Abstract
Background
Cell necrosis, oxidative damage, and fibrogenesis are involved in cirrhosis development, a condition in which insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) levels are diminished. This study evaluates whether the exogenous administration of low doses of IGF-1 can induce hepatoprotection in acute carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver damage compared to healthy controls (Wt Igf +/+). Additionally, the impact of IGF-1 deficiency on a damaged liver was investigated in mice with a partial deficit of this hormone (Hz Igf1 +/−).
Methods
Three groups of 25 ± 5-week-old healthy male mice (Wt Igf +/+) were included in the protocol: untreated controls (Wt). Controls that received CCl4 (Wt + CCl4) and Wt + CCl4 were treated subcutaneously with IGF-1 (2 µg/100 g body weight/day) for 10 days (Wt + CCl4 + IGF1). In parallel, three IGF-1-deficient mice (Hz Igf1 +/−) groups were studied: untreated Hz, Hz + CCl4, and Hz + CCl4 + IGF-1. Microarray and real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) analyses, serum aminotransferases levels, liver histology, and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels were assessed at the end of the treatment in all groups. All data represent mean ± SEM.
Results
An altered gene coding expression pattern for proteins of the extracellular matrix, fibrosis, and cellular protection were found, as compared to healthy controls, in which IGF-1 therapy normalized in the series including healthy mice. Liver histology showed that Wt + CCl4 + IGF1 mice had less oxidative damage, fibrosis, lymphocytic infiltrate, and cellular changes when compared to the Wt + CCl4. Moreover, there was a correlation between MDA levels and the histological damage score (Pearson’s r = 0.858). In the IGF-1-deficient mice series, similar findings were identified, denoting a much more vulnerable hepatic parenchyma.
Conclusions
IGF1 treatment improved the biochemistry, histology, and genetic expression of pro-regenerative and cytoprotective factors in both series (healthy and IGF-1-deficient mice) with acute liver damage, suggesting that low doses of IGF-1, in acute liver damage, could be a feasible therapeutic option.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Cell necrosis, inflammation, oxidative damage, hepatocellular regeneration, and fibrogenesis are processes that occur during the early stages of oxidative liver damage and lead to cirrhosis. Circulating levels of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) are diminished in advanced cirrhosis [1, 2] due to the loss of biosynthetic mass. Moreover, it has been recently proposed that reduced hepatic production of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) in ascitic liver disease could be one of the factors contributing to malnutrition in cirrhotic patients [3,4,5]. Moreover, our group has previously reported that, in an experimental cirrhosis model, low doses of IGF-1 improved nitrogen balance [3], jejunal sugar and amino-acid absorption [3, 4, 6, 7], osteopenia [8], testicular atrophy [9, 10], and somatostatinergic tone [11]. This treatment also induced additional hepatoprotective effects on the liver, including a reduction in lipid peroxidation, collagen content, and mechanisms of fibrogenesis with an improvement of histopathology, mitochondrial function, and antioxidant enzyme activities [5, 12,13,14].
As previously mentioned, serum IGF-1 levels are reduced in advanced liver cirrhosis; however, they are not applicable for acute liver oxidative damage. For this reason, the aim of the present work was to study whether low doses of IGF-1 resulted in hepatoprotection in carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced acute liver damage in healthy controls. We have recently shown the deleterious effects of partial IGF-1 deficiency in the liver [15]. Thus, we have extended our studies to analyze the effect of low doses of IGF-1 on IGF-1-deficient mice (Hz, Igf +/−) livers receiving acute CCl4-induced injury, in order to understand the impact and magnitude of such deficiency in terms of progression to liver cirrhosis.
Methods
Animals and experimental design
The experimental model was established and characterized as previously reported [16, 17]. Briefly, IGF-1 heterozygous mice were obtained by cross-breeding transgenic mice from lines 129SV and MF1Igf1tm1Arge. Animal genotype determination was performed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis (Applied Biosystems, 2720 Thermal Cycler, Spain). DNA was extracted from a piece of tail, and specific primers were used to identify both Igf1 and neo genes (Extract-N-Amp TM Tissue PCR KIT Sigma, USA).
Animals were housed in cages in a room with a 12-h light/dark cycle and constant humidity (50–55%) and temperature (20–22 °C). Food (Tekland Global, 18% protein rodent diet, Harlan Laboratories, Spain) and water were given ad libitum. All experimental procedures were performed in compliance with The Guiding Principles for Research Involving Animals, and approved by the bioethical committees of our institutions (School of Medicine, Tecnologico de Monterrey, Monterrey, México, and CEU-San Pablo University, Madrid, Spain).
Three groups of 25 ± 5-week-old healthy male mice [wild-type (Wt), Igf +/+] were included in the experimental protocol: untreated controls and wild-type mice (Wt Igf +/+, n = 6); controls that received CCl4 (50 μl of CCl4) (n = 6) and Wt + CCl4 mice were subcutaneously treated with IGF-1 (2 μg/100 g/body weight/day) for 10 days (Wt + CCl4 + IGF-1, Igf1 +/+, n = 6). Another three groups of the same age, these with partial IGF-1 deficiency (Hz, Igf1 +/−), were studied in parallel: untreated Hz (Igf1 +/−, n = 6), Hz + CCl4 (n = 6), and Hz + CCl4 + IGF-1 (2 μg/100 g/body weight/day) for 10 days (n = 6). IGF-1 was provided by Chiron Corporation, USA.
On day 0, blood was drawn from the submandibular vein to determine IGF-1 serum levels before treatment. On day 11, mice were weighed, blood was obtained from the submandibular vein, and then mice sacrificed by cervical dislocation. The liver was carefully removed, weighed (Denver Instruments, Germany), and divided into two sections: the left lobe was stored in RNA later (Qiagen-Izasa, Spain) at −80 °C for microarray and real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) analyses, and the right lobe was used for histologic examination and malondialdehyde (MDA) assessment. Serum was stored at −20 °C.
Histological study and semiquantitative liver damage and fibrosis scores
In liver sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and Masson’s trichrome, semiquantitative assessment of fibrosis and hepatic damage was blindly performed using a numerical scoring system, as used in previous works following validated models [18], based on the following criteria: (1) number and length of fibrous septa (0–2 points); (2) area of oxidative damage/necrosis (0–2 points); (3) lymphocyte infiltration as a marker of inflammation (0–1 points); (4) steatosis (0–1 points); and (5) cellular changes, such as misalignment of hepatocyte cords (0–1), aberrant nuclei (0–1), dead cells/cellular debris (0–1), and loss of the polyhedral shape of the hepatocytes (0–1); with a total partial score of 4 points (see Table 1).
All preparations were evaluated independently by three observers (double-blind), receiving a maximum score of 10 points. The arithmetical mean of the two scores was taken as the final score. This study was carried out using a light microscope (Leica, Switzerland). The slides were scanned using the Leica SCN400 (Leica Biosystems Pathology Imaging, Switzerland) and processed using Aperio ImageScope (v12.03.0.5056, Leica Biosystems Pathology Imaging).
Serum IGF-1 and transaminases (AST and ALT) circulating levels
Serum IGF-1 levels were determined by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) commercial kit following specific commercial assay protocol instructions (Chiron Corporation, USA), read in a Varioskan spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, Spain), and interpreted using SkanIt software (Fisher Scientific, Spain).
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) were assessed by routine laboratory methods, using a Cobas-Hitachi autoanalyzer (Mannheim, Germany).
MDA in liver homogenates
MDA was used as an index of lipid peroxidation, and was measured after heating samples at 45 °C for 60 min in an acidic medium. MDA was titrated by a colorimetric assay using 7.6 mM 1-methyl-2-phenylindole (modified from Gerard-Monnier) [19], which, after reacting with MDA, generates a stable chromophore that can be measured at 586 nm (Eppendorf Biophotometer plus, Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany). Determinations were performed from liver homogenates immersed in Tris–hydrochloride (Tris–HCl) solution (1 g of liver tissue per 10 ml) centrifuged at 3000g during 10 min at 4 °C.
Gene expression studies on the liver
Microarray analysis
Liver mRNA was isolated from animals belonging to each experimental group in accordance with the protocol outlined in the RNeasy Kit (Qiagen-Isaza, Spain). Technical procedures for microarray analysis, including quality control of mRNA, labeling, hybridization, and scanning of the arrays were performed according to standard operating procedures for Affymetrix protocols (GeneChipH Expression Analysis Manual, Affymetrix, USA). The mRNAs were profiled using Affymetrix HT MG-430 PM. The array signals were normalized using Robust Multichip Averages and batch-effects of the six replicates were corrected using ComBat. Differentially expressed genes between the six experimental groups were selected using FDR-corrected p values under 0.01 (p < 0.05).
Total RNA extraction, reverse transcription, and RT-qPCR
Hepatic lobules were cryopreserved in RNAlater (Qiagen-Izasa, Spain). The day RT-qPCR determinations were performed, hepatic samples were homogenized with TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, UK) in TissueLyser LT (Qiagen-Izasa, Spain), and RNA was extracted and purified using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, USA), including digestion with RNase-free DNase, following the manufacturer’s instructions. RNA quality was verified by A260/A280 ratio with a Nanodrop (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., USA), and fragment integrity and length were verified using a Bioanalyzer 2100 (Agilent Technologies Inc., USA). Purified RNA was then converted to cDNA using the RNA-to-DNA EcoDryTM Premix (Clonetech Labs, USA) for RT-qPCR assays. RT-qPCR assays were performed in a 3100 Avant Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems Hispania, Spain). The thermal profile consisted of an initial 5-min melting step at 95 °C followed by 40 cycles at 95 °C for 10 s and 60 °C for 60 s.
The following specific Taqman® probes for the selected genes were supplied by Applied Biosystems: Igf1, Igf1r, Igf2, Asma, Adam11, Cat, Ccl2, Ccl5, Ccl12, Col1a1, Col1a2, Col4a3, Col4a4, Col4a5, Ctgf, Gpx1, Gpx8, Hif1a, Hsp90b1, Hspa4l, Hspa5, Hspa8, Hspa13, Hspb1, Ifng, Igfbp2, Igfbp3, Igfbp4, Igfbp5, Igfbp6, Igfbp7, Il1b, Mmp2, Mmp3, Mmp9, Pcna, Pdgfrb, Sp3, Tgfa, Tgfb1, Tgfb2, Timp, Tnfa, Vegfa, and Xiap.
The relative mRNA levels of genes of interest were normalized to TBP expression using the simplified comparative threshold cycle delta, cycle threshold (CT) method [2−(ΔCT gene of interest − ΔCT actin)] [20].
Statistical analysis
All data represent mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed on SPSS 17 (IBM, USA). Significance was estimated by the U-Mann–Whitney test to compare non-parametric independent groups, or, when appropriate, by analysis of variance (ANOVA) to compare three parametric-dependent groups. The correlation between two parameters was analyzed by Spearman or Pearson’s tests. Differences were considered significant at a level of p < 0.05.
Results
Circulating levels of IGF-1 and body and liver weights
On day 0, significant differences of circulating levels of IGF-1 were found between healthy mice (Wt Igf +/+) and Hz groups (Hz: 495.21 ± 63.41 vs. Wt: 653.19 ± 41.18 ng/ml, p < 0.01). Both groups of animals were divided into three experimental subgroups, as mentioned above.
On day 11, IGF-1-deficient animals (Hz) showed a significant reduction in body weight as compared to Wt groups (Table 1). Liver weights were also significantly reduced in the Hz and Hz + CCl4 groups as compared to their respective controls (Wt and Wt + CCl4). However, no significant differences in liver weight were observed between Wt + CCl4 and Hz + CCl4 groups treated with IGF-1 therapy (see Table 1).
When liver weight was referred to body weight (relative liver weight, mg of liver/g of body weight) no differences were found between groups, with the exception of the Hz + CCl4 group treated with IGF-1, which presented an increase in relative liver weight as compared to the Wt + CCl4 + IGF-1 group. Table 1 summarizes all of these data.
Parameters of cytolysis and lipid peroxidation
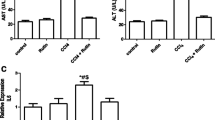
On day 11, ALT levels were found to be significantly increased in both the Wt + CCl4 and Hz + CCl4 groups as compared to the Wt and Hz groups (Fig. 1a). ALT levels were also higher in the Hz + CCl4 + IGF-1 group as compared to the Wt + CCl4 +IGF-1 group (p < 0.01). AST levels were only increased in the Hz group receiving CCl4. No effect of IGF-1 was found for this parameter (Fig. 1b).
a Alanine transaminase levels. b Aspartate transaminase levels. c Malondialdehyde, as a marker of lipid peroxidation in liver homogenates. d Semiquantitative score of histological findings in the three experimental groups of both series (Wt and Hz animals); and e correlation between oxidative damage (MDA levels) and semiquantitative score of histological findings. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. Wt; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs. Hz; &p < 0.05, &&p < 0.01 vs. Wt + CCl4; †p < 0.05, ††p < 0.01 vs. Hz + CCl4; £p < 0.05 vs. Hz + CCl4 + IGF-1
In both experimental groups, the hepatic levels of the lipid peroxidation products (estimated as nmol of MDA/g of tissue) were significantly increased in mice receiving CCl4, whereas IGF-1 dramatically reduced them to similar values to those found in controls (Fig. 1c). An increase in this lipid peroxidation marker was also found in Hz mice compared to that found in Wt groups, suggesting that the single IGF-1 deficiency renders the liver more vulnerable to oxidative damage. IGF-1 therapy was useful in both groups (Wt + CCl4 + IGF-1 and Hz + CCl4 + IGF-1), as shown in Fig. 1c.
Liver histology and semiquantitative score
Figure 2a shows relevant findings in the three experimental groups of healthy mice (Wt). The histopathological score was significantly lower in the Wt + CCl4 + IGF-1 group than in the Wt + CCl4 group (Wt + CCl4 + IGF-1: 4.68 ± 0.08 vs. Wt + CCl4: 7.01 ± 0.16 arbitrary units, p < 0.01) (Fig. 1d; Table 2).
Figure 2b corresponds to histological findings from the three IGF-1-deficient groups (Hz). The histopathological score was also found to be reduced in IGF-1-treated mice (Hz + CCl4 + IGF-1) as compared to untreated mice receiving CCl4 (Hz + CCl4 + IGF-1: 4.98 ± 0.25 vs Hz + CCl4: 8.00 ± 0.17, p < 0.01). Data are summarized in Table 2.
Emphasis must be placed livers from IGF-1-deficient mice, which show a greater vulnerability to CCl4-induced damage, expressing higher rates of lymphocytic infiltrates (Wt + CCl4, 0.53 ± 0.04 vs. Hz + CCl4, 0.78 ± 0.03 p < 0.05) and oxidative damage (Wt + CCl4, 1.30 ± 0.09 vs. Hz + CCl4, 1.60 ± 0.04 p < 0.05) (see Table 2).
Interestingly, a direct and significant correlation was found between MDA levels and the semiquantitative scores of histopathological damage (Pearson’s r = 0.858; Fig. 1e).
Gene expression studies of the liver
In light of these results, a study of hepatic gene expression was performed. Microarray analysis revealed 211 genes that were either over-expressed or under-expressed in IGF-1-deficient animals as compared to controls (fold-change over ± 1.5) and Hz mice treated with IGF-1 (see Additional file 1: Table S1).
Among genes with an altered expression, we focused on those coding for: (1) inflammatory, fibrogenic, or regenerative factors, and antioxidant enzymes; (2) proteins of the extracellular matrix (ECM) and its regulators; and (3) cytoprotective molecules involved in survival and mitochondrial protection.
RT-qPCR was subsequently performed to confirm changes depicted by the microarray over ±1.5 fold-change.
A significant increase in Igf1r was confirmed in the Hz + CCl4 group (1.712 ± 0.282; p < 0.05 vs. control), which was restored by IGF-1 therapy (Hz + CCl4 + IGF-1 = 0.817 ± 0.147).
Figure 3 summarizes RT-qPCR results from genes that encode growth factors involved in inflammation (Il1b, Ccl5, Pdgfrb, Ifng, Tnfa) and cell proliferation (Pcna). Additionally, Fig. 4 shows genes related to angiogenesis (Vegf), fibrogenesis (Tgfb2, Ctgf), and antioxidative enzymes (Gpx1, Gpx8, and Cat). In accordance with previous data [19], IGF-1 deficiency increased gene expression of pro-inflammatory factors, such as Ccl5 and Il1b.
Data from RT-qPCR for genes expressing (mRNA) encoding growth factors involved in inflammation (a Il1b, b Ccl5, c Pdgfr, d Ifng, e Tnfa) and cell proliferation (f Pcna). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs controls (Wt); #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 vs Hz; &p < 0.05, &&p < 0.01 vs corresponding group of the other series (i.e., Wt + CCl4 vs Hz + CCl4, or Wt + CCl4 + IGF-1 vs Hz + CCl4 + IGF-1)
RT-qPCR results for gene expression (mRNA) involved in angiogenesis (a Vegfa), fibrogenesis (b Tgfb2, c Ctgf), and antioxidants enzymes (d Gpx1, e Gpx8, and f Cat). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs controls (Wt); #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 vs Hz; &p < 0.05, &&p < 0.01 vs corresponding group of the other series (i.e., Wt + CCl4 vs Hz + CCl4, or Wt + CCl4 + IGF-1 vs Hz + CCl4 + IGF-1)
Hz animals responded differently than healthy ones (Wt) after CCl4 injury or IGF-1 therapy (Ifng, Pcna, Tnfa, Vegf, Ctgf, Gpx1, Gpx8, Cat).
In addition, Pcna gene expression was only increased in Wt + CCl4 + IGF-1 mice (p < 0.01 vs. other groups, including Hz + CCl4 + IGF-1), representing an increment in cellular proliferation. Tgfb2 expression was increased in all groups receiving CCl4 insult as compared to their corresponding controls (Wt or Hz). IGF-1 treatment did not modulate its expression in the Wt + CCl4 nor Hz + CCl4 groups.
Ifng expression was only augmented in the Hz + CCl4 group, particularly after IGF-1 treatment. Tnfa expression showed a significant increase in Wt + CCl4 animals, which is indicative of cell death. Surprisingly, animals with IGF-1 deficiency lacked such a physiological response.
With regard to genes encoding antioxidant enzymes, IGF-1 therapy increased the expression of catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX1) in Wt + CCl4 mice. However, it had no effect on Gpx8 gene expression.
Figure 5 includes results from genes coding for several types of collagen, its regulators [metalloproteinases (MMPs) and a desintegrin and metalloproteinase (ADAM)], and their inhibitors (TIMPs) (Fig. 6). Additionally, we have included gene expression for actin-alfa-2 (ASMA) as a marker of stellate cell transformation to myofibroblasts (Fig. 5).
Gene expression (mRNA) measured by RT-qPCR coding for collagens (a Col1a1, b Col1a2, c Col4a5, d Col4a4, e Col4a3), and aorta smooth muscle actin a2 (f Asma). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 all groups vs controls (Wt + vehicle); #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 Hz + CCl4 or Hz + CCl4 + IGF-1 vs corresponding control group (Hz + vehicle); &p < 0.05 between Wt + CCl4 + IGF-1 vs Hz + CCl4 + IGF-1 or Wt + CCl4 vs Hz + CCl4
RT-qPCR of gene expression (mRNA) that encodes proteases (a MMP2, b MMP13, c MMP9 and d a desintegrin and metallopeptidase—Adam11) as well as its inhibitor (e Timp1), and the inhibitor of apoptosis (f Xiap). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 all groups vs controls (Wt + vehicle); #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 Hz + CCl4 or Hz + CCl4 + IGF-1 vs corresponding control group (Hz + vehicle); &p < 0.05 between Wt + CCl4 + IGF-1 vs Hz + CCl4 + IGF-1 or Wt + CCl4 vs Hz + CCl4
Surprisingly, Hz mice did not respond to CCl4 injury by expressing Col1a1, while healthy mice (Wt + CCl4) expressed it in significant increments. However, the expression of the other collagen types depicted a reduction following IGF-1 therapy in Wt + CCl4 mice, with the only exception of Col4a3.
Regarding the gene expression of MMPs (Mmp2, Mmp13, Mmp9, and Adam11), an expected increase after CCl4 injury was observed and accompanied by a reduction after IGF-1 therapy that did not reach statistical significance.
Finally, the expression of Asma (actin-alfa-2) was significantly increased in healthy mice receiving CCl4, but not in IGF-1-deficient animals, which revealed a significant reduction when compared to the Wt + CCl4 group (Fig. 5).
Figure 7 summarizes the gene expression of chaperones, heat shock proteins, proteins involved in cytoprotective activities, and Xiap (X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis) (Fig. 6). Results indicated that Hsp gene expression (Hspb1) was significantly diminished in both groups receiving CCl4 as compared with their corresponding controls (Wt or Hz). Expression of Hspa13 was also significantly increased by IGF-1 therapy, as well as Hsp90b1, Hspa41, and Hspa5 in Wt + CCl4 + IGF-1 mice.
Gene expression (mRNA) measured by RT-qPCR coding for heat shock proteins (HSPs) involved in cytoprotective activities. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 all groups vs controls (Wt + vehicle); #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 Hz + CCl4 or Hz + CCl4 + IGF-1 vs corresponding control group (Hz + vehicle); &p < 0.05 between Wt + CCl4 + IGF-1 vs Hz + CCl4 + IGF-1 or Wt + CCl4 vs Hz + CCl4
IGF-1 deficiency significantly increased the expression of Xiap (Fig. 6) and Hspa8 (Fig. 7), while the expression of both of them was found to be reduced by IGF-1 therapy (Hz + CCl4 + IGF-1). Even though the expression of Hspa8 was not changed in the three experimental groups of Wt animals, IGF-1 therapy significantly increased the expression of Xiap.
Discussion
Results in this paper demonstrate that low doses of IGF-1, for short periods of time, induce hepatoprotective, antioxidant, and antifibrogenic effects in animals with acute liver damage, in accordance with previous results from experimental cirrhosis [5, 12, 13]. These findings suggest that low-dose-IGF-1 therapy could be an effective strategy to avoid the progression to cirrhotic hepatic disease in early stages of liver damage.
The histopathological damage induced by only three doses of CCl4, and the rapid recovery of the hepatic architecture in only 10 days of the experimental period in which the IGF-1 treatment was simultaneously administered with CCl4 is worthy of special mention. This can be seen in Fig. 2.
Healthy mice within the experimental model (Wt, Igf1 +/+) appeared to be suitable for testing the potential of therapeutic strategies to attenuate acute hepatic damage. Histopathological changes (lymphocytic infiltration, fibrosis, oxidative damage, steatosis, and serious cellular changes; see Table 2) were associated with a significant increase in hepatic lipid peroxidation levels (see Fig. 1c), which were restored to normal values following IGF-1 therapy.
Groups including healthy mice (not harboring Igf1 mutation Wt, Igf1 +/+) displayed a predictable genetic expression response to CCl4-induced oxidative damage, which was also the case for the IGF-1-treated mice. Oxidative insult increased the expression of all those genes encoding collagen proteins (see Fig. 5a–e), all of which were reduced by IGF-1 treatment, with the exception of collagens 3, 4α, and 4. Similarly, the gene coding expression for actin α2, as a marker for stellate cell differentiation to myofibroblasts, which produce collagens and proteoglycans during the fibrogenic process [21], was increased in Wt + CCl4 and reduced (p = ns vs. controls) in Wt + CCl4 receiving IGF-1 therapy.
On the other hand, TNF-α gene expression was significantly augmented in Wt + CCl4, showing a normal inflammatory response suggesting a better hepatic regeneration capability [22]. Additionally, IGF-1 therapy increased the expression of proliferation cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) in the Wt + CCl4 + IGF-1 group, suggesting an efficient stimulus for liver regeneration.
Gene expression assays revealed both antifibrogenic and fibrolytic properties for IGF-1 therapy, modulating the expression of collagen and MMP genes, as well as the inhibitor of MMPs (TIMP). IGF-1 therapy also reduced lipid peroxidation and increased the expression of genes coding for the antioxidant enzyme CAT (Fig. 4f).
The depletion circulating levels of IGF-1 in advanced liver cirrhosis is well documented; however, this does not occur in acute damage. Thus, this work aimed to link the consequences of chronically low levels of IGF-1 and acute liver damage, as several conditions resemble such a deficiency (metabolic syndrome [23], aging [24]…), which could render individuals more sensible to liver aggression. With this objective, we used a recently characterized model of haploinsufficient, heterozygous (Igf1 +/−) mice, which show partial IGF-1 deficiency.
The IGF-1 deficiency (Hz group) was associated with histological alteration with loss of hepatocyte cord alignment, apparent disruption of cell polarity, aberrant nuclei, and abundant cytosolic vacuolization. All of these are in accordance with previous results [15], where altered gene coding expression patterns were described for cytoskeleton proteins, as well as genes related to hepatocyte polarity, cell junctions, and ECM proteins. In fact, in the present work, the histopathological scores for histological damage and lipid peroxidation levels were significantly higher in the Hz group compared to controls (Wt group) (Fig. 1c, d).
In this context, mice with partial IGF-1 deficiency (Hz Igf ±), which received exogenous CCl4 insult (Hz + CCl4), bared a marked inflammatory response and oxidative damage (Figs. 1c, d , 3a–d; Table 2), whereas the expression of gene coding proteins involved in the ECM was paradoxical: hypo-expression of col1a1, hyper-expression of Timp (fibrolysis inhibitor), and reduction of Asma (alfa2-actin), which is a marker for stellate cell transformation into myofibroblasts [21]. Therefore, the genetic response of ECM proteins after CCl4 injury differs among animals with and without IGF-1 deficiency (Hz and Wt, respectively). In particular, the expression of collagen-alfa type-1, one of the main components of hepatic ECM, is virtually absent, even after the sole CCl4 administration in IGF-1-deficient mice.
Surprisingly, collagen deposition was similar in both groups (Wt and HZ) receiving CCl4 (Table 2), probably because in Hz groups, the fibrolytic mechanisms were also reduced by TIMPs (Fig. 7e).
Another potentially relevant finding could be the role of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF/IGFBP8) in the normal or pathological establishment of the ECM. This protein is a multi-modular molecule that binds and activates other factors, such as TGF-β and VEGF, and also possesses a domain for IGF-1. It is recognized as an ECM “organizer” [22]. Our results showed that after CCl4 insults in healthy mice, Ctgf expression increased significantly compared to controls, and that IGF-1 therapy downregulated its expression to normal values (Fig. 4c). However, IGF-1-deficient mice expressed low levels of Ctgf under all tested scenarios (Hz + CCl4, Hz + CCl4 + IGF-1).
The gene expression of cytoprotective heat shock proteins (HSPs) (Fig. 7), appeared to be acting as the protective mediator for IGF-1 activities, as previously reported in brain samples [20]. It is well known that HSPs act as sensors of cellular redox changes and contribute to the repair and clearance of damaged proteins [21]. Some of them, such as Hsp27, Hsp70 and Hsp90, play an important role in inhibiting apoptosis and inflammation [21].
In summary, this work supplies novel evidence suggesting low-dose-IGF-1 therapy as being potentially beneficial in avoiding the progression of early stages of liver damage to more chronic and deleterious conditions. In the early stages of hepatic disease, IGF-1 treatment induces cell regeneration and cytoprotection, and is also effective as an anti-inflammatory and antioxidant agent, resulting in a concomitant reduction in fibrosis (both fibrogenesis and fibrolysis).
Conclusions
To conclude, firstly, low doses of IGF-1 induce hepatoprotective, antioxidant, and antifibrogenic effects in animals after acute liver damage. IGF-1 also modulates the expression of collagen and MMP genes in animals with acute liver damage induced by CCl4, including antifibrogenic and fibrolytic mechanisms. Secondly, IGF-1 exogenous administration could be a strategic therapy in the early stages of liver damage, avoiding the progression to cirrhosis. Lastly, IGF-1 deficiency, present in liver cirrhosis, represents a negative factor for the magnitude and proportion of liver damage, since the livers from IGF-1-deficient mice (Hz Igf1 +/−) show a clear vulnerability to oxidative damage and inflammation.
Abbreviations
- ALT:
-
alanine aminotransferase
- AST:
-
aspartate aminotransferase
- GSHPx:
-
glutathione peroxidase
- CCl4 :
-
carbon tetrachloride
- HSP:
-
heat shock proteins
- IGF-1:
-
insulin-like growth factor-1
- MDA:
-
malondialdehyde
- ns:
-
not significant
- Hz:
-
heterozygous group
- Igf +/− :
-
mice with partial IGF-1 deficiency
- Hz + CCl4 + IGF-1:
-
heterozygous (Hz, Igf +/−) receiving CCl4 and treated with low doses of IGF-1
- MMP:
-
matrix metalloprotease
- RT-qPCR:
-
real time quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- SEM:
-
standard error of mean
- Wt:
-
control group (wild-type, Igf +/+)
- EMC:
-
extracellular matrix
- HSC:
-
hepatic stellate cells
- IGFBPs:
-
IGF binding proteins
- IGF-1:
-
insulin-like growth factor-1
- IGF-1R:
-
IGF-1 receptor
- rhIGF-1:
-
recombinant human insulin-like growth factor
- TGF-β1:
-
transforming growth factor-β1
- Xiap :
-
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis
References
Schimpff RM, Lebrec D, Donnadieu M. Somatomedin production in normal adults and cirrhotic patients. Acta Endocrinol. 1977;86:355–62.
Caufriez A, Reding P, Urbain D, Golstein J, Copinschi G. Insulin-like growth factor I: a good indicator of functional hepatocellular capacity in alcoholic liver cirrhosis. J Endocrinol Investig. 1991;14:317–21.
Picardi A, de Oliveira AC, Muguerza B, Tosar A, Quiroga J, Castilla-Cortázar I, Santidrián S, Prieto J. Low doses of insulin-like growth factor-I improve nitrogen retention and food efficiency in rats with early cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 1997;26:191–202.
Castilla-Cortazar I, Prieto J, Urdaneta E, Pascual M, Nuñez M, Zudaire E, Garcia M, Quiroga J, Santidrian S. Impaired intestinal sugar transport in cirrhotic rats: correction by low doses of insulin-like growth factor I. Gastroenterology. 1997;113:1180–7.
Castilla-Cortazar I, Garcia M, Muguerza B, Quiroga J, Perez R, Santidrian S, Prieto J. Hepatoprotective effects of insulin-like growth factor I in rats with carbon tetrachloride-induced cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1997;113:1682–91.
Castilla-Cortázar I, Picardi A, Tosar A, Ainzúa J, Urdaneta E, García M, Pascual M, Quiroga J, Prieto J. Effect of insulin-like growth factor I on in vivo intestinal absorption of d-galactose in cirrhotic rats. Am J Physiol. 1999;276(1 Pt 1):G37–42.
Castilla-Cortázar I, Pascual M, Urdaneta E, Pardo J, Puche JE, Vivas B, Díaz-Casares A, García M, Díaz-Sánchez M, Varela-Nieto I, Castilla A, González-Barón S. Jejunal microvilli atrophy and reduced nutrient transport in rats with advanced liver cirrhosis: improvement by insulin-like growth factor I. BMC Gastroenterol. 2004;4:12.
Cemborain A, Castilla-Cortázar I, García M, Quiroga J, Muguerza B, Picardi A, Santidrián S, Prieto J. Osteopenia in rats with liver cirrhosis: beneficial effects of IGF-I treatment. J Hepatol. 1998;28:122–31.
Castilla-Cortazar I, Garcia M, Quiroga J, Diez N, Diez-Caballero F, Calvo A, Diaz M, Prieto J. Insulin-like growth factor-I reverts testicular atrophy in rats with advanced cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2000;31:592–600.
Castilla-Cortazar I, Diez N, Garcia-Fernandez M, Puche J-E, Diez-Caballero F, Quiroga J, Diaz-Sanchez M, Castilla A, Casares A-D, Varela-Nieto I, Prieto J, Gonzalez-Baron S. Hematotesticular barrier is altered from early stages of liver cirrhosis: effect of insulin-like growth factor 1. World J Gastroenterol. 2004;10:2529–34.
Castilla-Cortázar I, Aliaga-Montilla MA, Salvador J, García M, Delgado G, González-Barón S, Quiroga J, Prieto J. Insulin-like growth factor-I restores the reduced somatostatinergic tone controlling growth hormone secretion in cirrhotic rats. Liver. 2001;21:405–9.
García-Fernández M, Castilla-Cortázar I, Díaz-Sanchez M, Navarro I, Puche JE, Castilla A, Casares AD, Clavijo E, González-Barón S. Antioxidant effects of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) in rats with advanced liver cirrhosis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2005;5:7.
Muguerza B, Castilla-Cortázar I, García M, Quiroga J, Santidrián S, Prieto J. Antifibrogenic effect in vivo of low doses of insulin-like growth factor-I in cirrhotic rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001;1536:185–95.
Pérez R, García-Fernández M, Díaz-Sánchez M, Puche JE, Delgado G, Conchillo M, Muntané J, Castilla-Cortázar I. Mitochondrial protection by low doses of insulin-like growth factor-I in experimental cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:2731–9.
Lara-Diaz VJ, Castilla-Cortazar I, Martín-Estal I, García-Magariño M, Aguirre GA, Puche JE, de la Garza RG, Morales LA, Muñoz U. IGF-1 modulates gene expression of proteins involved in inflammation, cytoskeleton, and liver architecture. J Physiol Biochem. 2017;73(2):245–58. doi:10.1007/s13105-016-0545-x.
Liu JP, Baker J, Perkins AS, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A. Mice carrying null mutations of the genes encoding insulin-like growth factor I (Igf-1) and type 1 IGF receptor (Igf1r). Cell. 1993;75:59–72.
Castilla-Cortazar I, Guerra L, Puche JE, Muñoz U, Barhoum R, Escudero E, Lavandera JL. An experimental model of partial insulin-like growth factor-1 deficiency in mice. J Physiol Biochem. 2014;70:129–39.
Klopfleisch R. Multiparametric and semiquantitative scoring systems for the evaluation of mouse model histopathology—a systematic review. BMC Vet Res. 2013;9:123.
Gérard-Monnier D, Erdelmeier I, Régnard K, Moze-Henry N, Yadan JC, Chaudière J. Reactions of 1-methyl-2-phenylindole with malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxyalkenals. Analytical applications to a colorimetric assay of lipid peroxidation. Chem Res Toxicol. 1998;11:1176–83.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−∆∆CT method. Methods. 2001;25:402–8.
Gressner OA, Gao C. Monitoring fibrogenic progression in the liver. Clin Chim Acta. 2014;433:111–22.
Tirnitz-Parker JEE, Viebahn CS, Jakubowski A, Klopcic BRS, Olynyk JK, Yeoh GCT, Knight B. Tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis is a mitogen for liver progenitor cells. Hepatology. 2010;52:291–302.
Aguirre GA, De Ita JR, de la Garza RG, Castilla-Cortazar I. Insulin-like growth factor-1 deficiency and metabolic syndrome. J Transl Med. 2016;14:3.
Puche JE, Castilla-Cortázar I. Human conditions of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) deficiency. J Transl Med. 2012;10:224.
Authors’ contributions
LA-M: data processing, literature revision, histopathological score (first observer), histological images processing and figure composition, manuscript writing, and statistical analysis; JE-P: experimental design, in vivo work, coordination of microarray and RT-PCR studies, and histopathological studies and score (second observer); A-GA: data processing, figure composition, manuscript writing, and performing histological studies; MM-U: statistical analysis, performing microarray and PCR studies; M-GM: figure composition and statistical analysis; R-GG: discussion of results and preliminary presentation of results to the International Liver Congress; IC-C: study and hypothesis design from previous studies, histopathological score (third observer), manuscript writing, and data interpretation. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to Prof. A. Efstratiadis (Columbia University, College of Physicians and Surgeons, NY) for kindly providing the heterozygous breeder mice. Special thanks to M.Cs. Irene Martín Del Estal, Ms. Susana Arahuetes, Ph.D. Paloma Fernández, and Ms. María Teresa Silva, for their expert assistances. This work was supported by the Fundación de Investigación HM Hospitales and Tecnológico de Monterrey.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experimental procedures were performed in compliance with The Guiding Principles for Research Involving Animals and approved by the bioethical committees of our institutions (School of Medicine, Tecnologico de Monterrey, Monterrey, México, and CEU-San Pablo University, Madrid, Spain).
Funding
This work was supported by Tecnológico de Monterrey and Fundación de Investigación HM Hospitales.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional file
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Morales-Garza, L.A., Puche, J.E., Aguirre, G.A. et al. Experimental approach to IGF-1 therapy in CCl4-induced acute liver damage in healthy controls and mice with partial IGF-1 deficiency. J Transl Med 15, 96 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-017-1198-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-017-1198-4