Abstract
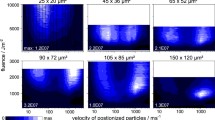
Glycerol, a liquid matrix material for matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry, was irradiated by a tunable pulsed infrared laser at wavelengths of 2.80 μ.m, 2.94 μ.m, 3.10 μ.m and 3.50 μ.m, covering the OH and CH stretch vibrations. A fast photography system was introduced to analyze the dynamic process of plume propagation induced by laser ablation up to 1000 μ.s of the delay time. Propagation distance of the plume front was measured and the corresponding velocities were calculated; they varied with the wavelength and decreased with the delay time. At the tunable wavelength of the peak of the OH absorption (3.0 μ.m), theoretical calculations indicate that energy deposition from the pulsed laser is in the regime of stress confinement. The mode of energy deposition depends on the wavelength of the OH vibration and its distance from the absorption maxima. However, stages after a 10 μ.s delay at various wavelengths show a certain similarity in the distance of plume propagation, which can be well fitted by a drag model.
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
15 October 2019
The editor has retracted this article [1] because it has significant overlap with a work published by Fan and Murray [2] and is therefore redundant. Xing Fan does not agree to this retraction. Jian Xiao, Guang-Zhou Hu, Yun-Peng Zhao, Shi-Gang Kang, Jin-Li Lu and Hong-Ru Fan have not responded to any correspondence from the editor about this retraction.
15 October 2019
The editor has retracted this article [1] because it has significant overlap with a work published by Fan and Murray [2] and is therefore redundant. Xing Fan does not agree to this retraction. Jian Xiao, Guang-Zhou Hu, Yun-Peng Zhao, Shi-Gang Kang, Jin-Li Lu and Hong-Ru Fan have not responded to any correspondence from the editor about this retraction.
References
Ansorge, R., & Sonar, T. (2009). Mathematical models of fluid dynamics: Modelling, theory, basic numerical facts — an introduction. Weinheim, Germany: Wiley-VCH Verlag. DOI: 10.1002/9783527627967.
Apitz, I., & Vogel, A. (2005). Material ejection in nanosecond Er:YAG laser ablation of water, liver, and skin. Applied Physics A, 81, 329–338. DOI: 10.1007/s00339–005–3213–5.
Dreisewerd, K., Berkenkamp, S., Leisner, A., Rohlfing, A., & Menzel, C. (2003). Fundamentals of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry with pulsed infrared lasers. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 226, 189–209. DOI: 10.1016/s1387–3806(02)00977–6.
Fan, X., Little, M. W., & Murray, K. K. (2008). Infrared laser wavelength dependence of particles ablated from glycerol. Applied Surface Science, 255, 1699–1704. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.06.033.
Fan, X., & Murray, K. K. (2009). UV laser irradiation of IR laser generated particles ablated from nitrobenzyl alcohol. Applied Surface Science, 255, 6297–6302. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.02.005.
Fan, X., Wang, S. Z., Zheng, A. L., Wei, X. Y., Zhao, Y. P., Zong, Z. M., & Zhao, W. (2013). Investigation on infrared laser desorption of solid matrix using scanning electron microscope and fast photography. Microscopy Research and Technique, 76, 744–750. DOI: 10.1002/jemt.22225.
Harilal, S. S., Bindhu, C. V., Tillack, M. S., Najmabadi, F., & Gaeris, A. C. (2003). Internal structure and expansion dynamics of laser ablation plumes into ambient gases. Journal of Applied Physics, 93, 2380–2388. DOI: 10.1063/1.1544070.
Hopp, B., Toth, Z., Gal, K., Mechler, A., Bor, Z., Moustaizis, S. D., Georgiou, S., & Fotakis, C. (1999). Time-resolved investigation of the transient surface reflection changes of subpicosecond excimer laser ablated liquids. Applied Physics A-Materials Science & Processing, 69, S191–S194. DOI: 10.1007/s003390051382.
Huang, F., Fan, X., & Murray, K. K. (2008). Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization of infrared laser ablated particles. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 274, 21–24. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijms.2008.04.006.
Jackson, S. N., Kim, J. K., Laboy, J. L., & Murray, K. K. (2006). Particle formation by infrared laser ablation of glycerol: implications for ion formation. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 20, 1299–1304. DOI: 10.1002/rcm.2443.
Karas, M., & Kruger, R. (2003). Ion formation in MALDI: The cluster ionization mechanism. Chemical Reviews, 103, 427–439. DOI: 10.1021/cr010376a.
Knochenmuss, R., & Zenobi, R. (2003). MALDI ionization: the role of in-plume processes. Chemical Reviews, 103, 441–452. DOI: 10.1021/cr0103773.
Ludemann, H. C., Redmond, R. W., & Hillenkamp, F. (2002). Singlet-singlet annihilation in ultraviolet matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization studied by fluorescence spectroscopy. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 16, 1287–1294. DOI: 10.1002/rcm.712.
Leisner, A., Rohlfing, A., Berkenkamp, S., Hillenkamp, F., & Dreisewerd, K. (2004). Infrared laser post-ionization of large biomolecules from an IR-MALD(I) plume. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 15, 934–941. DOI: 10.1016/s1044–0305(04)00183–7.
Leisner, A., Rohlfing, A., Rohling, U., Dreisewerd, K., & Hillenkamp, F. (2005). Time-resolved imaging of the plume dynamics in infrared matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization with a glycerol matrix. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 109, 11661–11666. DOI: 10.1021/jp050994l.
Menzel, C., Dreisewerd, K., Berkenkamp, S., & Hillenkamp, F. (2001). Mechanisms of energy deposition in infrared matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 207, 73–96. DOI: 10.1016/s1387–3806(01)00363–3.
Musapelo, T., & Murray, K. K. (2011). Particle formation in ambient MALDI plumes. Analytical Chemistry, 83, 6601–6608. DOI: 10.1021/ac201032g.
Rezenom, Y. H., Dong, J. N., & Murray, K. K. (2008). Infrared laser-assisted desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Analyst, 133, 226–232. DOI: 10.1039/b715146b.
Rohlfing, A., Menzel, C., Kukreja, L. M., Hillenkamp, F., & Dreisewerd, K. (2003). Photoacoustic analysis of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization processes with pulsed infrared lasers. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 107, 12275–12286. DOI: 10.1021/jp035554d.
Russo, R. E., Mao, X., Liu, H., Gonzalez, J., & Mao, S. S. (2002). Laser ablation in analytical chemistry — a review. Talanta, 57, 425–451. DOI: 10.1016/s0039–9140(02)00053-x.
Sampson, J. S., Hawkridge, A. M., & Muddiman, D. C. (2006). Generation and detection of multiply-charged peptides and proteins by matrix-assisted laser desorption electrospray ionization (MALDESI) Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 17, 1712–1716. DOI: 10.1016/j.jasms.2006.08.003.
Shiea, J., Huang, M. Z., Hsu, H. J., Lee, C. Y., Yuan, C. H., Beech, I., & Sunner, J. (2005). Electrospray-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry for direct ambient analysis of solids. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 19, 3701–3704. DOI: 10.1002/rcm.2243.
Singh, R. P., Gupta, S. L., & Thareja, R. K. (2013). Spectroscopic investigation of colliding plasma plumes. Spectrochim- ica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 88, 54–62. DOI: 10.1016/j.sab.2013.08.006.
Vertes, A. (2007). Soft laser desorption ionization — MALDI, DIOS, and nanostructures. In C. R. Phipps (Ed.) Laser ablation and its applications (pp. 505–528). New York, NY, USA: Springer. DOI: 10.1007/978–0–387–30453–3.
Vogel, A., & Venugopalan, V. (2003). Mechanisms of pulsed laser ablation of biological tissues. Chemical Reviews, 103, 577–644. DOI: 10.1021/cr010379n.
Zhigilei, L. V., & Garrison, B. J. (1999). Molecular dynamics simulation study of the fluence dependence of particle yield and plume composition in laser desorption and ablation of organic solids. Applied Physics Letters, 74, 1341–1343. DOI: 10.1063/1.123544.
Zhigilei, L. V., & Garrison, B. J. (2000). Microscopic mechanisms of laser ablation of organic solids in the thermal and stress confinement irradiation regimes. Journal of Applied Physics, 88, 1281–1298. DOI: 10.1063/1.373816.
Zhigilei, L. V., Yingling, Y. G., Itina, T. E., Schoolcraft, T. A., & Garrison, B. (2003). Molecular dynamics simulations of MALDI desorption — connections to experiment. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 226, 85–106. DOI: 10.1016/s1387–3806(02)00962–4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
The editor has retracted this article because it has significant overlap with a work published by Fan and Murray and is therefore redundant.
Xing Fan does not agree to this retraction. Jian Xiao, Guang-Zhou Hu, Yun-Peng Zhao, Shi-Gang Kang, Jin-Li Lu and Hong-Ru Fan have not responded to any correspondence from the editor about this retraction.
Electronic supplementary material
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, X., Xiao, J., Hu, GZ. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Analysis of the dynamics of laser induced plume propagation from liquid matrix using fast photography. Chem. Pap. 70, 848–855 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2016-0012
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2016-0012