Abstract
Background
The inverse relationship between case volume and postoperative mortality following high-risk surgical procedures have been reported. Thoracic aorta surgery is associated with one of the highest postoperative mortality. The relationship between institutional case volume and postoperative mortality in patients undergoing thoracic aorta replacement surgery was evaluated.
Methods
All thoracic aorta replacement surgeries performed in Korea between 2009 and 2016 in adult patients were analyzed using an administrative database. Hospitals were divided into low (< 30 cases/year), medium (30–60 cases/year), or high (> 60 cases/year) volume centers depending on the annual average number of thoracic aorta replacement surgeries performed. The impact of case volume on in-hospital mortality was assessed using the logistic regression.
Results
Across 83 hospitals, 4867 cases of thoracic aorta replacement were performed. In-hospital mortality was 8.6% (191/2222), 10.7% (77/717), and 21.9% (422/1928) in high, medium, and low volume centers, respectively. The adjusted risk of in-hospital mortality was significantly higher in medium (odds ratio [OR], 1.56; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.16–2.11, P = 0.004) and low volume centers (OR, 3.12; 95% CI, 2.54–3.85, P < 0.001) compared to high volume centers.
Conclusions
Patients who had underwent thoracic aorta replacement surgery in lower volume centers had increased risk of in-hospital mortality after surgery compared to those in higher volume centers. Our results may provide the basis for minimum case volume requirement or regionalization in thoracic aorta replacement surgery for optimal patient outcome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The association between case volume and patient outcome in complex surgical procedures have been reported consistently [1,2,3]. The mechanism behind the relationship is unclear but proposed explanations include accumulated experience at the individual or institutional level and preferential referral, which in turn may lead to increased case volume and improved outcomes. Numerous reports regarding the inverse relationship between case volume and postoperative mortality after high-risk procedures have led to debates/discussions concerning regionalization or efficient allocation of medical resources [4,5,6,7,8].
Thoracic aorta replacement surgery is one of the most complex surgical procedures requiring meticulous perioperative care with a reported 30-day mortality rate ranging from 5 to 10% [9, 10]. Moreover, serious postoperative complications including paraplegia or stroke are not uncommon, and thus, there is still room for improvement in patient outcomes despite recent improvement [10, 11]. Institutions with higher volume or more experience are likely to have a system or protocol regarding high-risk surgical procedures and the management thereafter [1]. However, the impact of institutional case volume in thoracic aorta replacement surgery on patient outcome has not been evaluated.
The aim of the study was to determine the relationship between institutional case volume and postoperative mortality in patients undergoing thoracic aorta replacement surgery. A population-based, retrospective observational study was performed by analyzing the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) database in Korea to evaluate the case volume effect in thoracic aorta replacement surgery.
Methods
The study design was a nationwide population-based retrospective observational study. The study protocol was determined exempt from review by the Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University Hospital due to the retrospective study design and the de-identified nature of the database.
Study population and data collection
Data from the NHIS database which covers more than 97% of Koreans was used for analysis [12, 13]. All adult cases of isolated thoracic aorta replacement surgery performed between January 2009 and December 2016 in Korea were analyzed using the procedure codes for ascending aorta, aortic arch, and descending thoracic aorta replacement surgeries. Preoperative comorbidities were identified using the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision (ICD-10) codes. Codes for emergent surgery and perioperative red blood cell transfusion were also extracted from the NHIS database. In-hospital, 1-year, and cumulative all-cause mortality were also collected. The institutional case volume was defined as the annual average number of thoracic aorta replacement surgeries performed during the study period. Centers were classified as low (< 30 cases/year), medium (30–60 cases/year), or high volume centers (> 60 cases/year) according to case volume of the center.
Study endpoints and statistical analysis
The primary outcome was in-hospital mortality after thoracic aorta replacement surgery according to the institutional case volume. Secondary outcomes included 1-year mortality and cumulative all-cause mortality.
Continuous data were expressed as mean (standard deviation) or median (interquartile range) where appropriate and categorical data as number (%). To compare patient characteristics and preoperative comorbidities, the one-way analysis of variance or the Kruskal-Wallis test was used for continuous variables and the χ2 test for categorical variables.
Logistic regression was performed to analyze the risk of in-hospital and 1-year mortality. Multivariable logistic regression was performed to adjust for extracted relevant variables including patient characteristics, preoperative comorbidities, and the year of surgery without applying any variable selection method. The amount of perioperative red blood cell transfusion was categorized: 0–1, 2–3, 4–5, and ≥ 6 units.
Cox proportional hazards model was used to compare the risk of cumulative all-cause mortality according to institutional case volume. The log-minus-log plot was used to check whether the proportional hazards assumption was met. Kaplan-Meier survival curves were also plotted.
All analyses were performed using SAS (ver. 9.4; SAS Institute, Cary, NC) and R (ver. 3.6.1; R Development Core Team, Vienna, Austria). A P value under 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Overall, 4867 cases of thoracic aorta replacement surgery were performed across 83 centers in Korea between January 2009 and December 2016. Thoracic aorta replacement surgery was performed on 1928 patients in 72 low volume centers, 717 patients in 5 medium volume centers, and 2222 in 6 high volume centers. Baseline characteristics according to case volume strata are presented in Table 1. Patients in high volume centers were older and had higher rate of comorbidities such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, and atrial fibrillation compared to patients in low and medium volume centers. In addition, descending thoracic aorta replacement and combined (2 or more of the 3 segments) thoracic aorta replacement were more frequently performed in high volume centers compared to lower volume centers (Table 1).
In-hospital mortality
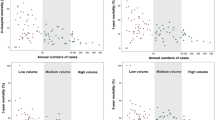
The overall in-hospital mortality was 14.2% (690/4867). The in-hospital mortality in high, medium, and low volume centers were 8.6% (191/2222), 10.7% (77/717), and 21.9% (422/1928), respectively. Figure 1a shows the in-hospital mortality of each center based on their case volume. The risk of in-hospital mortality was significantly higher in the medium (the adjusted odds ratio [OR], 1.56; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.16–2.11, P = 0.004) and low volume centers (the adjusted OR, 3.12; 95% CI, 2.54–3.85, P < 0.001) compared to high volume centers (Table 2).
One year mortality
The overall 1 year mortality rate after thoracic aorta replacement surgery was 19.7% (960/ 4867). One year mortality was 14.0% (312/2222), 15.5% (111/717), and 27.9% (537/1928) in high, medium, and low volume centers, respectively. The distribution of 1 year mortality according to institutional case volume are shown in Fig. 1b. Compared to high volume center, the adjusted OR of 1-year mortality in medium volume center was 1.45 (95% CI, 1.12–1.87; P = 0.005; Table 3). In low volume center, the adjusted OR was 2.62 (95% CI, 2.18–3.14; P < 0.001; Table 3).
Cumulative all-cause mortality
The results of Cox regression for cumulative all-cause mortality are presented in Table 4. The median (interquartile range) duration of follow-up after surgery was 3.1 (1.3–5.7) years. Low and medium volume centers were combined for the Cox regression analysis because the proportional hazards assumption was not met between the two groups. Patients who underwent thoracic aorta replacement surgery in low or medium volume centers showed a significantly higher risk of cumulative all-cause mortality compared to patients in high volume centers (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.55; 95% CI, 1.38–1.74; P < 0.001) (Table 4). The Kaplan-Meier survival curves with a follow-up period of up to 9 years showed a similar pattern (log-rank test, P < 0.001; Fig. 2).
Discussion
In this nationwide population-based study, low institutional case volume was an independent risk factor of mortality following thoracic aorta replacement surgery. The risk of in-hospital mortality was significantly higher in patients who underwent surgery in low (< 30 cases/year) and medium volume centers (30–60 cases/year), compared to high volume centers (> 60 cases/year). One year and cumulative all-cause mortality rates were both similarly higher in centers with low volume.
First described in the aircraft industry [14], the positive relationship between higher institutional case volume and improved patient survival have been consistently and repeatedly shown in high risk complex surgical procedures such as hepatectomy [4], esophagectomy [4, 5], lung resection [5, 15], and pelvic exenteration [4]. Thoracic aorta surgery is also a high-risk surgical procedure which requires complex and skilled surgical technique and immaculate perioperative care for best possible outcome. The reported incidence of operative mortality and major complications including stroke, infection, and renal failure following emergent surgical repair of acute thoracic or thoracoabdominal aortic dissection are exceptionally high, often exceeding 20 and 70%, respectively [16].
Numerous studies in cardiac surgery have shown that the risk of postoperative death was lower in high volume centers compared to lower volume centers including coronary artery bypass grafting [7], aortic valve replacement [17], mitral valve procedures [18], aortic root replacement [19], and heart transplantation [2]. A similar volume-outcome relationship have been reported in urgent or emergent abdominal aorta surgery [16, 20], but the relationship was between surgeon case volume, not institutional case volume, and patients outcome. The suggested cutoff was 10 ruptured abdominal aorta repairs and interestingly, there was no relationship between center volume and mortality [20]. Similarly, a previous national study in the United States revealed that the risk of mortality after emergent repair of thoracic or thoracoabdominal aortic dissection doubled in patients operated on by lower volume surgeons and centers (first quartile) compared to the highest volume surgeons [16]. The inverse association between institutional case volume and postoperative mortality was also noted in elective aortic root replacement surgery [19]. Our study included all types of thoracic aorta surgery and showed that the risk of postoperative death decreased significantly as institutional case volume increased.
Regionalization in the medical field is an attempt to concentrate resources to a few specialized health care centers /providers, often with an aim to improve patient outcome [21]. With a few exceptions such as in bariatric surgery [22], the literature in general tends to favor regionalization as shown in neonatal intensive care units [23] and designated pediatric trauma centers [24]. One recent relevant example may be the study which showed profound survival benefit in patients with influenza A-related (H1N1) acute respiratory distress syndrome after transfer to centers capable and experienced in extracorporeal membrane oxygenation [25]. A downside of regionalization may be decreased accessibility as shown in a simulated regionalization in pediatric cardiac surgery in the United States by closure of low volume hospitals which reduced postoperative mortality [26, 27]. Considering that previous studies were mostly performed in large countries, regionalization or concentration of high-risk cardiovascular surgeries to a limited number of select centers may be very effective for outcome optimization especially in relatively smaller countries where decreased geographical accessibility is negligible.
There are several limitations in our study that should be considered. First, although all cases of adult thoracic aorta replacement surgery performed during the past 8 years in Korea was included, bias may have been introduced due to the retrospective nature of the study design. Second, potential confounders such as laboratory data or clinical variables could not be obtained since the NHIS database was an administrative database in nature. Third, the information on the severity of thoracic aorta disease was lacking and may have affected postoperative patient outcome. Although a study suggested that the surgical indication for aorta surgery (dissection/ruptured aneurysm vs. intact aneurysms) had little effect on long-term mortality for 30-day survivors [28], another study suggested that in-hospital mortality seems to be worse in patients with ruptured thoracic aortic aneurysms compared to patients with intact thoracic aortic aneurysms [29]. Fourth, individual surgeon volume was not analyzed. Considering that most centers in Korea, including high volume centers, have a very limited number of surgeons who perform thoracic aorta surgery, the impact of institutional case volume on surgical outcomes may be comparable to that of surgeon volume.
Conclusions
In conclusion, patients who underwent thoracic aorta replacement surgery in lower volume centers had significantly higher risk of in-hospital, 1-year, and cumulative all-cause mortality compared to patients in higher volume centers. However, considering the emergent nature of some thoracic aorta replacement surgeries and the different accessibility to institutions competent of performing the surgery, factors other than case volume should be considered when interpreting our results.
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the National Health Insurance Service of Korea but restrictions apply to the availability of these Korean administrative data, which were used under license for the current study, and so are not publicly available.
Abbreviations
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- ICD-10:
-
International Classification of Diseases 10th revision
- NHIS:
-
National Health Insurance Service
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
References
Birkmeyer JD, Stukel TA, Siewers AE, Goodney PP, Wennberg DE, Lucas FL. Surgeon volume and operative mortality in the United States. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:2117–27.
Nam K, Jang EJ, Kim GH, Lee H, Kim DH, Ryu HG. Institutional case-volume and mortality after heart transplantation. Int Heart J. 2019;60:695–700.
Morche J, Mathes T, Pieper D. Relationship between surgeon volume and outcomes: a systematic review of systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 2016;5:204.
Begg CB, Cramer LD, Hoskins WJ, Brennan MF. Impact of hospital volume on operative mortality for major cancer surgery. JAMA. 1998;280:1747–51.
Finlayson EV, Goodney PP, Birkmeyer JD. Hospital volume and operative mortality in cancer surgery: a national study. Arch Surg. 2003;138:721–5.
Ho V, Heslin MJ, Yun H, Howard L. Trends in hospital and surgeon volume and operative mortality for cancer surgery. Ann Surg Oncol. 2006;13:851–8.
Kim LK, Looser P, Swaminathan RV, Minutello RM, Wong SC, Girardi L, et al. Outcomes in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft surgery in the United States based on hospital volume, 2007 to 2011. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016;151:1686–92.
Kahn JM, Linde-Zwirble WT, Wunsch H, Barnato AE, Iwashyna TJ, Roberts MS, et al. Potential value of regionalized intensive care for mechanically ventilated medical patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;177:285–91.
Higgins J, Lee MK, Co C, Janusz MT. Long-term outcomes after thoracic aortic surgery: a population-based study. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;148:47–52.
Bekkers JA, te Riele RJ, Takkenberg JJ, Bol Raap G, Hofland J, Roos-Hesselink JW, et al. Thoracic aortic surgery: an overview of 40 years clinical practice. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;147:332–43.
Cambria RP, Clouse WD, Davison JK, Dunn PF, Corey M, Dorer D. Thoracoabdominal aneurysm repair: results with 337 operations performed over a 15-year interval. Ann Surg. 2002;236:471–9.
Moon TJ. Light and shadows of the Korean healthcare system. J Korean Med Sci. 2012;27(Suppl):S3–6.
Song SO, Jung CH, Song YD, Park CY, Kwon HS, Cha BS, et al. Background and data configuration process of a nationwide population-based study using the korean national health insurance system. Diabetes Metab J. 2014;38:395–403.
Wright T. Factors affecting the cost of airplanes. J Aeronaut Sci. 1936;3:122–8.
Hannan EL, Radzyner M, Rubin D, Dougherty J, Brennan MF. The influence of hospital and surgeon volume on in-hospital mortality for colectomy, gastrectomy, and lung lobectomy in patients with cancer. Surgery. 2002;131:6–15.
Chikwe J, Cavallaro P, Itagaki S, Seigerman M, Diluozzo G, Adams DH. National outcomes in acute aortic dissection: influence of surgeon and institutional volume on operative mortality. Ann Thorac Surg. 2013;95:1563–9.
Patel HJ, Herbert MA, Drake DH, Hanson EC, Theurer PF, Bell GF, et al. Aortic valve replacement: using a statewide cardiac surgical database identifies a procedural volume hinge point. Ann Thorac Surg. 2013;96:1560–5.
Gammie JS, O'Brien SM, Griffith BP, Ferguson TB, Peterson ED. Influence of hospital procedural volume on care process and mortality for patients undergoing elective surgery for mitral regurgitation. Circulation. 2007;115:881–7.
Hughes GC, Zhao Y, Rankin JS, Scarborough JE, O'Brien S, Bavaria JE, et al. Effects of institutional volumes on operative outcomes for aortic root replacement in North America. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2013;145:166–70.
Dardik A, Burleyson GP, Bowman H, Gordon TA, Williams GM, Webb TH, et al. Surgical repair of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms in the state of Maryland: factors influencing outcome among 527 recent cases. J Vasc Surg. 1998;28:413–20.
Luft HS. Regionalization of medical care. Am J Public Health. 1985;75:125–6.
Dimick JB, Nicholas LH, Ryan AM, Thumma JR, Birkmeyer JD. Bariatric surgery complications before vs after implementation of a national policy restricting coverage to centers of excellence. JAMA. 2013;309:792–9.
Phibbs CS, Baker LC, Caughey AB, Danielsen B, Schmitt SK, Phibbs RH. Level and volume of neonatal intensive care and mortality in very-low-birth-weight infants. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:2165–75.
Wang NE, Saynina O, Vogel LD, Newgard CD, Bhattacharya J, Phibbs CS. The effect of trauma center care on pediatric injury mortality in California, 1999 to 2011. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2013;75:704–16.
Noah MA, Peek GJ, Finney SJ, Griffiths MJ, Harrison DA, Grieve R, et al. Referral to an extracorporeal membrane oxygenation center and mortality among patients with severe 2009 influenza A(H1N1). JAMA. 2011;306:1659–68.
Welke KF, Pasquali SK, Lin P, Backer CL, Overman DM, Romano JC, et al. Regionalization of congenital heart surgery in the United States. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2019;32:128–37.
Chang RK, Klitzner TS. Can regionalization decrease the number of deaths for children who undergo cardiac surgery? A theoretical analysis. Pediatrics. 2002;109:173–81.
Pan E, Kyto V, Savunen T, Gunn J. Early and late outcomes after open ascending aortic surgery: 47-year experience in a single centre. Heart Vessel. 2018;33:427–33.
Schermerhorn ML, Giles KA, Hamdan AD, Dalhberg SE, Hagberg R, Pomposelli F. Population-based outcomes of open descending thoracic aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg. 2008;48:821–7.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KN contributed to this study by study design, data analysis, and writing the manuscript. EJJ and Jun Woo Jo collected the data and performed statistical analyses. JWC and ML contributed to this study by study design and data. HGR designed the study and collected and analyzed the data. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study protocol was determined exempt from review by the Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University Hospital due to the retrospective study design and the de-identified nature of the database.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Nam, K., Jang, E.J., Jo, J.W. et al. Association between institutional case volume and mortality following thoracic aorta replacement: a nationwide Korean cohort study. J Cardiothorac Surg 15, 156 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13019-020-01204-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13019-020-01204-0