Summary
The pharmacokinetics of bisoprolol were investigated following oral administration of 10mg once daily for 7 days in 8 healthy subjects, in 14 patients with different degrees of renal impairment and in 18 patients with liver disease.
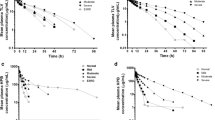
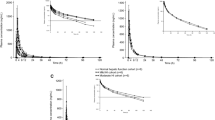
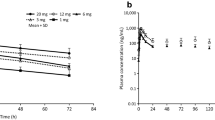
In healthy subjects peak and trough steady-state concentrations of 52 µg/L and 11 µg/ L, respectively, an elimination half-life of 10.0 hours and total body clearance of 14.2 L/ h were observed. 5.21 mg/24 hours of unchanged bisoprolol were recovered following urinary excretion during the dosage interval. In 11 patients with renal impairment (mean CLCR = 28 ± 5 ml/min/1.72m2) half-life was prolonged to 18.5 hours, and peak and trough concentrations were 74 and 32 µg/L, respectively. Correspondingly, urinary excretion decreased to 3.35 mg/24 hours and total body clearance to 7.8 L/h. In uraemic patients (CLCR < 5 ml/min/1.73m2) the total clearance of bisoprolol was 5.0 L/h and the elimination half-life was 24.2 hours. In patients with liver cirrhosis half- life increased to 13.5 hours, steady-state peak and trough concentrations increased to 62 and 22 µg/L, respectively, and total body clearance decreased to 10.8 L/h.
The present study indicates that in patients with impairment of kidney or liver function accumulation of bisoprolol above a factor of 2 did not occur. However, in the terminal stages of insufficiency of kidney or liver function bisoprolol dosage should not exceed 10mg.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bühring KU, Garbe A. Determination of the new β-blocker bisoprolol and of metoprolol, atenolol, and propranolol in plasma and urine by high performance liquid chromatography. Journal of Chromatography, Biomedical Applications 382: 215–224, 1986
Gibaldi M, Perrier D. Pharmacokinetics, 2nd ed. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York 1982
Jordö L, Attmann PO, Aureil M, Johansson L, Johnson G, et al. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of metoprolol in patients with impaired renal function. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 5: 169–280, 1980
Kirch W, Köhler W, Mutschier E, Schäfer M. Pharmacokinetics of atenolol in relation to renal function. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 19: 65–71, 1981
Kirch W, Köhler H, Berggren G, Braun W. The influence of renal function on plasma levels and urinary excretion of acebutolol and its main N-acetyl metabolite. Clinical Nephrology 18: 88–94, 1982
Kirch W, Schäfer-Korting M, Mutschler E, Ohnhaus EE, Braun W. Clinical experience with atenolol in patients with chronic liver disease. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 23: 171–177, 1983
Kirch W, Rose I, Klingmann I, Pabst J, Ohnhaus EE. Interactions of bisoprolol with cimetidine and rifampicin. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 31: 59–62, 1986
Leopold G, Pabst J, Ungethüm W, Bühring KU. Phase I studies on EMD 33 512, a new β1-selective adrenoceptor blocking agent. Abstract. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 31: 243, 1982
Leopold G, Pabst J, Ungethüm W, Bühring W. Basic pharmacokinetics of bisoprolol, a new highly β1-selective adrenoceptor antagonist. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, in press, 1986
Meier J. β-adrenoceptor-blocking agents: pharmacokinetic differences and their clinical implications illustrated on pindolol. Cardiology 64 (Suppl. 1): 1–13, 1979
Ohnhaus EE, Kirchhof B, Peheim E. Effect of enzyme induction on plasma lipids using antipyrine, phenobarbital, and rifampicin. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 25: 591–597, 1979
Regardh CG, Jordö L, Ervik M, Lundborg P, Olsson R, et al. Pharmacokinetics of metoprolol in patients with hepatic cirrhosis. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 6: 375–488, 1981
Schliep HJ, Halting J. β1-selectivity of bisoprolol, a new β-adrenoceptor antagonist, in anaesthetized dogs and guinea pigs. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 6: 1156–1160, 1984
Sassard J, Pozet M, McAinsh J, Legheand J, Zech P. Pharmacokinetics of atenolol in patients with renal impairment. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 12: 175–180, 1977
Sotaniemi EA. Role of liver enzyme activity in the metabolism of some beta-blocking compounds. Current Therapeutic Research 28: 45S–50S, 1980
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kirch, W., Rose, I., Demers, H.G. et al. Pharmacokinetics of Bisoprolol During Repeated Oral Administration to Healthy Volunteers and Patients with Kidney or Liver Disease. Clin-Pharmacokinet 13, 110–117 (1987). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-198713020-00003
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-198713020-00003