Abstract
Objective
To determine if real-time compression feedback using a non-automated hand-held device improves patient outcomes from in-hospital cardiac arrest (IHCA).
Methods
We conducted a prospective, randomized, controlled, parallel study (no crossover) of patients with IHCA in the mixed medical–surgical intensive care units (ICUs) of eight academic hospitals. Patients received either standard manual chest compressions or compressions performed with real-time feedback using the Cardio First Angel™ (CFA) device. The primary outcome was sustained return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), and secondary outcomes were survival to ICU and hospital discharge.
Results
One thousand four hundred fifty-four subjects were randomized; 900 were included. Sustained ROSC was significantly improved in the CFA group (66.7% vs. 42.4%, P < 0.001), as was survival to ICU discharge (59.8% vs. 33.6%) and survival to hospital discharge (54% vs. 28.4%, P < 0.001). Outcomes were not affected by intra-group comparisons based on intubation status. ROSC, survival to ICU, and hospital discharge were noted to be improved in inter-group comparisons of non-intubated patients, but not intubated ones.
Conclusion
Use of the CFA compression feedback device improved event survival and survival to ICU and hospital discharge.
Trial registration
The study was registered with Clinicaltrials.gov (NCT02845011), registered retrospectively on July 21, 2016.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Effective chest compression remains the cornerstone of successful cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. International guidelines note the critical importance of compression components including position, rate, force, depth, interruptions, recoil, excessive ventilation avoidance, no-flow time, and flow fraction [4,5,6,7,8]. However, observational data suggest that compressions delivered in practice may be suboptimal [9]. Strategies that improve guideline adherence may improve cardiac arrest outcomes. Real-time audiovisual feedback (AVF) and post-event debriefing have been identified as two such strategies [4, 10,11,12].
Several chest compression feedback devices have been marketed. Those not associated with automated external defibrillators (non-AED) require active chest compression, and most utilize passive decompression. The associated feedback technology ranges in complexity from a simple metronome to electromagnetic sensing [7, 13,14,15,16]. Despite a paucity of evidence, the American Heart Association (AHA) and the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR) have both made cautious recommendations supporting AVF device use [4, 6, 17].
To date, nine non-AED active compression-passive decompression feedback devices have been tested in simulation and clinical environments [7, 13,14,15,16, 18,19,20,21,22]. Only one study assessing the use of a hand-held AVF device during in-hospital cardiac arrest (IHCA) has been published [7]. In a study of patients with IHCA (n = 80), significant improvements in return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) rates, guideline adherence, CPR quality, and decreased rib (not sternum) fracture rates were observed for patients receiving compressions using the Cardio First Angel™ (CFA) device [7]. In the current study, we aim to determine if use of the CFA compression feedback device will improve rates of sustained ROSC, and survival to intensive care unit (ICU) and hospital discharge for patients with IHCA.
Methods
Study design and settings
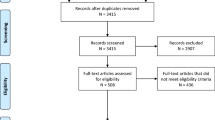
This was a prospective, randomized, controlled, parallel study of patients undergoing resuscitation with chest compressions for IHCA in the mixed medical-surgical ICUs of eight academic tertiary care hospitals in Iran from January 1, 2015, to September 15, 2015. All parts of the study were reviewed according to the Consolidated Standards for Reporting Trials (CONSORT) statement (Fig. 1) [23]. The trial was registered with Clinicaltrials.gov (identifier NCT02845011). The protocol is available for review upon reasonable request. Crossover was not allowed. Patients were blinded to randomization group. The healthcare provider was not blind during the resuscitation, as it was considered unethical to employ a sham device. The data analyzer was blinded to group randomization and was not present during resuscitation.
Block randomization (groups of 4) was performed using a random number list generated by Random Allocation Software© (RAS; Informer Technologies, Inc., Madrid, Spain; Fig. 1). Numbers were placed into sequential containers that were kept in a secure location until allocation consignment. To ensure blinding, the allocation sequence was kept by a different investigator than the one enrolling participants. A third investigator was responsible for patient follow-up and assessments. Enrollment and randomization occurred in the emergency department from available admitted ICU patients on a convenience basis. Only patients admitted to the ICU through the emergency department were eligible for inclusion. Patients suffering decompensation in clinical status on the floor or intermediate care units requiring transfer to the ICU were not eligible for study inclusion. Patients consented to enrollment in a study on cardiac arrest treatment should that event occur during the ICU stay. A container was kept at the foot of the bed that either contained the CFA device (intervention) or a weight but no device (control). Upon resuscitation, the container was opened, and providers proceeded with the resuscitation accordingly. There were no important changes to methods after trial commencement. The study ended because it achieved the necessary sample size.
Patient population
The pre-defined inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) age ≥ 18 years, (2) admitted to the ICU from the emergency department (ED), (3) resuscitation status (full code), and (4) informed consent. Patients were excluded from inclusion if pregnant. Subjects excluded from the final analysis were as follows: (1) any out-of-hospital cardiac arrest or ED cardiac arrest prior to study enrollment, (2) change in code status to anything not full code, (3) revoked consent, or for (4) lost or incomplete data due to logistical impediment to data collection. Consent decisions were accepted from either the patient or appropriate legal guardian or surrogate. Decisions to cease resuscitation efforts were made by the team leader in accordance with the European Resuscitation Council and AHA Guidelines for Resuscitation Ethics and included (1) asystole for > 20 min in the absence of a reversible cause [e.g., hypothermia at time of arrest, cardiac tamponade, tension pneumothorax, distributive shock from anaphylaxis, and chemical intoxication/overdose (e.g., opiate)], (2) > 30 min of resuscitation with no occurrence of ventricular fibrillation (VF) or ventricular tachycardia (VT) at any point (initial or subsequent rhythm), (3) injury not compatible with life, (4) severity of comorbidities, and (5) normothermia [24, 25]. For those patients in persistent pulseless VF or VT not responsive to CPR, defibrillation, and medications, the determination to cease resuscitation efforts was made by the resuscitation team leader based on the clinical variables including the following: witnessed versus unwitnessed arrest, time to CPR initiation, comorbid disease, and pre-arrest state.
Intervention
All arrests were classified as witnessed and monitored as they occurred in the ICU. Resuscitation teams were comprised of an intensivist, three to five ICU nurses, and a respiratory therapist. Resuscitation was in accordance with standard guidelines, including chest compressions performed by experienced ICU nurses, defibrillation (both automated and conventional available), indicated medications (epinephrine, vasopressin, atropine, amiodarone, sodium bicarbonate, calcium chloride, magnesium sulfate), and ventilation with or without endotracheal intubation [8, 26]. Defibrillation technique for all participants was unchanged from the standard baseline technique. Prior to study deployment, all ICU nurses at approved study sites received standardized CPR training in accordance with published guidelines and training on CFA device use [8, 26]. During resuscitation, patients in the control group received CPR in accordance to published guidelines, whereas patients in the intervention group received compressions with the aid of the CFA feedback device. Measurement of invasive hemodynamics was outside the scope of this study.
Cardio First Angel™ device
The Cardio First Angel™ is a handheld device consisting of three components. The rescuer side has a red palm-sized push button with a pictogram illustrating proper use (Fig. 2) [7]. The center unit is composed of a stable plastic base containing an arrangement of springs, and the patient side consists of liquid-absorbent polyurethane foam [7]. Application of 400 ± 30 N of force results in an audible click alerting the rescuer to cease compression, and an additional click on decompression alerts the rescuer to resume compression [7].
Data collection
Utstein variables were published after data collection; however, all available Utstein variables are reported [27]. The primary outcome was sustained ROSC (> 30 min). Secondary outcomes were survival to ICU and hospital discharge. Recorded data included age, sex, invasive mechanical ventilation status upon code onset, ICU and hospital length of stay (LOS), diagnoses, presence of known osteoporosis, initial cardiac rhythm, defibrillation, and administered drugs. Trial outcomes were not changed after trial commencement. Data for invasive arterial monitoring and wave form capnography were not routinely available for patients and is not reported. The assessment for multiple-organ dysfunction included (1) respiratory [ratio of partial pressure arterial oxygen and fraction of inspired oxygen (PaO2/FiO2), minute ventilation (MV)], (2) hematology [platelets, white blood cells], (3) liver [bilirubin, prothrombin time], (4) cardiovascular [mean arterial pressure, systolic blood pressure, heart rate, vasopressor requirement], (5) CNS [Glasgow coma score], and (6) renal [creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, urine output].
Availability of data and materials
All relevant data are within the paper and its supporting information files. De-identified individual subject data may be available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Sample size and data analysis
The sample size was based upon the survival and morbidity data reported from the pilot study [7] and was performed using STATA® 14 (StataCorp LLC, College Station, TX, USA). Assuming an alpha of 0.05 and a power of 0.9, the necessary sample size per group was 413. Accounting for anticipated 10% attrition, the final sample size needed was 450 per group.
All analyses were performed using SPSS 22.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Descriptive statistics were calculated for all variables. Normality was assessed via Shapiro–Wilk test. Normally distributed continuous variables were compared using the t test, with non-normally distributed variables compared via Mann–Whitney U test. Categorical variables were compared via chi-square and Fisher’s exact test, as appropriate. An alpha of 0.05 was significant. Multivariate binary logistic regression was performed with backward elimination (Wald) method. No interim analysis was planned or conducted.
Results
During the 9-month study period, the average hospital admission and expiration rates were 21,940 and 657 (3%), respectively. The average ICU admission and mortality rates per institution were 1693 (13,544 total) and 199 (1592 total, 12%), respectively. Of 1454 subjects approached for enrollment, 1396 were randomized, 554 were excluded (58 pre-randomization; 496 post-randomization), and 900 were included (Fig. 1). Patient demographics were similar between groups (Table 1), as were admission diagnoses (p = 0.62): (CFA vs. control) trauma (5% vs. 4%), neurological (20% vs. 17%), renal (24% vs. 24%), cancer (26% vs. 24.7%), respiratory (21% vs. 23%), and abdominal infection (4% vs. 6%). Time from ICU admission to cardiopulmonary arrest (10.5 ± 5.7 days vs. 10.3 ± 4.2 days, P = 0.38) and initial recorded rhythm were similar between groups (Table 2). Total electricity dose administered for defibrillation was similar between groups (627 J vs. 623 J, P = 0.93), as was first shock success rate (10.9% vs. 12.7%; P = 0.47; Table 2) and resuscitation drug and therapy administration (Table 3). Sustained ROSC rates were improved in the intervention group (66.7% vs. 42.4%, P < 0.001; Table 2), as was survival to ICU discharge (54% vs. 28.4%, P < 0.001) and survival to hospital discharge (54% vs. 28%, P < 0.001). Intra- and inter-group comparisons for the first and second half of the study are shown in Table 4. The CFA group outperformed controls in achieving ROSC and ICU survival in each subgroup comparison (Table 4). No intra-group difference was noted for ROSC or ICU survival in the CFA group over time; however, both improved over time in the control group. Intra- and inter-group comparisons for patients intubated (before or during CPR) versus those not intubated is shown in Table 5. No difference in ROSC or survival to discharge was noted within either group when comparing intubated to non-intubated patients. Similarly, no difference in ROSC or survival to ICU or hospital discharge was observed between groups for intubated patients. A significant difference, however, was noted for ROSC (66.8% vs. 42.8%, P < 0.0001), survival to ICU discharge (60.3% vs. 33.3%, P < 0.0001), and survival to hospital discharge (28.3% vs. 54.1%, P < 0.0001) between the intervention and control groups for non-intubated patients.
Five variables correlated with sustained ROSC on multivariate analysis including the following: no osteoporosis, no MOD, age < 65 years, initial rhythm of asystole, or ventricular fibrillation (compared to pulseless electrical activity; Table 6). Neither sex, CPR duration, time-of-day (shift), nor admission diagnosis grouping correlated with sustained ROSC. No patients were withdrawn for study-associated harms.
Discussion
A large gap exists between current knowledge of CPR quality and its optimal implementation, contributing to preventable deaths attributable to cardiac arrest [28]. As such, quality chest compression remains a focal point of international guidelines [5, 6], with important components including compression rate, force, depth, interruptions, allowing adequate recoil, and avoiding excessive ventilation [2, 3, 29, 30]. One would expect strategies that improve guideline adherence to improve patient outcomes following IHCA. Real-time AVF is one such strategy identified by the AHA and ILCOR as an area needing further investigation [6, 9, 11, 12, 25]. In the 2015 International Consensus on Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care Science with Treatment Recommendations, feedback device use was recommended to provide directive feedback on compression rate, depth, release, and hand position during training (weak recommendation, low-quality evidence). Furthermore, in the absence of AVF devices, tonal guidance (examples include music or metronome) during training is recommended to improve compression rate (weak recommendation, low-quality evidence) [4].
Real-time AVF may be provided by a range of devices, from basic metronomes to devices using accelerometers, springs, or electromagnetic sensing. A recent meta-analysis reported significant improvements in CPR quality, but not ROSC, with AED-associated AVF device use, but no available clinical studies for non-AED devices [31]. One subsequent clinical trial (n = 80) using the CFA device reported improved ROSC rates when compared to standard manual compressions [7]. This was followed by simulation studies using laypersons that showed improved hand position, mean compression depth, rate, and compression fraction with the CFA device [20, 21]. Several other non-AED compression feedback devices have shown promising results in simulation studies but lack clinical testing [7, 15, 16, 18, 22, 32].
This prospective randomized controlled study assessed the effect of using a non-AED hand-held compression AVF device on clinical outcomes in patients with IHCA. The overall rate of ICU mortality (12%) was similar to that reported in studies of adults in western ICU [33]. It is known that patient mortality may vary greatly between institutions and countries [34]. As shown in Table 4, the overall ROSC rate (55%) in this study was similar to prior reports from Iran (20%–56%) [7, 35,36,37], Brazil (71%) [38], USA (43%–52%) [39, 40], Europe (54%–73%) [41,42,43,44], Turkey (49%) [45], Japan (65%) [46], and Taiwan (58%–67%) [47, 48] and greater than China (36%) [49], Hong Kong (38%) [50], and Australia and New Zealand (46%) [51]. Although the overall discharge survival rate was higher than previous cohorts, this was due to improved survival in the experimental group. When looking only at the control group, the discharge survival rate was similar to many prior published cohorts (Table 7) [7, 39,40,41,42,43, 46, 51].
Other factors including sex, age, race, and code status may have played a role as well. In modern ICUs, circulatory failure events are often expected and due to gradual deterioration. Often, the goals of treatment are modified resulting in a change in code-status from Full code to a Limited or No-Code/Do Not Resuscitate status. Such patients were excluded from this study, resulting in a patient population at higher risk for cardiac arrest (but still salvageable).
Moreover, female sex and lower age have been associated with improved odds of IHCA survival, whereas black race has been associated with decreased survival [40, 52, 53]. Although the sex distribution in this study is consistent with Iran’s national census data, the proportion of females in our study was higher than other published cohorts [38, 40, 42, 44, 50, 53, 54]. Additionally, the mean age in our cohort was slightly lower than that in some prior reports (Table 7) [35, 42, 44, 45, 47,48,49,50, 54,55,56]. Furthermore, the rate of VF/VT may affect outcomes [53], and although the incidence in published reports of IHCA has been quite variable, the 18% noted in our cohort falls mid-spectrum [38, 44,45,46,47,48,49,50, 54, 56]. Rates of anti-arrhythmic administration (e.g., Amiodarone) were in keeping with other cohorts [54]. In this study, VF/VT rates were lower than in the pilot study [7], suggesting that factors other than arrhythmia type are driving improvements in ROSC and survival rates. Indeed, a trend toward improved ROSC and survival rates has been observed in IHCA patients, regardless of initial rhythm [53].
As it pertains to resuscitation outcomes over time, we performed both intra- and inter-group comparisons for the first and second halves of the study. ROSC and survival to hospital discharge were consistently observed in the intervention versus control group. This is thought to reflect CFA device use. Moreover, higher rates of ROSC and survival to hospital discharge were observed within the intervention group in the second half of the study period relative to the first. This may be related to greater familiarity and comfort with the CFA feedback device. However, the reasons for improved ROSC and survival to hospital discharge in the control group for the first relative to the second half of the study period remain unclear and necessitate further investigation targeted on this question as the study was not designed for this purpose.
It remains unknown whether endotracheal intubation offers ROSC or survival benefits over bag-valve-mask ventilation or supraglottic airway placement during resuscitation for IHCA. Small non-randomized studies have suggested a benefit [45, 48, 56, 57], whereas others have suggested the absence of need for endotracheal intubation as being associated with improved survival [58]. However, data from a large administrative database study (25,006 cardiopulmonary arrest events) found that early invasive airway insertion was not associated with improved ROSC rates, and only slightly better odds of 24 h survival (adjusted OR 0.94, 0.89–0.99) [59]. Moreover, data from both non-randomized clinical studies [47] and large administrative database [60] studies have reported that patients who were already intubated or had received mechanical ventilation before resuscitation had reduced ROSC and survival. We performed both intra- and inter-group comparisons to further assess the impact of intubation on resuscitation outcome. We found no difference in ROSC, or survival to ICU discharge, or survival to hospital discharge for intra-group comparisons based on intubation status. Furthermore, differences in these outcomes were noted only for inter-group comparisons of non-intubated patients, but not intubated ones. The etiology for this is thought to be due to improved CPR quality in the intervention group, but further investigation focused on this finding are needed to better clarify the matter.
Work environment may also play a role in IHCA survival [61,62,63,64]. It has been estimated that an increase by one full-time registered nurse per patient ICU day reduces IHCA relative risk by 28% [65]. Shift time (day, eve, night) does not seem to be a significant factor in IHCA survival in this and other studies [53]. Lastly, the use of therapeutic hypothermia after IHCA varies across studies, and in Iran, it is not common.
Limitations
This study did not enroll patients with primary cardiac conditions; such patients were admitted to the cardiac ICU. This study was not designed to follow neurologic outcomes, as such, data regarding functional outcome is not available. Unfortunately, the study was not designed to capture data on compression rate, depth, chest recoil, no flow time, or flow fraction. In future studies we will plan to incorporate some (or all) of these variables. Moreover, invasive arterial monitoring and wave form capnography were not routinely available at the time of the study and is not reported.
A significant limitation of compression feedback device studies is the inability to blind the clinical providers. Blinding the subject, the investigator, and the data analysts is easy and was done in this case. But to blind the clinical provider, one would need to either (1) use a sham device or (2) not allow the clinician to “see” the patient being resuscitated during device application and “hide” the device during compression pauses. Sham device use was deemed to be unethical, and the latter impractical. Furthermore, one criticism of the current non-AED compression feedback devices is that they do not account for complex changes that occur during CPR. Like other AVF devices, CFA accounts for neither complex changes in chest wall compliance and elasticity, nor the compressibility of the surface the patient is lying on (e.g., mattress). Lastly, future investigations would benefit from optimization of the methodology to detect morbidity including sternum and rib fractures.
Additionally, assessments for chest wall morbidity (rib or sternum fractures) were not uniform (X-ray, CT scan, autopsy) precluding extrapolation of conclusions. This was in part due to funding and resource limitations. Future investigations should improve upon these limitations.
Conclusion
This is the first large-scale clinical trial comparing chest compressions using a hand-held non-AED compression AVF device to standard manual chest compressions during IHCA. Use of the CFA device improved sustained ROSC, ICU survival, and survival to hospital discharge. This study is the first of its kind to show that use of an inexpensive compression AVF device may improve patient outcomes from IHCA. This may have tangible effects for both wealthy and resource-limited institutions. Further prospective clinical investigation comparing CFA to other commercially available AVF devices is needed to clarify the performance characteristics and potential benefit of using these devices.
Abbreviations
- AC-PD:
-
Active compression-passive decompression
- AED:
-
Automated external defibrillators
- AHA:
-
American Heart Association
- AVF:
-
Audiovisual feedback
- CFA:
-
Cardio First Angel™
- CPR:
-
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
- ED:
-
Emergency department
- ICU:
-
Intensive care unit
- IHCA:
-
In-hospital cardiac arrest
- ILCOR:
-
International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation
- LOS:
-
Length of stay
- ROSC:
-
Return of spontaneous circulation
- VF:
-
Ventricular fibrillation
- VT:
-
Ventricular tachycardia
References
Valenzuela TD, Kern KB, Clark LL, et al. Interruptions of chest compressions during emergency medical systems resuscitation. Circulation. 2005;112(9):1259–65.
Christenson J, Andrusiek D, Everson-Stewart S, et al. Chest compression fraction determines survival in patients with out-of-hospital ventricular fibrillation. Circulation. 2009;120(13):1241–7.
Idris AH, Guffey D, Aufderheide TP, et al. Relationship between chest compression rates and outcomes from cardiac arrest. Circulation. 2012;125(24):3004–12.
Bhanji F, Finn J, Lockey A, et al. Part 8: education, implementation, and teams: 2015 international consensus on cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care science with treatment recommendations. Circulation. 2015;132(16 Suppl 1):S242–68.
Hazinski M, Nolan J, Aickin R, et al. Part 1: executive summary: 2015 international consensus on cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care science with treatment recommendations. Circulation. 2015;132(16 Suppl 1):S2–S39.
Soar J, Mancini ME, Bhanji F, et al. Part 12: education, implementation, and teams: 2010 international consensus on cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care science with treatment recommendations. Resuscitation. 2010;81(Suppl 1):e288–330.
Vahedian-Azimi A, Hajiesmaeili M, Amirsavadkouhi A, et al. Effect of the Cardio First Angel™ device on CPR indices: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Crit Care. 2016;20(1):147.
Koster RW, Baubin MA, Bossaert LL, et al. European Resuscitation Council guidelines for resuscitation 2010 Section 2. Adult basic life support and use of automated external defibrillators. Resuscitation. 2010;81(10):1277–92.
Abella BS, Alvarado JP, Myklebust H, et al. Quality of cardiopulmonary resuscitation during in-hospital cardiac arrest. JAMA. 2005;293(3):305–10.
Abella BS, Edelson DP, Kim S, et al. CPR quality improvement during in-hospital cardiac arrest using a real-time audiovisual feedback system. Resuscitation. 2006;73(1):54–61.
Edelson DP, Litzinger B, Arora V, et al. Improving in-hospital cardiac arrest process and outcomes with performance debriefing. Arch Int Med. 2008;168(10):1063–9.
Couper K, Kimani P, Abella B, et al. The system-wide effect of real-time audiovisual feedback and post event debriefing for in-hospital cardiac arrest: the cardiopulmonary resuscitation quality improvement initiative. Crit Care Med. 2015;43(11):2321–31.
Kurowski A, Szarpak Ł, Bogdański Ł, et al. Comparison of the effectiveness of cardiopulmonary resuscitation with standard manual chest compressions and the use of TrueCPR and PocketCPR feedback devices. Kardiol Pol. 2015;73(10):924–30.
Truszewski Z, Szarpak L, Kurowski A, et al. Randomized trial of the chest compressions effectiveness comparing 3 feedback CPR devices and standard basic life support by nurses. Am J Emerg Med. 2016;34(3):381–5.
Kovic I, Lulic D, Lulic I. CPR PRO® device reduces rescuer fatigue during continuous chest compression cardiopulmonary resuscitation: a randomized crossover trial using a manikin model. J Emerg Med. 2013;45(4):570–7.
Yeung J, Davies R, Gao F, et al. A randomised control trial of prompt and feedback devices and their impact on quality of chest compressions—a simulation study. Resuscitation. 2014;85(4):553–9.
Morrison LJ, Neumar RW, Zimmerman JL, et al. Strategies for improving survival after in-hospital cardiac arrest in the United States: 2013 consensus recommendations: a consensus statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2013;127(14):1538–63.
Gruber J, Stumpf D, Zapletal B, et al. Real-time feedback systems in CPR. Trend Anaesthes Crit Care. 2012;2(6):287–94.
Ameryoun A, Meskarpour-Amiri M, Dezfuli-Nejad ML, et al. The assessment of inequality on geographical distribution of non-cardiac intensive care beds in Iran. Iran J Pub Health. 2011;40(2):25–33.
Liu Y, Huang Z, Li H, et al. CPR feedback/prompt device improves the quality of hands-only CPR performed in manikin by laypersons following the 2015 AHA guidelines 2018. Am J Emerg Med. 2018;36(11):1980–5.
Guenther SPW, Scirren M, Boulesteix AL, et al. Effects of the Cardio First Angel™ on chest compression performance. Technol Health Care. 2018;26(1):69–80.
Davis TL, Hoffman A, Vahedian-Azimi A, et al. A comparison of commercially available compression feedback devices in novice and experienced healthcare practitioners: a prospective randomized simulation study. Med Devices Sens. 2018;3(1):e10020.
Moher D, Schulz KF, Altman D, et al. The CONSORT statement: revised recommendations for improving the quality of reports of parallel-group randomized trials. JAMA. 2001;285(15):1987–91.
Baskett PJF, Steen PA, Bossaert L. European Resuscitation Council guidelines for resuscitation 2005. Section 8. The ethics of resuscitation and end-of-life decisions. Resuscitation. 2005;67(Suppl 1):S171–80.
Morrison LJ, Kierzek G, Diekema DS, et al. Part 3: ethics: 2010 American Heart Association guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care. Circulation. 2010;122(18 Suppl 3):S665–75.
Sayre MR, Koster RW, Botha M, et al. Part 5: adult basic life support: 2010 international consensus on cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care science with treatment recommendations. Circulation. 2010;122(16 Suppl 2):S298–324.
Perkins GD, Jacobs IG, Nadkarni VM, et al. Cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation outcome reports: update of the Utstein resuscitation registry templates for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. A statement for healthcare professionals from a task force of the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (American Heart Association, European Resuscitation Council, Australian and New Zealand Council on Resuscitation, Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, InterAmerican Heart Foundation, Resuscitation Council of Southern Africa, Resuscitation Council of Asia); and the American Heart Association Emergency Cardiovascular Care Committee and the Council on Cardiopulmonary, Critical Care, Perioperative and Resuscitation. Circulation. 2015;132(13):1286–300.
Meaney P, Bobrow B, Mancini M, et al. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation quality: improving cardiac resuscitation outcomes both inside and outside the hospital: a consensus statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2013;128(4):417–35.
Miller AC, Rosati SF, Suffredini AF, et al. A systematic review and pooled analysis of CPR-associated cardiovascular and thoracic injuries. Resuscitation. 2014;85(6):724–31.
Meskarpour-Amiri M, Mehdizadeh P, Barouni M, et al. Assessment the trend of inequality in the distribution of intensive care beds in Iran: using GINI index. Glob J Health Sci. 2014;6(6):28–36.
Kirkbright S, Finn J, Tohira H, et al. Audiovisual feedback device use by health care professionals during CPR: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised and non-randomised trials. Resuscitation. 2013;85(4):460–71.
Sugerman NT, Edelson DP, Leary M, et al. Rescuer fatigue during actual in-hospital cardiopulmonary resuscitation with audiovisual feedback: a prospective multicenter study. Resuscitation. 2009;80(9):981–4.
Prendergast TJ, Claessens MT, Luce JM. A national survey of end-of-life care for critically ill patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;158(4):1163–7.
Merchant RM, Berg RA, Yang L, et al. Hospital variation in survival after in-hospital cardiac arrest. J Amer Heart Assoc. 2014;3(1):e0004000.
Hajbaghery MA, Mousavi G, Akbari H. Factors influencing survival after in-hospital cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Resuscitation. 2005;66(3):317–21.
Movahedi A, Mirhafez SR, Behnam-Voshani H, et al. 24-hour survival after cardiopulmonary resuscitation is reduced in patients with diabetes mellitus. J Cardiovasc Thor Res. 2017;9(3):175–8.
Bolandparvaz SH, Mohammadzadeh A, Amini A, et al. Cardiopulmonary arrest outcome in Nemazee Hospital, Southern Iran. Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2009;11(4):437–41.
Silva RM, Silva BA, Silva FJ, et al. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation of adults with in-hospital cardiac arrest using the Utstein style. Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(4):427–35.
Donoghue AJ, Abella BS, Merchant R, et al. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation for in-hospital events in the emergency department: a comparison of adult and pediatric outcomes and care processes. Resuscitation. 2015;92:94–100.
Mallikethi-Reddy S, Briasoulis A, Akintoye E, et al. Incidence and survival after in-hospital cardiopulmonary resuscitation in nonelderly adults. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2017;10(2):e003194.
Fennelly NK, McPhillips C, Gilligan P. Arrest in hospital: a study of in hospital cardiac arrest outcomes. Ir Med J. 2014;107(4):105–7.
O'Sullivan E, Deasy C. In-hospital cardiac arrest at Cork University Hospital. Ir Med J. 2016;109(1):335–8.
Bergum D, Haugen BO, Nordseth T, et al. Recognizing the causes of in-hospital cardiac arrest: a survival benefit. Resuscitation. 2015;97:91–6.
Wallmuller C, Meron G, Kurkciyan I, et al. Causes of in-hospital cardiac arrest and influence on outcome. Resuscitation. 2012;83(10):1206–11.
Pembeci K, Yildirim A, Turan E, et al. Assessment of the success of cardiopulmonary resuscitation attempts performed in a Turkish university hospital. Resuscitation. 2006;68(2):221–9.
Yokoyama H, Yonemoto N, Yonezawa K, et al. Report from the Japanese registry of CPR for in-hospital cardiac arrest (J-RCPR). Circulation. 2011;75(4):815–22.
Huang C, Chen W, Ma MH, et al. Factors influencing the outcomes after in-hospital resuscitation in Taiwan. Resuscitation. 2002;53(3):265–70.
Wang CH, Chen WJ, Chang WT, et al. The association between timing of tracheal intubation and outcomes of adult in-hospital cardiac arrest: a retrospective cohort study. Resuscitation. 2016;105:59–65.
Shao F, Li CS, Liang LR, et al. Incidence and outcome of adult in-hospital cardiac arrest in Beijing, China. Resuscitation. 2016;102:51–6.
Chan, Jacky C., MSc, RN, Wong TW, MBBS and Graham, Colin A., MD, MPH. Factors associated with survival after in-hospital cardiac arrest in Hong Kong. Am J Emerg Med 2013; 31 (5):883–885.
Fennessy G, Hilton A, Radford S, et al. The epidemiology of in-hospital cardiac arrests in Australia and New Zealand. Int Med J. 2016;46(10):1172–81.
Razi RR, Churpek MM, Yuen TC, et al. Racial disparities in outcomes following PEA and asystole in-hospital cardiac arrests. Resuscitation. 2014;87:69–74.
Girotra S, Nallamothu BK, Spertus JA, et al. Trends in survival after in-hospital cardiac arrest. New Engl J Med. 2012;367(20):1912–20.
Peberdy MA, Kaye W, Ornato JP, et al. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation of adults in the hospital: a report of 14 720 cardiac arrests from the National Registry of cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Resuscitation. 2003;58(3):297–308.
Chan PS, Berg RA, Spertus JA, et al. Risk-standardizing survival for in-hospital cardiac arrest to facilitate hospital comparisons. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(7):601–9.
Bansal A, Singh T, Ahluwalia G, et al. Outcome and predictors of cardiopulmonary resuscitation among patients admitted in medical intensive care unit in North India. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2016;20(3):159–63.
Marwick TH, Case CC, Siskind V, et al. Prediction of survival from resuscitation: a prognostic index derived from multivariate logistic model analysis. Resuscitation. 1991;22(2):129–37.
Cohn AC, Wilson WM, Yan B, et al. Analysis of clinical outcomes following in-hospital adult cardiac arrest. Int Med J. 2004;34(7):398–402.
Wong ML, Carey S, Mader TJ, et al. Time to invasive airway placement and resuscitation outcomes after inhospital cardiopulmonary arrest. Resuscitation. 2009;81(2):182–6.
Al-Alwan A, Ehlenbach W, Menon P, et al. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation among mechanically ventilated patients. Intensive Care Med. 2014;40(4):556–63.
McHugh MD, Rochman MF, Sloane DM, et al. Better nurse staffing and nurse work environments associated with increased survival of in-hospital cardiac arrest patients. Med Care. 2016;54(1):74–80.
Chon GR, Lee J, Shin Y, et al. Clinical outcomes of witnessed and monitored cases of in-hospital cardiac arrest in the general ward of a university hospital in Korea. Resp Care. 2013;58(11):1937–44.
Cleverley K, Mousavi N, Stronger L, et al. The impact of telemetry on survival of in-hospital cardiac arrests in non-critical care patients. Resuscitation. 2013;84(7):878–82.
Schwartz BC, Jayaraman D, Warshawsky PJ. Survival from in-hospital cardiac arrest on the internal medicine clinical teaching unit. Can J Cardiol. 2013;29(1):117–21.
Kane RL, Shamliyan T, Mueller C, et al. Nursing Staffing and Quality of Patient Care. Evidence Report/Technology Assessment No. 151. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; 2007.
Aziz F, Paulo MS, Dababneh EH, Loney T. Epidemiology of in-hospital cardiac arrest in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2013-2015. Heart Asia. 2018;10(2):e011029.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Loghman Clinical Research Development Center, Loghman Hakim Hospital, and Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences in Tehran, Iran for methodological, logistical, and limited financial support.
Funding
The authors have received no specific funding for this work. Logistical support was provided by the Loghman Clinical Research Development Center, Loghman Hakim Hospital, and Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences in Tehran, Iran. These entities had no role in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript. No funding or collaboration was derived from the makers of the Cardio First Angel™.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Contributions
The authors that contributed to study design, implementation and data abstraction included BF, AVA, FRB, MH, SS, RG, SJM, KGM, SH, HJM, SMMM, and MK. Data analyses were performed by BF, AVA, and ACM. Manuscript writing and revision was performed by ACM, AVA, and BF. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The protocol was approved by the investigational review board at Baqiyatallah University of Medical Sciences (IR.BMSU.REC.1394.441), which was accepted by each of the participating medical centers: Baqiyatallah Hospital, Shariati Hospital, Masih Daneshvari Hospital, Loghman Hakim Hospital, Shahid Madani Hospital, Ghaem Hospital, Besat Hospital, and Rouhani Hospital. Consent was required and covered both study participation and publication of findings. Informed consent was required prior to cardiac arrest event and could be provided by the patient, legal guardian, or healthcare surrogate.
Consent for publication
The informed consent included permission to present and publish de-identified results.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Goharani, R., Vahedian-Azimi, A., Farzanegan, B. et al. Real-time compression feedback for patients with in-hospital cardiac arrest: a multi-center randomized controlled clinical trial. j intensive care 7, 5 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40560-019-0357-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40560-019-0357-5