Abstract
Background
Generally, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome develops after superovulation caused by ovulation-inducing drugs in infertile patients. However, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome associated with natural pregnancy is rare, and most cases of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome have been associated with a hydatidiform mole.
Case presentation
We describe a case of a 16-year-old Japanese girl with a complete hydatidiform mole. The patient was referred for intensive examination and treatment of the hydatidiform mole and underwent surgical removal of the hydatidiform mole at 9 weeks, 5 days of gestation. Histopathological examination revealed a complete hydatidiform mole. The patient’s blood human chorionic gonadotropin level decreased from 980,823 IU/L to 44,815 IU/L on postoperative day 4, and it was below the cutoff level on postoperative day 64. Transvaginal ultrasonography on postoperative day 7 revealed a multilocular cyst measuring 82 × 43 mm in the right ovary and a multilocular cyst measuring 66 × 50 mm in the left ovary. Both ovarian cysts enlarged further. Magnetic resonance imaging on postoperative day 24 revealed that the right multilocular ovarian cyst had enlarged to 10 × 12 cm and that the left multilocular ovarian cyst had enlarged to 25 × 11 cm. Blood examination showed an elevated estradiol level as high as 3482 pg/ml. We diagnosed the patient with bilateral giant multilocular cysts accompanied by ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome because of the rapid increase in the size of the cysts. The patient complained of mild abdominal bloating; however, symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, dyspnea, and abdominal pain were not observed. Therefore, we chose spontaneous observation in the outpatient clinic. The cysts gradually decreased and disappeared on postoperative day 242.
Conclusion
Physicians should be aware that ovarian cysts can occur and can increase rapidly after abortion of a hydatidiform mole. However, the ovarian cyst can return to its original size spontaneously even if it becomes huge.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) commonly develops after superovulation caused by ovulation-inducing drugs in infertile patients. Ninety percent of patients have mild OHSS that improves with only follow-up observation. However, symptomatic therapy is necessary for moderate or severe cases, and in severe cases, there is a possibility of death because of thrombus or embolism. OHSS associated with natural pregnancy is rare, and so far, most cases of OHSS have been associated with a hydatidiform mole. OHSS manifests with bilateral ovarian enlargement in addition to symptoms such as ascites or pleural effusion caused by hypervascular permeability, hemoconcentration, and oliguria. In this report, we describe a patient in whom a giant ovarian cyst measuring 25 cm appeared suddenly after surgical removal of a complete hydatidiform mole and returned to normal ovarian size during the follow-up observation period without treatment.
Case presentation
A Japanese girl aged 16 years, 7 months, gravida 1 para 0, was referred to our hospital because of a suspicious complete hydatidiform mole. Her height was 152 cm, weight was 40.8 kg, and body mass index (BMI) was 17.7 kg/m2. Her blood pressure and heart rate were 110/60 mmHg and 88/minute, respectively. Her age at menarche was 13 years, her menstrual cycle was 30 days, and her periods lasted 5 days. The patient had undergone surgery for choledochal dilation at 2 years of age and had no significant family history. She was diagnosed with a complete hydatidiform mole at 9 weeks, 0 days of gestation from the last menstruation.
A small amount of dark red genital bleeding was observed during the medical examination, and the uterus was the size of a neonatal head, which was larger than the size corresponding to 9 weeks, 0 days of gestation. Transvaginal ultrasonography did not show a gestational sac and embryo, but it revealed many small cysts in the uterus. No bilateral ovarian swelling was observed. The blood human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) level was markedly increased and was as high as 980,823 IU (normal limit < 5 IU). On the basis of these findings, we diagnosed her pregnancy as a complete hydatidiform mole, and legally induced abortion was performed at 9 weeks, 5 days of gestation using an aspiration instrument. We explained the necessity of the procedure to the patient and her parents and obtained written informed consent from them.
Macroscopically, the uterine content was only cystic villi without obvious fetal components. Histopathological examination also revealed a complete hydatidiform mole. The patient’s blood hCG level decreased to 44,815 IU/L on postoperative day 4 and to 120 IU/L on postoperative day 29, and it was below the cutoff level on postoperative day 64. Additionally, menstruation occurred spontaneously on postoperative day 32.
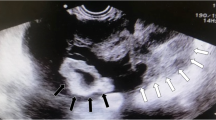
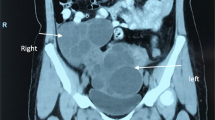
Transvaginal ultrasonography revealed a multilocular cyst measuring 71 × 43 mm in the right ovary on postoperative day 4, and the cyst increased to 82 × 43 mm on postoperative day 7 (Fig. 1a, b). No swelling was observed in the left ovary on postoperative day 4, but a multilocular cyst measuring 66 × 50 mm was observed on postoperative day 7 (Fig. 1c). The bilateral ovarian cysts enlarged further; magnetic resonance imaging on postoperative day 24 revealed that the right multilocular ovarian cyst had enlarged to 10 × 12 cm and that the left multilocular ovarian cyst had enlarged to 25 × 11 cm (Fig. 2a–d). Additionally, a small amount of ascites was recognized. The patient complained of mild abdominal bloating, but no symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, dyspnea, and abdominal pain were observed. Blood examination showed elevated E2 as high as 3482 pg/ml. However, hemoconcentration, electrolyte abnormalities, hypoalbuminemia, elevated liver enzyme levels, and renal dysfunction were not observed. Regarding blood tumor markers, only the cancer antigen 125 (CA 125) level was elevated, to 134.7 U/ml, but the α-fetoprotein, carcinoembryonic antigen, sialyl Tn antigen, and carbohydrate antigen 19-9 levels were within normal limits. A giant ovarian cyst with a high CA 125 level and a small amount of ascites are symptoms that mimic a malignant ovarian tumor. Therefore, we first considered an operation for the ovarian cyst. However, enlargement of the ovarian cyst was too rapid, even though the cyst might have been a malignant tumor. Additionally, we found few case reports describing an ovarian cyst accompanied by OHSS following hydatidiform mole in the literature. Therefore, we diagnosed the disease as bilateral giant multilocular cysts accompanied by OHSS following surgical removal of a complete hydatidiform mole. We also diagnosed the cause of the elevated CA 125 level as ascitic fluid accumulation associated with OHSS. Therefore, we opted for spontaneous observation in the outpatient clinic and expected the bilateral ovarian cysts to decrease in size.
As expected, the size of the cysts decreased gradually during the observation period, and we confirmed their disappearance on postoperative day 242 (Fig. 3a, b). The patient is still under observation, and we have confirmed the absence of ovarian cysts.
Discussion
Generally, OHSS is known as an iatrogenic disease caused by ovarian stimulation performed as a type of infertility treatment. Excessive ovarian stimulation causes multilocular ovarian cyst formation, dehydration, hemoconcentration, storage of ascites or pleural effusion, dyspnea, oliguria, and electrolyte abnormality (hyponatremia and hyperkalemia). Then hypotension, tachycardia, and decreased central venous pressure develop, and finally a critical event occurs [1]. The occurrence of OHSS accompanied by spontaneous pregnancy is rare. As shown in Table 1, only 11 cases of OHSS after spontaneous pregnancy, with abnormal chorionic villi, have been reported until now, and of those, 9 cases were associated with a hydatidiform mole, one with an invasive mole, and one with placental mesenchymal dysplasia [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12]. Among nine cases of OHSS that occurred after abortion of a hydatidiform mole, the first case was reported in 1966, and the ninth case was reported in 2015. Thus, nine cases of OHSS following hydatidiform mole were reported within a span of about 50 years (Table 1).
OHSS is classified as mild, moderate, or severe depending on the clinical symptoms and blood test findings. Most cases of OHSS are classified as mild, but 1–5% of cases are classified as moderate or severe [13]. In mild cases, spontaneous recovery is observed during the observation period, but in moderate or severe cases, appropriate symptomatic treatments are necessary [14]. In previously reported cases (Table 1), OHSS occurred after abortion of the hydatidiform mole; all patients were hospitalized; and the patients received treatments such as fluid infusion and albumin administration, heparin administration to prevent thrombosis or embolism, electrolyte replacement, and puncture or aspiration of ascites or pleural effusion. However, in our patient, neither severe clinical symptoms, such as massive ascites or pleural effusion, nor abnormal blood test results were found. Thus, neither hospitalization nor symptomatic treatment was required, although the patient had a huge ovarian mass. The absence of ascites or pleural effusion may have been because of the patient’s small and thin structure (BMI 17.7 kg/m2). Therefore, the intra-abdominal pressure of the patient was expected to be extremely high because the huge ovarian cyst occupied the abdominal cavity, and the leakage from the blood vessel may have been suppressed, preventing severe clinical symptoms.
Most cases of iatrogenic OHSS are caused by the administration of hCG, and the symptoms worsen with pregnancy and improve after abortion. In the above-referenced cases of OHSS associated with a hydatidiform mole, however, the onset of OHSS was after abortion, and the symptoms worsened. In all cases, OHSS developed when the serum hCG level was low, after induced or spontaneous abortions, and not when the serum hCG level was the highest. Regarding the discrepancy, Ludwig et al. pointed out the involvement of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in the onset of OHSS because the serum VEGF concentration was high at the onset of OHSS in their patient’s case [4]. However, Strafford et al. reported that the serum VEGF concentration did not increase at the onset of OHSS but that the serum E2 concentration increased [6]. In our patient, the serum E2 concentration was markedly high, even though induced abortion was performed. Our patient’s case also follows the same process as that reported by Strafford et al. [6]. However, De Leener et al. reported that a mutation of the follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) receptor was found in patients who developed OHSS, although the serum hCG concentration was within the normal limit [15]. Mutation of the FSH receptor was also reported by Wu et al. [11]. Thus, the onset of OHSS may be due to the effects of some factors such as the hCG level, E2 level, and abnormal FSH receptor.
According to the literature, the 25-cm ovarian cyst derived from the left ovary in our patient might be the second largest cyst among ovarian cysts accompanied by OHSS. The largest ovarian cyst was 30 cm, which was reported by Suzuki et al. [10]. Unfortunately, the authors did not show any image of the 30-cm ovarian cyst or describe whether the ovarian cyst was derived from the left ovary or the right ovary. In our patient, we measured the size of the ovarian cyst by using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) because transvaginal and abdominal ultrasonography could not reveal the size of the ovarian cyst. Additionally, MRI was convenient for distinguishing between the left cyst and the right cyst.
The duration for reduction of the size of multilocular ovarian cysts in OHSS to that of a normal ovary is reported to range from 1 month to 7 months. Surprisingly, Suzuki et al. reported that a 30-cm ovarian cyst returned to its original size within only 1 month [10]. Conversely, Wu et al. reported that it took 7 months for an 18-cm ovarian cyst to return to its original size [11]. In our patient, it took 8 months for the 25-cm ovarian cyst to return to its original size. It seems that the duration required for reduction of the cyst does not depend on the size of the ovarian cyst. These results suggest that ovarian cysts in OHSS consistently return to their original size, although they may be huge and the duration of reduction in size is long. Additionally, surgical procedures such as ovarian cystectomy and ovarian drilling may be unnecessary.
Conclusions
OHSS associated with natural pregnancy is rare, but most cases of OHSS have been associated with a hydatidiform mole. Therefore, physicians should be aware that ovarian cysts accompanied by OHSS can occur after abortion of a hydatidiform mole and that the size of the ovarian cyst can increase rapidly, although this is rare. Additionally, there is a reported case of a giant ovarian cyst with few symptoms of OHSS; most similar cases have many symptoms, including massive ascites and pleural effusion. However, most ovarian cysts return spontaneously to their original size after several months, even the huge ones.
Patient perspective
The patient understood why both her ovaries became enlarged after the legally induced abortion for a complete hydatidiform mole, and she hopes that ovarian enlargement will never recur.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed in the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- CA 125:
-
Cancer antigen 125
- FSH:
-
Follicle-stimulating hormone
- hCG:
-
Human chorionic gonadotropin
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- OHSS:
-
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
References
Kumar P, Sait SF, Sharma A, Kumar M. Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. J Hum Reprod Sci. 2011;4:70–5.
Hooper AA, Mascarenhas AM, O’Sullivan JV. Gross ascites complicating hydatidiform mole. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw. 1966;73:854–5.
Moneta E, Menini E, Scirpa P, Plotti G. Urinary excretion of steroids in a case of hydatidiform mole with ascites. Obstet Gynecol. 1974;44:47–52.
Ludwig M, Gembruch U, Bauer O, Diedrich K. Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) in a spontaneous pregnancy with fetal and placental triploidy: information about the general pathophysiology of OHSS. Hum Reprod. 1998;13:2082–7.
Arora R, Merhi ZO, Khulpateea N, Roth D, Minkoff H. Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome after a molar pregnancy evacuation. Fertil Steril. 2008;90:1197.e5–7.
Strafford M, Moreno-Ruiz N, Stubblefield P. Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome in a spontaneous pregnancy with a complete hydatidiform mole. Fertil Steril. 2009;92:395.e1–3.
Rachad M, Chaara H, Zahra Fdili F, Bouguem H, Melhouf A. Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome in a spontaneous pregnancy with invasive mole: report of a case. Pan Afr Med J. 2011;9:23.
Zhou X, Duan Z. A case of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome following a spontaneous complete hydatidiform molar pregnancy. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2012;28:850–2.
Diness M, Nilas L. Course of mole pregnancy complicated by ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. Ugeskr Laeger. 2012;174:1465–7.
Suzuki H, Matsubara S, Uchida S, Ohkuchi A. Ovary hyperstimulation syndrome accompanying molar pregnancy: case report and review of the literature. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2014;290:803–6.
Wu X, Zhu J, Zhao A. Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome in a spontaneous pregnancy with invasive mole. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2015;41:817–22.
Davoudian P. Placental mesenchymal dysplasia associated with spontaneous ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. BMJ Case Rep. 2015;2015:bcr2014207420.
Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Prevention and treatment of moderate and severe ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome: a guideline. Fertil Steril. 2016;106:1634–47.
Aboulghar M. Treatment of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. Semin Reprod Med. 2010;28:532–9.
De Leener A, Montanelli L, Van Durme J, Chae H, Smits G, et al. Presence and absence of follicle-stimulating hormone receptor mutations provide some insights into spontaneous ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome physiopathology. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:555–62.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Hisahide Sugimoto for providing medical information and Yukako Yamawaki for secretarial assistance.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HT and YI performed the gynecological examination and observation. TY and TY performed the legally induced abortion. KY was a major contributor to the writing of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Tsubokura, H., Ikoma, Y., Yokoe, T. et al. Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome following surgical removal of a complete hydatidiform mole: a case report. J Med Case Reports 13, 292 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-019-2181-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-019-2181-x