Abstract
Background
There is a paucity of information for predicting patient outcomes other than the American Association for the Surgery of Trauma (AAST) renal injury scale. The aim of this study was to evaluate the association between the patient characteristics and outcomes of patients with blunt renal trauma using a nationwide database in Japan.
Methods
We performed a retrospective analysis of the Japan Trauma Data Bank (JTDB) from 2004 to 2018. We identified patients with blunt renal trauma by AIS codes converted to AAST grades. We evaluated trends in patient characteristics and management and assessed factors associated with mortality and nephrectomy using a multivariable logistic regression analysis.
Results
We identified 3550 patients with blunt renal trauma. Their median age was 43 years and 74.2% were male. Nephrectomy was performed in 3.8%, and the overall mortality rate was 9.5%. We found increasing trends in age and emergency abdominal angiography and decreasing trends in nephrectomy and mortality over the 15-year period. The following factors were associated with mortality: age ≥ 65 years (adjusted OR 3.36); pedestrian accident (adjusted OR 1.94); fall from height (adjusted OR 1.91); shock on arrival (adjusted OR 4.02); concomitant injuries to the head/neck (adjusted OR 3.14), pelvis/lower-extremity (adjusted OR 1.59), liver (adjusted OR 1.68), spleen (adjusted OR 1.45), and gastrointestinal tract (adjusted OR 1.90); AAST grades III–V (adjusted ORs 1.42, 2.16, and 5.55); and emergency abdominal angiography (adjusted OR 0.70). The following factors were associated with nephrectomy: shock on arrival (adjusted OR 1.98), concomitant injuries to the thorax (adjusted OR 0.46) and spleen (adjusted OR 2.07), AAST grades III, IV, and V (adjusted ORs 18.40, 113.89, and 468.17), and emergency abdominal angiography (adjusted OR 0.28).
Conclusions
We demonstrated that the AAST grade and emergency angiography were associated with mortality and nephrectomy in blunt renal trauma in the Japanese population.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Renal trauma, which accounts for 1–5% of all trauma and up to 10% of abdominal trauma, is predominantly caused by blunt mechanisms of injury [1, 2]. A previous systematic review in 2005 noted that non-operative management of renal trauma was not yet universally accepted, despite the fact that many studies supported non-operative management [3]. However, more recent systematic reviews have reported favorable outcomes of non-operative management, even in high-grade renal trauma [4, 5]. In recent years, less invasive interventions, such as endovascular procedures, have increasingly been used for blunt renal trauma [6, 7]. Nevertheless, nephrectomy is still required for unstable patients those in whom non-operative management fails [8,9,10]. According to a report by van der Wilden et al., among patients injured by road traffic accidents, non-operative management failed in 27.3% of the patients who were > 55 years of age [11]. It is important to identify patients who require nephrectomy after renal trauma.
While multiple studies have shown the efficacy and safety of non-operative management, there is still a paucity of information on the characteristics of blunt renal trauma and current managements and their trends. Furthermore, there is little evidence on predictors of the need for nephrectomy other than the American Association for the Surgery of Trauma (AAST) renal injury scale [12]. The aim of this study was to evaluate the association between patient characteristics and outcomes such as mortality and the need for nephrectomy in patients with blunt renal trauma using a nationwide database in Japan, in considering trends in management.
Methods
Study design and setting
We performed a retrospective analysis of the Japan Trauma Data Bank (JTDB). The institutional ethics committee of Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine approved this study and waived the requirement for informed consent because all of the analyses used anonymous data (approval no. 16260).
Japan Trauma Data Bank
The JTDB is a nationwide voluntary hospital-based trauma registry that was established in 2003 by the Japanese Association for the Surgery and Trauma (Trauma Surgery Committee) and the Japanese Association for Acute Medicine (Committee for Clinical Care Evaluation) [13]. In 2018, 280 major emergency medical institutions across Japan participated in the JTDB registry [14]. The ability of these hospitals is equivalent to that of level I trauma centers in the USA. Data were collected from participating institutions via the internet. In most cases, physicians and medical assistants who completed the Abbreviated Injury Scale (AIS) coding course registered the patients’ data.
The JTDB captures the following data in trauma cases: age, sex, mechanism of injury, AIS code (version 1998), Injury Severity Score (ISS), vital signs on hospital arrival, date and time series from hospital arrival to discharge, medical managements (e.g., interventional radiology), surgical operations and computed tomography scanning, complications, and mortality at discharge. The ISS was calculated from the top three scores of the AIS in the nine anatomical regions classified by the AIS code.
Participants
The cases of patients who were admitted in the years 2004 to 2018 and whose information was registered in the JTDB were analyzed. We included blunt trauma patients with traumatic renal injuries, which were identified by AIS codes using the method described by Kuan et al. [12] AIS codes were converted to AAST renal injury grades, excluding codes that did not match [15,16,17]. We excluded patients who were in cardiac arrest on hospital arrival, and those whose records were missing information on age, sex, vital signs on arrival, ISS, or mortality. We defined cardiac arrest on hospital arrival as a systolic blood pressure of 0 mmHg or a heart rate of 0 bpm on hospital arrival.
Variables
We extracted the following patient data from the JTDB database: age, sex, mechanism of injury, AIS code, ISS, vital signs on hospital arrival, interventions (e.g., emergency abdominal angiography or nephrectomy), and mortality at discharge. To evaluate temporal trends, we divided the 15-year study period into five periods: 2004–2006, 2007–2009, 2010–2012, 2013–2015, and 2016–2018. We categorized age into three groups: < 20 years, 20–64 years, and ≥ 65 years. We defined shock as a systolic blood pressure of < 80 mmHg on hospital arrival [18]. To assess concomitant injuries, we mapped AIS-coded injuries to the following categories: head/neck, thorax, pelvis/extremities, and intra-abdominal organs (including the liver, spleen, pancreas, and gastrointestinal tract).
Statistical analyses
Continuous variables are presented as the median and interquartile range (IQR), and categorical variables are presented as the number and percentage. The Jonckheere-Terpstra test was used to analyze trends in continuous variables, and the Cochrane-Armitage test was used to analyze trends in categorical variables.
Factors associated with mortality were assessed by a multivariable logistic regression analysis, and adjusted odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated. A multivariable logistic regression analysis was performed with a forced entry procedure. The independent parameters included age group (< 20 years, 20–64 years, ≥ 65 years), sex, mechanism of injury, shock on arrival, each concomitant injury, AAST renal injury grade, and interventions (e.g., emergency abdominal angiography or nephrectomy), and the 3-year time period. We also assessed factors associated with nephrectomy using a multivariable logistic regression analysis. The fit of the models was evaluated with the Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test.
As a further analysis, we divided patients into those with isolated renal trauma and those with multiple trauma to evaluate the difference in patient demographics. The patient characteristics were compared between the groups using the Mann-Whitney U test for continuous variables and the chi-squared test for categorical variables.
All tests were two-tailed, and P values of < 0.05 were considered to indicate statistical significance. All statistical analyses were performed using R Statistical Software (version 3.6.2; R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria).
Results
Figure 1 shows the patient flow of the study. During the study period, 356,535 patients were recorded in the JTDB database and 322,659 patients had blunt injuries. There were 5159 patients with blunt renal trauma. Among them, 3550 (1.0%) patients with renal trauma that could be converted to an AAST grade from AIS codes were eligible for inclusion in the analysis. The patient characteristics and their temporal trends are summarized in Table 1. The median age of the overall patient population was 43 years (IQR, 23–65 years), 17.1% were younger than 20 years of age, 26.1% were 65 years of age or older, and 74.2% of the patients were male. The most frequent mechanism of injury was motorcycle accident (22.5%), followed by fall from height (17.4%) and car accident (15.7%). The median ISS was 22 (IQR, 14–34), and 11.4% were in shock on arrival at the hospital. Emergency abdominal angiography was performed in 33.5% of the patients, while nephrectomy was performed in 3.8%. The overall mortality rate in the cohort was 9.5%.
Over 15 years, the median age increased from 29 years to 48 years old (P for trend = 0.002). The proportion of patients of 20 to 64 years of age was decreased (P for trend < 0.001), while that of patients of ≥ 65 years of age was significantly increased (P for trend < 0.001). The percentage of male patients increased from 73.0 to 76.3% (P for trend = 0.014). The percentage of victims of motorcycle accidents decreased (P for trend < 0.001), while the percentages of patients with falls down stairs, falls on the ground, and sports-related injury increased (P for trend < 0.001, = 0.008, and = 0.018, respectively). The percentage of patients who were in shock on hospital arrival was decreased (P for trend < 0.001). Regarding the distribution of the AAST renal injury grades, there was a significant increase in patients with AAST grade III (P for trend < 0.001) and a significant decrease in patients with AAST grade V (P for trend = 0.008). There was a decrease in concomitant head/neck injury (P for trend = 0.001) and concomitant pelvis/lower-extremity injury (P for trend = 0.008), and there was an increase in concomitant thoracic injury (P for trend = 0.013). There was a significant increase in emergency abdominal angiography from 25.9% in 2004–2006 to 35.5% in 2016–2018 (P for trend < 0.001). Meanwhile, there was a corresponding decrease in nephrectomy from 5.3 to 2.4% (P for trend < 0.001). Mortality declined significantly from 15.3% in 2004–2006 to 7.3% in 2016–2018 (P for trend < 0.001).
Table 2 summarizes the associations between mortality and various factors. Age ≥ 65 years (adjusted OR 3.36 [95% CI 2.16 to 5.34]), pedestrian accident (adjusted OR 1.94 [95% CI 1.26 to 3.07]), fall from height (adjusted OR 1.91 [95% CI 1.25 to 2.96]), shock on hospital arrival (adjusted OR 4.02 [95% CI 3.01 to 5.34]), concomitant head/neck injury (adjusted OR 3.14 [95% CI 2.39 to 4.14]), concomitant pelvis/lower-extremity injury (adjusted OR 1.59 [95% CI 1.21 to 2.08]), concomitant liver injury (adjusted OR 1.68 [95% CI 1.27 to 2.21]), concomitant splenic injury (adjusted OR 1.45 [95% CI 1.06 to 1.97]), concomitant gastrointestinal tract injury (adjusted OR 1.90 [95% CI 1.01 to 3.55]), and AAST grade III, IV, and V (adjusted ORs 1.42 [95% CI 1.02 to 1.96], 2.16 [95% CI 1.48 to 3.13], and 5.55 [95% CI 3.22 to 9.49], respectively) were associated with higher mortality. Emergency abdominal angiography was associated with lower mortality (adjusted OR 0.70 [95% CI 0.53 to 0.93]), but nephrectomy was not. This model had a non-significant Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit statistic (P = 0.390).
Table 3 summarizes the associations between nephrectomy and various factors. Nephrectomy was significantly associated with shock on hospital arrival (adjusted OR 1.98 [95% CI 1.21 to 3.20]) and concomitant splenic injury (adjusted OR 2.07 [95% CI 1.27 to 3.33]). AAST grades III, IV, and V (adjusted ORs 18.40 [95% CI 5.31 to 115.88], 113.89 [95% CI 34.83 to 701.57], and 468.17 [95% CI 137.15 to 2941.20], respectively) were positively associated with nephrectomy, while concomitant thoracic injury (adjusted OR 0.46 [95% CI 0.29 to 0.75]) and emergency abdominal angiography (adjusted OR 0.28 [95% CI 0.18 to 0.44]) were negatively associated with nephrectomy. This model demonstrated good fit in a Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test (P = 0.863).
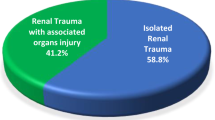
Table 4 summarizes the analysis of cases of isolated renal trauma. Patients with isolated renal trauma were significantly younger and showed a difference in the distribution of mechanisms of injury from those with multiple trauma. Falls down stairs, falls on the ground, and sports-related injuries were more frequent in the isolated renal trauma group. The proportion of nephrectomy did not differ between the groups. The median ISS of the isolated renal trauma group was significantly lower than that of the multiple trauma group (9 vs. 25, P < 0.001). The proportion of patients in shock on hospital arrival in the isolated renal trauma group was significantly lower than that of the multiple trauma group (3.7% vs. 12.7%, P < 0.001). The mortality rate in the isolated renal trauma group was significantly lower than that in the multiple trauma group (1.4% vs. 10.9%, P < 0.001).
Discussion
We reported the comprehensive analysis of the characteristics and management of cases with patients with blunt renal trauma, their temporal trends, and factors associated with patient outcomes using a nationwide database in Japan. Blunt renal trauma accounted for 1.0% of all blunt injuries registered in the JTDB, which was a similar rate to that reported in previous studies [17, 19]. As the number of institutions participating in the JTDB increased, the number of patients with blunt renal trauma increased. Patients of ≥ 65 years of age accounted for 26.1% of our total cohort, and this proportion increased significantly in each period. It may reflect the aging of the population in Japan, the change in the distribution of mechanisms of injury, and an increase in the number of institutions participating in the JTDB [20]. Although there is no apparent change in the median ISS, there was a decreasing trend in the percentage of patients in shock on hospital arrival. This may be partially due to changes in road safety regulations and behavioral patterns [21, 22]. Regarding the management of blunt renal trauma, we observed an increase in the use of emergency abdominal angiography and a decline in nephrectomy, which is a similar trend to Western countries [6, 7, 23]. The mortality rate decreased from 15.3 to 7.3% over 15 years, which is a similar trend to previous studies [24].
Analysis of mortality
We report that factors such as age ≥ 65 years, shock on hospital arrival, concomitant injuries to the head/neck, pelvis/lower-extremity, liver, spleen, gastrointestinal tract, and AAST grades III, IV, and V were significantly associated with mortality. The gradient of mortality in each AAST grade was consistent with that in the National Trauma Data Bank in the USA [25]. We validated the association between the AAST grade and mortality in the Japanese population. Emergency abdominal angiography was associated with a lower mortality rate, which may reflect a benefit of non-operative management after angiography.
Analysis of nephrectomy
Nephrectomy was more likely performed in those with shock on hospital arrival, concomitant splenic injury, and AAST grade ≥ III. Previous studies demonstrated the AAST grade, and other indications for laparotomy were associated with nephrectomy, which is consistent with our results [26, 27]. As high-grade renal trauma is associated with a higher risk of treatment failure in patients undergoing non-operative management in comparison to cases of lower-grade renal trauma, an appropriate assessment of the renal injury is important for selecting the appropriate management [16]. Patients with concomitant thoracic injury were less likely to receive nephrectomy, possibly because angiography and transcatheter arterial embolization (TAE) were less invasive and because it is relatively easy to control bleeding in cases involving trauma-induced coagulopathy and respiratory distress due to chest trauma [28,29,30].
Isolated renal trauma
Isolated renal trauma happened in young people and was more frequent in patients who had experienced falls down stairs, falls on the ground, and sports-related injury, which may be damaged by a relatively small but localized force. A previous study showed that sports-related blunt renal trauma is more likely to occur in isolation without other abdominal or thoracic injury [31]. The mortality rate in patients with isolated renal trauma was 1.4%; however, we could not examine the cause of death.
Limitations
The present study was associated with some limitations. First, although we analyzed a nationwide trauma database in which major critical care centers in Japan participated, the JTDB is not a population-based sample of trauma patients and the data are registered voluntarily. Therefore, selection and information biases both exist. Second, not all AIS codes correspond to AAST grades. However, the method to identify renal trauma has been successfully applied in multiple studies [15,16,17]. Third, because JTDB does not include data on TAE for renal injury and the failure of non-operative management, we could not assess these factors. Lastly, our results may not be fully applicable to other areas that have different healthcare systems, legislation, and age distribution of the population [21, 32, 33]. However, our results may be useful for improving trauma care in developed countries with an aging population.
Conclusions
This study provides a comprehensive analysis of blunt renal trauma cases registered in a nationwide trauma database over a 15-year period. We demonstrated that the AAST grade and emergency angiography were associated with mortality and the need for nephrectomy in patients with blunt renal trauma in the Japanese population. By understanding the current trends in patient characteristics and management, as well as the factors associated with important clinical outcomes, our findings can help to improve the quality of care for patients with blunt renal trauma.
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the JTDB, but the availability of these data is restricted.
Abbreviations
- AAST:
-
American Association for the Surgery of Trauma
- JTDB:
-
Japan Trauma Data Bank
- AIS:
-
Abbreviated Injury Scale
- ISS:
-
Injury Severity Score
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- TAE:
-
Transcatheter arterial embolization
References
Meng MV, Brandes SB, McAninch JW. Renal trauma: indications and techniques for surgical exploration. World J Urol. 1999;17(2):71–7.
Smith J, Caldwell E, D’Amours S, Jalaludin B, Sugrue M. Abdominal trauma: a disease in evolution. ANZ J Surg. 2005;75(9):790–4.
Santucci RA, Fisher MB. The literature increasingly supports expectant (conservative) management of renal trauma - a systematic review. J Trauma. 2005;59(2):493–503.
Mingoli A, La Torre M, Migliori E, Cirillo B, Zambon M, Sapienza P, Brachini G. Operative and nonoperative management for renal trauma: comparison of outcomes. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2017;13:1127–38.
Sujenthiran A, Elshout PJ, Veskimae E, MacLennan S, Yuan Y, Serafetinidis E, et al. Is nonoperative management the best first-line option for high-grade renal trauma? A systematic review. Eur Urol Focus. 2019;5(2):290–300.
Colaco M, Navarrete RA, MacDonald SM, Stitzel JD, Terlecki RP. Nationwide procedural trends for renal trauma management. Ann Surg. 2019;269(2):367–9.
Aldiwani M, Georgiades F, Omar I, Angel-Scott H, Tharakan T, Vale J, Mayer E. Traumatic renal injury in a UK major trauma centre – current management strategies and the role of early re-imaging. BJU Int 2019 (in press).
Morey AF, Brandes S, Dugi DD 3rd, Armstrong JH, Breyer BN, Broghammer JA, et al. Urotrauma: AUA guideline. J corUrol. 2014;192(2):327–35.
Lynch TH, Martínez-Piñeiro L, Plas E, Serafetinides E, Türkeri L, Santucci RA, Hohenfellner M. European Association of Urology. EAU guidelines on urological trauma. Eur Urol. 2005;47(1):1–15.
Coccolini F, Moore EE, Kluger Y, Biffl W, Leppaniemi A, Matsumura Y, et al. Kidney and uro-trauma: WSES-AAST guidelines. World J Emerg Surg. 2019;14(54):1–25.
van der Wilden GM, Velmahos GC, Joseph DK, Jacobs L, Debusk MG, Adams CA, et al. Successful nonoperative management of the most severe blunt renal injuries: a multicenter study of the research consortium of new England centers for trauma. JAMA Surg. 2013;148(10):924–31.
Kuan JK, Wright JL, Nathens AB, Rivara FP, Wessells H. American Association for the Surgery of Trauma Organ Injury Scale for Kidney Injuries predicts nephrectomy, dialysis. J Trauma Inj Infect Crit Care. 2006;60(2):351–6.
Shoko T, Shiraishi A, Kaji M, Otomo Y. Effect of pre-existing medical conditions on in-hospital mortality: analysis of 20,257 trauma patients in Japan. J Am Coll Surg. 2010;211:338–46.
Japan Trauma Data Bank Report 2019. Available from: https://www.jtcr-jatec.org/traumabank/dataroom/data/JTDB2019e.pdf. Accessed 8 July 2020.
Kurtz MP, Eswara JR, Vetter JM, Nelson CP, Brandes SB. Blunt abdominal trauma from motor vehicle collisions from 2007 to 2011: renal injury probability and severity in children versus adults. J Urol. 2017;197(3):906–10.
Bjurlin MA, Fantus RJ, Fantus RJ, Villines D. Comparison of nonoperative and surgical management of renal trauma: can we predict when nonoperative management fails? J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017;82(2):356–61.
Bjurlin MA, Renson A, Fantus RJ, Fantus RJ. Impact of trauma center designation and interfacility transfer on renal trauma outcomes: evidence for universal management. Eur Urol Focus. 2019;5(6):1135–42.
Neidel T, Salvador N, Heller R. Impact of systolic blood pressure limits on the diagnostic value of triage algorithms. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med 2017;25(118).
Wessells H, Suh D, Porter JR, Rivara F, MacKenzie EJ, Jurkovich GJ, Nathens AB. Renal injury and operative management in the United States: results of a population-based study. J Trauma. 2003;54(3):423–30.
Christensen K, Doblhammer G, Rau R, Vaupel JW. Ageing populations: the challenges ahead. Lancet. 2009;374:1196–208.
Nakahara S, Ichikawa M, Kimura A. Population strategies and high-risk-individual strategies for road safety in Japan. Health Policy (New. York). 2011;100(2–3):247–55.
Nagata T, Setoguchi S, Hemenway D, Perry MJ. Effectiveness of a law to reduce alcohol-impaired driving in Japan. Inj Prev. 2008;14(1):19–23.
Mann U, Zemp L, Rourke KF. Contemporary management of renal trauma in Canada: a 10-year experience at a level 1 trauma centre. Can Urol Assoc J. 2019;13(6):E177–82.
Mackenzie EJ. Epidemiology of injuries: current trends and future challenges. Epidemiol Rev. 2000;22(1):112–9.
Tinkoff G, Esposito TJ, Reed J, Kilgo P, Fildes J, Pasquale M, Meredith JW. American Association for the Surgery of Trauma Organ Injury Scale I: spleen, liver, and kidney, validation based on the National Trauma Data Bank. J Am Coll Surg. 2008;207:646–55.
Wright JL, Nathens AB, Rivara FP, Wessells H. Renal and extrarenal predictors of nephrectomy from the National Trauma Data Bank. J Urol. 2006;175:970–5.
McClung CD, Hotaling JM, Wang J, Wessells H, Voelzke BB. Contemporary trends in the immediate surgical management of renal trauma using a national database. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2013;75(4):602–6.
Chang R, Cardenas JC, Wade CE, Holcomb JB. Advances in the understanding of trauma-induced coagulopathy. Blood. 2016;128(8):1043–9.
Wright AP, Wade CE, Camp EA, Caga-Anan Z, Radwan Z, Minei K, et al. Pulmonary contusion on admission chest X-ray is associated with coagulopathy and mortality in trauma patients. Emerg Med Trauma Surg Care. 2015;2(3):1–5.
Brewer ME Jr, Strnad BT, Daley BJ, Currier RP, Klein FA, Mobley JD, Kim ED. Percutaneous embolization for the management of grade 5 renal trauma in hemodynamically unstable patients: initial experience. J Urol. 2009;181(4):1737–41.
Patel DP, Redshaw JD, Breyer BN, Smith TG, Erickson BA, Majercik SD, et al. High-grade renal injuries are often isolated in sports-related trauma. Injury. 2016;46(7):1245–9.
Nakao S, Katayama Y, Kitamura T, Hirose T, Sado J, Ishida K, et al. Epidemiological profile of emergency medical services in Japan: a population-based descriptive study in 2016. Acute Med Surg 2020;7(e485).
Ikegami N, Yoo BK, Hashimoto H, Matsumoto M, Ogata H, Babazono A, et al. Japanese universal health coverage: evolution, achievements, and challenges. Lancet. 2011;378:1106–15.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the emergency medical service personnel, nurses, emergency physicians, and healthcare workers who participated in the JTDB. This article was supported by the Clinical Investigator’s Research Project at Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine.
List of meetings at which the paper was presented:
This article has not been presented at any meetings.
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from the Osaka Kidney Foundation (OKF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.N. and A.H. participated in the data curation. S.N., Y.K., A.H., and Te.K. structured the methods and the statistical analysis. S.N. prepared the manuscript. S.N., Y.K., A.H., Te.K., T.H., K.I., Y.U., J.T., Ta.K., T.M., and K.K. performed the data interpretation. Y.N. and T.S. critically reviewed the manuscript. The authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The institutional ethics committee of Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine approved this study and waived the requirement for informed consent because all of the analyses used anonymous data (approval no. 16260).
Consent for publication
All authors have read the final manuscript and agreed for its publication in the present form.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Nakao, S., Katayama, Y., Hirayama, A. et al. Trends and outcomes of blunt renal trauma management: a nationwide cohort study in Japan. World J Emerg Surg 15, 50 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13017-020-00329-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13017-020-00329-w