Abstract
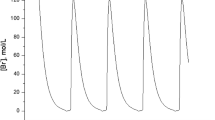
A new type of bulk liquid membrane system, which represents the first example of a bulk liquid membrane oscillator characterised by the presence of two coupled oscillators, is described. When the benzyldimethyltetradecylammonium chloride surfactant undergoes an oscillatory mass transfer through a nitromethane liquid membrane, a new liquid layer (phase X) appears between the membrane and the acceptor phase. Kinetic analysis provides evidence that the whole system is composed of two coupled oscillators with diffusion-mediated physical coupling. The first component oscillator (based on nitromethane) of lower frequency delivers the driving material to the second one (phase X-based oscillator) leading to additional higher frequency oscillations. A new molecular mechanism is proposed for interpreting the experimental observations. The results might enhance understanding of intercellular communication in biology, where periodic signalling is more efficient than any other type of signalling mode.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brian, P. L. T. (1971). Effect of Gibbs adsorption on Marangoni instability. AIChE Journal, 17, 765–772. DOI: 10.1002/aic.690170403.
Cussler, E. L. (1995). Diffusion: Mass transfer in fluid systems. Cambridge: UK: Cambridge University Press.
Epstein, I. R., & Pojman, J. A. (1998). An introduction to non-linear chemical dynamics. New York, NY, USA: Oxford University Press.
Goldbeter, A. (1996). Biochemical oscillations and cellular rhythms. Cambridge: UK: Cambridge University Press.
Gray, P., & Scott, S. K. (1990). Chemical oscillations and instabilities: Non-linear chemical kinetics. New York, NY, USA: Oxford University Press.
Hennenberg, M., Bisch, P. M., Vignes-Adler, M., & Sanfeld, A. (1979). Mass transfer, Marangoni effect, and instability of interfacial longitudinal waves: I. Diffusional exchanges. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 69, 128–137. DOI: 10.1016/0021-9797(79)90087-0.
Ikezoe, Y., Ishizaki, S., Yui, H., Fujinami, M., & Sawada, T. (2004). Direct observation of chemical oscillation at a water/nitrobenzene interface with a sodium-alkyl-sulfate system. Analytical Sciences, 20, 435–440. DOI: 10.2116/analsci.20.435.
Kovalchuk, N. M., & Vollhardt, D. (2006). Marangoni instability and spontaneous non-linear oscillations produced at liquid interfaces by surfactant transfer. Advances in Colloid Interface Science, 120, 1–31. DOI: 10.1016/j.cis.2006.01.001.
Kovalchuk, N. M., & Vollhardt, D. (2007). Instability and spontaneous oscillations by surfactant transfer through a liquid membrane. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical Engineers Aspects, 309, 231–239. DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2006.11.040.
Larter, R. (1990). Oscillations and spatial nonuniformities in membranes. Chemical Reviews, 90, 355–381. DOI: 10.1021/cr00100a002.
Lavabre, D., Pradines, V., Micheau, J. C., & Pimienta, V. (2005). Periodic Marangoni instability in surfactant (CTAB) liquid/liquid mass transfer. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 109, 7582–7586. DOI: 10.1021/jp045197m.
Marcus, Y. (1977). Introduction to liquid state chemistry. London, UK: Wiley.
Ostrovsky, M. V., & Ostrovsky, M. J. (1983). Dynamic interfacial tension in binary systems and spontaneous pulsation of individual drops by their dissolution. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 93, 392–401. DOI: 10.1016/0021-9797(83)90422-8.
Pimienta, V., Etchenique, R., & Buhse, T. (2001). On the origin of electrochemical oscillations in the picric acid/CTAB two-phase system. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 105, 10037–10044. DOI: 10.1021/jp013350w.
Płocharska-Jankowska, E., Szpakowska, M., Mátéfi-Tempfli, S., & B. Nagy, O. (2005). On the possibility of molecular recognition of taste substances studied by Gábor analysis of oscillations. Biophysical Chemistry, 114, 85–93. DOI: 10.1016/j.bpc.2004.10.004.
Płocharska-Jankowska, E., Szpakowska, M., Mátéfi-Tempfli, S. & B. Nagy, O. (2006). A new approach to the spectral analysis of liquid membrane oscillators by Gábor transformation. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 110, 289–294. DOI: 10.1021/jp0557870.
Rastogi, R. P., & Srivastava, R. C. (2001). Interface-mediated oscillatory phenomena. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 93, 1–75. DOI: 10.1016/s0001-8686(00)00037-3.
Reichardt, C. (1979). Solvent effects in organic chemistry. Weinheim, Germany: Verlag Chemie.
Sternling, C. V., & Scriven, L. E. (1959). Interfacial turbulence: Hydrodynamic instability and Marangoni effect. AIChE Journal, 5, 514–520. DOI: 10.1002/aic.690050421.
Suzuki, T., & Kawakubo, T. (1992). Convective instability and electric potential oscillation in a water-oil-water system. Biophysical Chemistry, 45, 153–159. DOI: 10.1016/0301-4622(92)87007-6.
Szpakowska, M., Czaplicka, I., Szwacki, J., & B. Nagy, O. (2002). Oscillatory phenomena in systems with bulk liquid membranes. Chemical Papers, 56, 20–23.
Szpakowska, M., Czaplicka, I., Płocharska-Jankowska, E., & B. Nagy, O. (2003). Contribution to the mechanism of liquid membrane oscillators involving cationic surfactant. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 261, 451–455. DOI: 10.1016/s0021-9797(03)00080-8.
Szpakowska, M., Płocharska-Jankowska, E., & B. Nagy, O. (2005). On the new possibility of applying oscillating liquid membrane systems for molecular recognition substances responsible for taste. Desalination, 173, 61–67. DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2004.06.209.
Szpakowska, M., Magnuszewska, A., & Płocharska-Jankowska, E. (2006a). Possibility of discrimination of sour substances by liquid membrane oscillators. Desalination, 198, 353–359. DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2006.04.003.
Szpakowska, M., Czaplicka, I., & B. Nagy, O. (2006b). Mechanism of four-phase liquid membrane oscillator containing hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 110, 7286–7292. DOI: 10.1021/jp057349z.
Szpakowska, M., Magnuszewska, A., & B. Nagy, O. (2008). Mechanism of nitromethane liquid membrane oscillator containing sodium oleate. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 325, 494–499. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2008.05.059.
Szpakowska, M., Płocharska-Jankowska, E., & B. Nagy, O. (2009). Molecular mechanism and chemical kinetic description of nitrobenzene liquid membrane oscillator containing benzyldimethyltetradecylammonium chloride surfactant. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 113, 15503–15512. DOI: 10.1021/jp9066873.
Tatsuno, Y., Kozuru, T., Yoshida, Y., & Maeda, K. (2012). Propagation and synchronization of potential oscillations in multiple liquid membrane systems. Analytical Science, 28, 1145–1151. DOI: 10.2116/analsci.28.1145.
Toko, K., Yoshikawa, K., Tsukiji, M., Nosaka, M., & Yamafuji, K. (1985). On the oscillatory phenomenon in an oil/water interface. Biophysical Chemistry, 22, 151–158. DOI: 10.1016/0301-4622(85)80037-5.
Weast, R. C., Astle, M. J., & Beyer, W. H. (1984). CRC handbook of chemistry and physics (64th ed.). Boca Ration, FL, USA: CRC Press.
Yoshikawa, K., & Matsubara, Y. (1983). Spontaneous oscillation of pH and electric potential in an oil-water system. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 105, 5967–5969. DOI: 10.1021/ja00357a001.
Yoshikawa, K., Shoji, M., Nakata, S., Maeda, S., & Kawakami, H. (1988). An excitable liquid membrane possibly mimicking the sensing mechanism of taste. Langmuir, 4, 759–762. DOI: 10.1021/la00081a046.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Szpakowska, M., Płocharska-Jankowska, E. & Nagy, O.B. New bulk liquid membrane oscillator composed of two coupled oscillators with diffusion-mediated physical coupling. Chem. Pap. 69, 1176–1186 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2015-0126
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2015-0126