Abstract
Background
Germline mutations in the RUNX1 transcription factor give rise to a rare autosomal dominant genetic condition classified under the entity: Familial Platelet Disorders with predisposition to Acute Myeloid Leukaemia (FPD/AML). While several studies have identified a myriad of germline RUNX1 mutations implicated in this disorder, second-hit mutational events are necessary for patients with hereditary thrombocytopenia to develop full-blown AML. The molecular picture behind this process remains unclear. We describe a patient of Malay descent with an unreported 7-bp germline RUNX1 frameshift deletion, who developed second-hit mutations that could have brought about the leukaemic transformation from a pre-leukaemic state. These mutations were charted through the course of the treatment and stem cell transplant, showing a clear correlation between her clinical presentation and the mutations present.
Case presentation
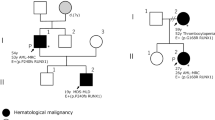
The patient was a 27-year-old Malay woman who presented with AML on the background of hereditary thrombocytopenia affecting her father and 3 brothers. Initial molecular testing revealed the same novel RUNX1 mutation in all 5 individuals. The patient received standard induction, consolidation chemotherapy, and a haploidentical stem cell transplant from her mother with normal RUNX1 profile. Comprehensive genomic analyses were performed at diagnosis, post-chemotherapy and post-transplant. A total of 8 mutations (RUNX1, GATA2, DNMT3A, BCORL1, BCOR, 2 PHF6 and CDKN2A) were identified in the pre-induction sample, of which 5 remained (RUNX1, DNMT3A, BCORL1, BCOR and 1 out of 2 PHF6) in the post-treatment sample and none were present post-transplant. In brief, the 3 mutations which were lost along with the leukemic cells at complete morphological remission were most likely acquired leukemic driver mutations that were responsible for the AML transformation from a pre-leukemic germline RUNX1-mutated state. On the contrary, the 5 mutations that persisted post-treatment, including the germline RUNX1 mutation, were likely to be part of the preleukemic clone.
Conclusion
Further studies are necessary to assess the prevalence of these preleukemic and secondary mutations in the larger FPD/AML patient cohort and establish their prognostic significance. Given the molecular heterogeneity of FPD/AML and other AML subtypes, a better understanding of mutational classes and their involvement in AML pathogenesis can improve risk stratification of patients for more effective and targeted therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a molecularly heterogeneous clonal disease that requires the accumulation of at least two classes of gene mutations in its development [1, 2]. Currently, mutations identified in AML can be stratified into the conventional Class I (FLT3, KRAS, KIT) and Class II (NPM1, CEBPA, RUNX1) mutations that affect cell signaling genes and transcription factors respectively [1,2,3], as well as emerging groups of mutations involving epigenetic modifiers (ASXL1, DNMT3A, EZH2, IDH1/2, TET2), tumor suppressors (TP53, WT1) and spliceosomes (SRSF2, ZRSR2) [4, 5].
Germline mutations in the RUNX1 transcription factor have a distinct causal implication in a rare entity of myeloid neoplasms known as Familial Platelet Disorder with predisposition to Acute Myeloid Leukemia (FPD/AML) [6,7,8,9,10]. This is an autosomal dominant genetic condition typically characterized by hereditary thrombocytopenia and qualitative platelet dysfunction that is associated with a high rate (approximately 40%) of AML transformation [6, 11]. While several previous studies have identified a myriad of germline RUNX1 mutations implicated in FPD/AML (Table 1), second-hit mutational events are necessary for patients with hereditary thrombocytopenia to develop full-blown AML. However, the molecular picture behind this transformation process remains unclear. We herein describe an FPD/AML patient with a hitherto unreported 7-bp germline RUNX1 frameshift deletion (NM_001754.4:c.554_560delAAGTCGC; NP_001745.2:p.Gln185ProfsTer24) who was diagnosed and treated at our hematological practice. We also sought to identify second-hit mutational events that could have brought about the AML transformation from a pre-leukemic germline RUNX1-mutated state.
Case presentation
A 27-year-old Malay woman presented at our hematology clinic with a fever and sore throat. She had a history of hereditary thrombocytopenia that affected her father and 3 brothers. Preliminary clinical investigation at diagnosis revealed abnormal levels of hematological markers - the patient had a white blood cell count of 1.97 × 109 /L (normal: 3.4–9.6 × 109 /L), hemoglobin levels of 7.0 g/dL (normal: 10.9–15.1 g/dL) and platelet count of 20 × 109 /L (normal: 132–372 × 109/L). On morphological analysis, her bone marrow was moderately cellular, with dysplastic changes as well as increased numbers of myeloblasts and monoblasts/promonocytes, indicative of AML with myelodysplastic changes (Fig. 1a). Initial molecular testing by conventional Sanger sequencing revealed the same novel RUNX1 mutation in the patient, her father and 3 brothers (Fig. 2). A buccal analysis also confirmed that the RUNX1 mutation identified in this FPD/AML patient is germline in nature.
a Bone marrow aspirate at diagnosis depicting red cell anisopoikilocytosis, hypogranular platelets, myeloblasts and monoblasts/promonocytes. b Bone marrow aspirate after induction chemotherapy depicting red cell dysplasia with intercytoplasmic bridging and occasional myeloblasts. c Bone marrow aspirate after stem cell transplant depicting a normal haematopoietic maturation and no myeloblasts or monoblasts seen
Capillary electropherogram obtained from the ABI PRISM 3700 genetic analyzer. Double peaks are observed from the nucleotide at marker position 42 (indicated above), revealing 2 different sequences: Sequence #1: AA GTC GCC ACC TAC CAC AGA GCC AT (wild-type). Sequence #2: -- --- --C ACC TAC CAC AGA GCC ATC AAA ATC (7-bp deletion)
The patient received standard induction chemotherapy that consisted of high-dose anthracycline and cytarabine in a 3 + 7 regimen and subsequently attained complete morphological remission. Post-induction evaluation of her bone marrow revealed a regenerating bone marrow in morphological remission with myelodysplastic changes (Fig. 1b), as well as 0.3% residual disease, measured using Flow Cytometry. Thereafter, she was given consolidation chemotherapy with cytarabine. As no matched sibling donor or matched unrelated donor was available, she received a haploidentical stem cell transplant (haplo-SCT) from her mother, who is RUNX1-mutation negative. While she engrafted on Day 15 of her transplant, her admission was complicated by Klebsiella bacteraemia, acute Graft-versus-Host Disease (GvHD) of her liver and Cytomegalovirus reactivation. Post-haplo-SCT, she was given Tacrolimus, Mycophenolate Mofetil and Methotrexate as GvHD prophylaxis. A post-transplant bone marrow aspirate after count recovery showed a normocellular reactive marrow (Fig. 1c) and 0% residual disease on Flow Cytometry.
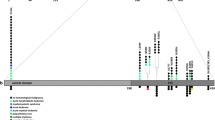
With informed consent obtained from the patient, a comprehensive genomic mutational analysis on a targeted next-generation sequencing (NGS) platform was conducted using either peripheral blood (PB) or bone marrow (BM) samples collected at three different stages – at diagnosis (pre-treatment), post-treatment (after induction and consolidation chemotherapy) and post-haplo-SCT. These time points coincided with the bone marrow examinations done for the patient, as mentioned above. In brief, 568 amplicons (‘tiles’) covering 54 genes that were previously implicated in myeloid neoplasms were assessed for the presence of genomic variants. At each stage, the patient’s genomic DNA was extracted and processed using the TruSeq Custom Amplicon (TSCA) assay for the TruSight Myeloid Sequencing Panel, according to a previously described methodology [12, 13]. The 54 genes evaluated in this targeted gene panel were as follows: ABL1, ASXL1, ATRX, BCOR, BCORL1, BRAF, CALR, CBL, CBLB, CBLC, CDKN2A, CEBPA, CSF3R, CUX1, DNMT3A, ETV6, EZH2, FBXW7, FLT3, GATA1, GATA2, GNAS, HRAS, IDH1, IDH2, IKZF1, JAK2, JAK3, KDM6A, KIT, KMT2A, KRAS, MPL, MYD88, NOTCH1, NPM1, NRAS, PDGFRA, PHF6, PTEN, PTPN11, RAD21, RUNX1, SETBP1, SF3B1, SMC1A, SMC3, SRSF2, STAG2, TET2, TP53, U2AF1, WT1 and ZRSR2. After sequence alignment against the reference GRCh37/hg19 human genome assembly, BAM and VCF files were produced by the TruSeq Amplicon software (V.1.1.0.0). Genome annotation was done on the VCF files using the Illumina VariantStudio (V.2.2). Only variants that met the following criteria were selected: non-synonymous mutation, variant not present in dbSNP, read-depth > 100×, variant-allele frequency (VAF) > 5% and acceptable sequence quality. The comprehensive list of mutations, including the hitherto unreported germline RUNX1 mutation, identified in the pre-treatment, post-treatment and post-haplo-SCT blood samples can be found in (Table 2; Fig. 3). A total of 8 mutations were detected in the pre-treatment sample when she had AML, 5 mutations remained on her post-chemotherapy analysis where there was residual myelodysplasia, and no mutations were present after haplo-SCT. At the time of writing, she is currently 14 months post-transplant, with no evidence of disease relapse, with 100% Donor chimerism.
Discussion and conclusions
Germline RUNX1-mutated FPD/AML, albeit rare, is a relatively well-established entity in myeloid neoplasms. The key publications on novel germline RUNX1 mutations identified in different FPD/AML pedigrees are listed in Table 1. However, the understanding of the molecular evolution in clonal hematopoietic cells of germline RUNX1-mutated patients that led to AML development remains unclear. It is known that less than half of the germline RUNX1-mutated patients with hereditary thrombocytopenia eventually develop AML [11] and for those FPD cases that do transform into myelodysplastic syndrome/AML (MDS/AML), the latency period can range from 6 to 76 years [14]. This is a strong indication that second-hit mutational events, on top of the primary germline RUNX1 mutation, are required for leukemogenesis to occur. In light of this, we herein report potential preleukemic and second-hit mutational events in an FPD/AML patient who was detected with a novel 7-bp germline RUNX1 deletion.
Firstly, to the best of our knowledge, we identified a hithertho unreported 7-bp germline RUNX1 deletion (c.554_560delAAGTCGC) in this FPD/AML patient that has not been previously documented in ClinVar (http://www.clinicalgenome.org/data-sharing/clinvar/). Given that the same RUNX1 deletion was also detected in the patient’s father and 3 brothers, we essentially identified a novel germline RUNX1 mutation in another FPD/AML pedigree. The patient’s father and 3 brothers all have thrombocytopenia with no evidence of MDS or AML, and are currently on follow-up at our clinic to monitor for onset of myeloid malignancies. This germline RUNX1 mutation is most likely monoallelic, as the VAF is close to 50%. This is in accordance to previous reports of heterozygous germline RUNX1 mutations in FPL/AML pedigrees that indicated RUNX1 haploinsufficiency [6,7,8, 15].
It is known that RUNX1, also known as CBFα2 or AML1, is a master transcription factor that plays a crucial role in regulating the expression of several genes involved in hematopoiesis [16, 17], such as GM-CSF [18] and c-Mpl [19]. In fact, RUNX1 is found to be required in the initiation of definitive hematopoiesis during embryological development [16], where the knockout of RUNX1 gene in mice led to a complete lack of liver hematopoiesis, culminating in CNS hemorrhage and death typically at embryonic day 12.5 [20]. Physiologically, it is most probable that a typical loss-of-function heterozygous RUNX1 mutation such as the one identified in this patient would, at the very least, disrupt hematopoietic differentiation [21], as with other Class II mutations [2, 22].
The 7-bp germline frameshift mutation identified in our patient affects the Runt domain of the RUNX1 protein. Most previously reported germline RUNX1 mutations in FPD/AML also implicate the Runt domain [6,7,8, 10, 23, 24]. In brief, the RUNX1 protein constitutes the α-subunit of the core binding factor (CBF) [25] and the Runt domain is a DNA-binding domain that binds to a TGT/cGGT consensus sequence in the promoter or enhancer region of the hematopoietic target genes that RUNX1 regulates [23]. Notably, the Runt domain also binds to the non-DNA binding β-subunit of CBF (CBFβ) to form a crucial heterodimeric transcriptional complex that significantly enhances RUNX1 DNA-binding affinity [25,26,27,28]. The 7-bp frameshift RUNX1 deletion identified in our patient results in a truncated protein that lacks the C-terminal moiety of the Runt domain and is therefore likely to be a loss-of-function mutation. Given RUNX1 haploinsufficiency [6], we believe that this would probably result in insufficient levels of RUNX1 protein product synthesized for proper hematopoietic regulation. As such, this can explain our patient’s history of congenital thrombocytopenia.
On targeted NGS analysis of the patient’s molecular profile, we identified a total of 8 mutations, including the germline 7-bp RUNX1 deletion, in the pre-treatment sample, of which 5 were found in the post-treatment sample and none were detected in the post-haplo-SCT sample (Table 2, Fig. 3). The 8 mutations detected during the pre-treatment molecular analysis included RUNX1 (germline), GATA2, DNMT3A, BCORL1, BCOR, 2 PHF6 and CDKN2A mutations. The 5 mutations that persisted in post-treatment molecular analysis were RUNX1 (germline), DNMT3A, BCORL1, BCOR and 1 out of 2 PHF6 mutations and the 3 mutations that were absent in the post-treatment sample were GATA2, CDKN2A mutations and a separate PHF6 mutation. The 3 mutations that were eradicated with induction chemotherapy were most probably somatic leukemic driver mutations that were only found in leukemic cells. Therefore, when complete morphological remission was attained, these 3 driver mutations were lost along with the malignant cells. On the contrary, the 5 mutations which were still present post-treatment were likely to be preleukemic mutations that are typically resistant to induction chemotherapy [11, 29]. The preleukemic mutant cells also seem to retain the ability to differentiate into mature cells [11].
In brief, a preleukemic clone can be described as a subpopulation of hematopoietic progenitor cells with a distinct aberrant molecular profile, which predispose individuals with it to AML development. The mutations carried in the preleukemic clone are not sufficient to cause AML and acquisition of secondary mutational events would be necessary. In our patient, it seems that the preleukemic clone contained RUNX1 (germline), DNMT3A, BCORL1, BCOR and PHF6 mutations and the secondary mutations acquired that drove AML transformation were likely GATA2, CDKN2A and an additional PHF6 mutation.
While the presence of chemotherapy-resistant leukemic driver mutations is possible, germline RUNX1 mutations [11] and DNMT3A mutations are well-reported preleukemic events [29, 30]. In fact, DNMT3A mutations have also been found to persist after complete morphological remission in AML [31, 32]. But to the best of our knowledge, BCORL1, BCOR and PHF6 mutations have not been reported as preleukemic mutations in FPD/AML and require further characterization. It was previously reported that patients with persisting mutations at complete morphological remission have a less favorable event-free and overall survival, as compared to patients without such mutations [33]. However, DNMT3A mutations detected at complete remission have not been found to affect survival outcome [31, 34]. Therefore, further studies would need to be conducted to better define mutations found in preleukemic clones and more importantly, determine the prognostic significance of such mutations. This may then provide a basis to screen AML patients for specific preleukemic mutations post-induction chemotherapy to guide further treatment decision.
Interestingly, in 2014, a Japanese study identified somatic CDC25C and GATA2 mutations as sequential preleukemic and secondary mutational events respectively, in the malignant transformation of germline RUNX1-mutated FPD/AML [35]. However, CDC25C mutations were not detected in a subsequent study in the United States, possibly due to ethnic differences [36].
In our patient, we identified GATA2, CDKN2A and PHF6 mutations as potential secondary leukemic driver mutations in germline RUNX1-mutated AML. Of note, PHF6 mutations are known to be closely associated with RUNX1 in myeloid neoplasms but in a different clonal evolution setting where PHF6 mutations precede RUNX1 mutations [37]. In general, second-hit mutational events responsible for propelling a preleukemic clone in germline RUNX1-mutated FPD/AML into frank leukemia are not commonly reported. Preudhomme et al. (2009) identified secondary RUNX1 somatic mutations as potential second-hit events in germline RUNX1-mutated FPD/AML [24] and subsequently, Shiba et al. (2012) reported an acquired CBL mutation as a possible second-hit mutational event in a case of FPD transformation to Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia (CMML) [38].
Overall, there were no concomitant driver mutations in de novo AML such as NPM1 or FLT3 mutations detected in our germline RUNX1-mutated FPD/AML patient, in accordance to what was previously reported [11]. More importantly, the Class II germline RUNX1 mutation in this patient was not accompanied by a Class I mutation. This suggests that an alternative to the conventional “2-hit” model for AML pathogenesis [2] that requires the presence of both Class I and Class II mutations is required in FPD/AML cases.
In summary, we identified a novel 7-bp germline RUNX1 deletion in an FPD/AML patient that is found in the important Runt domain of RUNX1. Through molecular analysis, we also identified possible preleukemic and second-hit mutational events implicated in the pathogenesis of germline RUNX1-mutated AML. Further studies at the cohort level are required to assess the prevalence of these putative preleukemic and secondary mutations in FPD/AML. In addition, prognostic significance of preleukemic mutations that persist after complete remission needs to be established. With better classification of mutations implicated in FPD/AML and other types of AML into preleukemic and second-hit events, this can potentially improve molecular risk stratification of AML patients that can guide disease management.
Abbreviations
- AML:
-
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- BM:
-
Bone marrow
- CBF:
-
Core binding factor
- FPD/AML:
-
Familial Platelet Disorder with predisposition to Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- GvHD:
-
Graft-versus-host Disease
- Haplo-SCT:
-
Haploidentical stem cell transplant
- MDS/AML:
-
Myelodysplastic Syndrome/Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- NGS:
-
Next-generation sequencing
- PB:
-
Peripheral blood
- TSCA:
-
TruSeq Custom Amplicon
- VAF:
-
Variant-allele Frequency
References
Takahashi S. Current findings for recurring mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. J Hematol Oncol. 2011;4:36.
Gary Gilliland D, Griffin JD. The roles of FLT3 in hematopoiesis and leukemia. Blood. 2002;100:1532–42.
Dombret H. Gene mutation and AML pathogenesis. Blood. 2011;118:5366–7.
Thiede C. Mutant DNMT3A: teaming up to transform. Blood. 2012;119:5615–7.
Murati A, Brecqueville M, Devillier R, Mozziconacci M-J, Gelsi-Boyer V, Birnbaum D. Myeloid malignancies: mutations, models and management. BMC Cancer. 2012;12:304.
Song WJ, Sullivan MG, Legare RD, Hutchings S, Tan X, Kufrin D, et al. Haploinsufficiency of CBFA2 causes familial thrombocytopenia with propensity to develop acute myelogenous leukaemia. Nat Genet. 1999;23:166–75.
Michaud J, Wu F, Osato M, Cottles GM, Yanagida M, Asou N, et al. In vitro analyses of known and novel RUNX1/AML1 mutations in dominant familial platelet disorder with predisposition to acute myelogenous leukemia: implications for mechanisms of pathogenesis. Blood. 2002;99:1364–72.
Walker LC, Stevens J, Campbell H, Corbett R, Spearing R, Heaton D, et al. A novel inherited mutation of the transcription factor RUNX1 causes thrombocytopenia and may predispose to acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2002;117:878–81.
Minelli A, Maserati E, Rossi G, Bernardo ME, De Stefano P, Cecchini MP, et al. Familial platelet disorder with propensity to acute myelogenous leukemia: genetic heterogeneity and progression to leukemia via acquisition of clonal chromosome anomalies. Genes Chromosom Cancer. 2004;40:165–71.
Buijs A, Poddighe P, Van Wijk R, Van Solinge W, Borst E, Verdonck L, et al. A novel CBFA2 single-nucleotide mutation in familial platelet disorder with propensity to develop myeloid malignancies. Blood. 2001;98:2856–8.
Koeffler HP, Leong G. Preleukemia: one name, many meanings. Leukemia. 2017;31:534–42.
Yan B, Ng C, Moshi G, Ban K, Lee P-L, Seah E, et al. Myelodysplastic features in a patient with germline CEBPA-mutant acute myeloid leukaemia. J Clin Pathol. 2016;69:652–4.
Yan B, Hu Y, Ng C, Ban KHK, Tan TW, Huan PT, et al. Coverage analysis in a targeted amplicon-based next-generation sequencing panel for myeloid neoplasms. J Clin Pathol. 2016;69:801–4.
Churpek JE, Lorenz R, Nedumgottil S, Onel K, Olopade OI, Sorrell A, et al. Proposal for the clinical detection and management of patients and their family members with familial myelodysplastic syndrome/acute leukemia predisposition syndromes. Leuk Lymphoma. 2013;54:28–35.
Béri-Dexheimer M, Latger-Cannard V, Philippe C, Bonnet C, Chambon P, Roth V, et al. Clinical phenotype of germline RUNX1 haploinsufficiency: from point mutations to large genomic deletions. Eur J Hum Genet. 2008;16:1014–8.
Lam K, Zhang D-E. RUNX1 and RUNX1-ETO: roles in hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis. Front Biosci. 2012;17:1120–39.
Vu LP, Perna F, Wang L, Voza F, Figueroa ME, Tempst P, et al. PRMT4 blocks myeloid differentiation by assembling a methyl- RUNX1-dependent repressor complex. Cell Rep. 2013;5:1625–38.
Satoh Y, Matsumura I, Tanaka H, Ezoe S, Fukushima K, Tokunaga M, et al. AML1/RUNX1 works as a negative regulator of c-Mpl in hematopoietic stem cells. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:30045–56.
Takahashi A, Satake M, Yamaguchi-Iwai Y, Bae SC, Lu J, Maruyama M, et al. Positive and negative regulation of granulocyte-macrophage colony- stimulating factor promoter activity by AML1-related transcription factor, PEBP2. Blood. 1995;86:607–16.
Okuda T, Van Deursen J, Hiebert SW, Grosveld G, Downing JR. AML1, the target of multiple chromosomal translocations in human leukemia, is essential for normal fetal liver hematopoiesis. Cell. 1996;84:321–30.
Sakurai M, Kunimoto H, Watanabe N, Fukuchi Y, Yuasa S, Yamazaki S, et al. Impaired hematopoietic differentiation of RUNX1-mutated induced pluripotent stem cells derived from FPD/AML patients. Leukemia. 2014;28:2344–54.
Döhner K, Döhner H. Molecular characterization of acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 2008;93:976–82.
Osato M. Point mutations in the RUNX1/AML1 gene: another actor in RUNX leukemia. Oncogene. 2004;23:4284–96.
Preudhomme C, Renneville A, Bourdon V, Philippe N, Boissel N, Dhedin N, et al. High frequency of RUNX1 biallelic alteration in acute myeloid leukemia secondary to familial platelet disorder. Blood. 2009;113:5583–7.
Fukunaga J, Nomura Y, Tanaka Y, Amano R, Tanaka T, Nakamura Y, et al. The runt domain of AML1 (RUNX1) binds a sequence-conserved RNA motif that mimics a DNA element. RNA. 2013;19:927–36.
Wolf-Watz M, Xiao-Qi X, Holm M, GrundstroÈm T, HaÈrd T. Solution properties of the free and DNA-bound runt domain of AML1. Eur J Biochem. 1999;261:251–60.
Wang Q, Stacy T, Miller JD, Lewis AF, Gu TL, Huang X, et al. The CBFbeta subunit is essential for CBFalpha2 (AML1) function in vivo. Cell. 1996;87:697–708.
Ogawa E, Maruyama M, Kagoshima H, Inuzuka M, Lu J, Satake M, et al. PEBP2/PEA2 represents a family of transcription factors homologous to the products of the Drosophila runt gene and the human AML1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993;90:6859–63.
Corces-Zimmerman MR, Hong W-J, Weissman IL, Medeiros BC, Majeti R. Preleukemic mutations in human acute myeloid leukemia affect epigenetic regulators and persist in remission. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2014;111:2548–53.
Shlush LI, Zandi S, Mitchell A, Chen WC, Brandwein JM, Gupta V, et al. Identification of pre-leukaemic haematopoietic stem cells in acute leukaemia. Nature. 2014;506:328–33.
Sun Y, Shen H, Xu T, Yang Z, Qiu H, Sun A, et al. Persistent DNMT3A mutation burden in DNMT3A mutated adult cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia patients in long-term remission. Leuk Res. 2016;49:102–7.
Pløen GG, Nederby L, Guldberg P, Hansen M, Ebbesen LH, Jensen UB, et al. Persistence of DNMT3A mutations at long-term remission in adult patients with AML. Br J Haematol. 2014;167:478–86.
Klco JM, Miller CA, Griffith M, Petti A, Spencer DH, Ketkar-Kulkarni S, et al. Association between mutation clearance after induction therapy and outcomes in acute myeloid leukemia. J Am Med Assoc. 2015;314:811–22.
Bhatnagar B, Eisfeld A-K, Nicolet D, Mrózek K, Blachly JS, Orwick S, et al. Persistence of DNMT3A R882 mutations during remission does not adversely affect outcomes of patients with acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2016;175:226–36.
Yoshimi A, Toya T, Kawazu M, Ueno T, Tsukamoto A, Iizuka H, et al. Recurrent CDC25C mutations drive malignant transformation in FPD/AML. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4770.
Churpek JE, Pyrtel K, Kanchi K, Shao J, Koboldt D, Miller CA, et al. Genomic analysis of germ line and somatic variants in familial myelodysplasia/acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2015;126:2484–90.
Przychodzen B, Gu X, You D, Hirsch CM, Clemente MJ, Viny AD, et al. PHF6 - somatic mutations and their role in pathophysiology of MDS and AML. Blood. 2015;126:1259.
Shiba N, Hasegawa D, Park MJ, Murata C, Sato-Otsubo A, Ogawa C, et al. CBL mutation in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia secondary to familial platelet disorder with propensity to develop acute myeloid leukemia (FPD/AML). Blood. 2012;119:2612–4.
Heller PG, Glembotsky AC, Gandhi MJ, Cummings CL, Pirola CJ, Marta RF, et al. Low Mpl receptor expression in a pedigree with familial platelet disorder with predisposition to acute myelogenous leukemia and a novel AML1 mutation. Blood. 2005;105:4664–70.
Owen CJ, Toze CL, Koochin A, Forrest DL, Smith CA, Stevens JM, et al. Five new pedigrees with inherited RUNX1 mutations causing familial platelet disorder with propensity to myeloid malignancy. Blood. 2008;112:4639–45.
Acknowledgements
All contributors have met the criteria for authorship and are included in the author list.
Funding
W-JC is supported by NMRC Singapore Translational Research (STaR) Investigatorship. This research is partly supported by the National Research Foundation Singapore and the Singapore Ministry of Education under the Research Centers of Excellence initiative.
Availability of data and materials
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Provenance and peer review
Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
IKSN and JL wrote the manuscript. JL, ES and LKT treated the patients and collected the clinical samples. CN, BK, LC, MM performed the experiments. IKSN, JL, CN, BK, KT, MO, W-JC and BY contributed to study design, data analysis and interpretation. All authors reviewed and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
NHG Domain Specific Review Board (DSRB).
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication for this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Ng, I.K., Lee, J., Ng, C. et al. Preleukemic and second-hit mutational events in an acute myeloid leukemia patient with a novel germline RUNX1 mutation. Biomark Res 6, 16 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40364-018-0130-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40364-018-0130-2