Abstract
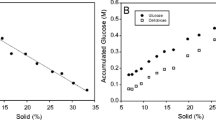
Following detoxification of the liquid hydrolysate produced in a corn stover pretreatment process, inhibitor levels are seen to increase with the re-addition of solids for the ensuing hydrolysis and fermentation processes. The solids that were separated from the slurry before detoxification of the liquor contain approx 60% (w/w) moisture, and contamination occurs owing to the diffusion of inhibitors from the moisture entrained in the porous structure of the corn stover solids into the bulk fluid. This evidence suggests the need for additional separation and detoxification steps to purge residual inhibitors entrained in the moisture in the solids. An overliming process to remove furans from the hydrolysate failed to reduce total organic acids concentration, so acids were removed by treatment with an activated carbon powder. Smaller carbon doses proved more efficient in removing organic acids in terms of grams of acid removed per gram of carbon powder. Sugar adsorption by the activated carbon powder was minimal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nguyen, Q. A., Tucker, M. P., Keller, F. A., Beaty, D. A., Connors, K. M., and Eddy, F. P. (1999), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 77–79, 133–142.
Larsson, S., Palmqvist, E., Hahn-Hagerdal, B., et al. (1999), Enzyme Microbiol. Technol. 24, 151–159.
Ranatunga, T. D., Jervis, J., Helm, R. F., McMillan, J. D., and Hatzis, C. (1997), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 67, 185–198.
Larsson, S., Reimann, A., Nilvebrant, N. O., and Jonsson, L. J. (1999), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 77–79, 91–103.
Martinez, A., Rodrigues, M. E., Wells, M. L., York, S. W., Preston, J. F., and Ingram, L. O. (2001), Biotechnol. Prog. 17, 287–293.
Mohagheghi, A., Ruth, M., and Schell, D. (2004), Tracking the fate of calcium and sulfur through the overliming process used to condition hydrolysates produced by dilute sulfuric-acid pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass, presented at the 26th Symposium on Biotechnology for Fuels and Chemicals, Chattanooga, TN.
Lee, W. G., Lee, J. S., Shin, C. S., Park, S. C., Chang, H. N., and Chaik, Y. K. (1999), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 77–79, 547–559.
Rivard, C. J., Engel, R. E., Hayard, T. K., Nagle, N. J., Hatzis, C., and Philippidis, G. P. (1996), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 57–58, 183–191.
Jonsson, L. J., Palmqvist, E., Nilvebrant, N. O., and Hahn-Hagerdal, B. (1998), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 49, 691–697.
Priddy, S. A. (2002), PhD Dissertation, University of Louisville, Louisville, Kentucky.
Priddy S. A. and Hanley, T. R. (2003), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 105–108, 353–364.
Berson, R. E., Young, J. S., Kamer, S. N., and Hanley, T. R. (2005), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. in press.
Morresi, A. C. and Cheremisinoff, P. N. (1978), In: Carbon Adsorption Handbook, Cheremisinoff, P. N. and Ellerbusch, F., eds., Ann Arbor Science Publishers, Ann Arbor, MI, pp. 1–54.
Fein, E. F., Tallim, S. R., and Lawford, G. R. (1984), Can. J. Microb. 30, 682–690.
Frazer, F. R. and McCaskey, T. A. (1989), Biomass. 18, 31–42.
Roberto, I. C., Lacis, L. S., Barbosa, M. F. S., and de Mancilha, I. M. (1991), Process Biochem. 26, 15–21.
Parajo, J. C., Dominguez, H., and Dominguez, J. M. (1997), Enzyme Microb. Technol. 21, 18–24.
Martinez, A., Rodrigues, M. E., York, S. W., Preston, J. F., and Ingram, L. O. (2000), Biotechnol. Prog. 16, 637–641.
Kamer, S. (2004), Masters thesis, University of Louisville, Louisville, Kentucky.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berson, R.E., Young, J.S. & Hanley, T.R. Reintroduced solids increase inhibitor levels in a pretreated corn stover hydrolysate. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 130, 612–620 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:130:1:612
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:130:1:612