Abstract
Background
The idea of mixing different grades of diatomite ores with certain ratios to obtain blends with tailored minerals constitution that can help on improving their thermal insulation applicability is introduced in this study. In this respect, three diatomite samples were collected for investigation from El-Masakheet, Kasr El-Sagha, and Demia deposits, El-Fayoum, Egypt. Complete chemical and phase analyses of these samples were carried out. The analyses showed that El-Masakheet sample was of low-grade diatomite with excess calcite content. In addition, Kasr El-Sagha and Demia samples were of high-grade diatomite with minor calcite contents. By firing the dried Kasr El Sagha and Demia yellow samples specimens at different temperatures for 1 h, they showed complete destruction at 900 °C. Different amounts of El-Masakheet sample was blended with Kasr El-Sagha and Demia yellow samples. The specimens were subjected to firing at different temperatures for 1 h. The physical properties of the fired mixed specimens were followed up.
Results
Results showed that by blending El-Masakheet sample with 50% mass ratio with Kasr El-Sagha or Demia yellow samples, a pronounced increase in the thermal applicability of the fired blends from 900 to 1100 °C was achieved. In addition, a notable increase in their open porosity was recorded. This improvement was attributed to the change in the minerals constitution ratios in the blends due to the increase in their calcite contents after El Masakheet addition, especially the Ca/Si and Ca/(Al + Si) atom ratios. This change served in forming high melting points minerals like α-wollastonite and akermanite on firing the blends specimens instead of low melting point minerals like cristobalite and alkali aluminosilicate which were formed on firing the high-grade ores alone. Consequently, an increasing in the porosity and the thermal applicability of the new specimens from 900 to 1100 °C was achieved.
Conclusions
The idea of mixing different grades of diatomite ores with certain ratios to obtain blends with tailored minerals constitution can help on improving their thermal insulation applicability and their open porosity. Besides, this concept gave a good solution to get use of the unexploited low-grade diatomite ores, especially of high calcite content.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Background
Insulation or thermal insulation is the process of reducing or increasing heat transfer between two or more objects that are in the range of thermal contact or relative influence. Materials that help in reducing heat gain or loss by offering a barrier within the areas are known as insulation materials. The insulation capability of the materials depends on their thermal conductivity. Materials that provide superior insulation especially in industrial applications are known as high-performance insulation materials. Some of the key attributes of high-performance insulation materials are superior heat regulation without having a support of air conditioning machine or heater, prevention from moisture damage, and an optimum in-house atmosphere. High-performance insulation materials also prevent fire damage. As per claims made at the Chalmers Energy Conference 2013, high-performance insulation materials can help reduce energy usage across sectors by 50% by 2050 (Lin and Wang 2009; Qian and Li 2018; Sari et al. 2018; Yao et al, 2018).
Growing awareness regarding greenhouse emissions and rising demand for energy savings are major factors boosting growth of the global high-performance insulation materials market. High-performance insulation processes are in high demand in the industrial sector, mainly due to its natural ability to regulate temperature. This is a very important attribute, as this helps avoid costs related to artificial thermal regulators such as air conditioners and heaters. Energy usage during insulation processes is minimal, which helps to cut down on associated production costs. However, some of the disadvantages associated with the usage of high-performance insulation processes are high set up and maintenance costs and relatively low service life. High-performance insulation materials need periodic maintenance, as majority of the materials are made of aerogel and ceramic fiber (Yurkov 2005; Skalkin 2006).
Asia Pacific is projected to be the fastest growing region in the global high-performance insulation materials market, mainly due to rampant growth of end-use industries such as construction and automotive, especially in emerging economies of India and China. As per stats released by Indian Brand Equity Foundation—part of the Department of Commerce, Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India—the real estate market is expected to be valued at US$ 180 billion by 2020. The automotive sector in India has attracted FDI worth US$ 15.79 billion during April 2000–September 2016, as per statistics released by the Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion (DIPP). On the other hand, Europe is expected to hold the largest share of the market throughout the forecast period owing its large base of end use industries and high awareness about greenhouse effect and lower energy usage among people.
Diatomite are light fine-porous siliceous rocks consisting mainly of extremely small opaline skeletons (or their fragments) of diatomic algae (diatoms). Diatomite are white, yellowish gray, light gray, and sometimes dark gray, and brownish gray. The dark and brown color of diatomite is due to the presence of organic impurities, including plant residues. The pores and the walls of pores of diatoms are often of nano-size, which justifies classifying them as nano-materials. It is evident on photomicrographs shown in Fig. 1, that each skeleton of diatoms in diatomite possesses a clearly ordered micro- and nano-porous structure (Ivanov and Belyalov 2008, Pustovgar 2006). The unique structure and the ordered size distribution of the pores give diatomite superior characters compared with other similar materials of heat-insulating properties, on account of which they are used for thermal insulation of surfaces with temperature 900–1000 °C (Stroemer and Smol 2001).
Skeletons of diatoms and their structure (Kazan 1976)
Insulating diatomite bricks are often prepared by firing the ore at 1000 °C through one of three methods: semi dry, plastic, and foam slip methods. To increase the porosity feature of the diatomite bricks, sawdust or cokes are sometimes used as pore former agent. Bricks made of diatomite are characterized by low thermal conductivity, high strength, and chemical resistance. Therefore, diatomite brick is used in ferrous and nonferrous metallurgy, power engineering, and glass application, in addition of cement and petrochemicals industries (Kashcheev et al. 2009a; Tsibin 1966; Kazan Musuem 1976; Ivanov & Belyakov 2008; Kashcheev et al. 2009a; Hanna et al. 2012; Ibrahim 2012; Da et al. 2014; Lui et al. 2017; Sari et al. 2018).
When diatomite is heated to above 1000 °C, its amorphous silica structure is damaged and converted to cristobalite (Kashcheev et al. 2009b; Ibrahim and Selim 2012). The phase transformation of cristobalite may be the reason of the strength reduction of the diatomite bricks. In addition, the possible reactions between the accompanied accessory minerals in the crude diatomite ore with the active diatomitic silica, on firing to above 1000 °C, may form different amounts of liquid phases, which cause deformation in the diatomite bricks. In order to overcome these problems and to increase the applicability temperature of diatomite as well, calcium oxide was added, in the form of chalk, with different mass ratios from 0 to 30%. This reaction between chalk and the diatomitic silica will result in the formation of wollastonite (CaO.SiO2) mineral and accordingly, the chance of cristobalite formation will be decreased, resulting in increasing the applicable firing temperature (Kashcheev et al. 2009a; Meradi et al. 2015; Merado et al. 2016; Galzerano et al. 2018).
In Egypt, diatomite ores are found in three main areas, El-Fayoum Depression (Western Desert), Ras Ghareb (Suez Gulf-Red Sea), and some scattered deposits in the west of the Northern Coast of Egypt (Ibrahim and Powers 2009). The diatomite deposits that are recorded at El-Fayoum Depression are in the north and south west of the Governorate. In the north, they are found in the north and northeast of Lake Qarun, in three areas, Kom Osheem in the East, Qasr El Sagha, and Demia (yellow and gray) in the West. In addition, diatomite ores cover a large area in the southwest of El-Fayoum between Wadi El Rayan and the small villages in the SW of El-Fayoum, particularly to the southeast of Gabel Elow El-Masakheet. This area is located to the SW of the EL Fayoum city by about 28 km and is called El-Masakheet. These deposits were formed in fresh water lakes that was covered most of El-Fayoum Depression in the Halocene era; lakes Moeris (Abdel 1958; Basta et al. 1971; Basta et al. 1972; Faris and Girgis 1969). The main minerals constitutions of these deposits are diatomite (amorphous silica), silica sand, inorganic carbonate (calcite and dolomite), clayey minerals, and organic materials (Ibrahim and Selim 2012). This means that the Egyptian diatomite contains beside silica, different oxide contents of calcium, magnesium, aluminum, and iron (Loukina et al. 1994; Hassan et al. 1999).
In connection with the sharp increase in the price of heat carriers, the use of materials that are made from diatomite as effective heat insulation is becoming more attractive (Hamdi and Hamdi 2013; Hanna et al. 2014; Hanna et al. 2015; Loganina and Karpova 2015; Öztaş et al. 2016; Da et al. 2014; Han et al. 2017). The drawback of heat-insulation materials made of diatomite is their low temperature of prolonged service in heating equipment (ordinarily no higher than 950 °C). Consequently, work on increasing the temperature level for prolonged service of heat insulation is a big challenge.
Methods
Three diatomite samples were collected from El-Fayoum depression, namely Masakheet (M2), Demia yellow (D2), and Kasr El Sagha (K2). The chemical composition of the samples was determined using Brunauer-Emmett-Teller and X-ray fluorescence (XRF), while their mineral composition was identified using a Philips X-ray diffractometer Model PW/1710 Cu K α radiation with Ni filter at 40 kV and 30 mA. The scanning speed was 2Ɵ = 2°/min. Particle size analysis of the samples was measured using BT-2001 laser particle size analyzer. The surface area and the porosity measures were determined using Brunauer Emmett-Teller unit. The bulk density and open porosity of the specimens were determined by water displacement after boiling for 2 h to eliminate residual air bubbles. A Vernier caliber with a precision of 0.005 cm was employed to measure the change in dimensions of the tested specimens.
Blended specimens preparation
Different amounts of 5, 15, 30, 40, and 50% by mass of El-Masakheet (M2) sample was blended with Kasr El-Sagha (K2) and Demia yellow (D2) samples. During mixing, appropriate amount of water was added. The resulted mixed masses were molded under low pressure into small cubic specimens of two inches length. The specimens were left to dry in two different conditions: at ambient temperature for 48 h at 110 °C for 24 h. The dried specimens were then subjected to firing at 1100 °C for 1 h. The physical properties of the fired mixed specimens such as the change in dimension, bulk density, and open porosity were followed up. The phase analyses of some fired specimens were followed up.
Results
Characterization of the original raw diatomite samples
The chemical analysis of the original diatomite samples show that the total silica content differs greatly between M2 sample and the other two samples K2 and D2 (Table 1). The total silica content reaches 17.03% in M2 sample, where it reaches 58.96% and 58.60% in K2 and D2 samples (Table 1). The CaO contents in the raw samples record 40.97% in M2 sample, where it reaches 2.82% and 7.21% in K2 and D2 samples (Table 1). The alumina and magnesia contents reach 3.42 and 1.52% in M2, 9.37 and 1.01% in K2, and 9.72 and 1.52% in D2 (Table 1). Additionally, iron oxide content reaches 3.75%, 7.05%, and 5.94% in the crude samples, respectively (Table 1). The loss on ignition content reaches 30.1%, 16.8%, and 13.2% in the raw M2, K2, and D2 samples, respectively (Table 1). This loss in the samples weights are due to removal of water of humidity and the organic matter, in addition to the decomposition of the inorganic carbonates and the dihydroxylation of the clayey minerals. In addition, the higher value of the loss on ignition content in Kasr El-Sagha diatomite than that in case of Demia yellow diatomite is due to the presence of high content of kaolin minerals in the former sample.
After firing at 1000 °C for 1 h., the SiO2 content in the three samples increases to 24.36%, 70.86%, and 67.51%, respectively (Table 1). The CaO content increases to 58.59%, 3.38%, and 8.31%, respectively (Table 1). The alumina and magnesia content increase to 4.89 and 2.16% in M2, 11.26 and 1.21 in K2, and 11.20 and 1.75% in D2 (Table 1).
The ratios Ca/Si and Ca/Al + Si reach 2.58% and 2.08% in the fired sample M2, where they reach 0.05%, 0.04% in the fired sample K2 and 0.12%, 0.10% in the fired sample D2 (Table 1). In addition, the ratios Al/Al + Si and Ca/Si + Mg reach 0.19% and 2.27% in the fired sample M2, where they reach 0.11%, 0.05% in the fired sample K2, and in the fired sample D2 these ratios reach 0.15% and 0.13% (Table 1).
In the XRD analysis of the three raw samples, the broad hump registered between 2 Ѳ = 20–26, indicates the presence of opal-A; representing the well preserved diatom frustules, is appeared at K2 > D2 > M2 (Fig. 2). Crystalline silica is shown as a major constituent in samples D2 and M2 in sequence, with lesser intensity in sample K2 (Fig. 2). Calcite is shown as the major constituent at sample M2, ten times more intensive than in the samples K2 and D2 (Fig. 2). In addition, kaolinite and montmorillonite are detected in the XRD patterns of K2 and D2 samples, potassium alumino-silicate and sodium alumino-silicate (alkali feldspar) phases appear in D2 and K2 samples, while they are nearly not found in M2 sample (Fig. 2).
The surface area measures of the raw samples show that Demia yellow sample has the highest porosity, where its surface area reaches 48.98 m2/g followed by Kasr El-sagha sample 37.76 m2/g and El Masakheet sample shows the lowest porosity with 29.04 m2/g surface area measure (Table 2). The pore volumes of the three samples reach 0.072, 0.067, and 0.052 cm3/g, respectively (Table 2). Particle size analysis show that the D 50 of the three samples are about 10.93, 18.52, and 11.24 μm for M2, K2, and D2 samples (Figs. 3, 4, and 5), respectively.
Characterization of the fired raw diatomite samples
On increasing the firing temperature up to 900 °C, Demia yellow 2 (D2) and Kasr El Sagha 2 (K2) specimens show a sign of softening. This is appeared in a decrease in their shrinkage% and increase in their bulk densities when they are fired from 800 to 900 °C (Fig. 6a, b). By increasing the firing temperature up to 900 °C for 1 h, they show low open porosity values, reaching 34.3% and 28.2%, respectively (Fig. 6c). These specimens show low open porosity values reach 34.3 and 28.2%, respectively, when they are fired at 900 °C (Fig. 6c). Quite the contrary is occurred with respect to sample M2 (Fig. 3a, b). There was no remarkable change in its shrinkage% or its bulk density on firing the sample even up to 1100 °C for 1 h (Fig. 6a, b). Yet, it showed high open porosity reaching 61.8% (Fig. 6c). The strong effect of firing temperature appears in M2 that is fired at high temperature (1100 °C). This behavior is related to the process of sintering which becomes stronger at higher temperatures.
The Al2O3/SiO2 mass ratio of M2, K2, and D2 samples are 20.09, 15.90, and 16.59%, respectively. Therefore, the low Al2O3/SiO2 mass ratio of K2 and D2 samples may be the reason of their lower softening point. The presence of alkalies even in small amount with the low Al2O3/SiO2 % renders the formed liquid phase after firing, more fluid (Hinz 1972). On firing the K2 and D2 samples, the present alkali feldspar transformed to Na and K tecto alumino-silicate leading to a decrease in the softening point of the fired samples (> 900 °C). In addition, the high CaO content and consequently the high CaO/SiO2 mass ratio in M2 sample leads to formation of dicalcium silicate and calcium magnesium alumino-silicate which increase the softening point of the fired M2 sample. This clearly noticed where Ca/Si, Ca/Al + Si, and Ca/Si + Mg in sample M2 are higher than Al/Al + Si atom ratio (Table 1).
The XRD analysis of the fired raw samples M2 at 1100 °C for 1 h detect calcium magnesium alumino-silicates [Ca2Mg0.25 Al0.75], [Ca2 (Mg0.25 Al0.75) Si1.25 AlO0.75 O7], larsnite [2CaO2 SiO2], and quartz (Fig. 4). The existence of the former two phases is due to the high CaO/SiO2 mass ratio in sample M2 compared with that in case of the other two samples K2 and D2 (Fig. 7). On the other hand, quartz, cristobalite, and iron oxide peaks are detected in the XRD pattern of the fired K2 and D2 samples (900 °C for 1 h) (Fig. 7). In addition, anorthite sodian intermediate (Ca, Na)(Si,Al4)O8 and sodium potassium tecto-aluminosilicate (NaO75 K 25) (Al Si3 O8) anorthic are detected also in the XRD analyses of samples K2 and D2 (Fig. 7). The low softening point of fired K2 and D2 specimens is mainly due to the formation of these two phases, where their softening points are rather low. Sodium and potassium are more active than calcium and magnesium, so they form tecto-silicate, before calcium or magnesium, leading to decrease in the melting point of the silica. A high background is noticed in the XRD patterns of the fired samples K2 and D2 indicating the formation of a glassy phase during the firing process (Fig. 7).
Characterization of the M2-K2 and M2-D2 fired blends
M2-K2 fired blends
By increasing the M2 amount in the K2 sample from 5, 15, 30, 40 to 50% additions by mass, the Al2O3 and Fe2O3 contents decreased from 11.26 and 8.48% in the fired raw sample to 11.00, 10.44, 9.58, 8.99, and 8.26 for Al2O3 and to 8.35, 8.08, 7.66, 7.37, and 7.06% for Fe2O3 in different blends, respectively (Tables 1 and 3). In addition, MgO and CaO contents increased from 1.21 and 3.38% in the fired raw sample to 1.25, 1.33, 1.46, 1.56, and 1.65 for MgO and to 5.72, 10.52, 18.01, 23.24, and 28.60% for CaO in different blends, respectively (Tables 1 and 3). Additionally, the silica content decreased from 70.86% in the fired raw K2 sample to 68.90, 64.86, 58.55, 54.23, and 49.63% in different fired M2-K2 blends, respectively (Tables 1 and 3).
At the blend specimen M2-K2 (50/50 by mass %), a lowering in the shrinkage character and in the bulk density value from − 0.02% and 1.20 in the fired raw K2 to − 1.0% and 1.05 in the fired M2-K2 blend is remarked (Figs. 6 and 8a, b). Additionally, the open porosity of the fired M2-K2 (50/50 by mass %) is increased, from 28.20 to 45.20 (Figs. 6 and 8c). This is due to the relatively large amount of volatile matter evolved during the firing process, in addition to the decrease in the impurities content in the specimens as a result of their dilution as a result of M2 addition.
The XRD analysis of M2-K2 (30/70% mass) diatomite specimens fired at 1100 °C for 1 h (Fig. 9) shows that quartz, wollastonite (CaO.SiO2), and anorthoclase ((Na, K) AlSi3O8) are the main phases detected in this pattern. In addition, intense XRD patterns of akermanite (Ca2 Mg Si2 O7), hematite, and magnetite were also detected. The formation of hematite and magnetite phases is due to relatively high iron content of K2 diatomite sample (7.05% mass). Anorthoclase is a crystalline solid solution in the alkali feldspar series, in which the sodium-aluminum silicate member exists in larger proportion. It typically consists of between 10 and 36% of KAlSi3O8 and between 64 and 90% of NaAlSi3O8.
On the other hand, quartz, wollastonite (CaO.SiO2), and akermanite (Ca2MgSi2O7) are the main phases detected in the XRD analysis of M2-K2 (50/50% mass) specimens which are fired at 1100 °C for 1 h (Fig. 10). In addition, an intense XRD patterns of ferrosilite magnesian [Mg (0.318 Fe0.66 CaO16 SiO3)] is detected (Fig. 10). This is due to relatively high iron content in K2 sample (7.05% Fe2O3). The interaction between ferrosilite magnesian and enstatite (Mg SiO3) and ferrosilite (Fe SiO3) minerals forms series of solid solutions due to the presence of the elements of iron and magnesium which can substitute each other in the formed crystals without much alteration of structure (The Mineral Hypersthene 2014).
M2-D2 fired blends
By increasing the M2 amount in sample D2 from 5, 15, 30, 40 to 50% additions, Al2O3 and Fe2O3 contents decreased from 11.20 and 6.84% in the fired sample D2 to 11.00, 10.44, 9.58, 8.99, and 8.26 (for 5%, 15%, 30%, 40%, and 50% by mass addition of M2 for Al2O3) and to 6.78, 6.66, 6.49, 6.33, and 6.19% (for 5%, 15%, 30%, 40%, and 50% by mass addition of M2 for Fe2O3) in different fired blends M2-D2, respectively, Table 4. In addition, by increasing the M2 amount in the D2 sample, MgO and CaO contents increased from 1.75 and 8.31% in the fired sample D2 to 1.76, 1.80, 1.86, 1.89, and 1.93 (for 5%, 15%, 30%, 40%, and 50% by mass addition of M2 for MgO) and to 10.35, 14.57, 21.31, 25.88, and 30.75% (for 5%, 15%, 30%, 40%, and 50% by mass addition of M2 for CaO) in different fired M2-D2 blends, respectively (Tables 1 and 4). Additionally, the silica content decreased from 67.51% in the fired D2 sample to 65.77, 62.15, 56.70, 52.44, and 48.27% (for 5%, 15%, 30%, 40%, and 50% by mass addition of M2) in different fired M2-D2 blends, respectively (Tables 1 and 4).
The effect of increasing the firing temperature from 900 to 1100 °C for 1 h shows a limited increase in the shrinkage% and in the bulk density of the fired M2-D2 specimens (Fig. 11). However, this effect is less than that is shown in the case of M2-K2 specimens when they are fired from 1000 to 1100 °C (Figs. 8 and 11).
The XRD analysis of M2–D2 (30/70% mass) specimens that are fired at 1100 °C for 1 h shows quartz, wollastonite, anorthoclase [(Na, K) AlSi3O8], and akermanite as the main detected minerals phases (Fig. 12).
On the other hand, quartz (SiO2), wollastonite (CaO.SiO2), and akermanite (Ca2 Mg Si2 O7) are the main detected mineral phases in the XRD patterns of the fired M2-D2 (50/50% mass) at 1100 °C for 1 h (Fig. 13). It is remarked also that there is no high background in the XRD patterns is detected, indicating that a very small amount of glassy phase was formed during firing the specimens (Fig. 13).
It is remarked that there is complete absence of the anorthoclase phase in the XRD patterns of M2-K2 and M2-D2 specimens at (50/50% mass) (Fig. 13). In addition, it is noticed that when M2 sample is added to K2 or D2 samples and according to the increase in the calcium content in the new blends, the values of Ca/Si, Ca/Al + Si, and Ca/Si + MgO atomic mass ratios increase from 0.05, 0.04, and 0.05 in K2, and 0.12, 0.10, and 0.13 in D2 to 0.58, 0.49, and 0.55 in M2-K2 and 0.66, 0.57, and 0.64 in M2-D2 (Tables 1, 3, and 4). The increases in the values of these ratios lead to the formation of wollastonite and akermanite in the fired blends at the expense of cristobalite and alkali alumino-silicate.
Discussions
The phase diagram of the Al2O3-SiO2 system contains the composition at wide range of alumino-silicate refractories (Fig. 14). The addition of 5% by mass alumina lowers the melting point of the silica from 1725 to 1595 °C (Fig. 14). Thus 5% alumina acts as weak flux for silica (Heimann 2010). On increasing the alumina addition above this amount, the melting point of alumina-silica composition increases. In the three investigated diatomite samples, the Al2O3/SiO2 mass ratio of Demia yellow (D2) and Kasr El Sagha (K2) are less than in case of El-Masakheet (M2) diatomite sample. These ratios are 16.59, 15.90, and 20.09, respectively. Therefore, the low Al2O3/SiO2 mass ratio of the two formers samples may be responsible for their lower softening point.
Silica-alumina phase diagram (Heimann 2010)
However, the presence of alkalis even in small amount beside low alumina/silica weight ratio renders the liquid more fluid. The alkalis that are present in the two samples as alkali feldspar and forms on firing Na and K tecto alumino-silicate leading to a decrease of their softening point (> 900 °C). On the other hand, the existence of high CaO content or in other words high CaO/SiO2 mass ratio in El-Masakheet (M2) sample leads to the formation of dicalcium silicate and calcium magnesium alumino-silicate which increases the softening point of El Masakheet (M2) sample (Table 1). This appears clearly from its chemical composition, where Ca/Si, Ca/Al + Si, and Ca/Si + Mg are higher than Al/Al + Si atom ratio, recording 2.58, 2.08, 2.27, and 0.19, respectively (Table 4).
This is in contrast to what was obtained in the case of Demia yellow (D2) and Kasr El sagha (K2) diatomite samples where the values of Al/Al + Si atom ratios (0.15 and 0.11) are higher than the values of Ca/Si, Ca/Al + Si, and Ca/Si + Mg (0.12, 0.10, 0.13 and 0.05, 0.04, 0.05), in the two samples respectively (Table 4).
When El-Masakheet M2 diatomite sample was added to Demia yellow D2 or Kasr El Sagha K2 diatomite samples, the values of Ca/Si, Ca/Al + Si, and Ca/Si + MgO atom ratio increase and at the same time the value of Al/Al + Si atom ratio decreases. This leads to the formation of wollastonite and akermanite at the expense of alkali alumino-silicate. The formed phases have higher melting points reaching 1540 and 1450 °C, respectively. Therefore, the specimens prepared from mixtures show improvement in their thermal stability from 900 to 1100 °C.
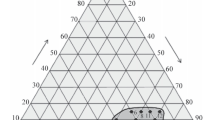
The ternary phase diagram for CaO-MgO-SiO2 system (Fig. 15) shows the effect of 10 wt.% of alumina on the relation between the phases formed (Fig. 16). In this diagram, melilite (akermanite is one mineral of this group) and α-wollastonite exist together in temperature range between 1300 and 1400 °C (Silikate 1970). This leads to increase in the thermal stability and decrease in the densification of specimens that is fired at 1100 °C. In this respect, the effect of high mass loss on ignition and the low impurities content as a result of mixing assist in decreasing the densification of the fired specimens and hence more porous materials are produced.
Ternary phase diagram for CaO-MgO-SiO2 (Silikate 1970)
Effect of 10 mass % of alumina on the phases formed in the ternary phase diagram for CaO-MgO-SiO2 (Silikate 1970)
Conclusions
Despite high-grade diatomite ores contain high content of opal silica, yet they sometimes show limitation in their thermal applicability as heat-insulating materials. This is due to their low softening points, which depend upon their minerals constitution. In order to circumvent this issue and, in addition, to take advantage of low-grade diatomite ores which have low silica content and in most cases high calcite content, the idea to blend such high grade diatomite with those ores having high calcite content is introduced.
In this study, low-grade El-Masakheet diatomite of high calcite content is blended at 50/50 mass ratio with high-grade Kasr El-Sagha or Demia yellow diatomite ores of low calcite contents. This mixing leads to changes in the minerals constituents’ ratios, especially the Ca/Si and Ca/(Al + Si) atom ratios of the new specimens. On firing, it serves in forming high melting points minerals like α-wollastonite and akermanite instead of low melting point minerals like cristobalite and alkali aluminosilicate, which are formed on firing the high grade ores alone. Consequently, an increasing in the porosity and the thermal applicability of the new specimen blends from 900 to 1100 °C is achieved.
References
Abdel AA (1958) A taxonomic and paleoecological investigation of the diatomite flora of the extinct. Fayium Lake-Upper Egypt. Faculty of Science Bulletin, Alex. Univ. Egypt 2:217–244
Basta EZ, Abdallah AM, Kadi MB (1971) Geology and mineralogy of diatomite clay deposits north of Fayoum. Faculty of Science Bulletin, Cairo Univ., Egypt
Basta EZ, Abdallah AM, Kadi MB (1972) Geology and mineralogy of diatomtic clay deposits north of Fayoum, Egypt. Faculty of Science Bulletin, Cairo Univ., Egypt 45:319–329
Da J, Du YH, Li MD, Zhang CB (2014) The Preparation and Performance Study of Thermal Insulating Materials with Diatomite. Advanced Materials Research 941–944:1562–1565. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.941-944.1562.
Faris MI, Girgis GF (1969) Proceeding of the 6th Arab Science Congress. 4b:751–767
Galzerano B, Capasso I, Verdolotti L, Lavorgna M, Vollaro P, Caputo D, Iannace S, Liguori B (2018) Design of sustainable porous materials based on 3D-structured silica exoskeletons, diatomite: chemico-physical and functional properties. Mater Des 145:196–204
Hamdi B, Hamdi S (2013) Thermal properties of Algerian diatomite, study of the possibility to its use in the thermal insulation. International Congress on Energy Efficiency and Energy Related Materials. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-05521-3_42013
Han L, Li F, Deng X, Wang J, Zhang H, Zhang S (2017) Foam-gelcasting preparation, microstructure and thermal insulation performance of porous diatomite ceramics with hierarchical pore structures. Journal of the European Ceramic Society 2017 37(7):2717–2725
Hanna SB, Ibrahim SS, Wahsh MMS, Mansour TS (2014) Diatomic heat insulating material combined by ceramic bond. African Journal of Engineering Research 2-2:26–38
Hanna SB, Ibrahim SS, Wahsh MMS, Mansour TS, Saad EA (2012) Characterization of lightweight diatomite-clay refractories. Ceram Ind:18–23
Hanna SB, Ibrahim SS, Wahsh MMS, Mansour TS, Saad EA (2015) Diatomic heat insulating material combined by hydrolautic bond. Refractories Engineer. (2015):15–20
Hassan MS, Ibrahim AI, Ismael IS (1999) Diatomaceous deposits of Fayium, Egypt: characterization and evaluation for industrial application. Chin J Geochem 18:233–241
Heimann BR (2010) Classic and advanced ceramics: from fundamentals to applications, 1st edn. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co., KGaA; ISBN: 978-3-527-32517-7
Ibrahim SS (2012) Diatomite Ores: origin, characterization and applications, J. Int Environmental Applications and Science 7(1):191–199
Ibrahim SS, Powers K (2009) Preparation of some diatomaceous earth products for special industrial applications, US-Egypt cooperative research, award#0329136, ID: 0329136
Ibrahim SS, Selim AQ (2012) Heat treatment of natural diatomite. Physicochem Probl Miner Process 48(2):413–424
Ivanov SE, Belyakov AV (2008) Diatomite and its applications. Translated from Steklo i Keramika 2:18–21
Kashcheev D, Popov AG, Ivanov SE (2009a) Improving the thermal insulation of high-temperature furnaces by the use of diatomite. Refract Ind Ceram 50(2):98–100
Kashcheev D, Sychev SN, Zemlyanai KG, Klimovski AB, Nesterova SA (2009b) Diatomite heat insulation material with increased application temperature. Refract Ind Ceram 50(5):354–358
Lin J, Wang L (2009) Adsorption of dyes using magnesium hydroxide-modified diatomite. Desalination and Water Treatment 8(1–3):263–271. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2009.786
Lui Z, Hu D, Lv H, Zhang Y, Wu F, Shen D, Fu P (2017) Mixed mill-heating fabrication and thermal energy storage of diatomite/paraffin phase change composite incorporated gypsum-based materials. Appl Therm Eng 118:703–713
Loganina VI, Karpova OV (2015) Heat-insulating dry mixes with using of diatomite. Contemporary Engineering Sciences 8(2):97–101
Loukina SM, El-Hefnawi MA, Abayzeed SD (1994) Minerology and geochemistry of diatomaceous earth from Fayoum region, Egypt, the mineralogical society of Egypt, proceeding of 1st international symposium on industrial application of clays. Cairo, Egypt:282–305
Meradi H, Atoui L, Bahloul L, Labiod K, Ismail F (2015) Characterization of diatomite from Sig region (West Algeria) for industrial application. International Conference on Technologies and Materials for Renewable Energy, Environment and sustainability. Beirut – Lebanon, TMREES15:17–20
Merado H, Bahloul L, Bedoud K, Benayache S. Study of physico-chemical properties of diatomite Algeria: application to the thermal insulation of liquid steel bath. 4ème Conference Internationale des energies renouvenables (CIER-2016). 2016; Dec. 20–22. Hammamet, Tunisie
Öztaş S, Karakaya U, İskender U (2016) Investigation of thermo-physical properties of diatomite/water nanofluid. Gazi Journal of Engineering Sciences 2(1):1–22
Pustovgar P (2006) Effectiveness of activated diatomite in dry construction mixtures. Stroit Mater 10:2–4
Qian T, Li J (2018) Octadecane/C-decorated diatomite composite phase change material with enhanced thermal conductivity as aggregate for developing structural–functional integrated cement for thermal energy storage. Energy 142:234–249
Sari A, Bicer A, Al-Sulaiman FA, Karaipekli A, Tyagi VV (2018) Diatomite/CNTs/PEG composite PCMs with shape-stabilized and improved thermal conductivity. Preparation and thermal energy storage properties, Energy and Buildings 164:166–175
Silicaceous Rock of the USSR (Diatomites, Opokas, Tripolis, Spongiolites, Radiolarites). Tatarskoe Knizhn. Izd. Kazan. 1976
Silikate HW (1970) Basics of the science and technology. Germany, Berlin
Skalkin MN (2006) Application of foam diatomaceous brick in ferrous and nonferrous metallurgy. Novye Ogneup. 7:19–23
Stroemer EF, Smol JP (2001) The diatoms application for environmental and earth science. Cambridge University press, Cambridge
Tsibin P (1966) Replacing fireclay insulant BL-0.8 by diatomite in tunnel kiln car linings. Ogneupory 10:26–27
Yao G, Lei J, Zhang X, Sun Z, Zheng S (2018) One-step hydrothermal synthesis of zeolite X powder from natural low-grade diatomite. Materials 11(6):906. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11060906
Yurkov L (2005) Properties of heat insulation materials. Novye Ogneup 3:18–25
Acknowledgements
The authors of this research work thank Dr. Khaled Ezzat (CMRDI) for his kind help.
Funding
This study was not funded by any source.
Availability of data and materials
The authors declare that the data and material are available.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed in the practical work of this research. They also share in preparing the manuscript for publication. They approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The authors declare that the work is ethically approved and consent to participate.
Consent for publication
The authors declare that the work has consent for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Mansour, T.S., Abdallah, N.M., Ibrahim, S.S. et al. To blend is a good solution to improve the heat insulation applicability of diatomite ores. Bull Natl Res Cent 42, 25 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-018-0028-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-018-0028-z