (1971): Structure of oriented lipid bilayers. Nature New Biol 230:69–72
Mcintosh TJ, Simon SA (1986): Hydration force and bilayer deformation: A reevaluation. Biochemistry 25:4058–4066
Pascher I, Lundmark M, Nyholm P-G, Sundell S (1992): Crystal structures of membrane lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta 1113:339–373
Pastor RW (1994): Molecular dynamics and Monte Carlo simulations of lipid bilayers. Curr Opin Struct Biol 4:486–492
Pearson RH, Pascher I (1979): The molecular structure of lecithin dihydrate. Nature 281:499–501
Press WH, Flannery BP, Teukolsky SA (1989): Numerical Recipes. The Art of Scientific Computing. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press
Ranck JL, Keira T, Luzzati V (1977): A novel packing of the hydrocarbon chains in lipids: The low temperature phases of dipalmitoylphosphatidylglycerol. Biochim Biophys Acta 488:432–441
Schoenborn BP (1975): Advantages of neutron scattering for biological structure analysis. Brookhaven Symp Biol 27:110–117
Schwartz S, Cain JE, Dratz EA, Blasie JK (1975): An analysis of lamellar X-ray diffraction from disordered membrane multilayers with application to data from retinal rod outer segments. Biophys J 15:1201–1233
Seelig A, Seelig J (1977): Effect of a single cis double bond on the structure of a phospholipid bilayer. Biochemistry 16:45–50
Seelig A, Seelig J (1974): The dynamic structure of fatty acyl chains in a phospholipid bilayer measured by deuterium magnetic resonance. Biochemistry 13:4839–4845
Smith GS, Safinya CR, Roux D, Clark NA (1987): X-ray studies of freely suspended films of a multilamellar lipid system. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst 144:235–255
Strenk LM, Westerman PW, Doane JW (1985): A model of orientational ordering in phosphatidylcholine bilayers based on conformational analysis of the glycerol backbone region. Biophys J 48:765–773
Warren BE (1969): X-ray Diffraction. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley
White SH (1994): Hydropathy plots and the prediction of membrane protein topology. In: Membrane Protein Structure: Experimental Approaches, White SH, ed. New York: Oxford University Press
White SH, Wiener MC (1995): Determination of the structure of fluid lipid bilayer membranes. In: Permeability and Stability of Lipid Bilayers, Disalvo EA, Simon SA, eds. Boca Raton: CRC Press
White SH, Wimley WC (1994): Peptides in lipid bilayers: Structural and thermodynamic basis for partitioning and folding. Cur Opinion Struc Biol 4:79–86
Wiener MC, King GI, White SH (1991): Structure of a fluid dioleoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer determined by joint refinement of x-ray and neutron diffraction data. I. Scaling of neutron data and the distribution of double-bonds and water. Biophys J 60:568–576
Wiener MC, White SH (1991a): Transbilayer distribution of bromine in fluid bilayers containing a specifically brominated analog of dioleoylphosphatidylcholine. Biochemistry 30:6997–7008
Wiener MC, White SH (1991b): Fluid bilayer structure determination by the combined use of X-ray and neutron diffraction. I. Fluid bilayer models and the limits of resolution. Biophys J 59:162–173
Wiener MC, White SH (1991c): Fluid bilayer structure determination by the combined use of X-ray and neutron diffraction II. “Compostion-Space” refinement method. Biophys J 59:174–185
Wiener MC, White SH (1992a): Structure of a fluid dioleoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer determined by joint refinement of x-ray and neutron diffraction data. III. Complete structure. Biophys J 61:434–447
Wiener MC, White SH (1992b): Structure of a fluid dioleoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer determined by joint refinement of x-ray and neutron diffraction data. II. Distribution and packing of terminal methyl groups. Biophys J 61:428–433
Willis BTM, Pryor AW (1975): Thermal Vibrations in Crystallography. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press
Worcester DL (1975): Structural analysis of hydrated egg lecithin and cholesterol bilayers. Brookhaven Symp Biol 27:11137–11157
Worcester DL, Franks NP (1976): Structural analysis of hydrated egg lecithin and cholesterol bilayers. II. Neutron diffraction. J Mol Biol 100:359–378
Zaccai G, Büldt G, Seelig A, Seelig J (1979): Neutron diffraction studies on phosphatidylcholine model membranes. II. Chain conformation and segmental disorder. J Mol Biol 134:693–706
Zhou F, Schulten K (1995): Molecular dynamics study of a membrane-water interface. J Phys Chem 99:2194–2207
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1996 Birkhäuser Boston
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
White, S.H., Wiener, M.C. (1996). The Liquid-Crystallographic Structure of Fluid Lipid Bilayer Membranes. In: Merz, K.M., Roux, B. (eds) Biological Membranes. Birkhäuser Boston. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-8580-6_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-8580-6_5
Publisher Name: Birkhäuser Boston
Print ISBN: 978-1-4684-8582-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-4684-8580-6
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive