Abstract
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) is a significant threat to the global swine industry. Porcine sialoadhesin (poSn) has been previously shown to mediate PRRSV attachment and internalization. In the current study, we report its unidentified role in antagonism of type I interferon (IFN) production during PRRSV infection. We determined that poSn facilitated PRRSV infection via inhibition of type I IFN transcription. Mechanistically, poSn interacted with a 12 kDa DNAX-activation protein (DAP12), which was dependent on residues 51–57 within DAP12 transmembrane domain (TMD). PRRSV exploited the poSn-DAP12 pathway to attenuate activation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB). More importantly, the poSn-DAP12 pathway was involved in inhibiting poly (I:C)-triggered IFN production. All these results reveal a novel role of poSn in suppressing host antiviral responses, which deepens our understanding of PRRSV pathogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) has been causing significant economic losses to the global swine industry [1]. Its clinical signs are respiratory distress and reproductive failure [2]. PRRS virus (PRRSV), as the causative agent, belongs to the Porarterivirus genus, Arteriviridae family in the order Nidovirales [3]. It is a single-stranded positive RNA virus with a genome of 14.9 to 15.5 kb in length. All PRRSV isolates are classified into PRRSV-1 and PRRSV-2, and PRRSV-2 strains are predominantly prevalent in China [4].
Porcine sialoadhesin (poSn) was first identified to be involved in PRRSV entry [5]. Subsequent research indicated that poSn is responsible for virus attachment and internalization, which is dependent on the sialic acid-binding activity of its N-terminal immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domain [6,7,8]. Non-permissive cells with co-expression of recombinant poSn and CD163 produce much more viral progenies than that expressing CD163 alone [9]. However, a recent report demonstrated that poSn knockout pigs are still susceptible to PRRSV [10]. These studies suggested that poSn might play certain unappreciated roles instead of an indispensable receptor during PRRSV infection.
poSn is a member of the sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin (Siglec) family, namely Siglec-1 [11, 12]. Increasing evidence has shown that Siglecs modulate type I interferon (IFN) responses during viral infections. For example, Siglec-G is reported to be induced and exploited by RNA viruses to inhibit retinoic acid-inducible gene-I (RIG-I)-mediated type I IFN production [13]. Siglec-H is demonstrated to negatively regulate IFN-α production in response to murine cytomegalovirus infection in vitro and in vivo [14]. Murine Siglec-1 has been recently shown to inhibit IFN responses through impairing tank binding kinase 1 (TBK1)-interferon regulatory factor (IRF)-3 pathway during vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) infection [15]. As a Siglec, whether poSn plays an immunosuppressive role during PRRSV infection has not been elucidated.
In this work, we unraveled that PRRSV utilized poSn to repress type I IFN production in favor of its infection. poSn associated with DNAX-activation protein of 12 kDa (DAP12) to attenuate PRRSV-triggered nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) activation. More importantly, poSn-DAP12 pathway negatively modulated transcription of type I IFNs in response to poly (I:C), suggesting that the pathway might be involved in maintaining homeostasis by avoiding excessive immune responses.
Materials and methods
Cells and virus
Pulmonary alveolar macrophages (PAMs) were obtained from lung lavage samples of 4-week-old pigs. CRL-2843-CD163 (the continuous PAM cell line stably expressing porcine CD163), MARC-145 (the derivative from African green monkey kidney cell line MA-104) and HEK-293T (human embryonic kidney 293 cell line stably expressing SV40 large T antigen) cells were used in our studies. HEK-293T and MARC-145 cells were maintained in Dulbecco modified Eagle medium (DMEM, Solarbio life sciences, Beijing, China) supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS, Gibco, Logan, UT, USA) and penicillin–streptomycin mixtures (Solarbio life sciences). PAMs and CRL-2843-CD163 cells were cultured in Roswell Park Memorial Institute-1640 medium (RPMI-1640, Solarbio life sciences) supplemented with 10% FBS and antibiotics.
A typical PRRSV-2 strain BJ-4 (GenBank accession no. AF331831) was a gift from Professor Hanchun Yang of China Agricultural University. rBJ4-EGFP was constructed by inserting enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) between open reading frame (ORF) 1b and ORF2a of PRRSV strain BJ-4 in our laboratory. These viruses used in our study were propagated in MARC-145 cells in DMEM with 3% FBS, and the virus titers were measured by 50% tissue culture infective dose (TCID50) assay in MARC-145 cells [16].
Antibodies and reagents
Antibodies: Mouse anti-poSn monoclonal antibody (mAb, clone 3B11/11) was purchased from LifeSpan BioSciences (LSBio, Seattle, WA, USA). Mouse anti-DAP12 mAb was from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA, USA). Rabbit anti-IRF-3, phospho-IRF-3 (Ser386), NF-κB p65 (D14E12), phospho-NF-κB p65 (Ser536) (93H1), myc-tag (71D10), Flag (DYKDDDDK)-tag (D6W5B), Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) (D16H11) and DAP12 mAbs, as well as mouse anti-nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor-alpha (IκBα) (L35A5), myc-Tag (9B11), Flag (DYKDDDDK) tag (9A3) and β-actin (8H10D10) mAbs were all purchased from Cell Signaling Technology (CST, Boston, MA, USA).
Reagents: In-Fusion HD Cloning Kit was purchased from TaKaRa (Dalian, Liaoning, China). Poly (I:C) and bovine serum albumin (BSA) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). pGL3-basic vector and pRL-TK control vector were from Promega (Madison, WI, USA). pcDNA3.1-myc-hisA was purchased from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA, USA) and p3 × Flag-CMV-7.1 was from Sigma-Aldrich [17].
Quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR)
Total RNAs were extracted using TRIzol reagents (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Hanover Park, IL, USA) from the indicated cells and reverse-transcribed into cDNA by PrimeScript™ RT Reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser (TaKaRa) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. RT-qPCR was performed using the Universal SYBR Green Master (Roche, Basel, Basel-Stadt, Switzerland) on the 7500 Fast RT-PCR system (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). PCR was conducted with 1 μL of cDNA with primers specific for PRRSV ORF7, poSn, DAP12, IFN-α and IFN-β (Table 1). GAPDH was set as the endogenous control. Data analysis of relative gene expression was applied to the 2−ΔΔCt method [18].
Immunoblotting (IB)
The indicated cells were lysed with radio immunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) lysis buffer (Beyotime Biotechnology, Shanghai, China) supplemented with protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche). After boiling, the indicated samples were subjected to sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) followed by transferring onto polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes (Merck Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA). The membranes were blocked with 5% skimmed-milk at room temperature (RT) for 2 h, and then incubated with the specific primary antibodies at RT for 2 h. After extensive washing with phosphate-buffered saline-Tween 20 (PBST), the membranes were incubated with the corresponding horse radish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated secondary antibodies at RT for 1 h. An enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) detection system was used to detect the indicated proteins (Solarbio life sciences).
Flow cytometry (FCM) analysis
After trypsin treatment, the transfected PAMs were collected and washed with PBS twice. The cells were centrifuged (200 × g) at 4 °C for 5 min and subsequently resuspended in 2% BSA-PBST buffer at 4 °C for 15 min. After centrifugation, the cells were incubated with the commercial anti-poSn mAb in 2% BSA-PBST buffer at 4 °C for 1 h. After washing with PBST 3 times, the cells were then incubated with Dylight 649 (red) conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (H+L) secondary antibody (Thermo Fisher Scientific) in 2% BSA-PBST buffer at 4 °C for 30 min. After washing, the cells were resuspended in 0.5% paraformaldehyde (PFA) in BSA-PBST buffer. Based on the acquisition of 2.0 × 104 cells, the data were analyzed using CytoFLEX (Beckman Coulter, Brea, CA, USA).
Knockdown assays
Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) targeting poSn or DAP12 (Table 2) were designed and synthesized by GenePharma (Shanghai, China). Transfection of siRNA was conducted in PAMs with Lipofectamine RNAiMAX Reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific) for the indicated time periods (35 h or 47 h). The knockdown efficiencies were determined by RT-qPCR or FCM analyses.
Plasmid construction and overexpression
All target genes were cloned from PAM cDNA. Complete poSn, poSn-extracellular domain (ECD, residues 1–1642, the numbering is according to UniProt entry A7LCJ3) and poSn-helical transmembrane plus cytoplasmic domain (TCD, residues 1643–1730) were cloned into pcDNA3.1-mychisA. DAP12, DAP12-Δ intracellular domain (ICD, residues 1–57, the numbering is according to UniProt entry Q9TU45), DAP12-ΔECD (residues 37–108), DAP12-ΔTM1 (the absence of residues 37–43), -ΔTM2 (the absence of residues 44–50) and -ΔTM3 (residues 51–57) were inserted into p3×Flag-CMV-7.1, respectively. Overexpression assays were performed with transfection of the indicated plasmids by Lipofectamine® LTX with Plus™ Reagent according to Thermofisher’s instructions in CRL-2843-CD163, or HEK-293T cells. The primers were listed in Table 1. All constructs were verified by Shanghai Sangon Biotechnology (Shanghai, China).
Dual-luciferase assays
Luciferase assays were conducted by Dual-Luciferase® Reporter Assay System according to Promega’s instructions. In brief, CRL-2843-CD163 cells were transfected with 1 μg pig IFN-β-promoter [19] and 100 ng pRL-TK renilla luciferase reporter plasmid as an internal control, and then transfected with 350 ng 3×Flag-DAP12 and 650 ng poSn-myc-his. pRIG-I [19] was used to stimulate the activity of pig IFN-β promoter. The transfected cells were lysed in passive lysis buffer and subjected to luciferase activity measurement.
Indirect immunofluorescence assay (IFA)
PRRSV-infected PAMs were fixed with 4% PFA buffer (Solarbio life sciences) at RT for 15 min followed by membrane permeabilization with 0.2% Tween-20. The cells were then incubated with mouse anti-poSn mAb and rabbit anti-DAP12 mAb in 2% BSA-PBST buffer at 4 °C overnight. After washing with PBST, the cells were incubated with DyLight 405 (blue) conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) secondary antibody and Dylight 649 (red) conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (H+L) secondary antibody (Thermo Fisher Scientific) at 4 °C for 1 h, respectively. After washing, the cells with SlowFade® Gold buffer (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA) were visualized by a laser scanning confocal microscope (LSM 800, Carl Zeiss AG, Oberkochen, Germany).
Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP)
Transfected HEK-293T cells were lysed in IP lysis buffer (Beyotime Biotechnology) at 4 °C for 30 min. After centrifugation at 12 000 g at 4 °C for 15 min, whole cell lysates (WCLs) were harvested to mix with anti-myc or anti-Flag mAbs (CST), and then incubated with Protein A/G beads (GE Healthcare, Pittsburgh, PA, USA) at the rotator at 4 °C for 3 h or overnight. After extensive washing with Tris-buffered saline with 0.5% Tween-20 (TBST), the beads were vortexed with elution buffer (0.05 M glycine–HCl buffer pH 2.2) thoroughly. The eluted proteins were subjected to IB.
Poly (I: C) stimulation
Poly (I:C), the synthetic analog of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), is experimentally used to trigger type I IFN production [20]. We transfected the various amounts (0.25, 2 or 2.5 μg/mL) of poly (I:C) into CRL-2843-CD163 cells or poSn (or DAP12) knockdown PAMs with Lipofectamine RNAiMAX Reagent for the indicated time points (0, 2, 4, 12 h or 0, 3, 6 h). The cells were then subjected to RT-qPCR to detect the transcription of poSn and IFN-α/β.
Statistical analysis
All experiments were independently repeated at least 3 times and each experiment included at least three replicates. RT-qPCR data were analyzed using Student t test method with GraphPad Software (San Diego, CA, USA), and denoted as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). The asterisk (*) indicated for statistical significance: *p < 0.05, **p <0.01, ***p <0.001; ns: not significant.
Results
poSn facilitates PRRSV infection and inhibits PRRSV-induced IFN-α/β transcription
To verify the biological significance of poSn during PRRSV infection, we examined the effects of poSn knockdown on PRRSV infection and PRRSV-triggered type I IFN production. We pre-inoculated PRRSV into its primary in vivo target, PAMs [21], and then extensively washed the cells with serum-free medium followed by poSn knockdown assays. Two siRNAs (332# and 1983#) targeting poSn were synthesized and transfected into PAMs. The knockdown efficiencies were determined by FCM analysis (Figure 1A). First, we determined PRRSV replication by detecting expression of the viral nucleocapsid (N) protein. poSn knockdown decreased the abundance of PRRSV N protein (Figure 1B). Subsequently, we measured the viral titers from the supernatants of poSn knockdown or untreated PAMs. poSn knockdown suppressed PRRSV release as shown by TCID50 assay (Figure 1C). Furthermore, we checked PRRSV-induced transcription of type I IFN after poSn knockdown. poSn knockdown promoted the IFN-β transcription (Figure 1D), which suppressed PRRSV infection (Figures 1B and C). All these results suggest that poSn facilitates PRRSV infection by inhibiting the virus-triggered type I IFN production.
poSn promotes PRRSV infection by inhibiting PRRSV-triggered IFN-βtranscription.A–D PAMs were pre-inoculated with PRRSV (MOI = 1) at 37 °C for 1 h. After washing with serum-free RPMI-1640, PAMs were transfected with sipoSn-332# or sipoSn-1983# for 47 h. poSn knockdown was determined by FCM A. IB was used to detect the abundance of PRRSV N protein B. PRRSV TCID50/mL of supernatants was measured, which was independently repeated three times C. IFN-β transcription was detected by RT-qPCR, which was independently repeated three times D. Data were denoted as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was applied to Student t test: *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001. FCM images were representative from two independent experiments.
poSn is determined to interact with DAP12 during PRRSV infection
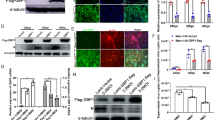
Murine Siglec 1, the homolog of poSn, has been reported to inhibit type I IFN production by interacting with DAP12 during VSV infection [15]. To dissect the mechanism by which poSn played the IFN-suppressive role during PRRSV infection, we examined whether poSn interacted with DAP12 upon viral infection. We first observed that poSn co-localized with DAP12 by confocal microscopy in PRRSV-infected PAMs (Figure 2A). Subsequently, we immunoprecipitated DAP12 or poSn from the WCLs of HEK-293T cells co-transfected with poSn-myc-his and 3×Flag-DAP12. The Co-IP results confirmed the interaction between poSn and DAP12 (Figure 2B).
poSn interacts with DAP12 in PRRSV-infected PAMs.A PAMs were infected with rBJ4-EGFP (MOI = 1) for 24 h. Cells were fixed by 4% PFA for 15 min at RT and permeabilized with 0.2% Tween-20 for membrane protein staining. poSn was stained with DyLight 405 (blue) and DAP12 was stained with DyLight 649 (red). The co-localization of the two proteins was visualized by confocal microscopy. Scale bars, 10 μm. B HEK-293T cells were co-transfected with poSn-myc-his (10 μg) and 3×Flag-DAP12 (6 μg) for 48 h. WCLs were subjected to IP assays with anti-myc mAb or anti-Flag mAb. IB was performed to detect the indicated proteins. The confocal images were representative from two independent experiments, and IB panels were representative from three independent experiments.
Next, we explored how poSn interacted with DAP12. We divided poSn into two fragments, the poSn-ECD (residues 1–1642) and poSn-TCD (residues 1643–1730), into pcDNA3.1-mychisA as poSn-ECD-myc-his and poSn-TCD-myc-his, respectively. We conducted IP assays with anti-myc mAb and WCLs from HEK-293T co-transfected with 3×Flag-DAP12 and poSn-ECD-myc-his or poSn-TCD-myc-his. IB analysis showed that poSn ECD was not required for its interaction with DAP12 (Figure 3A).
poSn-TCD and DAP12 TMD are responsible for their interaction.A HEK-293T cells were transfected with 3×Flag-DAP12 (6 μg) and poSn-TCD-myc-his (6 μg) or poSn-ECD-myc-his ( μg) for 48 h. WCLs were subjected to IP assays with anti-myc mAb at 4 °C for 3 h. IB was used to detect the indicated proteins. B IP assays with anti-myc mAb were performed using WCLs from HEK-293T cells co-transfected with poSn-myc-his (10 μg) and 6 μg 3×Flag-DAP12-ΔICD or 3×Flag-DAP12-ΔECD for 48 h. IB analysis was performed to examine the specific proteins. IB panels were representative from three independent experiments.
We constructed two DAP12 fragments: 3×Flag-DAP12-ΔICD (residues 1–57), DAP12 with deletion of ICD, and 3×Flag-DAP12-ΔECD (residues 37–108), DAP12 with deletion of ECD. WCLs were subjected to IP analysis from HEK-293T cells co-transfected with poSn-myc-his and 3×Flag-DAP12-ΔICD or 3×Flag-DAP12-ΔECD. We found that DAP12-ΔICD and DAP12-ΔECD both bound to poSn, suggesting that DAP12 transmembrane domain (TMD) was responsible for its interaction with poSn (Figure 3B).
The negatively charged aspartic acid at position 50 (D50) of DAP12 is essential for its electrostatic interaction with certain immunoreceptors possessing positively charged residues within their TMDs [22, 23]. We sought to determine whether D50 was required for DAP12′s association with poSn. We mutated D50 to alanine (DAP12-D50A), and found that this mutation had no effects on the interaction (Figure 4A). We further deleted partial residues within DAP12 TMD and obtained three DAP12 mutants (DAP12-ΔTM1, -ΔTM2, and -ΔTM3) [17]. Using anti-Flag mAb to immunoprecipitate Flag-tagged DAP12 or its mutants, we demonstrated that residues 51–57 were indispensable for the interaction between DAP12 and poSn-TCD (Figure 4B). The IP assay with anti-myc mAb also confirmed the above result (Figure 4B). Collectively, these results revealed that, in PRRSV-infected cells, poSn interacted with DAP12 dependent on poSn TCD and DAP12 residues 51–57.
Residues 51–57 are responsible for interaction between DAP12 and poSn.A HEK-293T cells were co-transfected with 6 μg poSn-TCD-myc-his and 6 μg 3×Flag-DAP12 or DAP12-D50A for 48 h. Co-IP experiments were performed with anti-Flag mAb or anti-myc mAb. The indicated proteins were analyzed by IB from eluted proteins and WCLs. B HEK-293T cells were co-transfected with 6 μg poSn-TCD-myc-his and 6 μg 3×Flag-DAP12 or the indicated DAP12 mutants (DAP12-ΔTM1, ΔTM2 or ΔTM3) for 48 h. WCLs were incubated with Protein A/G beads bound to anti-Flag or anti-myc mAb at 4 °C overnight. IB analysis was conducted for detecting DAP12, DAP12 mutants or poSn-TCD. IB panels were representative from three independent experiments.
poSn-DAP12 pathway mediates inhibition of type I IFN production during PRRSV infection
Since DAP12 was a binding partner of poSn during PRRSV infection, we investigated the effects of DAP12 knockdown on PRRSV-triggered IFN-α/β transcription. As shown in Figures 5A and B, knockdown of DAP12 (siDAP12-433#) suppressed PRRSV replication as indicated by decreased PRRSV ORF7 mRNA levels. We further evaluated the viral release by TCID50 assay. DAP12 knockdown decreased the viral titers from the supernatants of PRRSV-infected PAMs (Figure 5C). In contrast, DAP12 knockdown increased the mRNA abundance of IFN-α/β in response to PRRSV (Figure 5D). These results were similar to that in poSn knockdown PAMs (Figure 1). Moreover, we conducted dual-luciferase assays in the continuous PAM cell line CRL-2843-CD163 that stably expresses porcine CD163 and is permissive to PRRSV [24]. Co-expression of poSn and DAP12 inhibited IFN-β promoter activation triggered by pig RIG-I (pRIG-I) overexpression (Figure 5E). Together, these results suggest that the poSn-DAP12 pathway is involved in restraining PRRSV-induced type I IFN production, which is beneficial for the viral infection.
poSn-DAP12 pathway facilitates PRRSV infection through suppressing type I IFN production.A–D PAMs were transfected with siDAP12-433# for 36 h, and then infected with PRRSV (MOI = 1) for the indicated time periods (4, 12, 24, 48 h). DAP12 knockdown was determined by RT-qPCR and IB A. PRRSV ORF7 was examined by RT-qPCR at 4 or 12 h post-infection B. TCID50 assay was performed to measure the viral titers at 24 or 48 h post-infection C. RT-qPCR was used to detect transcription of IFN-α/β at 4 or 12 h post-infection D, E Pig IFN-β promoter was activated by 3×Flag-pRIG-I overexpression, and the relative luciferase activity (Rel. luc. Act) of pig IFN-β promoter was measured in CRL-2843-CD163 cells transfected with poSn-myc-his and/or 3×Flag-DAP12 by dual-luciferase reporter assays. Data were indicated as mean ± SEM. Statistical significances were shown by Student t test: *p < 0.05, **p <0.01, ***p <0.001.
poSn-DAP12 pathway is involved in suppression of NF-κB activation in response to PRRSV
NF-κB and IRF-3 are key transcription factors for type I IFN production [25]. Therefore, we evaluated whether poSn-DAP12 pathway suppressed type I IFN production by impairing NF-κB and IRF-3 activation triggered by PRRSV. We first investigated the effects of poSn knockdown on their activation. We pre-incubated PAMs with PRRSV followed by knockdown assays. poSn knockdown (Figure 6A) augmented p65 phosphorylation via promoting IκB-α degradation, while the IRF-3 phosphorylation was not influenced (Figure 6B). PRRSV infection was inhibited indicated by the decreased PRRSV N protein expression in poSn knockdown PAMs (Figure 6B).
poSn-DAP12 pathway mediates inhibition of NF-κB in response to PRRSV.A, B PAMs were pre-incubated with PRRSV (MOI = 1) for 1 h. After washing with serum free medium extensively, the cells were transfected with the indicated sipoSns for 35 h. poSn knockdown efficiencies were examined by RT-qPCR (A). IB analysis was performed to examine the expression of PRRSV N protein, and the activation of IRF-3 and NF-κB (B). C, DDAP12 knockdown PAMs were infected with PRRSV (MOI = 1) for indicated time periods (0, 3, 6, 9, 12, 24 h). IB was conducted to determine the abundance of PRRSV N protein (C ,D), and the activation of NF-κB (C) and IRF-3 (D). E DAP12-overexpressed CRL-2843-CD163 cells were infected with PRRSV (MOI = 5) for the indicated time periods (0, 3, 6 h). IB was adopted to detect IκB-α degradation and phosphorylation of IRF-3 and p65. IB panels were representative from three independent experiments. RT-qPCR data were indicated as mean ± SEM. Statistical significances were shown by the Student t test: ***p <0.001.
Additionally, we examined the role of DAP12 in PRRSV-triggered NF-κB and IRF-3 activation. We inoculated untreated or DAP12 knockdown PAMs with PRRSV. DAP12 knockdown enhanced the phosphorylation of p65 and IRF-3, while suppressing PRRSV infection (Figures 6C and D). On the contrary, we found that DAP12 overexpression in CRL-2843-CD163 cells suppressed p65 phosphorylation by reducing IκB-α degradation, as well as IRF-3 phosphorylation, during PRRSV early infection (Figure 6E).
Collectively, all these results indicate that the poSn-DAP12 pathway participates in inhibiting NF-κB-mediated type I IFN signaling during PRRSV infection.
poSn-DAP12 participates in antagonism of type I IFN production in response to poly (I:C)
To further probe the IFN-suppressive role of poSn, we examined the effects of poSn knockdown on poly (I:C)-stimulated type I IFN production in PAMs. As shown in Figure 7A, knockdown of poSn increased the mRNA abundance of IFN-α/β in response to poly (I:C). On the contrary, poSn overexpression in CRL-2843-CD163 cells attenuated IFN-β transcription triggered by poly (I:C) (Figures 7B and C). In the following experiments, we investigated the effects of DAP12 knockdown on type I IFN production triggered by poly (I:C). DAP12 knockdown promoted IFN-α/β transcription during poly (I:C)-stimulated periods (Figures 7D and E). In summary, these data suggest that poSn-DAP12 pathway participates in suppressing type I IFN production in response to poly (I:C).
poSn-DAP12 pathway mediates the inhibition of type I IFN production in response to poly (I:C).A PAMs were transfected with sipoSn-332# or sipoSn-1983# for 36 h, and then stimulated with 0.25 μg/mL poly (I:C) for 12 h. RT-qPCR analysis was performed to measure the mRNA abundance of poSn and IFN-α/β. B, C CRL-2843-CD163 cells with poSn overexpression were transfected with 2.5 μg/mL poly (I:C) for the indicated time periods (0, 2, 4 h). poSn expression was determined by IB (B). IFN-β transcription was examined by RT-qPCR (C). D, EDAP12 knockdown PAMs were stimulated with 2 μg/mL poly (I:C) for the indicated time periods (0, 3, 6 h). DAP12 knockdown was determined by IB (D). IFN-α/β transcription was detected by RT-qPCR (E). Quantification data were indicated as mean ± SEM. Statistical significances were shown by Student t test: *p < 0.05, **p <0.01, ***p <0.001.
Discussion
Viral infections usually elicit host innate immune responses, including type I IFN (such as IFN-α/β) production [26, 27]. Various pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) sense the pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) to induce activation of IRF-3 or NF-κB [28, 29], which promotes the transcription of type I IFNs and other cytokines [30]. PRRSV has evolved various strategies, such as targeting NF-κB- and/or IRF-3/7-mediated signaling pathways, to antagonize the production of type I IFNs [31,32,33]. Here, we reveal a novel strategy in which PRRSV exploits poSn to negatively regulate host innate immune responses.
We first explored the biological role of poSn in PRRSV infection, and found that poSn knockdown inhibited PRRSV infection by promoting production of type I IFNs in PAMs (Figure 1). Furthermore, we demonstrated that poSn suppressed type I IFN production in response to poly (I:C) (Figure 7), suggesting that poSn-mediated inhibition of IFN responses might be a generic mechanism for host immune regulation. Our study actually uncovered that poSn plays an immunosuppressive role instead of an essential receptor during PRRSV infection.
DAP12 is an immune adaptor involved in modulating innate immune responses [34]. In most cases, DAP12-associated receptors recruit DAP12 and activate the innate immune responses upon recognizing PAMPs [35, 36]. In contrast, we here demonstrated that DAP12 suppressed the virus-triggered type I IFN responses, which was consistent with other reports [37, 38]. DAP12 knockdown restricted PRRSV infection by increasing type I IFN production (Figures 5A–D), which was similar to the effects of poSn knockdown (Figure 1). Since some previous studies indicated that murine Siglec-1 or human Siglec-H interacts with DAP12 to attenuate IFN responses [14, 15, 39, 40], we explored the interaction between poSn and DAP12 during PRRSV infection. We first observed the co-localization of poSn and DAP12 during viral infection (Figure 2A). Subsequently, we confirmed the interaction between poSn and DAP12 by Co-IP (Figure 2B). Moreover, dual-luciferase reporter assays in CRL-2843-CD163 cells indicated that co-expression of poSn and DAP12 inhibited pRIG-I-mediated pig IFN-β promoter activation (Figure 5E). These findings demonstrate that the poSn-DAP12 pathway is involved in dampening type I IFN production, which might be exploited by PRRSV for persistent infection.
In the current study, we further showed that poSn interacted with DAP12, which was dependent on poSn TCD and DAP12 TMD (Figures 2 and 3). We constructed the eukaryotic plasmid poSn without TMD, but failed to express the indicated protein in HEK-293T cells. We hypothesized that poSn TMD was critical for expression and responsible for the interaction between poSn and DAP12. In general, DAP12 D50 is essential for its association with some receptors possessing positively charged residues in their TMDs [35]. We found that there were no positively charged residues in poSn TMD (UniProt entry A7LCJ3), and DAP12 D50 was dispensable for the interaction. Furthermore, we constructed three DAP12 truncations where certain residues within their TMDs were deleted. After a series of Co-IP experiments, we proved that residues 51–57 are critical for the interaction (Figure 4). In another paper, we also found that DAP12 with deletion of residues 51–57 was unable to interact with nonmuscle myosin heavy chain IIA [17]. According to these findings, we speculate that DAP12 residues 51–57 are essential for its interaction with some DAP12-associated receptors, which do not possess any positively charged residues in their TMDs [36].
Since NF-κB or IRF-3-mediated type I IFN production is a classical antiviral response [41, 42], we hypothesized that PRRSV utilized poSn-DAP12 pathway to inhibit their activation, thereby decreasing the production of IFN-α/β. As expected, poSn knockdown promoted PRRSV-triggered NF-κB activation by inducing IκB-α degradation (Figures 6A and B), while IRF-3 activation was unaffected. Furthermore, we found that DAP12 knockdown increased the phosphorylation of p65 and IRF-3 in response to PRRSV (Figures 6C and D), while DAP12 overexpression inhibited their activation (Figure 6E). The poSn-DAP12 pathway indeed contributed to PRRSV infection (Figures 6B–D). The divergence between poSn knockdown and DAP12 knockdown suggested that DAP12 might be involved in various negative regulation pathways mediated by other unidentified receptors. All these findings revealed that the poSn-DAP12 pathway is involved in suppression of PRRSV-triggered NF-κB activation for viral infection. In fact, we have not figured out the underlying mechanism of how poSn-DAP12 pathway influences activation of NF-κB. This work will be our next issue to be resolved.
Taken together, we reveal an unappreciated role of poSn in suppressing host innate immune responses during PRRSV infection (Figure 8). poSn interacts with DAP12 through poSn TCD and DAP12 TMD during the PRRSV-post entry process. The poSn-DAP12 pathway targets NF-κB activation to facilitate the viral infection. More importantly, the pathway is involved in antagonizing type I IFN production stimulated by poly (I:C). All these data contribute to the understanding of PRRSV pathogenesis and provide a molecular basis for viral prevention and control.
Abbreviations
- PRRSV:
-
porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus
- poSn:
-
porcine sialoadhesin
- IFN:
-
type I interferon
- DAP12:
-
DNAX-activation protein of 12 kDa
- TMD:
-
transmembrane domain
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor-kappa B
- Ig:
-
immunoglobulin
- Siglec:
-
sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin
- RIG-I:
-
retinoic acid-inducible gene-I
- TBK1:
-
tank binding kinase 1
- IRF:
-
interferon regulatory factor
- VSV:
-
vesicular stomatitis virus
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium
- RPMI-1640:
-
Roswell Park Memorial Institute-1640 medium
- FBS:
-
fetal bovine serum
- PAMs:
-
pulmonary alveolar macrophages
- TCID50 :
-
50% tissue culture infective dose
- mAb:
-
monoclonal antibody
- BSA:
-
bovine serum albumin
- RT-qPCR:
-
quantitative real-time PCR
- ORF:
-
open reading frame
- GAPDH:
-
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- IB:
-
immunoblotting
- SDS-PAGE:
-
sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- PVDF:
-
polyvinylidene fluoride
- PBST:
-
phosphate-buffered saline-Tween 20
- RT:
-
room temperature
- HRP:
-
horse radish peroxidase
- ECL:
-
enhanced chemiluminescence
- FCM:
-
flow cytometry
- siRNA:
-
small interfering RNA
- ECD:
-
extracellular domain
- TCD:
-
helical transmembrane plus cytoplasmic domain
- IFA:
-
indirect immunofluorescence assay
- Co-IP:
-
co-immunoprecipitation
- TBST:
-
Tris-buffered saline with 0.5% Tween-20
- N:
-
nucleocapsid
- ICD:
-
intracellular domain
- IκB:
-
NF-κ light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor
- PRRs:
-
pattern recognition receptors
- PAMPs:
-
pathogen-associated molecular patterns
- ORF:
-
open reading frame
References
Holtkamp DJ, Kliebenstein JB, Neumann EJ, Zimmerman JJ, Rotto HF, Yoder TK, Wang C, Yeske PE, Mowrer CL, Haley CA (2013) Assessment of the economic impact of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus on U.S. pork producers. J Swine Health Prod 21:72–84
Rossow KD (1998) Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome. Vet Pathol 35:1–20
Adams MJ, Lefkowitz EJ, King AMQ, Harrach B, Harrison RL, Knowles NJ, Kropinski AM, Krupovic M, Kuhn JH, Mushegian AR, Nibert M, Sabanadzovic S, Sanfacon H, Siddell SG, Simmonds P, Varsani A, Zerbini FM, Gorbalenya AE, Davison AJ (2017) Changes to taxonomy and the International Code of Virus Classification and Nomenclature ratified by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2017). Arch Virol 162:2505–2538
Guo Z, Chen XX, Li R, Qiao S, Zhang GP (2018) The prevalent status and genetic diversity of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in China: a molecular epidemiological perspective. Virol J 15:2
Vanderheijden N, Delputte PL, Favoreel HW, Vandekerckhove J, Van Damme J, Van Woensel PA, Nauwynck HJ (2003) Involvement of sialoadhesin in entry of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus into porcine alveolar macrophages. J Virol 77:8207–8215
Delputte PL, Nauwynck HJ (2004) Porcine arterivirus infection of alveolar macrophages is mediated by sialic acid on the virus. J Virol 78:8094–8101
Van Breedam W, Van Gorp H, Zhang JQ, Crocker PR, Delputte PL, Nauwynck HJ (2010) The M/GP(5) glycoprotein complex of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus binds the sialoadhesin receptor in a sialic acid-dependent manner. PLoS Pathog 6:e1000730
Delputte PL, Van Breedam W, Delrue I, Oetke C, Crocker PR, Nauwynck HJ (2007) Porcine arterivirus attachment to the macrophage-specific receptor sialoadhesin is dependent on the sialic acid-binding activity of the N-terminal immunoglobulin domain of sialoadhesin. J Virol 81:9546–9550
Van Gorp H, Van Breedam W, Delputte PL, Nauwynck HJ (2008) Sialoadhesin and CD163 join forces during entry of the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. J Gen Virol 89:2943–2953
Prather RS, Rowland RR, Ewen C, Trible B, Kerrigan M, Bawa B, Teson JM, Mao J, Lee K, Samuel MS, Whitworth KM, Murphy CN, Egen T, Green JA (2013) An intact sialoadhesin (Sn/SIGLEC1/CD169) is not required for attachment/internalization of the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. J Virol 87:9538–9546
Hartnell A, Steel J, Turley H, Jones M, Jackson DG, Crocker PR (2001) Characterization of human sialoadhesin, a sialic acid binding receptor expressed by resident and inflammatory macrophage populations. Blood 97:288–296
Crocker PR, Mucklow S, Bouckson V, McWilliam A, Willis AC, Gordon S, Milon G, Kelm S, Bradfield P (1994) Sialoadhesin, a macrophage sialic acid binding receptor for haemopoietic cells with 17 immunoglobulin-like domains. EMBO J 13:4490–4503
Chen W, Han C, Xie B, Hu X, Yu Q, Shi L, Wang Q, Li D, Wang J, Zheng P, Liu Y, Cao X (2013) Induction of Siglec-G by RNA viruses inhibits the innate immune response by promoting RIG-I degradation. Cell 152:467–478
Schmitt H, Sell S, Koch J, Seefried M, Sonnewald S, Daniel C, Winkler TH, Nitschke L (2016) Siglec-H protects from virus-triggered severe systemic autoimmunity. J Exp Med 213:1627–1644
Zheng Q, Hou J, Zhou Y, Yang Y, Xie B, Cao X (2015) Siglec1 suppresses antiviral innate immune response by inducing TBK1 degradation via the ubiquitin ligase TRIM27. Cell Res 25:1121–1136
Ma H, Jiang L, Qiao S, Zhi Y, Chen XX, Yang Y, Huang X, Huang M, Li R, Zhang GP (2017) The crystal structure of the fifth scavenger receptor cysteine-rich domain of porcine CD163 reveals an important residue involved in porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection. J Virol 91:e01897–01816
Liu Y, Li R, Chen XX, Zhi Y, Deng R, Zhou EM, Qiao S, Zhang GP (2019) Nonmuscle myosin heavy chain IIA recognizes sialic acids on sialylated rna viruses to suppress proinflammatory responses via the DAP12-Syk pathway. MBio 10:e00574–19
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108
Xie S, Chen XX, Qiao S, Li R, Sun Y, Xia S, Wang LJ, Luo X, Deng R, Zhou EM, Zhang GP (2018) Identification of the RNA pseudoknot within the 3′ end of the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus genome as a pathogen-associated molecular pattern to activate antiviral signaling via RIG-I and Toll-like receptor 3. J Virol 92:e00097–18
Zhang Q, Guo XK, Gao L, Huang C, Li N, Jia X, Liu W, Feng WH (2014) MicroRNA-23 inhibits PRRSV replication by directly targeting PRRSV RNA and possibly by upregulating type I interferons. Virology 450–451:182–195
Duan X, Nauwynck HJ, Pensaert MB (1997) Virus quantification and identification of cellular targets in the lungs and lymphoid tissues of pigs at different time intervals after inoculation with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV). Vet Microbiol 56:9–19
Zhong L, Chen XF, Zhang ZL, Wang Z, Shi XZ, Xu K, Zhang YW, Xu H, Bu G (2015) DAP12 stabilizes the C-terminal fragment of the triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-2 (TREM2) and protects against LPS-induced pro-inflammatory response. J Biol Chem 290:15866–15877
Hamerman JA, Ni M, Killebrew JR, Chu CL, Lowell CA (2009) The expanding roles of ITAM adapters FcRgamma and DAP12 in myeloid cells. Immunol Rev 232:42–58
Lee YJ, Park CK, Nam E, Kim SH, Lee OS, du Lee S, Lee C (2010) Generation of a porcine alveolar macrophage cell line for the growth of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. J Virol Methods 163:410–415
Hu MM, Shu HB (2018) Cytoplasmic mechanisms of recognition and defense of microbial nucleic acids. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 34:357–379
Zhang Y, Liang C (2016) Innate recognition of microbial-derived signals in immunity and inflammation. Sci China Life Sci 59:1210–1217
Ivashkiv LB, Donlin LT (2014) Regulation of type I interferon responses. Nat Rev Immunol 14:36–49
Honda K, Takaoka A, Taniguchi T (2006) Type I inteferon gene induction by the interferon regulatory factor family of transcription factors. Immunity 25:349–360
Zhang Q, Lenardo MJ, Baltimore D (2017) 30 years of NF-kappaB: a blossoming of relevance to human pathobiology. Cell 168:37–57
Garcia-Sastre A, Biron CA (2006) Type I interferons and the virus-host relationship: a lesson in detente. Science 312:879–882
Wang R, Zhang YJ (2014) Antagonizing interferon-mediated immune response by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Biomed Res Int 2014:315470
Lunney JK, Fang Y, Ladinig A, Chen N, Li Y, Rowland B, Renukaradhya GJ (2016) Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV): pathogenesis and interaction with the immune system. Annu Rev Anim Biosci 4:129–154
Huang C, Zhang Q, Feng WH (2015) Regulation and evasion of antiviral immune responses by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Virus Res 202:101–111
Turnbull IR, Colonna M (2007) Activating and inhibitory functions of DAP12. Nat Rev Immunol 7:155–161
Lanier LL (2009) DAP10- and DAP12-associated receptors in innate immunity. Immunol Rev 227:150–160
Zhao D, Han X, Zheng X, Wang H, Yang Z, Liu D, Han K, Liu J, Wang X, Yang W, Dong Q, Yang S, Xia X, Tang L, He F (2016) The myeloid LSECtin is a DAP12-coupled receptor that is crucial for inflammatory response induced by ebola virus glycoprotein. PLoS Pathog 12:e1005487
Hamerman JA, Tchao NK, Lowell CA, Lanier LL (2005) Enhanced Toll-like receptor responses in the absence of signaling adaptor DAP12. Nat Immunol 6:579–586
Chu CL, Yu YL, Shen KY, Lowell CA, Lanier LL, Hamerman JA (2008) Increased TLR responses in dendritic cells lacking the ITAM-containing adapters DAP12 and FcRgamma. Eur J Immunol 38:166–173
Wu Y, Lan C, Ren D, Chen GY (2016) Induction of Siglec-1 by endotoxin tolerance suppresses the innate immune response by promoting TGF-beta1 production. J Biol Chem 291:12370–12382
Blasius AL, Cella M, Maldonado J, Takai T, Colonna M (2006) Siglec-H is an IPC-specific receptor that modulates type I IFN secretion through DAP12. Blood 107:2474–2476
Rahman MM, McFadden G (2011) Modulation of NF-κB signalling by microbial pathogens. Nat Rev Microbiol 9:291–306
Tamura T, Yanai H, Savitsky D, Taniguchi T (2008) The IRF family transcription factors in immunity and oncogenesis. Annu Rev Immunol 26:535–584
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Funds of China (31490601, 31972690 and 31602036), the grant from Henan Academy of Agricultural Sciences (2019ZC60), the Earmarked Fund for Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System of China (CARS-35) and the Special Fund for Henan Agriculture Research System (S2012-06). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and interpretation, or the decision to submit the work for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YL, RL, SQ, and GZ designed the experiments. YL performed the experiments and processed the corresponding data. YL and RL analyzed the results. RD provided the technique assistance. YL wrote the manuscript. YL, RL, SQ and XC revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experiments were performed according to the Chinese Regulations of Laboratory Animals—The Guidelines for the Care of Laboratory Animals (Ministry of Science and Technology of People’s Republic of China). PAMs were collected from 6–8-week piglets, which was authorized and supervised by the Ethical and Animal Welfare Committee of Key Laboratory of Animal Immunology of the Ministry of Agriculture of China (Permit No. 2017001).
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Li, R., Qiao, S. et al. Porcine sialoadhesin suppresses type I interferon production to support porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection. Vet Res 51, 18 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13567-020-00743-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13567-020-00743-7