Abstract
Background
Benzo[a]anthracene (BAA), also known as “tetraphene” belongs to the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) which are considered as an important class of environmental genotoxins. The present work focused on the evaluation of the efficiency of the biodegradation of the BAA by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens using animal bioassays, which include micronucleus (MN) and DNA fragmentation as end point of genotoxicity of the resulting metabolites from BAA biodegradation.
Results
B. amyloliquefaciens was exposed to different doses of γ radiation (0.5, 1.0, 1.5, and 2.0 kGy) kGy. The colonies for the wild strain and its variants obtained after radiation were counted. The final counts for variant 3 (V3), variant 4 (V4), and variant 5 (V5) have been increased from its initial count by (0.3, 0.48, and 0.1 log cycle) respectively at 1 mg/100 ml (BAA). For animal bioassay, male mice were divided into seven groups; control group received vehicle only, groups II and III were injected with 5 and 10 mg/kg b.wt (BAA) respectively, and groups IV, V, VI, and VII were injected with the residues of BAA after biodegradation with wild type, V3, V4, and V5 of B. amyloliquefaciens respectively.
Conclusions
Results of the micronucleus test and the DNA fragmentation as end point of genotoxicity of (BAA) indicated that B. amyloliquefaciens have the efficiency in biodegradation of (BAA) to nongenotoxic metabolites where (V3) and (V4) are more efficient than the wild type and (V5). So B. amyloliquefaciens could solve the problem of soil and water contamination by oil spill or industrial petroleum waste by ecofriendly manner.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are considered as pollutants which consist of two or more fused aromatic rings. It formed after incomplete combustion of the organic materials such as fossil fuels, wood, or coal, also present in the smoke of cigarette (Li et al. 2018). It found in different environment places as fresh water, marine sediment, sand, and also in the atmosphere.
These environmental pollution has a global concern; this is because almost all PAHs are highly toxic, mutagenic, and carcinogenic to humans, plant, and also to microorganisms (Rengarajan et al. 2015). Wiley (2012) mentioned the genotoxicity and carcinogenicity to benzo[a]anthracene (BAA). Jacob et al. (1983) proved that the formation of epoxides and dihydrodiolsas is a result of BAA metabolization. The PAHs metabolizing enzymes are present in all tissues and are involved in detoxification of BAA as indicated by Slooff et al. (1989). DNA adducts were formed in epithelial cells and blood lymphocytes, and unscheduled DNA synthesis was observed in HeLa cells; in addition, BAA was found to be genotoxic in many different organisms in vivo (McCarrick et al. 2019). Toxic effects of BAA, benzo-a-pyrene (BAP) and naphthalene were described in experimental embryo of animals and laboratory studies conducted on mice have demonstrated that ingestion of high levels of BAP during pregnancy results in birth defects and a decreased body weight in the offspring (Ng et al 2009).
Also, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has classified the following seven PAH compounds as being one of the cause of human carcinogens: BAA, BAP, benzo(b) fluoranthene, benzo(k)fluoranthene, chrysene, dibenz[a,h]anthracene, and indeno (1,2,3-cd) pyrene (Ramesh et al. 2010).
Bone marrow where the rapid cell proliferation occurs is the most preferred organ for the evaluation of genotoxicity of different chemicals (Vikram et al. 2007). The micronucleus (MN) test is widely used for screening the genotoxic potential of different agents (Asanami et al. 1995). Micronuclei are formed in dividing cells due to either a compound’s interaction with DNA leading to breakage of chromosome or of its interaction with non-DNA targets leading to loss of chromosome (De Boeck et al. 2005). This bioassay is recommended for genotoxicity evaluation and has become increasingly common for regulatory acceptance. For the in vivo genotoxicity studies, the mice is preferred than the rats (Ramirez-Munoz et al. 1999).
Microbial degradation is considered to be the main process involved in the bioremediation of PAH (Yuan et al. 2002). This method was better than physical and chemical such as combustion, photolysis, and ultrasonic decomposition; this is due to their ecofriendly and environmental way for removal of PAHs (Toledo et al. 2006). Some microorganisms have the ability to utilize PAHs as a source of carbon and energy and degraded them to carbon dioxide and water, or transformed to other nontoxic or low-toxic substances (Perelo 2010).
Partila (2013) determined BAA degradation percentage by different isolates with HPLC and indicated that the best BAA degrader was MAM-62; this isolate degraded 39% of 500 μg/L BAA. And identified by DNA sequencing as Bacillus amyloliquefaciens with accession No. JN03805, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens is a non-pathogenic soil bacterium capable of producing endospores allowing it to survive.
For extended periods of time, it also shows some antifungal properties which are influenced by environmental nitrogen availability (Caldeira et al. 2008).
Also the intermediates as determined by GC-MS analysis of BAA degradation by B. amyloliquefaciens after 24-h incubation are hexanoic acid, hepatanoic acid, benzeneethanol, hexanoic acid,2-ethyl, octanoic acid, nonanoic acid, indol-5-aldhyde, n-hexadecanoic acid, benz(a)anthracene 7,12 dione, and b-sitosterol acetate (Partila 2013). The proposed pathway for degradation of BAA by B. amyloliquefaciens, as shown in Fig. 1, considered as novel pathway for the bacterial metabolism of BAA. This pathway contains a set of metabolites, not present in previously known pathways, like benzo[a]quinone, phthalic acid, phthalicaciddehydroxy, phthalic acid methylester, hydroxytetralone, naphthalonedione and dihydroxy naphthalene (Cajthaml et al. 2006), and BAA-dihydrodiol (Schneider et al. 1996). Also, the variants showed better results than a wild type; this may be due to a variety and increasing of enzymes which increase the rate of biodegradation for BAA. The parent strain MAM-62 produced nine intermediates. However, the mutant strain MAM-62(4) produced 15 intermediates (Partila 2013).
Proposed pathway of benzo-a-anthracene degradation by B. amyloliquefaciens (Partila 2013)
So, the aim of this work is to evaluate the efficiency of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens for biodegradation of the (BAA) by using micronucleus (MN) and DNA fragmentation as end point of BAA genotoxicity.
Material and methods
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens culture media and treatments
The bacterial strain was Bacillus amyloliquefaciens with accession No. JN038054. BAA was purchased from (AcRos organics, New Jersey, USA). B. amyloliquefaciens was inoculated in LB (Luria-Bertani) broth medium prepared according to Martin et al. 1981 and incubated at 30 °C for 24 h in shaking incubator. The well grown bacterial culture were centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 10 min and washed twice with basal salt media (BSM) (Ogawa and Miyashita 1995). The washed bacterial cells were resuspended in BSM supplemented with 1 mg/100 ml BAA. The bacterial count for the bacterial culture was determined after 7 days incubation to confirm their ability to grow and degrade the compound.
Effect of gamma radiation on the viability of the most potent strain
B. amyloliquefaciens was grown in LB broth medium for 24 h at 37 °C in shaking incubator (150 rpm). The well grown bacterial cells were harvested by centrifugation at 8000 rpm for 10 min then washed and resuspended in sterile saline. Cell suspensions were distributed into 5.0 ml sterile screw capped test tubes and then exposed to different doses of gamma radiation (0.5, 1.0, 1.5, and 2.0 kGy) (Indian cell Co-60) with dose rate kGy/15 min in the National Center for Radiation Research and Technology (NCRRT), Nasr City, Cairo, Egypt. Three replicates were used for each dose. Serial dilution and pore plate technique were established. The plates were incubated at 30 °C for 24 h. The changes in morphological characters (color, shape, margin, size) of the colonies at different doses were picked up as variants.
Each picked irradiated bacterial colony was inoculated in LB broth medium and incubated at 30 °C for 24 h in shaking incubator along with the wild type B. amyloliquefaciens.
The well-grown bacterial culture were centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 10 min and washed twice with BSM.
The washed bacterial isolated strains were used to inoculate 100 ml BSM in 250 ml conical flask amended with 0.5 mg of BAA. Three replicates were used for each concentration for each strain. The inoculated flasks were incubated at 30 °C in shaking incubator.
Samples were examined for O.D. at 600 nm by using spectrophotometer (LW-V-200 RS UV/Vis., Germany) and for count of cells (CFU/ml) at the beginning and after 1, 2, 7, 14, and 21 days incubation (Partila 2013).
Experimental animals and treatments
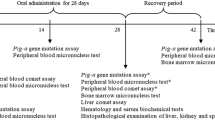
Swiss albino male mice weighting 20–25 g were obtained from National Center for Radiation Research and Technology, Cairo, Egypt. They were housed in steel mesh cages in a temperature of 25–30 °C with alternating 12 h light and dark cycles and allowed free access to standard diet and tap water. The animals were housed five mice per cage and randomly divided into seven groups, five mice for each group. Group I was used as control treated with the vehicle only i.p.(0.1 ml DMSO diluted with 0.2 ml saline). Groups II and III were injected by (BAA), which was dissolved in the vehicle, at dose of 5 and 10 mg/kg b.wt. respectively. Groups VI, V, VI, and VII were injected i.p. with the residues of the equivalent dose of 10 mg/kg b.wt. after biodegradation with wild type, V3, V4, and V5.
Micronucleus assay
The animals were sacrificed after 24 h of treatment and the bone marrow was collected for the micronucleus assay (Schmid 1975) modified from the femurs were washed with 2 ml of fetal calf serum (Sigma) in a centrifuge tubes, homogenizing the cell suspension, and centrifuging it at 1000 rpm for 10 min, after which the supernatant was partially discarded to leave few drops of fetal calf serum in which the cell pellet was re-suspended and then smeared on clean and dry slides, which then fixed with absolute methanol for 10 min and stained for 8 min with 5% (v/v) Giemsa stain diluted with phosphate buffer (Na2HPO4 0.06 M and KH2PO4 0.06 M, pH 6.8). For each animal, 1500 polychromatic erythrocytes (PCEs) were analyzed to ascertain the frequencies of micronuclei and micronucleated cells in mice exposed to the different treatments. The slides were scored blindly according to the established criteria (Titenko-Holland et al. 1997). Microscopic examination was done under oil immersion using (LeitzWetzlar, Germany)—Orthomat binocular optical microscope with magnification × 1000.
DNA fragmentation assay by diphenylamine
Quantification of fragmented DNA was estimated by diphenylamine (DPA) assay. The method was carried out according to Perandones et al. (1993). Cell lysates was obtained by mechanically dissociation of 0.5 g. of liver in 400 μl hypotonic lysis buffer which was prepared by dissolving 5 mM, tris HCl, 20 mM EDTA, and 0.5% Triton-100 in distilled water then the solution was adjusted to 100 ml. The cell lysates were centrifuged then the supernatant containing small DNA fragmentations was removed in another tubes and the pellet containing large pieces of DNA and cell debris was left in the tubes, then the reagent was added as following TCA 10% then centrifuge; the precipitate was resuspended in 400 μl 5% TCA. The tubes were incubated in boiling water for 30 min and then were centrifuged. The extracted DNA was left to cool at room temperature. Further, 1 ml DPA solution (0.88 M diphenylamine dissolved in 98% glacial acetic acid) then 1.5% concentrated sulfuric acid was added to the solution. This solution was stored in a dark glass bottle. On the day of use, 0.5% of freshly prepared (1.6% v/v acetaldehyde) was added to 0.5 ml of extracted DNA and the samples were kept at 4 °C for 48 h. The absorbance of samples was recorded at 578 nm. The percentage of DNA fragmentation was expressed by the formula:
Statistical analysis
The data obtained in the present work were represented as mean ± standard deviation. Statistical analysis was carried out using (Statistical Package for Social Science) (SPSS) software version 20 for windows; significant differences among groups were evaluated using one-way analysis of variance (one-way ANOVA); least-significant difference (LSD) was used for multi-group comparisons. P values ≤ 0.05 were considered as significant (Festing and Altman 2002).
Results
The bacterial growth and count
The growth of B. amyloliquefaciens wild type and its variants in 1 mg/100 ml BAA as indicated in Table 1 cleared a variation in the O.D., but in all samples the final OD was not higher than the initial OD so in this experiment, it was not recognized which sample can get the highest growth under the effect of BAA, which could be cleared in the bacterial count experiment. Table 2 indicated that the initial count in 1 mg/100 ml BAA for variants (V1 and V2) was (36 × 106 and 18 × 106 CFU/ml) respectively. It was cleared to be more than its count after 21 days incubation (6 × 106, 3 × 106CFU/ml) respectively. But for the other variants V3, V4, and V5, the count after 21 days incubation was (76 × 106, 83 × 106, and 40 × 106 CFU/ml) respectively exceeding their initial count (36 × 106, 27 × 106, and 32 × 106 CFU/ml) respectively. According to these results, only V3, V4, and V5 were chosen for further evaluation by animal bioassay.
Effect of BAA on the formation of micronuclei
As shown in Table 3, a significant increases in the percent of micronuclei induction in the groups that were injected with (BAA) at different doses as compared with the control group. As expected, the significant increase in the total number of the cells with MN, mononucleated cells, binucleated cells, and multinucleated cells was proportionally related to the dose of (BAA). On the other hand, the genotoxic effect of (BAA) residue, after biodegradation with wild and variant types of bacteria, was significantly lower than that before biodegradation but still significantly higher than that of control group except for the groups of variant 3 and variant 4 which have non-significant genotoxic effect as compared with the control group.
Effect of BAA on the % of DNA fragmentation
The percentage of DNA fragmentation increased proportionally with increasing the dose of BAA as shown in Fig. 2. The genotoxic effect of BAA significantly reduced after the biodegradation with wild and variant types of bacteria as compared with that before biodegradation. Meanwhile, the residue of biodegradated BAA with V3 and V4 has insignificant genotoxic effect as compared with control group; the residue from V5 is still significantly higher as compared with control group.
Discussion
Many studies previously showed that MN is a biomarker of chromosomal damage, but now we should reconsider MN as an important cause of genetic variation that may be critical during the genesis of some diseases and cancer (Bayram et al. 2016). Chromothripsis, a sole pattern of localized chromosome rearrangements and it was suggested that DNA damage from MN could lead to a moderate level of rearrangement (Zhang et al. 2015). As indicated in Table 1, the variation of O.D. may be due to the interference between the yellow color of BAA and the turbidity of the B. amyloliquefaciens growth, so as Juhasz et al. (1997) observed that the culture supernatant turned to a yellow color when BAA was utilized as a sole carbon and energy source. In addition, the decrease in the amount of PAH was evidenced by a color change in the medium and was approved by GC-MS analysis of BAA degradation by B. amyloliquefaciens as was mentioned by Partila (2013).
Bacteria initiate PAH degradation by the action of intracellular dioxygenases; the PAHs must be taken up by the cells before degradation takes place (Smith 1990). In the present study, the count after incubation time as indicated in Table 2 was less than the initial in the case of wild, V1, and V2; this may be due to the decrease of the enzymes necessary for the consumption of the compound. While in the case of V3, V4, and V5, the final count were more than the initial, better than the wild type, V1, and V2; this may be due to the sufficient enzymes which are secreted by these variants that might play an important role in the transformation and the degradation of BAA.
PAH dioxygenase (PDO) and catechol 2,3-oxyenase (C23O) are identified as two key PAH-degrading-related enzymes (Meyer et al. 1999). However, to the best of our knowledge, there is no information regarding the simultaneous change of these key enzyme activities in a biodegradation process (Grifoll et al. 1995).
Ting et al. (2011) showed that the degradation rate constants for phenanthrene and pyrene increased when the PAH concentration in the cultures contains (from 2 to 50 mg/lPAHs). But, at the level of 100 mg/l, the degradation rate does not change due to the failure of the organism to degrade the remaining PAHs after 6 days. It appears that the organism entered an inactive phase after 6 days incubation in the liquid culture.
It is well known that very few organisms have been able to degrade a single compound completely (You-Qing et al. 2008). Bacillus cereus and Bacillus megaterium were observed consuming 65.8% and 33.7% of pyrene (50 mg/l) within 3 weeks, respectively.
The results of control group presented micronucleated cells < 3/100 cells which are the normal value of the mean spontaneous micronucleus frequency (Salamone and Mavournin 1994). The present data is in agreement with many previous studies indicated that bone marrow cells of mice are susceptible to the genetic damaging action of BAA. This damage is due to the effect of metabolites of BAA which have been indicated for their ability to induce mutations, cell transformation, and form nucleic acid adducts covalently (Conney 1982). Even without external metabolic activation, BAA caused DNA strand breaks (Platt et al. 2008). The 3,4-diol-1,2-epoxide metabolite is mutagenic; its metabolic precursor, the 3,4-dihydrodiol, is also mutagenic. The 3,4-dihydrodiol and a 3,4-diol-1,2-epoxide also have high carcinogenic activity (Li et al. 2018). DNA analysis from skin of mice or cultured cells treated with BAA indicates that a 3,4-diol-1,2-epoxide and a 8,9-diol-10,11-epoxide form nucleic acid adducts covalently (IARC 1972).
For some metabolites from other work like benz[a]anthracene-trans-3,4-dihydrodiol (BA-3,4-dihydrodiol) which consider the minor metabolite getting from BAA, it shows higher mutagenicity and tumorigenicity than parent BAA; this cause the damage of DNA. Its liberation enhanced by addition of NADH. Also, BA o-quinone type metabolite, benz[a]anthracene-3,4-dione (BA-3,4-dione) both induced oxidative DNA damage in the presence of cytochrome P450 reductase (Seike et al. 2003). Cooper et al. (1980) declared that diol-epoxide for anthracene thought to be involved in the binding of BAA to DNA in some situations reacts mainly with deoxyguanosine.
Conclusions
From the results of the present study, it could be concluded that B. amyloliquefaciens and its variants have the efficiency in biodegradation of (BAA), which are considered as an important class of environmental genotoxins; this is confirmed by micronucleus (MN) and DNA fragmentation as end point of genotoxicity of BAA and its resulting metabolites. So, B. amyloliquefaciens may be used for degradation of BAA in contaminated water and soil by oil spill or industrial petroleum waste.
Abbreviations
- BAA:
-
Benzo[a]anthracene
- MN:
-
Micronucleus
References
Asanami S, Shimono K, Sawamoto O, Kurisu K, Uejima M (1995) The suitability of rat peripheral blood in subchronic studies for the micronucleus assay. Mutat Res 347:73–78.
Bayram SE, Rencüzoğullar A, Almas M, Genc A (2016) Effect of p53 Arg72Pro polymorphism on the induction of micronucleus by aflatoxin B1 in in vitro in human blood lymphocytes. Drug Chem Toxicol 39:331–337.
Cajthaml T, Erbanová P, Šašek V, Moeder M (2006) Breakdown products on metabolic pathway of degradation of benz[a]anthracene by a ligninolytic fungus. Chemosphere. 64(4):560–564.
Caldeira AT, Feio SS, Arteiro JMS, Coelho AV, Roseiro JC (2008) Environmental dynamics of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens CCMI 1051 antifungal activity under different nitrogen patterns. J Appl Microbiol 104(3):808–816.
Conney AH (1982) Induction of microsomal enzymes by foreign chemicals and carcinogenesis by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: G.H.A. Clowes memorial lecture. Cancer Res 42:4875–4917.
Cooper CS, Ribeiro O, Farmer PB, Hewer A, Walsh C, Pal K et al (1980) The metabolic activation of benz[a]anthracene in hamster embryo cells: evidence that diol-epoxides react with guanosine, deoxyguanosine and adenosine in nucleic acids. Chem Biol Interact 32(1–2):209–231.
De Boeck M, Van der Leede B, Van Goethem F, De Smedt A, Steemans M, Lampo A et al (2005) Flow cytometric analysis of micronucleated reticulocytes: time- and dose-dependent response of known mutagens in mice, using multiple blood sampling. Environ Mol Mutagen 46(1):30–42.
Festing MF, Altman DG (2002) Guidelines for the design and statistical analysis of experiments using laboratory animals. ILAR J 43(4):244–258.
Grifoll M, Selifonov SA, Gatlin CV, Chapman PJ (1995) Actions of a versatile fluorene-degrading bacterial isolate on polycyclic aromatic compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol 61(10):3711–3723.
IARC (1972) Monographs on the evaluation of the carcinogenic risk of chemicals to humans. W Health Organiz .Int Agen for Res on Cancer, Geneva.
Jacob J, Schmoldt A, Raab G, Hamann M, Grimmer G (1983) Induction of specific monooxygenases by isosteric heterocyclic compounds of benz[a]anthracene, benzo[c]phenanthrene and chrysene. Canc Lett 20(3):341–348.
Juhasz AL, Britz ML, Stanley GA (1997) Degradation of fluoranthene, pyrene, benzo(a)anthracene and dibenz(a,h)anthracene by Burkholderiacepacia. J Appl Microbiol 83(2):189–198.
Li B, Ou P, Wei Y, Zhang X, Song J (2018) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons adsorption onto graphene: a DFT and AIMD study. Mat 11(5):726.
Martin PA, Lohr JR, Dean DH (1981) Transformation of Bacillus thuringiensis protoplasts by plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol 145:980–983.
McCarrick S, Cunha V, Zapletal O, Vondráček J, Dreij K (2019) In vitro and in vivo genotoxicity of oxygenated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ Poll 246:678–687.
Meyer S, Moser R, Neef A, Stahl U, Kämpfer P (1999) Differential detection of key enzymes of polyaromatic-hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria using PCR and gene probes. Microbiology. 145:1731–1741.
Ng SP, Conklin NSDJ, Bhatnagar AA, Bolanowski DD, Lyon J, Zelikoff JT (2009) Prenatal exposure to cigarette smoke induces diet- and sex dependent dyslipidemia and weight gain in adult murine offspring. Environ Health Perspect 117(7):1042–1048.
Ogawa N, Miyashita K (1995) Recombination of a 3-chlorobenzoatecatabolic plasmid from Alcaligeneseutrophus NH9 mediated by directrepeatelements. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3788–3795.
Partila AM. Biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in petroleum oil contaminating the environment. 2013; Ph.D. thesis, faculty of science, Cairo University.
Perandones CE, IlleraVA PD, Stunz LL, Ashman RF (1993) Regulation of apoptosis in vitro in mature murine spleen T cells. J Immunol 151:3521–3529.
Perelo LW (2010) Review: in situ and bioremediation of organic pollutants in aquatic sediments. J Haz Mat 177:81–89.
Platt KL, Aderhold S, Kulpe K, Fickler M (2008) Unexpected DNA damage caused by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons under standard laboratory conditions. Mutat Res 650(2):96–103.
Ramesh A, Archibong AE, Niaz MS (2010) Ovarian susceptibility to benzo[a]pyrene: tissue burden of metabolites and DNA adducts in F-344 rats. J Toxicol Environ Health A 73(23):1611–1625.
Ramirez-Munoz MP, Zuniga G, Torres-Bugarin O, Portilla E, Garcia-Martinez D, Ramos A et al (1999) Evaluation of the micronucleus test in peripheral blood erythrocytes by use of the splenectomized model. Lab AnimSci 49:418–420.
Rengarajan T, Rajendran P, Nandakumar N, Lokeshkumar B, Rajendran P, Nishigaki I (2015) Exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with special focus on cancer. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 5(3):182–189.
Salamone MF, Mavournin KH (1994) Bone marrow micronucleus assay: a review of the mouse stocks used and their published mean spontaneous micronucleus frequencies. Environ Mol Mutagen 23:239–273.
Schmid W (1975) The micronucleus test. Mutat Res 31:9–15.
Schneider J, Grosser R, Jayasimhulu K, Xue W, Warshawsky D (1996) Degradation of pyrene, bezo(a) anthracene, and benzo(a) pyrene by Mycobacterium sp. strain RJGII-135, isolated from a former coal gasification site. Appl Environ Microbiol 62(1):13–19.
Seike K, Murata M, Oikawa S, Hiraku Y, Hirakawa K, Kawanishi S (2003) Oxidative DNA damage induced by benz[a]anthracene metabolites via redox cycles of quinone and unique non-quinone. Chem Res Toxicol 16(11):1470–1476.
Slooff W, Janus JA, AJCM M, Montizaan CK, Ros JP (1989) Integrated criteria document PAH. Report No. 758474011. National Institute of Public Health and Environmental Protection, Bilthoven.
Smith MR (1990) The biodegradation of aromatic hydrocarbons by bacteria. Biodegr. 1:191–206.
Ting WTE, Yuan SY, Wu SD, Chang BV (2011) Biodegradation of phenanthrene and pyrene by Ganodermalucidum. Int Biodeter Biodegr 65:238–242.
Titenko-Holland N, Windham G, Kolachana P, Reinisch F, Parvatham S, Osorio AM et al (1997) Genotoxicity of malathion in human lymphocytes assessed using the micronucleus assay in vitro and in vivo: a study of malathion exposed workers. Mutat Res 338:85–95.
Toledo FL, Calvo C, Rodelasand B, González-López J (2006) Selection and identification of bacteria isolated from waste crude oil with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons removal capacities. Syst Appl Microbiol 29(3):244–252.
Vikram A, Ramarao P, Jena G (2007) Prior bleeding enhances the sensitivity of peripheral blood and bone marrow micronucleus tests in rats. Mutagenesis 22(4):287–291.
Wiley V (2012) The MAK-collection part I: occupational toxicants. Wiley-VCH Verlag Gmb H & Co. KGa A.; 27 DFG, Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
You-Qing LI, Hong-Fang LIU, Zhen-Le TIAN, Li-Hua ZHU, Ying-Hui WU, He-Qing TANG (2008) Diesel pollution biodegradation: synergetic effect of Mycobacterium and filamentous Fungi1. Biomed Environ Sci 21(3):181–187.
Yuan SY, Shiung LC, Chang BV (2002) Biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by inoculated microorganisms in soil. Bull Environ ContToxicol 69:66–73.
Zhang CZ, Spektor A, Cornils H, Francis JM, Jackson EK, Liu S et al (2015) Chromothripsis from DNA damage in micronuclei. Nature. 522:179–184.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the radiation department at NCRRT Cairo, Egypt.
Funding
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
I agree to be the data available to “Bulletin of the National Research Centre” for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AMP subcultured Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and test for b-a-anthracene degradation, then apply the organism to gamma radiation. Test wild and variants for degradation of the compound. Then bring the wild strains and its variants to MRM. MRM inject mice and made micronucleus (MN) and DNA fragmentation test to declare the effect of radiation for getting variant can degrade b-a-anthracene more than wild strain. Both MRM and AMP participate in writing their parts and MRM reviews the text. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All authors agree to participate according to the ethics.
Consent for publication
All authors agree for publication at “Bulletin of the National Research Centre”.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Partila, A.M., Mohammed, M.R. Evaluation of the benzo[a]anthracene biodegradation by animal bioassays. Bull Natl Res Cent 43, 72 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-019-0115-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-019-0115-9