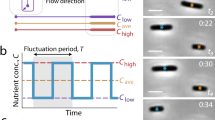
Abstract
The presence of spatial gradients in fundamental culture parameters, such as dissolved gases, pH, concentration of substrates, and shear rate, among others, is an important problem that frequently occurs in large-scale bioreactors. This problem is caused by a deficient mixing that results from limitations inherent to traditional scale-up methods and practical constraints during large-scale bioreactor design and operation. When cultured in a heterogeneous environment, cells are continuously exposed to fluctuating conditions as they travel through the various zones of a bioreactor. Such fluctuations can affect cell metabolism, yields, and quality of the products of interest. In this review, the theoretical analyses that predict the existence of environmental gradients in bioreactors and their experimental confirmation are reviewed. The origins of gradients in common culture parameters and their effects on various organisms of biotechnological importance are discussed. In particular, studies based on the scale-down methodology, a convenient tool for assessing the effect of environmental heterogene ities, are surveyed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C * :
-
Dissolved oxygen concentration at saturation with air
- CFD:
-
Computational fluid dynamics
- CHO:
-
Chinese hamster ovary
- dCO2 :
-
Dissolved carbon dioxide
- dH2 :
-
Dissolved hydrogen
- Di :
-
Impeller diameter
- DO:
-
Dissolved oxygen concentration
- dw:
-
Dry weight
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- HGH:
-
Human growth hormone
- k La:
-
Volumetric oxygen transfer coefficient
- N :
-
Impeller rotation speed
- PFR:
-
Plug-flow reactor
- P o :
-
Power input
- Q :
-
Pump rate
- SD:
-
Scale-down
- SDS:
-
Scale-down system
- STR:
-
Stirred-tank reactor
- t c :
-
Circulation time
- TCA:
-
Tricarboxylic acid
- tm :
-
Mixing time
- t MT :
-
Characteristic time for mass transfer
- tO2u :
-
Characteristic time for oxygen uptake
- V :
-
Volume
- ’:
-
Density
- μ:
-
Viscosity
References
Oldshue, J. Y. (1966). Fermentation mixing scale-up technique. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 8, 3–24.
Palomares, L. A. and Ramírez, O. T. (2000) Bioreactor Scale-Down, in The Encyclopedia of Cell Technology, vol. 1 (Spier, R. E., ed.), John Wiley and Sons, New York, NY, pp. 174–183.
Bylund, F., Collet, E., Enfors, S. O., and Larsson, G. (1998) Substrate gradient formation in the large-scale bioreactor lowers cell yield and increases by-product formation. Bioprocess Eng. 18, 171–180.
Guillard, F. and Trägardh, C. (1999) Modeling of the performance of industrial bioreactors with a dynamic microenvironmental approach: A critical review. Chem. Eng. Technol. 22, 187–195.
Palomares, L. A. and Ramírez, O. T. (2000) Bioreactor Scale-Up, in The Encyclopedia of Cell Technology, vol. 1 (Spier, R. E., ed.), John Wiley and Sons, New York, NY, pp. 183–201.
Vlaev, D., Mann, R., Lossev, V., Vlaev, S. D., Zahradnik, J., and Seichter, P. (2000) Macro mixing and Streptomyces fradiae. Modelling oxygen and nutrient segregation in an industrial bioreactor. Trans IChemE part A 78, 354–362.
Enfors, S.-O., Jahic, M., Rozkov, A., et al. (2001) Physiological responses to mixing in large scale bioreactors. J. Biotechnol. 82, 175–185.
Hristov, H., Mann, R., Lossev, V., Vlaev, S. D., and Seichter, P. (2001) A 3-D analysis of gas-liquid mixing, mass transfer and bioreaction in a stirred bioreactor. Trans IChem E part C 79, 232–241.
Amanullah, A., Buckland, B. C., and Nienow, A. W. (2004) Mixing in the fermentation and cell culture industries, in Handbook of Industrial Mixing: Science and Practice (Paul, E. L., Atiemo-Obeng, V. A., and Kresta, S. M., eds.), John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ, pp. 1071–1170.
Doran, P. M. (1993). Design of bioreactors for plant cells and organs, in Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology, vol. 48 (Fietcher, A., ed.), Springer-Verlag, Berlin: pp. 115–168.
Marten, M. R., Wenger, K. R., and Khan, S. A. (1997) Rheology, mixing time and regime analysis for a production-scale Aspergillus oryzae fermentation. Proceedings of the 4th International Conference in Bioreactor & Bioprocess Fluid Dynamics”, (Nienow, A. W., ed.), Mechanical Engineering Publications, BurySt. Edmonds, UK, pp. 295–313.
Larsson, G., Törnkvist, M., Stahl-Wernersson, E., Trägardh, C., Noorman, H., and Enfors, S. O. (1996) Substrate gradients in fed-batch bioreactors: origin and consequences. Bioprocess Eng. 14, 281–289.
Larsson, G. and Törnkvist, M. (1996) Rapid sampling, cell inactivation and evaluation of low extracellular glucose concentrations during fed-batch cultivation. J. Biotechnol. 49, 69–82.
Bylund, F., Guillard, F., Enfors, S., Trägardh, C., and Larsson, G. (1999). Scale down of recombinant protein production: a comparative study of scaling performance. Bioprocess Eng. 20, 377–389.
Bylund, F., Castan, A., Mikkola, R., Veide, A., and Larsson, G. (2000). Influence of scale-up on the quality of recombinant human growth hormone. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 69, 119–128.
Sinacore, M. S., Charlebois, T. S., Drapeu, D., Leonard, M., Harrison, S., and Adamson, S. R. (2000) Cell stability, in The Encyclopedia of Cell Technology, vol. 1, (Spier, R. E., ed.), John Wiley and Sons, New York, NY, pp. 458–472.
Choi, J. H., Keum, K. C., and Lee, S. Y. (2006) Production of recombinant proteins by high cell-density cultures of Escherichia coli. Chem. Eng. Sci. 61, 876–885.
Ozturk, S. S. (1996) Engineering challenges in high cell density cell culture systems. Cytotechnol. 22, 3–16.
Reuss, M., Schmalzriedt, S., and Jenne, M. (1994) Structured Modelling of Bioreactors, in Advances in Bioprocess Engineering (Galindo E. and Ramírez, O. T., eds.), Kluwer Academic Press, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp. 207–215.
Langheinrich, C., Nienow, A. W., Stevenson, N. C., Enery, A. N., Clayton, T. M., and Slater, N. K. H. (1995) Mixing and oxygen transfer in a large scale animal cell bioreactor, in Biochemical Engineering 3 (Schmid, R. D., ed.) Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, pp. 162–164.
Oosterhuis, N. M. G. and Kossen, N. W. F. (1984) Dissolved oxygen concentration profiles in a productionscale bioreactor. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 26, 546–550.
Borys, M. C., Linzer, D. I. H., and Papoutsakis, E. T. (1993) Culture pH affects expression rates and glycosylation of recombinant mouse placental lactogen proteins by chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells. Bio/Technology 11, 720–724.
Häggstrom, L. (2000) Cell Metabolism, Animal, in The Encyclopedia of Cell Technology, vol. 1 (Spier, R. E., ed.), John Wiley and Sons, New York, NY, pp. 392–411.
Langheinrich, C. and Nienow, A. W. (1999) Control of pH in large-scale, free suspension animal cell bioreactors: alkali addition and pH excursions. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 66, 171–179.
McDowell, C. Papoutsakis, E. T., and Borys, M. C. (2000) Animal cell Culture, Physiochemical effects of pH, in The Encyclopedia of Cell Technology, vol. 1 (Spier, R. E., ed.), John Wiley and Sons, New York, NY, pp. 63–70.
Amanullah, A., McFarlane, C. M., Emery, A. N., and Nienow, A. W. (2001) Seale-down model to simulate spatial pH variations in large-scale bioreactors. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 73, 390–399.
Onyeaka, H., Nienow, A. N., and Hewitt, C. J. (2003) Further studies related to the scale-up of high cell density Escherichia coli fed-batch fermentation: the additional effect of a changing microenvironment when using aqueous ammonia to control pH. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 84, 474–484.
Zheng, J. Y. and Janis, L. J. (2006) Influence of pH, buffer species, and storage temperature on physicochemical stability of a humanized monoclonal antibody LA298. Int. J. Pharmaceutics 308, 46–51.
Gray, D. R., Chen, S., Howarth, W., Inlow, D., and Maiorella, B. L. (1996) CO2 in large-scale and high-density CHO cell perfusion culture. Cytotechnol. 22, 65–78.
Nienow A. W., Langheinrich, C., Stevenson, N. C., Emery, A. N., Clayton, T. M., and Slater, N. K. H. (1996) Homogenisation and oxygen transfer rates in large agitated and sparged animal cell bioreactors: Some implications for growth and production. Cytotechnol. 22, 87–94.
Mostafa, S. S. and Gu, X. S. (2003). Strategies for improved dCO2 removal in large-scale fed-batch cultures. Biotechnol Prog. 19, 45–51.
Bothun, G. D., Knutson, B. L., Berberich, J. A., Strobel, H. J., and Nokes, S. E. (2004) Metabolic selectivity and growth of Clostridium thermocellum in continuous culture under elevated hydrostatic pressure. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 65, 149–157.
Lamed, R. J., Lobos, J. H., and Su, T. M. (1988) Effects of stirring and hydrogen on fermentation products of Clostridium thermocellum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54, 1216–1221.
Zanghi, J. A., Schmelzer, A. E., Mendoza, T. P., Knop, R. H., and Miller, W. M. (1999). Bicarbonate concentration and osmolarity are key determinants in the inhibition of CHO polysialylation under elevated pCO2 or pH. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 65, 182–191.
Castan, A., Näsman, A., and Enfors, S. O. (2002) Oxygen enriched air supply in Escherichia coli processes: production of biomass and recombinant human growth hormone. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 30, 847–854.
Mashego, M. R. (2005) Robust experimental methods to study in-vivo pre-steady state kinetics of primary metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PhD Thesis. Delft University of Technology.
Mitchell-Logean, C. and Murhammer, D. W. (1997) Bioreactor headspace purging reduces dissolved carbon dioxide accumulation in insect cell cultures and enhances cell growth. Biotechnol. Prog. 13, 875–877.
Garnier, A., Voyer, R., Tom, R., Perret, S., Jardin, B., and Kamen, A. (1996) Dissolved carbon dioxide accumulation in a large scale and high density production of TGF β receptor with baculovirus infected Sf-9 cells. Cytotechnol. 22, 53–63.
Contreras, A., García, F., Molina, E., and Merchuk, J. C. (1998) Interaction between CO2-mass transfer, light availability, and hydrodynamic stress in the growth pf Phaedactylum tricornutum in a concentric tube airlift photobioreactor. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 60, 317–325.
Johnston, J. S., Jensen, A., Czeschin, D. G., and Price, H. J. (1996) Environmentally induced nuclear 2C DNA content instability in Helianthus annuus (Asteraceae). Am. J. Bot. 83, 1113–1120.
Weber, W., Rimann, M., de Glutz, F.-N., Weber, E., Memmert, K., and Fussenegger, M. (2005) Gas-inducible product gene expression in bioreactors. Metabolic Eng. 7, 174–181.
Weber, W., Spielmann, M., Daoud El-Baba, M., Keller, B., Aubel, D., and Fussenegger, M. (2005) Tobacco smoke as inducer for gas phase-controlled transgene expression in mammalian cells and mice. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 90, 893–897.
Mollet, M., Ma, N., Zhao, Y., Brodkey, R., Taticek, R., and Chalmers, J. J. (2004) Bioprocess equipment: Characterization of energy dissipation rate and its potential to damage cells. Biotechnol. Prog. 20, 1437–1448.
Garcia-Briones, M. A. and Chalmers, J. J. (1994) Flow parameters associated with hydrodynamic cell injury. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 44, 1089–1098.
Taticek, R. A., Moo-Young, M., and Legge, R. L. (1991) The scale-up of plant cell culture: Engineering considerations. Plant Cell Tissue and Organ Culture 24, 139–158.
Toma, M. K., Ruklisha, M. P., Vanags, J. J., et al. (1991) Inhibition of microbial growth and metabolism by excess turbulence. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 38, 552–556.
Cruz, P. E., Cuhna, A., Peixoto, C. C., Clemente, J., Moreira, J. L., and Carrondo, M. T. J. (1998) Optimization of the production of virus-like particles in insect cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 60, 408–418.
Thomas, C. R. and Zhang, Z. (1998) The effect of hydrodynamics on biological materials, in Advances in Bioprocess Engineering II (Galindo E. and Ramírez, O. T., eds.), Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordretch, pp. 137–170.
Chisti, Y. (2001) Hydrodynamic damage to animal cells. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 21, 67–110.
Palomares, L. A., Estrada-Mondaca, S., and Ramírez, O. T. (2006) Principles and Applications of the Insect-Cell-Baculovirus Expression Vector System, in Cell Culture-Technology for Pharmaceutical and Cellular Applications (Ozturk, S. and Hu, W. S., eds.), Taylor and Francis, New York, pp. 627–692.
Sahoo, S., Rao, K., and Suraishkumar, G. K. (2006) Reactive oxygen species induced by shear stress mediate cell death in Bacillus subtillis. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 94, 118–127.
Lu, G. Z., Thompson, B. G., Suresh, M. R., and Gray, M. R. (1995) Cultivation of hybridoma cells in an inclined bioreactor. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 45, 176–186.
McDowell, C. L. and Papoutsakis, E. T. (1998) Increased agitation intensity increases CD13 receptor surface content and mRNA levels, and alters the metabolism of HL60 cells cultures in stirred tank reactors. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 60, 239–250.
Senger, R. S. and Karim, M. N. (2003) Effect of shear stress in intrinsic CHO culture state and glycosylation of recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator protein. Biotechnol. Prog. 19, 1199–1209.
Ranjan, V., Waterbury, R., Xiao, Z., and Diamond, S. L. (1996) Fluid shear stress induction of the transcriptional activator c-fos in human and bovine endothelial cells, HeLa, and Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 49, 383–390.
Lakhotia, S., Bauer, K. D., and Papoutsakis, E. T. (1992) Damaging agitation intensities increase DNA synthesis rate and alter cell-cycle phase distributions of CHO cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 40, 978–990.
Gao, Q., Fang, A., Oierson, D. L., Mishra, S. K., and Demain, A. L. (2001) Shear stress enhances microcin B17 production in a rotating wall bioreactor, but ethanol stress does not. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 56, 384–387.
Abu-Reesh, I. and Kargi, F. (1989) Biological responses of hybridoma cells to defined hydrodynamic shear stress. J. Biotechnol. 9, 167–178.
Goldblum, S., Bae, Y.-K., Hink, W. F., and Chalmers, J. (1990) Protective effect of methylcellulose and other polymers on insect cells subjected to laminar shear stress. Biotechnol. Prog. 6, 383–390.
Michaels, J. D., Petersen, J. F., McIntire, L. V., and Papoutsakis, E. T. (1991) Protection mechanisms of freely suspended animal cells (CRL 8018) from fluidmechanical injury. Viscometric and bioreactor studies using serum, Pluronic F68 and polyethylene glycol. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 38, 169–180.
Palomares, L. A., González, M., and Ramírez O. T. (2000) Evidence of Pluronic F-68 direct interaction with insect cells: Impact on shear protection, recom binant protein and baculovirus production, Enzyme Microb. Technol. 26, 324–331.
Ramírez, O. T. and Mutharasan, R. (1990) The role of plasma membrane fluidity on the shear sensitivity of hybridomas grown under hydrodynamic stress. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 36, 911–920.
Al-Rubeai, M., Singh, R. P., Goldman, M. H., and Emery, A. N. (1995) Death mechanisms of animal cells in conditions of intensive agitation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 45, 463–472.
Wase, D. A., and Ratwatte, H. A. M. (1985) Variation of intracellular sodium and potassium concentration with changes in agitation rate for chemostat-cultivated Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 22, 325–328.
Rocha-Valadez, J. A., Hassan, M., Corkidi, G., Flores, C., Galindo, E., Serrano-Carreón, L. (2005) 6-Pentyl-α pyrone production by Trichoderma harzianum: The influence of energy dissipation rate and its implications of fungal physiology. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 91, 54–61.
Manfredini, R., Cavallera, V., Marini, L., and Donati, G. (1983) Mixing and oxygen transfer in conventional strirrer fermentors. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 25, 3115–3131.
Gorenflo, V. M., Beauchesne, P., Tayi, V., et al. Acoustic cell processing for viral transduction or bioreactor cell retention. Proceedings of the 19th ESACT meeting. In press.
Tsao, E. I., Bohn, M. A., Naumsuwan, V., Ostead, D. R., and Munster, M. J. (1992) Effects of heat shock on the production of human erythropoietin from recombinant CHO cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 40, 1190–1196.
Yamamori, T. and Yura, T. (1980) Temperature-induced synthesis of specific proteins in Escherichia coli: Evidence for trancriptional control. J. Bacteriol. 142, 843–851.
Oosterhuis, N. M. G. (1984) Scale-up of bioreactors: a scale-down approach. PhD thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands.
De León, A., Galindo, E., and Ramírez, O. T. (1995) Effect of oscillating dissolved oxygen tension on penicillin acylase production by a recombinant E coli, in Biochemical Engineering 3 (Schmid, R. D., ed.), Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, pp. 200–202.
Serrato, J. A., Palomares, L. A., Meneses-Acosta, A., and Ramírez, O. T. (2004) Heterogeneous conditions in dissolved oxygen affect N-glycosylation but not productivity of a monoclonal antibody in hybridoma cultures. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 88, 176–188.
Sandoval-Basurto, E., Gosset, G., Bol'var, F., and Ramírez, O. T. (2005) Culture of Escherichia coli under dissolved oxygen gradients simulated in a two-compartments scale-down system: metabolic response and production of recombinant protein. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 89, 453–463.
Lara, A. R., Leal, L. I., Flores, N., Gosset, G., Bolívar, F., and Ramírez, O. T. (2006) Transcriptional and metabolic response of recombinant Escherichia coli to spatial dissolved oxygen tension gradients simulated in a scale-down system. Biotechnol Bioeng. 93, 372–385.
Serrato, J. A., Hernández, V., and Ramírez, O. T. (2006) Heterogeneous conditions in pH and dissolved CO2 concentration on hybridoma cultures: Implications on growth and monoclonal antibody glycosylation. Presented at the Cell Culture Engineering X meeting. Whitsler, BC, Canada.
Schilling, B. M., Pfefferle, W., Bachmann, B., Leuchtenberger, W., and Deckwer, W. (1999) A special reactor design for investigations of mixing time in a scaled-down industrial L-lysine fed-batch fermentation process. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 64, 599–606.
Papagianni, M., Mattey, M., and Kristiansen, B. (2003) Design of a tubular loop bioreactor for scale-up and scale-down of fermentation processes. Biotechnol. Prog. 19, 1498–1504.
Oosterhuis, N. M. G., Kossen, N. W. F., Olivier, A. P. C., and Schenk, E. S. (1985) Scale-down and optimization studies of the gluconic acid fermentation by Gluconobacter oxydans. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 27, 711–720.
Namdev, P. K., Yegneswaran, P. K., Thompson, B. G., and Gray, M. R. (1991) Experimental simulation of large-scale bioreactor environments using a Monte Carlo method. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 69, 513–519.
Schweder, T., Krüger, E., Xu, B., Jürgen, B., Blomsten, G., Enfors, S., and Hecker, M. (1999) Monitoring genes that respond to process-related stress in largescale bioprocesses. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 65, 151–159.
Cronan, J. E. and Laporte, D. (1996) Tricarboxylic acid cycle and glyoxylate bypass, in Escherichia coli and Salmonella. Cellular and Molecular Biology, (Neidhardt F. C., et al., eds.), ASM Press, Washington, DC, pp. 206–216.
Konz, J. O., King, J., and Cooney, C. L. (1998) Effects of oxygen on recombinant protein expression. Biotechnol. Prog. 14, 393–409.
Poole, R. K. and Ingledwe, W. J. (1987) Patways of electron to oxygen, in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhiparium: Cellular and Molecular Biology (Neidhardt F. C., et al., eds.), ASM Press, Washington, DC, pp. 170–200.
Gennis, R. B. and Stewart, V. (1996) Respiration, in Escherichia coli and Salmonella. Cellular and Molecular Biology, (Neidhardt, F. C., et al., eds.), ASM Press, Washington, DC, pp. 217–261.
O'Beirne, D., and Hamer, G. (2000) Oxygen availability and growth of Escherichia coli W3110: A problem exacerbated by scale-up. Bioprocess Eng. 23, 487–494.
Cashel, M., Gentry, D. R., Hernandez, V. J., and Vinella, D. (1996) The stringent response. In Escherichia coli and Salmonella. Cellular and Molecular Biology, (Neidhardt, F. C., et al., eds.), ASM Press, Washington, DC, pp. 1458–1496.
Neubauer, P., Ahman, M., Törkvist, M., Larsson, G., and Enfors, S.O. (1995) Response of guanosine tetraphosphate to glucose fluctuations in fed-batch cultivations of Escherichia coli. J. Biotechnol. 43, 195–204.
Xu, B., Jahic, M., Blomsten, G., and Enfors, S. (1999) Glucose overflow metabolism and mixed-acid fermentation in aerobic large-scale fed-batch processes with Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 51, 564–571.
Lin, H. Y. and Neubauer, P. (2000) Influence of controlled glucose oscillations on a fed-batch process of recombinant Escherichia coli. J. Biotechnol. 79, 27–37.
Hewitt, C., Caron, G., Axelsson, B., McFarlane, C., and Nienow, A. (2000) Studies related to the scale-up of high-cell-density E. coli fed-batch fermentations using multiparameter flow cytometry: effect of a changing microenvironment with respect to glucose and dissolved oxygen concentration. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 70, 381–39.
Hopkins, D. J., Betenbaugh, M. J., and Dhurjati, P. (1987) Effects of dissolved oxygen tension on the stability of recombinant Escherichia coli containing plasmid pKN401. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 29, 85–91.
Oosterhuis, N. M. G., Groesbeek, N. M., Olivier, A. P. C., and Kossen, N. W. F. (1983) Scale-down aspects of the gluconic acid fermentation. Biotechnol. Lett. 5, 141–146.
Buse, R., Qazi, G. N., and Onken, U. (1992) Influence of constant and oscillating dissolved oxygen concentrations on keto acid production by Gluconobacter oxydans subsps. melanogenum. J. Biotechnol. 26, 231–244.
Moes, J., Griot, M., Heinzle, E., Dunn, I. J., and Bourne, J. R. (1985) A microbial culture with oxygen-sensitive product distribution as a potential tool for characterizing bioreactor oxygen transport. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 27, 482–489.
Griot, N., Sanee, U., Heinzle, E., Dunn, I. J., and Bourne, J. R. (1988) Fermenter scale-up using an oxygen sensitive culture. Chem. Eng. Sci. 43, 1903–1908.
Griot, M., Moes, J., Heinzle, E., Dunn, I. J., and Bourne, J. R. (1986) A microbial culture for the measurement of macro and micromixing phenomena in biological reactors, in Proc. Int. Conf. on Bioreactor Fluid Dynamics. (Stanbury, J., ed.) Cambridge, England, pp. 203–216.
Amanullah, A., Nienow, A. W., Emery, A. N., and McFarlane, C. M. (1993) The use of Bacillus subtilis as an oxygen sensitive culture to simulate dissolved oxygen cycling in large scale fermenters. Trans. Inst. Chem. Eng. Part C. 71, 206–208.
Suphantharika, M., Ison, A. P., and Lilly, M. D. (1995) The effect of cycling dissolved oxygen tension on the synthesis of the antibiotic difficidin by Bacillus subtillis. Bioprocess. Eng. 12, 181–186.
Galindo, E. (1994) Aspects of the process for xanthan production. Trans. Inst. Chem. Eng. C. 72, 227–237.
Serrano-Carreón, Corona, R. M., Sánchez, A., and Galindo, E. (1998) Prediction of xanthan fermentation development by a model linking kinetics, power drawn and mixing, Process Biochem. 33, 133–146.
Amanullah, A., Tuttiet, B., and Nienow, A. W. (1998) Agitator speed and dissolved oxygen effects in xanthan fermentations. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 57, 198–210.
Trujillo-Roldán, M. A., Peña, C., Ramírez, O.T., and Galindo, E. (2001) Effect of oscillating dissolved oxygen tension on the production of alginate by Azotobacter vinelandii. Biotechnol. Prog. 17, 1042–1048.
Trujillo-Roldán, M. A., Moreno, S., Espín, G., and Galindo, E. (2004) Roles of the polymerase complex and alginate-lyase in determining the molecular weight of alginate produced by Azotobacter vinelandii, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 63, 742–747.
Wills, C. (1990) Regulation of sugar and ethanol metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 25, 245–280.
Kappeli, O., Gschwend-Petrik, M., and Fiechter, A. (1985) Transient responses of Saccharomyces uvarum to a change of the growth-limiting nutrient in continuous culture. J. Gen. Microbiol. 131, 47–52.
Cortés, G., Trujillo-Roldán, M. A., Ramírez, O. T., and Galindo, E. (2005) Production of β-galactosidase by Kluyveromyces marxianus under oscillating dissolved oxygen tension. Process Biochem. 40, 773–778.
Kacmar, J., Zamamiri, A., Carlson, R., Abu-Absi, N. R., and Srienc, F. (2004) Single-cell variability in growing Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell populations measured with automated flow cytometry. J. Biotechnol. 109, 239–254.
Einsele, A. (1978) Scaling up bioreactors. Process Biochem. 7, 13–14.
Vardar, F., and Lilly, M. D. (1982) Effect of cycling oxygen concentrations on product formation in penicillin fermentations. Eur. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 14, 203–211.
Larsson, G. and Enfors, S.-O. (1988) Studies of insufficient mixing in bioreactors: effect of limiting oxygen concentrations and short term oxygen starvation on Penicillium chrysogenum. Bioproc. Eng. 3, 123–127.
Yegneswaran, P. K., Gray, M. R., and Thompson, B. G. (1991) Experimental simulation of dissolved oxygen fluctuations in large fermentors: effect on Streptomyces clavuligerus. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 38, 1203–1209.
Bhargava, S., Wenger, K. S., Rane, K., Rising, V., and Marten, M. R. (2005) Effect of cycle time on fungal morphology, broth rheology, and recombinant enzyme productivity during pulsed addition of limiting carbon source. Biotechnol. Bioeng 89, 524–529.
Langheinrich, C., Nienow, A. W., Eddleston, T., Stevenson, N. C., Emery, A. N., Clayton, T. M., and Slater, N. K. H. (1998) Liquid homogenization studies in animal cell bioreactors of up to 8 m3 in volume. Trans IChemE 76, 107–116.
Varley, J., and Birch, J. (1999) Reactor design for large-scale suspension animal cell culture. Cytotechnol. 29, 177–205.
Bödeker, B. G. D., Newcomb, R., Yuan, P., Braufman, A., Kelsey, W. (1994) Production of recombinant factor VIII from perfusion cultures: I. Large-scale fermentation, in Animal Cell Technology: Products of today, prospects of tomorrow (Spier, R. E., Griffiths, J. B., and Berthold, W., eds.), Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, pp. 580–583.
Palomares, L. A., Estrada-Mondaca, S., and Ramírez, O. T. (2004) Production of recombinant proteins: Challenges and solutions, in Methods in Molecular Biology. Recombinant Gene Expression Protocols (Balbás, P. and Lorence, A., eds.), Humana, Totowa, NJ, 267, 15–51.
Jem, J. K., Fateen, S., and Michaels, J. (1994) Mixing phenomena in industrial bioreactors with perfusion spin filters, in Animal Cell Technology: Products of Today. Prospects for Tomorrow (Spier, R. E., Griffits, J. B., and Berthold, W., eds.), Butterworth Heinemann, Oxford, UK, pp. 392–396.
Dalm, M. C. F., Jansen, M., Keijzer, T. M. P., et al. (2005) Stable hydridoma cultivation in a pilot-scale acoustic perfusion system: Long-term process performance and effect of the recirculation rate. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 91, 894–900.
Palomares, L. A., López, S., and Ramírez, O. T. (2004) Utilization of oxygen uptake rate to assess the role of glucose and glutamine in the metabolism of insect cell cultures. Biochem. Eng. J. 19, 87–93.
Curtis, W. R. (2000) Hairy roots, bioreactor growth, in The Encyclopedia of Cell Technology, vol. 2: (Spier, R. E., ed.), John Wiley and Sons, New York, NY, pp. 827–841.
Gerecht-Nir, S., Cohen, S., and Itskovitz-Eldor, J. (2004) Bioreactor cultivation enhances the efficiency of human embryoid body (hEB) formation and differentiation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 86, 493–502.
Bibila, T. A., and Robinson, D. K. (1995) In pursuit of the optimal fed-batch operation process for monoclonal antibody production. Biotechnol. Prog. 11, 1–13.
Palomares, L. A., and Ramírez, O. T. (1996) The effect of dissolved oxygen tension and the utility of oxygen uptake rate in insect cell culture. Cytotechnol. 22, 225–237.
Hevehan, D. L. and Miller, W. M. (1999) Hypoxia, effects on animal cells, in Encyclopedia of Bioprocess Technology, Fermentation, Biocatalysis and Bioseparation (Flickinger, M. C., and Drew, S. W., eds.), John Wiley & Sons, New York, pp. 1418–1433.
Rhiel, M. and Murhammer, D. W. (1995) The effect of oscillating dissolved oxygen concentrations on the metabolism of a Spodoptera frugiperda IPLB-Sf21-AE clonal isolate. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 47, 640–650.
Kimura, R. and Miller, W. M. (1997) Glycosylation of CHO-derived recombinant tPA produced under elevated pCO2. Biotechnol. Prog. 13, 311–317.
Goldman, M. H., James, D. C., Rendall, M., Ison, A. P., Hoare, M., and Bull, A. T. (1998) Monitoring recombinant human interferon-gamma N-glycosylation during perfused fluidized-bed and stirred tank batch culture of CHO cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 60, 596–607.
Hayter, P. M., Curling, E. M. A., Baines, A. J., et al. (1992) Glucose-limited chemostat culture of Chinese hamster ovary cells producing recombinant human interferon-γ. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 39, 327–335.
Cudna, R. E. and Dickson, A. J. (2002) Endoplasmic reticulum signaling as a determinant of recombinant protein expression. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 81, 56–65.
Lipscomb, M. L., Palomares, L. A., Hernández, V., Ramírez, O. T., and Kompala, D. S. (2005) Effect of production method and gene amplification on the glycosylation pattern of a secreted reporter protein in CHO cells. Biotechnol. Prog. 21, 40–49.
Osman, J. J., Birch, J., and Varley, J. (2002) The response of GS-NS0 myeloma cells to single and multiple pH perturbations. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 79, 398–407.
Andersson, H. and van den Berg, A. (2004) Microtechnologies and nanotechnologies for single cell analysis. Curr. Opinion Biotechnol. 15, 44–49.
Samorski, M., Muller-Newen, G., and Buchs, J. (2005) Quasi-continuous combined scattered light and fluorescence measurements: A novel measurement technique for shaken microtier plates. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 92, 61–68.
Harms, P., Kostov, Y., French, J. A., et al. Design and performance of a 24-station high throughput microbioreactor. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 93, 6–13.
Lara, A. R., Vázquez, C., Gosset, G., Bolívar, F., López-Munguía, A., and Ramírez, O. T. (2006) Engineering Escherichia coli to improve culture performance and reduce formation of by-products during recombinant protein production under transient intermittent anaerobic conditions. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 94, 1164–1175.
Kenty, B., Li, Z., Vanden, T., and Lee, S. (2005) Mixing in laboratory-scale bioreactors used for mammalian cell culture. Presented at the 229th American Chemical Society National Meeting, San Diego, CA.
Leckie, F., Scragg, A. H., and Cliffe, K. C. (1991) Effect of bioreactor design and agitator speed on the growth and alkaloid accumulation by cultures of Catharantus roseus. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 13, 296–305.
Jolicoeur, M., Chavarie, C., Carreu, P. J., and Archambault, J. (1992) Development of a helicalribbon impeller bioreactor for high density plant cell suspension culture. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 39, 511–521.
Kiss, R., Croughan, M., Trask, J., et al. (1994) Mixing time characterization in large scale mammalian cell bioreactors. AIChE Annual meeting, November 1994, San Francisco, CA. Paper No 55c.
Vrábel, P., van der Lans, R. G. J. M., Luyben, K. Ch. A. M., Boon, L., and Nienow, A. (2000) Mixing in large-scale vessels with multiple radial or radial and axial up-pumping impellers: modelling and measurements. Chem. Eng. Sci. 55, 5881–5896.
Schügerl, K. (1993). Comparison of different bioreactor performances. Bioprocess Eng. 9, 215–223.
Sweere, A. P. J., Luyben, K. Ch. A. M., and Kossen, N. W. F. (1987) Regime analysis and scale-down: tools to investigate the performance of bioreactors. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 9, 386–398.
Namdev, P. K., Irwin, N., Thompson, B. G., and Gray, M. R. (1993) Effect of oxygen fluctuations on recombinant Escherichia coli fermentation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 41, 666–670.
Neubauer, P., Häggstrom, L., and Enfors, S. O. (1995) Influence of substrate oscillations on acetate formation and growth yield in E. coli glucose limited fed-batch fermentations. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 47, 139–146.
Sweere, A. P. J., Janse, L., Luyben, K. Ch. A. M., and Kossen, N. W. F. (1988) Experimental simulation of oxygen profiles and their influence of Baker's yeast production: II. Two-fermenter system. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 31, 579–586.
Sweere, A. P. J., Matla, Y. A., Zandvliet, J., Luyben, K. Ch. A. M., and Kossen, N. W. F. (1988) Experimental simulation of glucose fluctuations. The influence of continually changing glucose concentrations of the fed batch baker's yeast production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 28, 109–115.
Sweere, A. P. J., Mesters, J. R., Janse, L., Luyben, K. Ch. A. M., and Kossen, N. W. F. (1988) Experimental simulation of oxygen profiles and their influence of baker's yeast production: I. One-fermenter system. Biotechnol Bioeng. 31, 567–578.
George, S., Larsson, G., and Enfors, S. O. (1993) A scale-down two-compartmentreator with controlled substrate oscillations: metabolic response of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Bioprocess Eng. 9, 249–257.
Abel, C., Hübner, U., and Schügerl, K. (1994) Transient behaviour of Baker's yeast during enforced periodical variation of dissolved oxygen concentration. J. Biotechnol. 32, 45–47.
Alexeeva, S., de Kort, B., Sawers, G., Hellingwerf, K. J., and Teixeira de Mattos, M. J. (2000) Effects of limited aeration and of the arcAB system on intermediary pyruvate catabolism in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 182, 4934–4940.
Carlson, R. and Srienc, F. (2004) Fundamental Escherichia coli biochemical pathways for biomass and energy production: creation of overall flux states. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 86, 149–162.
Vemuri, G. N., Minning, T. A., Altman, E., and Eiteman, M. A. (2005) Physiological response of central metabolism in Escherichia coli to deletion of pyruvate oxidase and introduction of heterologous pyruvate carboxylase. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 90, 64–76.
Ramírez, O. T. and Mutharasan, R. (1990) Cell cycleand growth phase-dependent variations in size distribution, antibody productivity and oxygen demand in hybridoma cultures. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 36, 839–848.
Higareda, A. E., Possani, L. D., and Ramírez, O. T. (1997) The use of culture redox potential and oxygen uptake rate for assessing glucose and glutamine depletion in hybridoma cultures. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 56, 555–563.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lara, A.R., Galindo, E., Ramírez, O.T. et al. Living with heterogeneities in bioreactors. Mol Biotechnol 34, 355–381 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/MB:34:3:355
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/MB:34:3:355