Abstract
Background
In Europe, the first Thelazia callipaeda infections were found in the eyes of some dogs in Italy three decades ago. Since that time, this vector-borne nematode species has been diagnosed in domestic and wild carnivores and humans in some western European countries. During the last few years, autochthonous thelaziosis of dogs, red foxes, cats and humans has also been reported from eastern Europe. The first cases of ocular infections caused by T. callipaeda have been described in dogs living in the eastern and southern part of Slovakia and Hungary.
Methods
Whitish parasites found in the conjuctival sac and/or under the third eyelid of one or both eyes of animals were removed and morphologically identified according to species and sex. To confirm the morphological identification with molecular analysis a single step conventional PCR was carried out.
Results
A total of 116 adult worms (1–37 per dog, median: 7, IQR: 14.5 and 7 from a cat) were collected from the eyes of 11 animals. Nematodes were identified as T. callipaeda according to the morphological keys and molecular analysis. The sequences of a portion of the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 (cox1) gene were identical to those representing T. callipaeda haplotype 1, previously reported in neighbouring and other European countries. Since the infected cat and dogs had never travelled abroad, all of the cases were autochthonous thelaziosis.
Conclusions
The present study reports the first case of thelaziosis in a cat and new cases in 10 dogs found in the southern and northern region of Hungary, respectively. Further studies are needed to clarify whether wild carnivores (e.g. red foxes, golden jackals) may act as reservoirs of this eyeworm species in the country.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Thelazia callipaeda (Spirurida: Thelaziidae) has been known for a long time as the “oriental eyeworm” due to its original geographical distribution in the Far East where it is widely distributed [1]. The adult worms and the first stage larvae parasitize the conjunctival sac of dogs, cats, wild carnivores [foxes (Vulpes vulpes), wolves (Canis lupus), wild cats (Felis silvestris), golden jackals (Canis aureus), beech martens (Martes foina), racoon dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides) and lynx (Lynx lynx)], wild European rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus), brown hares (Lepus europaeus) [2,3,4,5] and sometimes humans [6,7,8]. Thelazia callipaeda is responsible for a range of subclinical to clinical signs such as conjunctivitis, lacrimation, ocular discharge or keratitis in animals and humans [9,10,11]. The lachryphagous Phortica variegata (Drosophilidae, Steganinae) has been confirmed as the vector for this spirurid nematode species in Europe [12,13,14,15] where the first presence of Thelazia callipaeda was found in the Piedmont region of Italy in 1989 [2]. Since that time, an increasing number of imported and/or autochthonous cases of thelaziosis in dogs, red foxes, cats, lagomorphs [2, 3, 5, 16,17,18,19] and humans [6,7,8, 5, 11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20] have been reported in some western European countries. During the last few years, this eyeworm infection of animals and humans has been reported from eastern Europe [7, 8, 21,22,23,24,25]. Recently, the first cases of ocular infections caused by T. callipaeda have been described in dogs and red foxes found in the eastern part of Slovakia [26, 27]. Thelazia callipaeda was found for the first time in a dog living in the southern part of Hungary [25, 28].
The present paper reports the first autochthonous thelaziosis in a cat and new ocular worm infections of ten dogs caused by T. callipaeda found in the northern area of Hungary.
Methods
Sample collection
Between October 2015 and December 2017, 11 cases of ocular worm infection in a cat and 10 dogs were signalled by practitioners to the Department of Parasitology and Zoology, University of Veterinary Medicine, Budapest. The cat was a one-year-old male of the European shorthair breed. Affected dog breeds were German Shepherd, Rottweiler, Collie, Hanoverian Hound, Hungarian Vizsla and crossbreeds, aged from 0.8 to 14 years, mostly males except for one (Table 1). Each animal was born in Hungary. All animals examined spent most or all of their time outdoors. The cat and dogs’ owners confirmed that their pets had never travelled abroad.
Clinical examination, parasite collection and treatment
On clinical examination after administration of a local anaesthetic, threadlike motile whitish parasites were observed in the conjunctival sac and/or under the third eyelid of one or both eyes of each animal. The worms were removed using sterile cotton swabs or fine forceps and the conjunctival sacs were thoroughly flushed with sterile physiological saline solution. The parasites were collected into 70% ethanol and sent to the Department of Parasitology and Zoology for morphological and molecular identification.
The dogs were treated with a spot-on application of 10% imidacloprid and 2.5% moxidectin (Advocate Spot-On; Bayer HealthCare, Leverkusen, Germany) or Milprazon tablets (milbemicin-oxim 2.5 mg and praziquantel 12.5 mg, KRKA, Novo mesto, Slovenia). The cat did not receive any anti-parasitic treatment.
Morphological and molecular identification of the worms
Nematodes collected from the eyes of each animal were morphologically identified according to species and sex under a light microscopy combined with a camera (EURmex HD II with IS Capture software) using the previous descriptions [29]. To confirm the morphological identification with molecular analysis a single step conventional PCR was carried out. Genomic DNA was extracted from one or more specimen of worms from each animal, with the NucleoSpin Tissue Kit (Macherey-Nagel GmbH & Co. KG, Düren, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. An approximately 689 bp partial fragment of the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 gene (cox1) was amplified with the primer pair NTF (5'-TGA TTG GTG GTT TTG GTA A-3') and NTR (5'-ATA AGT ACG AGT ATC AAT ATC-3') [30]. The PCR reaction was carried out in a final volume of 25 μl of mixture containing 0.5 U (0.1 μl) HotStarTaq Plus DNA polymerase (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), 2.5 μl 10× CoralLoad Reaction buffer (including 15 mM MgCl2), 0.5 μl PCR nucleotide Mix (0.2 mM each), 0.5 μl (1.0 μM final concentration) of each primer, 15.9 μl ddH2O and 5 μl of template DNA using the following thermal conditions: an initial denaturation step at 95 °C for 5 min followed by 40 cycles of denaturation at 95 °C for 30 s, annealing at 46 °C for 1 min and extension at 72 °C for 1 min. Final extension was performed at 72 °C for 10 min. Reaction mixture without adding template DNA served as a negative control and sequenced Thelazia callipaeda DNA (confirmed by sequencing) was used as a positive control to test the efficacy of the reactions. PCR products were electrophoresed in 1.5% agarose gel and visualized under UV-light. Positive amplification products were purified and submitted for Sanger sequencing to the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Biological Research Centre, Szeged, Hungary. Obtained sequences were manually edited and then aligned and compared to reference GenBank sequences by the nucleotide BLASTN program (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov). Representative sequences were submitted to GenBank.
Results
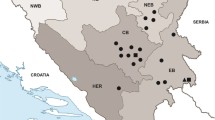
Nine out of ten infected dogs were kept in five settlements of Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén county and one animal in Budapest (Fig. 1). Except for two dogs, the others were taken by the owners many times for walking to Bükk National Park located in the north-eastern part of Hungary.
For the cat and all dogs, conjunctival hyperaemia and ocular purulent discharge due to conjunctivitis were observed in one or both eyes. The third eyelid protrusion occurred in one dog. The ophthalmological examination revealed the presence of motile nematodes on the eye surface, in the conjunctival sac and/or under the third eyelids of one or both eyes. A total of 116 adult worms (1–37 per dog, median: 7, IQR: 14.5 and 7 from a cat) were collected from 11 infected animals (Table 1). All specimens recovered were morphologically identified as T. callipaeda adults. The eyes of four and six dogs were infected with females and parasites of both sexes, respectively (Table 1). Four weeks after removing the worms and starting treatment, the infection had resolved in each animal. Their eyes appeared normal, and no parasites were observed.
The cox1 sequences obtained in this study from the cat (GenBank: KX372681.1) and dogs (GenBank: MG677577, MG677578, MG874787, MG874788, MG874790-MG874792, MH178370, MH178371) showed a 100% identity to the sequence of T. callipaeda haplotype-1 (GenBank: AM042549.1) reported by Otranto et al. [30] and isolated from dogs in Romania (GenBank: KP087796) and Slovakia (GenBank: KY476400).
Discussion
In Europe, the first documented T. callipaeda infections were found in the eyes of some dogs in Italy three decades ago [2]. In the following decades our knowledge about the distribution of this vector-borne eyeworm species in Europe has greatly expanded. Autochthonous and/or imported thelaziosis affecting domestic and/or wild carnivores has been reported in Germany [16], France [17], Portugal [31,32,33], Switzerland [18, 34], Spain [19] and Italy [3]. Thelazia callipaeda infection has also been found in wild European rabbits [5]. The human ocular thelaziosis reported from Italy and Spain [6, 20] confirms the medical importance of this nematode species in Europe. The occurrence of this spirurid nematode species has also been reported in Eastern Europe. The adult worms have been found in one or both eyes of dogs, cats, foxes and/or humans in Croatia [7, 21], Serbia [8, 22, 35], Romania [23, 24], Bosnia and Herzegovina [21], Bulgaria [25] and Slovakia [26, 27]. Before this study, only a single canine ocular thelaziosis was reported in Hungary [28]. In January 2014, a ten-year-old, male poodle dog with unilateral chronic conjunctivitis and epiphora was presented to a veterinary practice in Pécs, Baranya county, located in the southern part of the country (Fig. 1). The worms were identified as T. callipaeda both morphologically and molecularly [25, 28]. However, there has been no explanation of how this dog acquired this eyeworm infection. A year later, in October 2015, seven adult worms were removed from the right conjunctival sac of a one-year-old male cat in Mohács (Fig. 1). This town is 36 km away from Pécs where the infected dog was examined. Ocular worm infections caused by T. callipaeda were found in nine dogs originating from five settlements (Table 1 and Fig. 1) of Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén county. The specimens of this spirurid worm species were found in both eyes of a dog kept in Budapest at the end of 2017. The cat and all the dogs had autochthonous thelaziosis because they had no history of travelling abroad. The infections presented here confirm the parasite’s establishment in two areas of the country. Like in other European countries [12, 19, 32] most Hungarian cases have been diagnosed in late summer and autumn relating to the maximum activity of the vector [15, 36]. The dogs found to be infected with T. callipaeda adults in December became infected in summer or earlier because the third stage larvae released by flies in the spring and/or late summer will reach the adult stage many weeks later [9]. It has been experimentally demonstrated that T. callipaeda survives at least nine months in definitive hosts [1, 12].
Considering the sporadic cases of feline thelaziosis reported in Europe [17, 21, 22, 32, 35] (except for Switzerland [34]) it is not surprising that only one cat was found in Hungary with a confirmed T. callipaeda infection. Scientists related the occurrence of rare feline eyeworm infections with the intensive cleaning habits of cats resulting in less contact with the vectors [34]. On the other hand, difficulties in inspecting cats’ eyes by practitioners are also assumed [37]. According to the former dipterological studies, Phortica variegata, the vector species of T. callipaeda occurs in Hungary [38, 39] where it finds suitable habitat predicted earlier by a geoclimatic model [15]. It is unknown how long T. callipaeda has been present in Hungary. This vector-borne nematode species was probably imported to the country in the last decade. It is unlikely that the parasites arrived from abroad with vectors because fruit flies are not good flyers, and they are not known to disperse by wind [40]. Considering the first cases of canine thelaziosis found close to the southern and northern borders of Hungary, we assume that T. callipaeda may have been introduced recently or arrived in the country several years ago by infected host(s) from neighbouring countries where the occurrence of this nematode species has been reported [21, 22, 26, 27]. Thelazia callipaeda seems more likely to be transmitted to Hungary by wild carnivores, which play an important role in the sylvatic cycle of this eyeworm species [3, 21, 24, 37]. It has been reported that the specimens of this nematode were found in the eyes of red foxes in the northern regions of Balkans [21] and in the southern part of Slovakia close to the Hungarian border [27] (Fig. 1). Another possible explanation is also plausible. Thelazia callipaeda might have arrived in Hungary by infected dogs, such as hunting dogs that spent time in a thelaziosis-endemic area. Although there have been some hypotheses of how this eyeworm species could have arrived in the country, the origin and spreading of T. callipaeda remains unclear because the haplotype 1 reported in the neighbouring [22,23,24] and other [19, 21, 31,32,33] countries has also been found in this study. Our findings also confirm the low genetic variability of this parasite species in Europe [30].
Based on the results of this study, the most urgent need is for improving the knowledge of the local veterinarians who have been largely unaware of this eyeworm infection of dogs and cats. Besides preventative measures, correct diagnosis and appropriate treatment of infected dogs and cats, the veterinarians are also responsible for preventing this parasite infection of pet owners with education. Due to the potential risk of human infestation, physicians and medical ophthalmologists must be informed about the occurrence of this zoonotic parasite in the endemic regions. To date, we have no information about T. callipaeda infection of wild canids in Hungary. Therefore, research is needed to clarify whether red foxes and golden jackals act as reservoirs and spreaders of this eyeworm species.
Conclusions
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report on the detection of T. callipaeda in a cat in Hungary. After reporting the first case of thelaziosis in a dog living in the southern part of the country, ten autochthonous canine thelaziosis have been found in the northern region of Hungary. Further studies are needed to clarify whether wild carnivores (e.g. red foxes, golden jackals) may act as reservoirs of the parasite species in the country.
References
Anderson RC. Nematode parasites of vertebrates. Their development and transmission, 2nd ed. Wallingford: CABI Publishing; 2000.
Rossi L, Bertaglia P. Presence of Thelazia callipaeda Railliet and Henry, 1910, in Piedmont, Italy. Parassitologia. 1989;31:167–72.
Otranto D, Dantas-Torres F, Mallia E, DiGeronimo PM, Brianti E, Testini G, et al. Thelazia callipaeda (Spirurida, Thelaziidae) in wild animals: report of new host species and ecological implications. Vet Parasitol. 2009;166:262–7.
Odoevskaya IM, Khrustalev AV, Shaitanov VM, Seriodkin IV, Panayotova-Pencheva MS. Occurrence of the nematode Thelazia callipaeda Railliet and Henry, 1910 (Spirurida, Thelaziidae) in wild carnivores in the Russian Far East. Acta Zool Bulgarica. 2015;67:561–6.
Gama A, Pires I, Canado M, Coutinho T, Lopes AP, Latrofa MS, et al. First report of Thelazia callipaeda infection in wild European rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus) in Portugal. Parasit Vectors. 2016;9:236.
Fuentes I, Montes I, Saugar JM, Latrofa S, Gárate T, Otranto D. Thelaziosis in humans, a zoonotic infection, Spain, 2011. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012;18:2073–5.
Samardžić K, Paradžik MT, Janjetović Ž, Živičnjak T, Arar ŽV, Martinković F, et al. The first case of ocular thelaziasis in Croatia. Acta Med Croatica. 2015;69:475–80.
Tasić-Otašević S, Gabrielli S, Trenkić-Božinović M, Petrović A, Gajić B, Colella V. Eyeworm infections in dogs and in a human patient in Serbia: a One Health approach is needed. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2016;45:20–2.
Otranto D, Traversa D. Thelazia eyeworm an original endo- and ecto-parasitic nematode. Trends in Parasitol. 2005;21:1–4.
Otranto D, Eberhard ML. Zoonotic helminths affecting the human eye. Parasit Vectors. 2011;4:41.
Otranto D, Dantas-Torres F, Brianti E, Traversa D, Petrić D, Genchi C, et al. Vector-borne helminths of dogs and humans in Europe. Parasit Vectors. 2013;6:16.
Otranto D, Lia RP, Buono V, Traversa D, Giangaspero A. Biology of Thelazia callipaeda (Spirurida, Thelaziidae) eyeworms in naturally infected definitive hosts. Parasitology. 2004;129:627–33.
Otranto D, Lia RP, Cantacessi C, Testini G, Troccoli A, Shen JL, et al. Nematode biology and larval development of Thelazia callipaeda (Spirurida, Thelaziidae) in the drosophilid intermediate host in Europe and China. Parasitology. 2005;131:847–55.
Otranto D, Cantacessi C, Testini G, Lia RP. Phortica variegata as an intermediate host of Thelazia callipaeda under natural conditions: evidence for pathogen transmission by a male arthropod vector. Int J Parasitol. 2006;36:1167–73.
Otranto D, Brianti E, Cantacessi C, Lia RP, Máca J. The zoophilic fruitfly Phortica variegata: morphology, ecology and biological niche. Med Vet Entomol. 2006;20:358–64.
Hermosilla C, Herrmann B, Bauer C. First case of Thelazia callipaeda infection in a dog in Germany. Vet Rec. 2004;154:568–9.
Dorchies P, Chaudieu G, Siméon LA, Cazalot G, Cantacessi C, Otranto D. Reports of autochthonous eyeworm infection by Thelazia callipaeda (Spirurida, Thelaziidae) in dogs and cat from France. Vet Parasitol. 2007;149:294–7.
Malacrida F, Hegglin D, Bacciarini L, Otranto D, Nägeli F, Nägeli C, et al. Emergence of canine ocular thelaziosis caused by Thelazia callipaeda in southern Switzerland. Vet Parasitol. 2008;157:321–7.
Mir ó G, Montoya A, Hernández L, Dado D, Vázquez MV, Benito M, et al. Thelazia callipaeda: infection in dogs: a new parasite for Spain. Parasit Vectors. 2011;4:148.
Otranto D, Dutto M. Human thelaziosis, Europe. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:647–9.
Hodžić A, Latrofa MS, Annoscia G, Alić A, Beck R, Lia RP, et al. The spread of zoonotic Thelazia callipaeda in the Balkan area. Parasit Vectors. 2014;7:352.
Bojan G, Bogunović D, Stevanović J, Kulišić Z, Simeunović P, Stanimirović Z. Canine and feline thelaziosis caused by Thelazia callipaeda in Serbia. Acta Vet Beograd. 2014;64:447–55.
Mihalca AD, Amico G, Scurtu I, Chirilă R, Matei IA, Ionică AM. Further spreading of canine oriental eyeworm in Europe: first report of Thelazia callipaeda in Romania. Parasit Vectors. 2015;8:48.
Mihalca AD, Ionică MA, D’Amico G, Daskalaki AA, Deak G, Matei IA, et al. Thelazia callipaeda in wild carnivores from Romania: new host and geographical records. Parasit Vectors. 2016;9:350.
Colella V, Kirkova Z, Fok E, Mihalca AD, Tasic-Otasevic S, Hodzic A, et al. Increase in eyeworm infections in eastern Europe. Emerg Inf Dis. 2016;22:1513–5.
Čabanová V, Kocák P, Bronislava VM, Miterpáková M. First autochthonous cases of canine thelaziosis in Slovakia: a new affected area in central Europe. Parasit Vectors. 2017;10:179.
Čabanová V, Miterpáková M, Kocák P, Bronislava VM, Oravec M, Hurnokova, et al. Nematode Thelazia callipaeda is spreading across Europe. The first survey of red foxes from Slovakia. Acta Parasitol. 2018;63:160–6.
Fok É, Horváth É, Molnár Á, Otranto D. Thelazia callipaeda infection in a dog in Hungary. The 12th European Multicolloquium of Parasitology Turku, Finland, July 20-24th; 2016. p. P9.07.
Otranto D, Lia RP, Traversa D, Giannetto S. Thelazia callipaeda (Spirurida, Thelaziidae) of carnivores and humans: morphological study by light and scanning electron microscopy. Parassitologia. 2004;45:125–33.
Otranto D, Testini G, Deluca F, Hu M, Shamsi S, Gasser RB. Analysis of genetic variability within Thelazia callipaeda (Nematoda: Thelazioidea) from Europe and Asia by sequencing and mutation scanning of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1. Mol Cell Probes. 2005;19:306–13.
Vieira L, Rodrigues FT, Costa A, Diz-Lopes D, Machado J, Coutinho T, et al. First report of canine ocular thelaziosis by Thelazia callipaeda in Portugal. Parasit Vectors. 2012;5:124.
Rodrigues FT, Cardoso L, Coutinho T, Otranto D, Diz-Lopes D. Ocular thelaziosis due to Thelazia callipaeda in a cat from northeastern Portugal. J Feline Med Surg. 2012;14:952–4.
Soares C, Ramalho-Sousa S, Anastacio S, Goreti-Matias M, Marques I, Mascarenhas S, et al. Feline thelaziosis caused by Thelazia callipaeda in Portugal. Vet Parasitol. 2013;196:528–31.
Motta B, Nägeli F, Nägeli C, Solari-Basano F, Schiessl B, Deplazes P, et al. Epidemiology of the eye worm Thelazia callipaeda in cats from southern Switzerland. Vet Parasitol. 2014;203:287–93.
Marčić D, Pavlović I, Prodanov-Radulović J, Stojanov I, Pušić I. Occurrence of Thelazia callipaeda in cats - case report. Arch Vet Med. 2016;9:71–6.
Máca J, Otranto D. Drosophilidae feeding on animals and the inherent mystery of their parasitism. Parasit Vectors. 2014;7:516.
Otranto D, Ferroglio E, Lia R, Traversa D, Rossi L. Current status and epidemiological observations of Thelazia callipaeda (Spirurida, Thelaziidae) in dogs, cats and foxes in Italy: a ‘coincidence’ or a parasitic disease of the Old Continent? Vet Parasitol. 2003;116:315–25.
Aradi MP. Dies drosophiliden-fauna des Karpatenbeckens. Rovt Közlem. 1959;12:409–26.
Papp L. Dipterous guilds of small-sized feeding sources in forest of Hungary. Acta Zool Acad Sci Hung. 2002;48:197–213.
Ruytoor P, Déan E, Pennant O, Dorchies P, Chermette R, Otranto D, et al. Ocular thelaziosis in dogs, France. Emerging Infect Dis. 2010;16:1943–5.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Caoimhe Murray for proofreading the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the 12190-4/2017/FEKUTSTRAT grant of the Hungarian Ministry of Human Capacities.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article. Sequences obtained during the current study are available in the GenBank database with accession numbers KX372681.1, MG677577, MG677578, MG874787, MG874788, MG874790-MG874792, MH178370 and MH178371.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Collected samples: RF, NH, AV, GYB, and JK. Processed samples: RF and MGY. Performed molecular analysis: NT. Analysed sequences: RF and NT. Analysed the data: RF and SN. Wrote the paper: RF, NT, and SN. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All medical procedures were carried out with the owner’s approval. All animals were examined and treated by a veterinarian to ensure that no dog or cat suffered any harm during the ocular examination, according to current regulations.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Farkas, R., Takács, N., Gyurkovszky, M. et al. The first feline and new canine cases of Thelazia callipaeda (Spirurida: Thelaziidae) infection in Hungary. Parasites Vectors 11, 338 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-018-2925-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-018-2925-2