Abstract
Background
Numerous quantitatively biomechanical studies measuring the fixation stability of femoral stem using micromotions at the bone-implant interfaces in different directions and levels remain inconclusive. This network meta-analysis performed systematically aims to explore the rank probability of micromotions at the bone-implant interfaces based on biomechanical data from studies published.
Methods
Two electronic databases, PubMed/MEDLINE and Embase, were utilized to retrieve biomechanical studies providing the data of micromotions at the bone-stem interfaces. After screening and diluting out, the studies that met inclusion criteria will be utilized for statistical analysis. In order to contrast the stability of commonness and differences of the different parts of the femoral stem, the horizontal and vertical comparison of micromotions at the bone-implant interfaces were conducted using the pooled evaluation indexes including the mean difference (MD) and the surface under the cumulative ranking (SUCRA) curve, while inconsistency analysis, sensitivity analysis, subgroup analyses, and publication bias were performed for the stability evaluation of outcomes.
Results
Screening determined that 20 studies involving a total of 249 samples were deemed viable for inclusion in the network meta-analysis. Tip point registered the highest micromotions of 13 measurement points. In the horizontal level, the arrangements of 4 measurement points at the proximal (P1–P4), middle (P5–P8) and distal part of the stem (P9–P12) were P1 = P2 = P3 = P4, P7 > P8 > P6 = P5 and P10 ≥ P12 = P9 = P11, respectively. In the vertical level, the arrangements of 3 measurement points at the anterior, posterior, medial, and lateral directions was P9 > P5 = P1, P10 > P6 > P2, P11 > P7 > P3, and P12 > P8 > P4, respectively.
Conclusion
The network meta-analysis seems to reveal that the distal part of the femoral stem is easier to register higher micromotion, and tip point of femoral stem registers the highest micromotions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Currently, biomechanical tests are usually performed on synthetic or cadaveric specimens to evaluate the fixation stability of orthopedic implants at the hip, shoulder, and radius and for tendon repairs using bone anchoring devices [1,2,3,4,5,6]. In vitro investigations represent a decisive part in preclinical testing of cementless implants [7]. Though cemented as well as cementless total hip arthroplasty (THA) demonstrated a satisfactory survival rate (90%, 95%, and 97% at 5, 10, and 15 years follow-up, respectively) [8], aseptic loosening of artificial joint, resulting from the absence of primary stability, wear, and periprosthetical osteolysis as a result of the implant-specific bone remodeling, is one of the most common long-term complications in clinical, which limits the prospective efficacy and service life of prostheses [8].
With the development of the surgical technique and improvement of the material and design of the implant, these complications will reduce, but a further follow-up is still necessary. In contrast to cemented implants that achieve ultimate stability directly after implantation, cementless implants rely on their mechanically firm fit and lock between implant and bone (primary stability) and consequently biological osseous integration of the implant (secondary stability) [9], which has become increasingly popular over the past few years [10].
In total hip replacement, key point of prophylaxis for aseptic loosening was prophylaxis for periprosthetic osteolysis which was due to particulate wear debris induced-biological reaction in histiocyte surrounding the prosthesis. The rationale for the measurement micromotion between bone and implant is based on animal studies that demonstrated that excess movement (150 μm or more) can result in the failure of osseous integration of cementless implants [11, 12]. Therefore, the importance where the aseptic looseness occurs firstly cannot be overstressed, since they are essential for implant design.
To date, various methods have been developed and introduced to register micromotions [13,14,15]. Biomechanical investigation, as the most frequently used survey method, is applied to measure the relative micromotions at the bone-implant interface in total hip replacement arthroplasty (THA) based on two different kinds of specimens, fresh frozen cadaver bones and artificial composite femurs [16].
In fact, multiple biomechanical studies [13,14,15, 17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33] have reported to measure the relative micromotions at the bone-implant interface in the THA, with different length of femoral stem, sizes of femurs, loading scenarios, different specimens, implant types and sizes, and implant designs. Due to various loading scenarios along with numerous measurement devices and locations, comparisons of the micromotions of different research laboratories are very difficult [16].
To the best of our knowledge, results of the micromotions between bone and implant in the same specimen at different points on biomechanical test remain unknown, while various biomechanical studies have been performed which attempted to quantitatively measuring of the micromotions of femoral stem prosthesis at different levels. As such, the aims of the present study were to pool all available scientific published biomechanical material using strict inclusion and exclusion criteria followed by meta-analysis, compare the implant bone interface micromotions at different points of femoral stem, and explore the mechanism of aseptic loosening of artificial hip joint.
Materials and methods
This investigation was conducted based on “the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA)” statement [34].
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria were (1) biomechanical studies, (2) studies evaluating the micromotions between femoral stem and bone, and (3) studies providing available data to calculate evaluation index including mean and standard deviation of each point.
The exclusion criteria were (1) correspondence, commentary, reviews, editorials, systematic review, meta-analysis, and other non-original studies; (2) congress proceedings; (3) animal experiments; (4) finite analysis, and (5) biomechanical studies providing no data to calculate the evaluation index.
Data sources and search strategy
The following search terms were adopted in the network meta-analysis: “femoral” [All Fields], “femur” [All Fields], “femora” [All Fields], “total hip arthroplasty” [All Fields], “THA” [All Fields], “hip replacement” [All Fields], or “hemi-hip replacement” [All Fields] AND “biomechanics” [All Fields], “biomechanical” [All Fields], “biology mechanics” [All Fields], “finite element analysis” [All Fields], “finite element” [All Fields] or “FEA” [All Fields].
To be fully searched, potential relevant articles came from two sources. Firstly, two electronic databases including PubMed/MEDLINE and Embase were searched for all potential relevant articles without any language and search restrictions. Subsequently, all bibliographies of pertinent articles (included studies, reviews, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses) were further screened manually to retrieve additional studies that were omitted in the initial search.
Data extraction and quality assessment
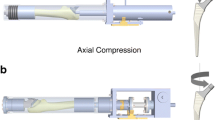
The following information was deemed appropriate for inclusion: (1) basic information including the first author’s surname, year of publication, and country of origin; (2) specimen information including the number of femurs and donors, age and gender of donors, and femoral osteotomy based on cadaver specimens; (3) composite femur information including characteristics and femoral osteotomy based on composite specimens; (4) implant information including brand, coating, characteristics, material testing machine, and test jig; (5) loading information including action and anatomical features of simulation, load force, femur orientation, and test cycles; and (6) micromotion of 13 measurement points (P1, P5, and P9 at the anterior direction in the proximal, middle, and distal part of femoral stem; P2, P6, and P10 at the posterior direction in the proximal, middle, and distal part of femoral stem, respectively; P3, P7, and P11 at the medial direction in the proximal, middle, and distal part of femoral stem; P4, P8, and P12 at the lateral direction in the proximal, middle, and distal part of femoral stem; P13 at the tip of femoral stem) (Fig. 1).
A modified version of the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) [35] checklist, a quality assessment tool, was used to estimate the methodological quality of the included studies, which considered 10 items including aim description, dependent variables description, interventions description, load/speed order randomized, setting description, date collection description, data analysis description, statistical description, drop outs, and point estimate/variability. Modifications were made to the STROBE checklist to only identify reporting criteria essential for the judgment of risk of bias, judgment of external generalizability of results, and replicability of the study’s methods.
Statistical analysis
To reduce potential bias, two blinded and independently working investigators (LFX and DJL) searched two electrical databases to screen and identify the targeted articles using the aforementioned keyword and inclusion criteria, extracted the useful data, and assessed the quality of included studies using STROBE [35]. Any discrepancies were resolved by consensus from discussion. Inter-reviewer agreement was calculated at title, abstract, and full-text stage, including the quality assessment of the included studies stage, and quality was assessed with a Kappa (κ) statistic. Agreement was categorized a priori as follows: 0.20 or less, poor agreement; 0.21 to 0.40, fair agreement; 0.41 to 0.60, moderate agreement; 0.61 to 0.80, substantial agreement; and 0.81 to 0.99, nearly perfect agreement [36].
R (R-v-3.4.3), rjags, and package of gemtc was used to perform the Bayesian network meta-analysis [37, 38]. Inconsistency test and homogeneity analysis were performed using node analysis method. According to the Cochrane handbook, heterogeneity cross studies was assessed using Q test (P < 0.05 indicating the presence of heterogeneity) and I2 test (0–40%, heterogeneity might not be present; 30–50%, moderate heterogeneity; 50–90%, substantial heterogeneity; and 75–100%, considerable heterogeneity) [39, 40]. The sensitivity analysis was performed by comparing the differences of two effect models including fixed-effect and random-effect model. The clinical outcome indicators were evaluated by the mean difference (MD) for continuous outcomes. The difference in mean values of displacement outcome was compared and had undergone 13 measurement points. The surface under the cumulative ranking (SUCRA) curve was conducted to discuss rank probability [37, 38]. P < 0.05 was accepted as indicative of statistical significance.
Results
Selection process, study characteristic, and quality assessment
The detailed article search and study selection process is listed in Fig. 2. A total of 3202 articles were retrieved after the initial search of the chosen electronic databases, with 37 additional articles being localized that originated from the references lists from the relevant studies scanned for in the databases. Of the 3239 articles scanned, 92 could be the target trails. Seventy-four articles were excluded from the selection process after further scanning where 23 articles were irrelevant publications, 21 articles only presenting finite element analysis data, one article that was a review, and 20 articles lacked sufficient data to be feasible for inclusion in the meta-analyses to calculate statistical index. After careful selection, eventually, 20 articles involving 249 specimens (148 composites and 101 cadaver femurs) were used for the network meta-analysis (website links enabling direct access to the abstract of included studies in Appendix 1). Articles with sample sizes ranging from 1 to 20 specimens were published from 2000 to 2017. Substantial agreement among the reviewers was achieved at each stage: title (κ = 0.73, 95% CI 0.69 to 0.78), abstract (κ = 0.87, 95% CI 0.82 to 0.93), and full-text (κ = 0.85, 95% CI 0.75 to 0.95) as well as the substantial agreement regarding the quality assessment of the included studies (κ = 0.83, 95% CI 0.72 to 0.89). The main characteristics of the studies utilized in the network meta-analysis are represented in Tables 1, 2, 3, and 4. The detail methodological quality of the studies utilized in the network meta-analysis is represented in Table 5.
Evidence network
As shown in Fig. 3, the lines between two connected points represent direct comparison. Points without connection indicate comparisons indirectly through the network meta-analysis. The width of the lines represents the number of sets of data from included studies, whereas the size of the nodes demonstrates the overall sample size of P1 to P13.
Forest plots of network meta-analyses
As indicated in Fig. 4 and Table 6, P13 ranked the highest micromotion, which means it is most likely to occur aseptic loosening. In the horizontal level, the arrangements of micromotions between femoral stem and bone using MDs for the comparisons at the proximal, middle, and distal part was P1 = P2 = P3 = P4, P7 > P8 > P6 = P5 and P10 ≥ P12 = P9 = P11, respectively. In the vertical level, the arrangements of micromotions between femoral stem and bone for the comparisons involving the anterior, posterior, medial, and lateral directions was P9 > P5 = P1, P10 > P6 > P2, P11 > P7 > P3, P12 > P8 > P4, respectively, which demonstrated that the micromotions in the distal part of femoral stem is higher than that in the medial and proximal part, while the micromotions in the medial part of femoral stem is higher than that in the proximal part. Contribution plot of network meta-analysis shows the contribution of each direct and indirect comparison to the network summary effects in the Appendix 2.
Inconsistency test of network meta-analyses
The node-splitting method and its Bayesian P value used to report the inconsistency of our results showed that the confidential intervals in all loops were crossed over with blank value (P > 0.05), and direct and indirect estimates of the effects in network meta-analysis were not significantly different, with good homogeneity (Fig. 5). And then sensitivity analysis was performed to compare the analysis result of the random-effects model ([Dbar] = 49.48, [pD] = 32.37, [DIC] = 81.85, and I2 = 0) and fixed-effect model ([Dbar] = 56.92, [pD] = 26.00, [DIC] = 82.92, and I2 = 3%), which demonstrated that the results of two models were similar; therefore, the results were steady.
The SUCRA of micromotions of 13 measurement points
As indicated in Figs. 6 and 7, P13 ranked the highest micromotion, which means it is most likely to occur aseptic loosening. In the horizontal level, the arrangement of rank probability for the comparisons of micromotions between femoral stem and bone in four directions at the proximal, middle, and distal part was P1 > P4 = P2 > P3, P7 > P8 > P6 > P5 and P10 > P12 > P9 > P11, respectively (Fig. 6). In the vertical level, the arrangement of rank probability for the comparisons of anterior, posterior, medial, and lateral micromotions between femoral stem and bone was P9 > P1 > P5, P10 > P6 > P2, P11 > P7 > P3 and P12 > P8 > P4, respectively (Fig. 7).
Publication bias
Figure 8 implied that no evident publication bias of the comparison for micromotions of four directions in the proximal, middle, and distal portion of femoral stem surface was observed in this network meta-analysis. However, funnel plots provide only hints of publication bias and not definite proof; therefore, the results should be interpreted cautiously.
Discussion
It is a well-known fact that infectious loosening and aseptic loosening are the problems of artificial joint in clinical which needs to be addressed. This network meta-analysis provides evidence-based principles from the biomechanical rationale that micromotions between femoral stem and bone in four directions is similar at the proximal, P7 is the highest point at the middle part, and P10 is the highest point at the distal part. P13 is the highest point of micromotions at implant bone surface, while the results demonstrated that the micromotions in the distal part of the femoral stem seem to be higher than that in the middle and proximal part. Additionally, the micromotions in the medial part of femoral stem seem to be higher than that in the proximal part.
The biomechanical method for measurement of micromotions is very accurate due to a resolution of 0.1 μm but also a very complex procedure. The accurate measurement lies within the 3D measurement. However, most studies examined relative micromotion of every measurement point at implant bone surface utilizing only one LVDT [16, 28, 41], which usually only measured the spatial dimension of the movement orthogonal to the bone in most cases. At such, comparing published results of micromotion measurements at implant bone surface is challenging due to multiple factors such as different test set-ups, loading conditions, and specimen used and may bring errors for the final results. Fortunately, numerous studies have tried to figure out these factors. Previous biomechanical studies demonstrated that undersizing of cementless hip stems is a risk factor for aseptic loosening and early subsidence than appropriate size [25, 26]. Meanwhile, composite femur size and different offset versions (increased femoral offset and altered neck version) of cementless hip prostheses seem to be a minor influence factor for the primary stability [18, 24,25,26, 29]. Micromotions may be underestimated and the primary stability overestimated without a special emphasis on active simulation of muscle forces [28]. A biomechanical analysis performed by Heller et al. presented that the anchorage concept of cementless stems had a significant influence on the initial interface micromotions [27]. Two biomechanical studies presented that loading cycles (40,000 vs.100,000 and 3000 vs. 8000) seem to be a minor influence factor for the measurement of micromotion [13, 19]. Another biomechanical study suggested that stair climbing of patient activity induced the highest mechanical instability at the bone-prosthesis interface, which may compromise the necessary osseointegration process [28]. There were no significant differences in the anterior, lateral, or posterior interface cyclical motions for any of the stem shortening levels in neither one leg stance nor stair climbing [15]. Nevertheless, with the chosen position of the leg with adduction as well as flexion, a reasonable amount of torsional moment is applied, taking to some extent torsional moments into account that occur during stair climbing [42].
As specimens for the measurement of micromotions, fresh frozen human cadaveric femurs with the more similar biomechanical characteristics and anatomical structures to human and synthetic composite femurs with the advantages of consistent geometry and mechanical properties are commonly used. According to our results, a total of ten studies [14, 25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33] that chose the composite femurs and 10 studies [13, 15, 17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24] that chose the cadaver femurs demonstrated that femur difference did not notably influence their micromotions.
In this network meta-analysis, the highest 3D micromotion is registered at the distal tip of the femoral stem, which is in accordance with the previous biomechanical studies [14, 18, 27, 30]. Three studies [25, 29, 33] demonstrated that the highest micromotion of the femoral stem at the distal tip reached or exceeded the threshold for osseous integration of 150 μm, which was related to the design rationale with a proximal anchorage and load transfer.
This network meta-analysis provided evidence-based principles from the biomechanical rational that micromotions between femoral stem and bone in four directions was similar in the proximal part while medial point and posterior point registered the highest micromotions in the middle and distal part, respectively, while the results demonstrated that the micromotions in the distal part of the femoral stem seem to be higher than that in the middle and proximal part. Even though we could not detect significant different results in respect to comparison of P9 vs. P5, there was a tendency towards higher micromotion registers at P9 compared to the P5. Additionally, the micromotions in the medial part of femoral stem seem to be higher than that in the proximal part.
The concept of cementless fixation can be addressed with different design concepts [10], which at a certain presented the locking sites, such as the Zweymüller-type prosthesis locking in the distal metaphysis and proximal diaphysis with a four-point fixation concept and the CLS Spotorno stem involving the stem designs of the proximal anchoring [10, 43]. These two kinds of stems exhibited similar movement patterns moved mainly in the distal direction. Relatively small interface movements were registered in the antero-posterior direction. These results reflect the stem design with an intended proximal load transfer and a thin distal part of the stem not filing the intramedullary canal to prevent load transmission in this area [44, 45]. Distal locking mechanism of the Zweymüller stem showed proximal bone atrophy as a result of stress shielding in vivo [46]. The thin distal stem is not intended to fit and fill the medullary canal in order to avoid stress shielding [22] and also does not need osseous integration to result in a secondary stable stem [12]. 3D micromotion of CLS stem at the distal tip reached the design rationale with a proximal anchorage and load transfer. In contrast, the 3D micromotions of the remaining measurement points 1 to 4 were clear below 100 μm in all examined sizes. This finding indicates that osseous integration is to be expected from the level of the lesser trochanter till the middle of the stem.
There are still some limitations even through the rigorous analyses that were conducted. First of all, methodological variability and different loading scenarios along with varying measurement devices and locations, and comparisons of the experimental outcome of different research laboratories are very difficult. Besides different sizes of cadaver and composite femurs and various types of prostheses, the evaluation and comparison of micromotions varied in these biomechanics meaning that heterogeneity was unavoidable even though subgroup and sensitivities analyses were performed with rigorous methods. Second, some characteristics of the femurs and prostheses, such as simulated action, anatomical features simulated, femoral osteotomy, and test cycles were not provided by the literature. Third, several subgroup analyses were based on a small number of studies or were impossible because of incomplete data, which influence statistical algorithms and their deductions. Finally, the present study only enrolled published literature. Some unpublished ones which met inclusion criteria might be missed and publication bias was shown in some subgroup analyses.
Conclusions
The network meta-analysis providing evidence-based principles from the biomechanical rationale for micromotions between femoral stem and bone seems to reveal that the distal part of the femoral stem is easier to register higher micromotion and the tip point of the femoral stem registers the highest micromotions.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- MD:
-
Mean difference
- PRISMA:
-
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
- STROBE:
-
Strengthening the Reporting of Observational studies in Epidemiology
- SUCRA:
-
Surface under the cumulative ranking curve
- THA:
-
Total hip arthroplasty
References
Fottner A, Baur-Melnyk A, Birkenmaier C, Jansson V, Durr HR. Stress fractures presenting as tumours: a retrospective analysis of 22 cases. Int Orthop. 2009;33(2):489–92.
Fottner A, Steinbruck A, Sadoghi P, Mazoochian F, Jansson V. Digital comparison of planned and implanted stem position in total hip replacement using a program form migration analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(7):1013–9.
Pietschmann MF, Holzer A, Rosl C, Scharpf A, Niethammer T, Jansson V, Muller PE. What humeri are suitable for comparative testing of suture anchors? An ultrastructural bone analysis and biomechanical study of ovine, bovine and human humeri and four different anchor types. J Biomech. 2010;43(6):1125–30.
Pietschmann MF, Sadoghi P, Hauser E, Scharpf A, Gulecyuz MF, Schroder C, Jansson V, Muller PE. Influence of testing conditions on primary stability of arthroscopic knot tying for rotator cuff repair: slippery when wet? Arthroscopy. 2011;27(12):1628–36.
Burkner A, Fottner A, Lichtinger T, Teske W, Vogel T, Jansson V, von Schulze PC. Primary stability of cementless threaded acetabular cups at first implantation and in the case of revision regarding micromotions as indicators. Biomed Tech (Berl). 2012;57(3):169–74.
Pietschmann MF, Frohlich V, Ficklscherer A, Gulecyuz MF, Wegener B, Jansson V, Muller PE. Suture anchor fixation strength in osteopenic versus non-osteopenic bone for rotator cuff repair. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009;129(3):373–9.
Scheerlinck T, Casteleyn PP. The design features of cemented femoral hip implants. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88(11):1409–18.
Garellick G, Kärrholm J, Lindahl H, Malchau H, Rogmark C, Rolfson O. The Swedish Hip Arthroplasty Register: annual report 2014. Sahlgrenska: University Hospital; 2015.
Ruben RB, Fernandes PR, Folgado J. On the optimal shape of hip implants. J Biomech. 2012;45(2):239–46.
Khanuja HS, Vakil JJ, Goddard MS, Mont MA. Cementless femoral fixation in total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(5):500–9.
Pilliar RM, Lee JM, Maniatopoulos C. Observations on the effect of movement on bone ingrowth into porous-surfaced implants. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986;208:108–13.
Soballe K, Hansen ES, B-Rasmussen H, Jorgensen PH, Bunger C. Tissue ingrowth into titanium and hydroxyapatite-coated implants during stable and unstable mechanical conditions. J Orthop Res. 1992;10(2):285–99.
Bieger R, Freitag T, Ignatius A, Reichel H, Durselen L. Primary stability of a shoulderless Zweymuller hip stem: a comparative in vitro micromotion study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016;11(1):73.
Fottner A, Woiczinski M, Kistler M, Schroder C, Schmidutz TF, Jansson V, Schmidutz F. Influence of undersized cementless hip stems on primary stability and strain distribution. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017;137(10):1435–41.
Ostbyhaug PO, Klaksvik J, Romundstad P, Aamodt A. Shortening of an anatomical stem, how short is short enough? An in vitro study of load transfer and primary stability. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2013;227(5):481–9.
Gheduzzi S, Miles AW. A review of pre-clinical testing of femoral stem subsidence and comparison with clinical data. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2007;221(1):39–46.
Abdul-Kadir MR, Hansen U, Klabunde R, Lucas D, Amis A. Finite element modelling of primary hip stem stability: the effect of interference fit. J Biomech. 2008;41(3):587–94.
Bieger R, Ignatius A, Decking R, Claes L, Reichel H, Durselen L. Primary stability and strain distribution of cementless hip stems as a function of implant design. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2012;27(2):158–64.
Bieger R, Ignatius A, Reichel H, Durselen L. Biomechanics of a short stem: in vitro primary stability and stress shielding of a conservative cementless hip stem. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(8):1180–6.
Gotze C, Steens W, Vieth V, Poremba C, Claes L, Steinbeck J. Primary stability in cementless femoral stems: custom-made versus conventional femoral prosthesis. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2002;17(4):267–73.
Klestil T, Morlock MM, Schwieger K, Sellenschloh K, Curda B, Biedermann R, Hennerbichler A, Schmoelz W, Rabl W, Blauth M. Migration of two different cementless hip arthroplasty stems in combination with two different heads: a biomechanical in vitro study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2006;126(6):387–93.
Ostbyhaug PO, Klaksvik J, Romundstad P, Aamodt A. Primary stability of custom and anatomical uncemented femoral stems: a method for three-dimensional in vitro measurement of implant stability. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2010;25(4):318–24.
Pettersen SH, Wik TS, Skallerud B. Subject specific finite element analysis of implant stability for a cementless femoral stem. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2009;24(6):480–7.
Wik TS, Enoksen C, Klaksvik J, Ostbyhaug PO, Foss OA, Ludvigsen J, Aamodt A. In vitro testing of the deformation pattern and initial stability of a cementless stem coupled to an experimental femoral head, with increased offset and altered femoral neck angles. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2011;225(8):797–808.
Fottner A, Peter CV, Schmidutz F, Wanke-Jellinek L, Schroder C, Mazoochian F, Jansson V. Biomechanical evaluation of different offset versions of a cementless hip prosthesis by 3-dimensional measurement of micromotions. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2011;26(8):830–5.
Fottner A, Schmid M, Birkenmaier C, Mazoochian F, Plitz W, Volkmar J. Biomechanical evaluation of two types of short-stemmed hip prostheses compared to the trust plate prosthesis by three-dimensional measurement of micromotions. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2009;24(5):429–34.
Heller MO, Kassi JP, Perka C, Duda GN. Cementless stem fixation and primary stability under physiological-like loads in vitro. Biomed Tech (Berl). 2005;50(12):394–9.
Kassi JP, Heller MO, Stoeckle U, Perka C, Duda GN. Stair climbing is more critical than walking in pre-clinical assessment of primary stability in cementless THA in vitro. J Biomech. 2005;38(5):1143–54.
Schmidutz F, Woiczinski M, Kistler M, Schroder C, Jansson V, Fottner A. Influence of different sizes of composite femora on the biomechanical behavior of cementless hip prosthesis. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2017;41:60–5.
Tuncay I, Yildiz F, Bilsel K, Uzer G, Elmadag M, Erden T, Bozdag E. Biomechanical comparison of 2 different femoral stems in the shortening osteotomy of the high-riding hip. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(6):1346–51.
Viceconti M, Monti L, Muccini R, Bernakiewicz M, Toni A. Even a thin layer of soft tissue may compromise the primary stability of cementless hip stems. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2001;16(9):765–75.
Viceconti M, Muccini R, Bernakiewicz M, Baleani M, Cristofolini L. Large-sliding contact elements accurately predict levels of bone-implant micromotion relevant to osseointegration. J Biomech. 2000;33(12):1611–8.
Yan SG, Woiczinski M, Schmidutz TF, Weber P, Paulus AC, Steinbruck A, Jansson V, Schmidutz F. Can the metaphyseal anchored Metha short stem safely be revised with a standard CLS stem? A biomechanical analysis. Int Orthop. 2017;41(12):2471–7.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ. 2009;339:b2535.
von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Pocock SJ, Gotzsche PC, Vandenbroucke JP, Initiative S. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet. 2007;370(9596):1453–7.
Cohen J. Weighted kappa: nominal scale agreement with provision for scaled disagreement or partial credit. Psychol Bull. 1968;70:213–20.
Zhang Q, Dong J, Zhou D, Liu F. Comparative risk of fracture for bariatric procedures in patients with obesity: a systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis. International journal of surgery. 2020;75:13–23.
Liu F, Dong J, Shen WJ, Kang Q, Zhou D, Xiong F. Detecting rotator cuff tears: a network meta-analysis of 144 diagnostic studies. Orthopaedic journal of sports medicine. 2020;8(2):2325967119900356.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327(7414):557–60.
Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane Collaboration.: Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Chichester, England; Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Blackwell; 2008.
Britton JR, Walsh LA, Prendergast PJ. Mechanical simulation of muscle loading on the proximal femur: analysis of cemented femoral component migration with and without muscle loading. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2003;18(7):637–46.
Bergmann G, Deuretzbacher G, Heller M, Graichen F, Rohlmann A, Strauss J, Duda GN. Hip contact forces and gait patterns from routine activities. J Biomech. 2001;34(7):859–71.
Korovessis P, Droutsas P, Piperos G, Michael A, Baikousis A, Stamatakis M. Course of bone mineral content changes around cementless Zweymueller total hip arthroplasty. A 4-year follow-up study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1997;116(1-2):60–5.
Evola FR, Evola G, Graceffa A, Sessa A, Pavone V, Costarella L, Sessa G, Avondo S. Performance of the CLS Spotorno uncemented stem in the third decade after implantation. The bone & joint journal. 2014;96-B(4):455–61.
Spotorno L, Romagnoli S, Ivaldo N, Grappiolo G, Bibbiani E, Blaha DJ, Guen TA. The CLS system. Theoretical concept and results. Acta orthopaedica Belgica. 1993;59(Suppl 1):144–8.
Korovessis P, Piperos G, Michael A, Baikousis A, Stamatakis M. Changes in bone mineral density around a stable uncemented total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 1997;21(1):30–4.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was supported by the China Scholarship Council (CSC) which funded the author (Fanxiao Liu, No. 201808080126).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LFX, DJL, and WBM conceived and designed the study. LFX, DJL, and WBM performed the search, extraction of data, and methodological assessment. All authors analyzed the data and wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors read the final manuscript and approved it for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1: Appendix Table 1.
Included studies, with website links enabling direct access to each corresponding article abstract. Appendix figure 1. Contribution plot for the comparison of micromotions in four directions at the proximal, middle and distal portion of femoral stem surface.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Li, Q., Dong, J. et al. Comparisons of the surface micromotions of cementless femoral prosthesis in the horizontal and vertical levels: a network analysis of biomechanical studies. J Orthop Surg Res 15, 293 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-020-01794-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-020-01794-4