Abstract
Background
Kruppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) induces tumorigenesis or suppresses tumor growth in a tissue-dependent manner. However, the roles of KLF4 in hematological malignancies and the mechanisms of action are not fully understood.
Methods
Inducible KLF4-overexpression Jurkat cell line combined with mouse models bearing cell-derived xenografts and primary T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) cells from four patients were used to assess the functional role of KLF4 in T-ALL cells in vitro and in vivo. A genome-wide RNA-seq analysis was conducted to identify genes regulated by KLF4 in T-ALL cells. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) PCR was used to determine direct binding sites of KLF4 in T-ALL cells.
Results
Here we reveal that KLF4 induced apoptosis through the BCL2/BCLXL pathway in human T-ALL cell lines and primary T-ALL specimens. In consistence, mice engrafted with KLF4-overexpressing T-ALL cells exhibited prolonged survival. Interestingly, the KLF4-induced apoptosis in T-ALL cells was compromised in xenografts but the invasion capacity of KLF4-expressing T-ALL cells to hosts was dramatically dampened. We found that KLF4 overexpression inhibited T cell-associated genes including NOTCH1, BCL11B, GATA3, and TCF7. Further mechanistic studies revealed that KLF4 directly bound to the promoters of NOTCH1, BCL2, and CXCR4 and suppressed their expression. Additionally, KLF4 induced SUMOylation and degradation of BCL11B.
Conclusions
These results suggest that KLF4 as a major transcription factor that suppresses the expression of T-cell associated genes, thus inhibiting T-ALL progression.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
KLF4, also known as GKLF (gut KLF), is a member of the KLF zinc finger-containing transcription factor family [1,2]. Klf4 together with Oct4, Sox2, and c-Myc are widely referred to as ‘Yamanaka factors’ enforced expression of which makes adult cells reprogram into pluripotent stem cells [3]. Consistently, the expression levels of Klf4, Sox2, and Oct4 may need to be decreased during the differentiation of pluripotent cells [4]. Klf4 has critical function in development. Mice homozygous for a null mutation in Klf4 die within a day after birth and show defects in epidermis and colonic epithelial cell differentiation [5]. A recent study reports that the downregulation of Klf4 is required for T cell lineage commitment in mice and Klf4 overexpression blocks T cell development primarily at early stage through suppressing the transcription of several genes that are crucial for early T cell development [6].
T cell development involves progenitor homing and lineage specification and commitment [7]. During early T cell development, several key T cell genes, including Notch1, Bcl11b, Gata3, and Tcf7 are upregulated [8-11]. T cell development is tightly regulated by key transcription factors, such as Notch1 [12] and Bcl11b [13]. One important mechanism in T cell development is small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) modification because several T cell-associated transcription factors are regulated by SUMO-specific proteases [14]. A previous study identified two SUMO acceptor sites in Bcl11b and demonstrated that prolonged sumoylation resulted in degradation of Bcl11b [15].
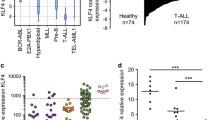
T-ALL is thought to result from malignant thymocytes that arise at defined stages of T cell differentiation. Moreover, the expression of certain oncogenes or mutated T cell-specific genes has been closely linked to developmental arrest at particular stages of normal T cell development [16]. Activating mutations of NOTCH1 were identified in roughly 60% of primary human T-ALLs [17]. Murine T-ALLs studies revealed the presence of acquired gain-of-function Notch1 mutations at frequencies varying from 30% to 80%, depending on the genetic model [18]. In addition, BCL11B mutations are associated with T cell proliferative disorders. The inversion inv(14)(q11.2q32.31) disrupting the BCL11B locus has been identified in two cases of T-ALL [19], and monoallelic BCL11B deletions or missense mutations were detected in 9% of T-ALL cases[20]. KLF4 has obtained attention as a negative regulator in T-ALL, because DNA methylation of KLF4 gene makes its silencing in T-ALL cells and KLF4 overexpression induces apoptosis in ATL-43 T cell line [21]. A recent study identified novel mutations in 3′ untranslated region (UTR) of the KLF4 gene that resulted in loss of miR-2909-mediated regulation in pediatric T-ALL [22]. However, the molecular mechanisms involved in KLF4-induced apoptosis in T-ALL have not been well characterized.
To systematically analyze the genes regulated by KLF4 in T-ALL, we have performed the genome-wide RNA-seq analysis in KLF4 overexpressing Jurkat cells engrafted in immune-compromised NOD-SCID mice. As a negative regulator in human T-ALL in vitro and in vivo, KLF4 was shown to inhibit a variety of T-cell associated genes by directly binding to NOTCH1 promoter and inducing SUMOylation of BCL11B. Our study thus establishes KLF4 as a critical transcriptional factor directly suppressing T-cell associated transcription factors such as NOTCH1 and BCL11B in malignant T cells.
Results
Enforced KLF4 expression induces apoptosis in Jurkat cells through the BCL2/BCLXL pathway
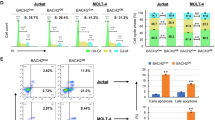
To investigate the function of KLF4 in Jurkat cells, the TRE-KLF4 and TRE-empty Jurkat cell lines that were constitutively GFP+ were established (Additional files 1 and 2: Figures S1-S2). In TRE-KLF4 cells, the KLF4 overexpression was induced by Doxycycline (Dox) treatment (Figure 1a-b). Dox treatment did not change the expression levels of KLF4 and genes that are related to apoptosis and T cell development in WT Jurkat cells (Additional files 1 and 2: Figure S3). Indeed, we detected massive cell death in Dox-induced TRE-KLF4 cells at 48 hours after Dox treatment, concomitant with the increase of CASP3 (Figure 1b) and accumulation of apoptotic cells, whereas TRE-KLF4 cells without Dox treatment and Dox-treated TRE-empty cells grew well (Figure 1c-d). The protein degradation during cell death might explain why the KLF4 protein level decreased at 50 hours after Dox treatment (Figure 1b). To validate whether KLF4 overexpression induced apoptosis by affecting Caspase activities in Jurkat cells, we treated the Dox-induced TRE-KLF4 cells with Z-VAD-FMK, a pan caspase inhibitor, in an attempt to rescue Jurkat cells from KLF4-mediated apoptosis. Indeed, we found that Z-VAD-FMK treatments reduced the apoptotic rate of Jurkat cells with KLF4 overexpression (Figure 1d). Furthermore, we detected the catalytic activity of CASP3 (Additional files 1 and 2: Figure S4) and the decrease of mitochondrial membrane potential in KLF4 overexpressing Jurkat cells but not in TRE-KLF4 cells without Dox treatment or WT Jurkat cells with Dox treatment (Additional files 1 and 2: Figure S5). These results suggested that the BCL2 pathway was involved in KLF4-induced apoptosis in Jurkat cells.
Enforced expression of KLF4 induces apoptosis and suppresses BCL2 in Jurkat cells. (a) Quantification of KLF4 mRNA levels in TRE-KLF4 Jurkat cells. The results were normalized to the GAPDH mRNA levels and are represented as the mean +/- SEM (n = 3). (b) Western blot analysis of KLF4, CASP3, and ACTIN protein levels in TRE-KLF4 Jurkat cells. (c) TRE-KLF4 Jurkat cell cultures with (black squares) or without (black diamonds) Dox treatment. TRE-empty Jurkat cell cultures with (grey triangles) Dox treatment. Data are represented as the mean +/- SEM (n = 3). (d) TRE-KLF4 Jurkat cells were treated (+Dox) or not (-Dox) with Dox. Z-VAD-FMK (I) and Dox were added at the same time (Dox + I). 48 hours later, cells were subjected to apoptosis assays. Top, representative of flow cytometry profiles of Jurkat cells in apoptosis assays. Bottom, summary of percentages of apoptotic cells (Annexin-V + 7-AAD+) from three independent apoptosis assays. Data are represented as the mean +/- SEM. **P ≤ 0.01 versus bar 1 (for bar 2), *** P ≤ 0.001 versus bar 1 (for bars 3 and 4). (e) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of the expression of selected genes in TRE-KLF4 cells. Data are shown as the mean +/- SEM. (f) Western blot analysis of the protein levels of selected apoptosis genes in TRE-KLF4 cells 48 hours post Dox treatment. (g) Jurkat cells were transfected with indicated lentiviruses. 48 hours later, GFP+ cells were subjected to apoptosis assays. Top, representative of flow cytometry profiles of Jurkat cells in apoptosis assays. Bottom, summary of percentages of apoptotic cells from three independent assays. Data are represented as the mean +/- SEM. For Annexin-V + 7-AAD+, ***P ≤ 0.001 versus bar 1 (for bars 2-4); For Annexin-V+, ***P ≤ 0.001 versus bar 1 (for bars 2-4).
Upon Dox-induced KLF4 overexpression in Jurkat cells, we measured the expression levels of several genes related to apoptosis at different time points and observed that TRAIL expression was upregulated after Dox treatment, whereas the expression of BCL2 was suppressed, and BCLXL expression remained unchanged (Figure 1e-f). To evaluate whether BCL2 or BCLXL participated in KLF4-induced apoptosis, two lentiviral vectors encoding KLF4-BCL2 and KLF4-BCLXL were constructed and transduced into Jurkat cells (Additional files 1 and 2: Figure S1). Co-expression of BCL2 or BCLXL did not affect KLF4 expression levels in Jurkat cells (Additional files 1 and 2: Figure S6). Jurkat cells transduced with the KLF4 lentivirus demonstrated an apoptotic cell (Annexin-V+, 7-AAD+) frequency of 19.5%, whereas only 0.9% of cells transduced with the KLF4-BCL2 lentivirus underwent apoptosis (Figure 1g). Similarly, the percentage of apoptotic population was reduced to 3.3% when BCLXL was co-expressed with KLF4 (Figure 1g). Thus, enforced expression of BCL2 or BCLXL almost completely rescued Jurkat cells from apoptosis upon KLF4 overexpression, indicating that KLF4 induced apoptosis by suppressing the BCL2 pathway in T-ALL cells.
To exclude the possibility that the effects of KLF4 on Jurkat cells were cell line-specific, we next tested whether KLF4 could induce apoptosis in MOLT4 or CCRF-CEM cells, which are two γ-secretase inhibitors (GSI)-resistant T-ALL cell lines [22] and expressed minimal KLF4 (Additional files 1 and 2: Figure S7). Both cell lines underwent apoptosis upon KLF4 overexpression (Additional files 1 and 2: Figures S8-S9). Furthermore, we confirmed that KLF4 overexpression induced apoptosis in CUTLL1 cells that are sensitive to GSI and did not express KLF4 either [22] (Additional files 1 and 2: Figures S7 and S10). In contrast, KLF4 overexpression did not induce apoptosis either in RL (Additional files 1 and 2: Figure S11), a B cell lymphoma cell line [23], or in K562 (Additional files 1 and 2: Figure S12), a myeloid leukemia cell line [24].
KLF4 overexpression induces apoptosis in primary T-ALLs
To validate whether KLF4 induced apoptosis in primary T-ALL cells, we transduced a KLF4-GFP lentivirus into primary T-ALL samples from four patients, in which more than 75% mononuclear BM cells were T-ALL cells (Additional files 1 and 2: Figure S13). KLF4 overexpression caused elevated apoptosis in these cells compared to GFP-transduced controls (Figure 2). To investigate whether there were any mutations in the 3′ UTR of the KLF4 genes that were previously identified in pediatric T-ALL [25], we sequenced the same regions in Jurkat and the two primary T-ALL samples but did not find any mutations (Additional files 1 and 2: Figure S14). These results demonstrate that KLF4 overexpression could induce apoptosis in primary T-ALL cells in vitro.
Effects of KLF4 overexpression on primary T-ALL cells. Primary T-ALL patient BM samples (n = 3) were transduced with either KLF4-GFP (KLF4) or GFP (CTL) lentiviruses. 72 hours after transduction, GFP+ cells were subjected to apoptosis assays as measured by Annexin-V binding and 7-AAD staining. Top, representative of flow cytometry profiles of primary T-ALL cells in apoptosis assays. Bottom, summary of percentages of apoptotic cells (Annexin-V + 7-AAD+) from three independent apoptosis assays. Data are represented as the mean +/- SEM. *P ≤ 0.05 versus bar 1 (for bar 2).
KLF4 overexpression reduces aggression of Jurkat cells in vivo
To examine the effect of KLF4 overexpression on Jurkat cells in vivo, we injected TRE-KLF4 cells and TRE-empty cells into immunodeficient NOD-SCID mice and started Dox treatments one day after injection of Jurkat cells (Figure 3a). The mice injected with TRE-KLF4 cells without Dox treatment and the mice injected with TRE-empty cells with Dox treatment died within 25 days, while all of the mice that were injected with TRE-KLF4 cells and received Dox treatment started to die two months after injection of Jurkat cells (Figure 3b). To our surprise, the percentages of Jurkat cells in the Dox-treated mice were similar to than that in Dox-untreated mice (Figure 3c-d). In addition, the sizes and cellularity of the spleens in Dox-treated mice were significantly larger than that in Dox-untreated mice (Additional files 1 and 2: Figure S15). Thus, the absolute numbers of Jurkat cells in the spleens of Dox-treated mice were significantly higher than that in Dox-untreated mice (Figure 3e). In addition, cell cycle analysis showed that KLF4 overexpression did not alter the proliferation of Jurkat cells in vivo (Additional files 1 and 2: Figure S16). Taken together, these results indicated that Jurkat cells with KLF4 overexpression survived in vivo but their aggression to hosts was reduced.
Overexpression of KLF4 in Jurkat cells in vivo. (a) Experimental design for studying KLF4 function in Jurkat cells in vivo. TRE-KLF4 Jurkat cells in which KLF4 expression was induced by Dox treatment were intravenously injected into NOD-SCID mice. The injected mice were separated into two groups (n = 15) with Dox treatment or without Dox treatment. In the third group, NOD-SCID mice were injected with TRE-empty Jurkat cells and were subsequently treated with Dox. The three groups of mice were monitored for tumors. Dox was intraperitoneally administered every two days. (b) Survival curves for the NOD/SCID mice injected with TRE-KLF4 Jurkat cells. 15 mice were used in each group. Red dots represent Dox-treated mice with injection of TRE-KLF4 Jurkat cells (KLF4 + Dox); Blue dots represent mice injected with TRE-KLF4 cells without Dox treatment (KLF4-Dox); Green dots represent Dox-treated mice with injection of TRE-empty cells (CTL + Dox). (c) Two weeks after injection of Jurkat cells, four mice from each group were culled for detection of Jurkat cells. Representative FACS profiles of mononuclear cells of spleen, BM, and peripheral blood from the three groups of mice described in b. (d) Summary of percentages of TRE-KLF4 Jurkat cells in spleen, BM, and peripheral blood from the three groups of mice described in b. (e) Summary of absolute numbers of TRE-KLF4 Jurkat cells in spleen and BM from the three groups of mice described in b.
We then compared the gene expression profile of TRE-KLF4 Jurkat cells from Dox-treated mice to that from Dox-untreated mice by RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) analyses. About 11,000 of the 20860 Refseq genes were detectably expressed (R1 reads per kilo-base exon model per-million reads [RPKM]) in each population after murine transcripts were excluded (Figure 4a). Additional file 3: Table S2 contains a list of genes with greater-than-two fold difference in expression between Dox-treated Jurkat cells and Dox-untreated Jurkat cells. We confirmed the RNA-seq results by quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) to measure the expression levels of KLF4, BID [26], S100A6 [27], FAT1 [28], FN1 [29], CKAP4 [30], genes known to play important roles during apoptosis or cell proliferation (Additional files 1 and 2: Figure S17). With KLF4 overexpression, pro-apoptotic genes including BID [26] and BIK [31] decreased, while genes involved in anti-apoptosis were upregulated (Figure 4b). Interestingly, CCR7 [32] that regulates CNS infiltration in T-ALL and CXCR4 [33,34], which is essential for stem cell and leukemia cell localization were both repressed upon KLF4 overexpression in Jurkat cells (Figure 4b). Furthermore, TMBIM4 that promotes cell adhesion and migration was downregulated after KLF4 was overexpressed [35]. FAT1, a therapeutic target in high-risk preB-ALL, was also suppressed upon KLF4 overexpression [28]. Conversely, cell adhesion proteins including FN1 [36] and THBS1 [37] were upregulated after KLF4 was overexpressed (Figure 4b). It was surprising to find that all T cell-associated genes, including T cell specific transcription factors (BCL11B, TCF7, and GATA3), T cell surface markers (CD1d, CD3E, and CD28), and TCR-related genes (ZAP70, RAG1, RAG2, and ADA) were uniformly silenced in Jurkat cells upon KLF4 overexpression (Figure 4b). Interestingly, TAL1, of which aberrant activation is involved in up to 60% of T-ALL cases [38], was severely repressed in Jurkat cells upon KLF4 overexpression (Figure 4b). In contrast, expression of BCL11A [39], CEBPB [40], and GATA2 [41] that are important for B, or myeloid cell lineages were upregulated upon KLF4 overexpression (Figure 4b). These results suggested that the tissue homing capacity of Jurkat cells was compromised and T cell transcription program of the T-ALL cell line was disrupted when KLF4 was overexpressed.
Downstream targets of KLF4 in T-ALL. (a) Scatter plots of Dox-treated versus Dox-untreated TRE-KLF4 Jurkat transcriptomes. (b) Unsupervised hierarchical cluster analysis of expression levels of 32 genes that are important for apoptosis, metastasis, T cell, or non-T cell lineages in Dox-treated and Dox-untreated TRE-KLF4 Jurkat cells (red, increased expression; green, decreased expression). (c) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of selected gene expression in KLF4 overexpressing Jurkat cells. Data are represented as the mean +/- SEM. (d) Western blot detection of T cell specific transcription factors in Jurkat cells 48 hours after KLF4 overexpression. (e) KLF4 binds to the promoters of NOTCH1, CXCR4, and BCL2 through regions containing conserved KLF4 consensus sequences. Chromatin immunoprecipitates were performed on cross-linked fragmented DNAs prepared from Jurkat cells that forcefully expressed KLF4. Eluted DNAs were then analyzed by qPCR performed with primers flanking putative KLF4-binding sites. The amount of DNA amplified from immunoprecipitated DNAs was normalized to that amplified from input DNA. Data are represented as the mean +/- SEM.
Identification of KLF4 target genes in T-ALL
To validate the results of RNA-seq analysis, we transduced a KLF4-GFP lentivirus and a GFP-only lentivirus as control into Jurkat cells respectively (Additional files 1 and 2: Figures S1 and S18). Forty-eight hours after enforcing the expression of KLF4, we observed that mRNA and protein levels of T cell-associated genes, including NOTCH1, BCL11B, TCF7, and GATA3, decreased significantly upon KLF4 overexpression (Figure 4c-d). To detect potential direct KLF4 target genes in T-ALL, we selected KLF4-repressed candidate genes identified from RNA-seq analysis (Additional file 3: Table S2) that contained KLF4 motif in the promoter regions [42] or were identified by ChIP-seq analysis as direct Klf4 target genes in a mammary epithelial cell line [43] for ChIP validation. Chromatin immunoprecipitates prepared from Jurkat cells, in which the transduction efficiencies of KLF4-GFP lentivirus were about 40% (Additional files 1 and 2: Figure S18), revealed that KLF4 associated with putative binding sites in the promoter regions of NOTCH1, CXCR4, and BCL2 (Figure 4e). In contrast, KLF4 did not associated with DNA fragments in the promoters of βACTIN (Figure 4e). Taken together, these data suggest that KLF4 downregulated NOTCH1, CXCR4, and BCL2 directly.
KLF4 induces the SUMOylation and degradation of BCL11B
Although the transcription levels of BCL11B decreased 50% upon KLF4 overexpression (Figure 4c), the levels of BCL11B protein significantly decreased in TRE-KLF4 Jurkat cells 72 hours after the induction of KLF4 overexpression (Figure 4d), while BCL11B protein levels did not change in wild-type Jurkat cells after Dox treatment (Additional files 1 and 2: Figure S19). These results drove us to investigate whether KLF4 affected BCL11B post-translation. SUMOylation is commonly associated with protein degradation; therefore, we speculated that the overexpression of KLF4 might induce the SUMOylation of BCL11B, leading to the degradation of BCL11B protein. We observed SUMOylation of BCL11B at 30 hours after KLF4 was overexpressed in Jurkat cells (Figure 5a). As calyculin A can potently inhibit SUMOylation [15], we found that the SUMOylation of BCL11B was gradually suppressed following calyculin A treatment (Figure 5b). Furthermore, calyculin A partially rescued Jurkat cells from KLF4-induced apoptosis (Figure 5c). Because SUMOylation triggers a secondary signal mediating ubiquitin-dependent degradation by the proteasome [14], we further validated that MG132, a potent proteasome inhibitor [44], could also rescue Jurkat cells from KLF4-induced apoptosis (Figure 5d). Taken together, these results suggested that KLF4 overexpression induced BCL11B protein degradation by SUMOylation.
KLF4 induces the SUMOylation and degradation of BCL11B. (a) Western blot detection of slowly migrating SUMOylated BCL11B at the indicated time points. (b) Western blot analysis of BCL11B SUMOylation status in the presence of SUMO-inhibitor treatment in TRE-KLF4 Jurkat cells. (c) Inhibition of SUMOylation reduces KLF4-induced cell death in the Jurkat cell line. Cells were treated with Dox prior to SUMO inhibitor (Calyculin A, 50 nM) addition. At the indicated time points after SUMO inhibitor addition, cells were collected and stained with Annexin-V and 7-AAD for apoptosis detection. Top, representative of flow cytometry profiles of TRE-KLF4 Jurkat cells in apoptosis assays. Bottom, summary of percentages of apoptotic cells (Annexin-V + 7-AAD+) from three independent apoptosis assays. Data are represented as the mean +/- SEM. +Dox 24 h: ** P < 0.01 versus bar 1 (for bar 2), *** P < 0.001 versus bar 1 (for bar 3); +Dox 48 h: ** P < 0.01 versus bar 1 (for bar 2), *** P < 0.001 versus bar 1 (for bar 3); +Dox 72 h: ** P < 0.01 versus bar 1 (for bar 2), * P < 0.05 versus bar 1 (for bar 3). (d) Inhibition of proteasome reduces KLF4-induced cell death in the Jurkat cell line. Cells were treated with Dox prior to proteasome inhibitor (MG132, 10 nM) addition. At the indicated time points after MG132 addition, cells were collected and stained with Annexin-V and 7-AAD for apoptosis detection. Top, representative of flow cytometry profiles of TRE-KLF4 Jurkat cells in apoptosis assays. Bottom, summary of percentages of apoptotic cells (Annexin-V + 7-AAD+) from three independent apoptosis assays. Data are represented as the mean +/- SEM. * P < 0.05 versus bar 2 (for bar 1), ** P < 0.01 versus bar 2 (for bar 3).
Discussion
KLF4 acts as a tumor suppressor gene or oncogene depending on cellular contexts. A previous report identified that the KLF4 locus is hypermethylated in T-ALLs and KLF4 overexpression induced apoptosis in a T-ALL cell line [21]. However the mechanisms of KLF4-induced apoptosis and KLF4 targets in T-ALLs remain unclear. In this study, we used T-ALL as a model system, and demonstrated that the overexpression of KLF4 induced profound apoptosis in four human T-ALL cell lines and primary T-ALL cells in vitro (Figure 6) and increased survival rates in xenografts (Figure 3b). To systematically uncover the transcriptional downstream targets of KLF4, we performed ChIP assays and global gene expression profile analyses and identified that KLF4 directly bound to the promoters of NOTCH1, BCL2, and CXCR4 and suppressed their expression in T-ALL. In addition, we demonstrated that KLF4 induced BCL11B degradation by post-translational modification. Consistently, we found that KLF4 negatively regulated human T cell development and homeostasis.
Our studies has clearly demonstrated that KLF4-induced apoptosis was rescued by overexpression of BCL2, which was directly suppressed by KLF4. Interestingly, we noticed that the KLF4 expressing Jurkat cells survived after being injected into immunodeficient mice, suggesting that the KLF4-induced apoptosis was rescued in vivo. Consistently, we observed that pro-apoptotic genes, including BID, BIK, and SIVA1, were downregulated and EP300, RYBP, S100A6, and HSPA2 that have anti-apoptotic activities were upregulated in KLF4-expressing Jurkat cells two weeks after being injected into hosts. The long term survival of Jurkat cells may explain why secondary effects of KLF4 overexpression, including downregulation of tissue homing genes and upregulation of cell adhesion and non-T cell determination genes, were not observed in cultured Jurkat cells that underwent apoptosis upon KLF4 overexpression within four days. Further investigation is required to identify the molecules or proteins in the in vivo microenvironment that regulated the expression of apoptotic-related genes. This might be helpful to explain why some anti-leukemia drug candidates can efficiently eliminate leukemia cells in vitro but do not work in patients.
The present study also suggested that KLF4 overexpression reduced the invasion capacity of T-ALL cells in hosts. Though there were more Jurkat cells in the Dox-treated mice, these leukemia-bearing mice survived much longer than the Dox-untreated group. It is possible that KLF4-expressing Jurkat cells are less capable of infiltrating into important organs, such as central nervous system, than normal Jurkat cells. T-ALL patients are at an increased risk of CNS relapse [16]. CCR7 is the essential adhesion signal required for the targeting of T-ALL cells in to the CNS [32]. Here, we found that CCR7 expression was silenced upon KLF4 overexpression in Jurkat cells. In addition, we found CXCR4, which promotes T-ALL cells to infiltrate into liver and lung tissues in vivo [34], was directly repressed by KLF4 in Jurkat cells. Furthermore, the expression of TMBIM4 that increased cell adhesion, spreading, and migration also decreased upon KLF4 overexpression [35]. Downregulation of FAT1 might also contribute the loss of aggressiveness in T-ALL, because knockdown of FAT1 in tumor cells results in a drastic inhibition of cell migration and invasion [45]. Thus, KLF4 was identified as a potential repressor of CCR7, CXCR4, TMBIM4, and FAT1, the pro-metastasis genes, in T-ALL, which might provide us clues to reduce the invasion capacity of T-ALL in clinics.
Inhibition of NOTCH1 signaling with GSIs has been proposed a molecular targeted therapy for T-ALL. However, GSIs seem to have limited anti-leukemic activity in human T-ALL and are associated with severe gastrointestinal toxicity [46]. Thus, alternative anti-NOTCH1 approaches are in demand for improving T-ALL therapies. We found that KLF4 directly bound to NOTCH1 promoter, and suppressed NOTCH1 signaling and its downstream targets (Figure 6). Although a recent report showed that Klf4 suppresses Notch signaling in murine angiogenesis [47], for the first time, we identified that NOTCH1 was a direct target of KLF4 for transcription suppression in T-ALLs. Followed by repression of NOTCH signaling, BCL11B, TCF7, and GATA3, the downstream targets of NOTCH signaling, were all decreased upon KLF4 overexpression in T-ALL. In addition, downregulation of T cell surface markers and TCR signaling and upregulation of non-T cell transcription factors in KLF4-expressing Jurkat cells could be caused by the silence of these T cell transcription factors. It will be worthy to develop a chemical approach to initiate endogenous KLF4 expression for inhibition of NOTCH1 signaling in T-ALL.
BCL11B mutations are associated with T cell proliferative disorders, even though it is arguable whether BCL11B acts as tumor suppressor or oncogene in T-ALL. The inversion inv(14)(q11.2q32.31) disrupting the BCL11B locus was identified in two cases of T-ALL [19], and monoallelic BCL11B deletions or missense mutations were detected in 9% of T-ALL cases [20]. Furthermore, deletions within BCL11B were found in irradiation-induced lymphomas in mice, suggesting that BCL11B is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor. However, BCL11B overexpression was found in the acute type of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma and the majority of T-ALL cell lines [19,48]. It was previously reported that the downregulation of BCL11B by RNAi triggered human T-ALL cells to undergo apoptosis through the BCL2/BCLXL pathway, implicating that BCL11B acts as an oncogene [49,50]. Consistently, we found that overexpression of KLF4, an indicated tumor suppressor gene in T-ALL, promoted the SUMOylation and degradation of BCL11B in T-ALL, suggesting that BCL11B acted as an oncogene in T-ALL. However, it remains unclear whether KLF4 directly induces BCL11B SUMOylation or degradation.
Conclusions
In summary, this study demonstrated that KLF4 directly repress NOTCH1 and serves as a negative regulator in human T-ALL and T cell development. Therefore, reactivation of KLF4 in T-ALL cells may pave a new road for T cell leukemia therapy.
Methods
Cell culture
All T-ALL cell lines were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, Virginia, USA) and maintained in RPMI-1640 media (Gibco, New York, USA) with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Hyclone, Utah, USA). The 293 T cells used for lentivirus packaging were kindly provided by Professor Duanqing Pei and maintained in DMEM media (Hyclone, Utah, USA) with 10% FBS. OP9-DL1 cells were obtained from Dr. J. C. Zuniga Pflucker (University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada). All cells were incubated at 37°C in 5% CO2.
All primary samples were obtained with informed consent for research purposes, and the procedures were approved by the Research Ethics Board of GIBH. T-ALL clinical samples were obtained with informed consent from donors, and related studies were approved by the Institutional Review Boards at Jinan University Medical School. In all four T-ALL patients, more than 80% of PBMC were T-ALL cells.
Reagents
All chemicals were from Sigma Chemicals (Munich, Germany) unless otherwise specified. The pan caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK was purchased from Beyotime (Jiangsu, China). Antibodies to BCL11B (ab18465), NOTCH1 (ab27526), GATA3 (ab61168), TCF7 (ab30961), KLF4 (ab106629) and SUMO1 (ab32058) were purchased from Abcam (Cambridge, UK). Anti-FLAG, anti-beta-ACTIN, and anti-TRAIL antibodies were purchased from Cell Signal Technologies (Beverly, MA, USA). Antibodies against BCL2, and BCLXL were obtained from Beyotime (Jiangsu, China). All secondary antibodies used in this study were purchased from Sigma (Munich, Germany). A second-generation lentiviral plasmid and related helper plasmids were kindly provided by Professor Xiaoping Chen. The human KLF4 coding sequence was PCR-amplified (Additional file 4: Table S1) and inserted into the EcoRI and SpeI restriction sites in the pWPXLD lentiviral vector. The correctly ligated plasmid was then sequenced and prepared for virus packaging. Lentiviral vectors encoding the rtTA element and KLF4 driven by a TRE promoter (TRE-KLF4) were generously provided by Professor Duanqing Pei.
Mice
Animal experiments were performed in the Laboratory Animal Center of Guangzhou Institutes of Biomedicine and Health (GIBH), and all animal procedures were approved by the Animal Welfare Committee of GIBH. NOD-SCID mice were bred and maintained in SPF-grade cages and provided with autoclaved food and water. Mice at 8-12 weeks of age were given 3 Gy of sublethal irradiation and intravenously injected with 5 × 107 Jurkat cells 6 hours following the irradiation. Mice were monitored daily for signs of weight loss or lethargy, and leukocytes from the peripheral blood were subjected to fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis.
Analysis of gene expression
The sequencing reads were mapped to the mouse RefSeq-RNA reference sequence (downloaded from http://hgdownload.cse.ucsc.edu/downloads) using the FANSe 2 algorithm (http://bioinformatics.jnu.edu.cn/software/fanse2/) with the parameters − L85 − E3 − U0 − S10 [51]. Reads mapped with tophat2 were associated with genes using the custom Perl scripts that allowed no more than 2 unmapped bases. Cufflinks (version 2.1.1) were used to identify reads that were consistent with the annotated genes download from Ensembl database (http://asia.ensembl.org/downloads.html) [52]. These genes were quantified using RPKM method [53]. For small genes (less than 200 bps) a minimum of 10 mappable reads were required. The mappable reads were imported into DEGseq software package to calculate the up-/down-regulation of genes comparing among PL08, 3 T3, and PL08-M with a cut-off value that 2-fold ratio in RPKM and fisher-test FDR of less than 0.05, respectively [54].
ChIP assay
ChIP was performed as previously described in a previous study [55]. Briefly, 1 × 107 Jurkat cells were transduced by a KLF4-GFP lentivirus, crosslinked with 1% formaldehyde, and subjected for sonication to generate 500-750 bp DNA fragments. The soluble DNA fragments were immunoprecipitated by anti-KLF4 antibody (ab106629, Abcam, United Kingdom) or normal rabbit IgG (ab190495, Abcam, United Kingdom). The immunoprecipitated DNA was eluted and amplified by quantitative PCR on Bio-Rad CFX96 PCR equipment with the following primers specific for the NOTCH1, CXCR4, BCL2 or an irrelevant genomic region (βACTIN) (Additional file 4: Table S1). All ChIP experiments were independently prepared and repeated at least for three times.
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism 4 with Student’s t-test. P values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
For detailed information, please find it in Additional file 5.
Abbreviations
- T-ALL:
-
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- ChIP:
-
Chromatin immunoprecipitation
- SUMO:
-
Small ubiquitin-like modifier
- GSI:
-
γ-secretase inhibitors
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative reverse transcription PCR
- RNA-seq:
-
RNA-sequencing
References
Ghaleb AM, Nandan MO, Chanchevalap S, Dalton WB, Hisamuddin IM, Yang VW. Kruppel-like factors 4 and 5: the yin and yang regulators of cellular proliferation. Cell Res. 2005;15(2):92–6.
Wei D, Kanai M, Huang S, Xie K. Emerging role of KLF4 in human gastrointestinal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2006;27(1):23–31.
Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126(4):663–76.
Kim J, Chu J, Shen X, Wang J, Orkin SH. An extended transcriptional network for pluripotency of embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2008;132(6):1049–61.
Segre JA, Bauer C, Fuchs E. Klf4 is a transcription factor required for establishing the barrier function of the skin. Nat Genet. 1999;22(4):356–60.
Wen X, Liu H, Xiao G, Liu X. Downregulation of the transcription factor KLF4 is required for the lineage commitment of T cells. Cell Res. 2011;21(12):1701–10.
Ciofani M, Zuniga-Pflucker JC. The thymus as an inductive site for T lymphopoiesis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2007;23:463–93.
Weber BN, Chi AW, Chavez A, Yashiro-Ohtani Y, Yang Q, Shestova O, et al. A critical role for TCF-1 in T-lineage specification and differentiation. Nature. 2011;476(7358):63–8.
Liu P, Li P, Burke S. Critical roles of Bcl11b in T-cell development and maintenance of T-cell identity. Immunol Rev. 2010;238(1):138–49.
Hosoya T, Maillard I, Engel JD. From the cradle to the grave: activities of GATA-3 throughout T-cell development and differentiation. Immunol Rev. 2010;238(1):110–25.
Radtke F, Wilson A, MacDonald HR. Notch signaling in T- and B-cell development. Curr Opin Immunol. 2004;16(2):174–9.
Radtke F, Wilson A, Stark G, Bauer M, van Meerwijk J, MacDonald HR, et al. Deficient T cell fate specification in mice with an induced inactivation of Notch1. Immunity. 1999;10(5):547–58.
Li P, Burke S, Wang J, Chen X, Ortiz M, Lee SC, et al. Reprogramming of T cells to natural killer-like cells upon Bcl11b deletion. Science. 2010;329(5987):85–9.
Van Nguyen T, Angkasekwinai P, Dou H, Lin FM, Lu LS, Cheng J, et al. SUMO-specific protease 1 is critical for early lymphoid development through regulation of STAT5 activation. Mol Cell. 2012;45(2):210–21.
Zhang LJ, Vogel WK, Liu X, Topark-Ngarm A, Arbogast BL, Maier CS, et al. Coordinated regulation of transcription factor Bcl11b activity in thymocytes by the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways and protein sumoylation. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(32):26971–88.
Aifantis I, Raetz E, Buonamici S. Molecular pathogenesis of T-cell leukaemia and lymphoma. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(5):380–90.
Weng AP, Ferrando AA, Lee W, Morris JPT, Silverman LB, Sanchez-Irizarry C, et al. Activating mutations of NOTCH1 in human T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Science. 2004;306(5694):269–71.
Lin YW, Nichols RA, Letterio JJ, Aplan PD. Notch1 mutations are important for leukemic transformation in murine models of precursor-T leukemia/lymphoma. Blood. 2006;107(6):2540–3.
Przybylski GK, Dik WA, Wanzeck J, Grabarczyk P, Majunke S, Martin-Subero JI, et al. Disruption of the BCL11B gene through inv(14)(q11.2q32.31) results in the expression of BCL11B-TRDC fusion transcripts and is associated with the absence of wild-type BCL11B transcripts in T-ALL. Leukemia. 2005;19(2):201–8.
Gutierrez A, Kentsis A, Sanda T, Holmfeldt L, Chen SC, Zhang J, et al. The BCL11B tumor suppressor is mutated across the major molecular subtypes of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2011;118(15):4169–73.
Yasunaga J, Taniguchi Y, Nosaka K, Yoshida M, Satou Y, Sakai T, et al. Identification of aberrantly methylated genes in association with adult T-cell leukemia. Cancer Res. 2004;64(17):6002–9.
Malik D, Kaul D, Chauhan N, Marwaha RK. miR-2909-mediated regulation of KLF4: a novel molecular mechanism for differentiating between B-cell and T-cell pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemias. Mol Cancer. 2014;13:175.
Beckwith M, Longo DL, O’Connell CD, Moratz CM, Urba WJ. Phorbol ester-induced, cell-cycle-specific, growth inhibition of human B-lymphoma cell lines. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990;82(6):501–9.
Ortaldo JR, Oldham RK, Cannon GC, Herberman RB. Specificity of natural cytotoxic reactivity of normal human lymphocytes against a myeloid leukemia cell line. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977;59(1):77–82.
Abadir AM, Lang A, Klein T, Abenhaim HA. Influence of qualitative research on women’s health screening guidelines. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2014;210(1):44. e1-6.
Tsuno T, Mejido J, Zhao T, Phillips T, Myers TG, Bekisz J, et al. BID is a critical factor controlling cell viability regulated by IFN-alpha. J Immunother. 2012;35(1):23–31.
Bao L, Odell AF, Stephen SL, Wheatcroft SB, Walker JH, Ponnambalam S. The S100A6 calcium-binding protein regulates endothelial cell-cycle progression and senescence. FEBS J. 2012;279(24):4576–88.
de Bock CE, Ardjmand A, Molloy TJ, Bone SM, Johnstone D, Campbell DM, et al. The Fat1 cadherin is overexpressed and an independent prognostic factor for survival in paired diagnosis-relapse samples of precursor B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 2012;26(5):918–26.
Deng X, Ma Q, Zhang B, Jiang H, Zhang Z, Wang Y. Migration-stimulating factor (MSF) is over-expressed in non-small cell lung cancer and promotes cell migration and invasion in A549 cells over-expressing MSF. Exp Cell Res. 2013;319(17):2545–53.
Ferone G, Mollo MR, Thomason HA, Antonini D, Zhou H, Ambrosio R, et al. p63 control of desmosome gene expression and adhesion is compromised in AEC syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 2013;22(3):531–43.
Chinnadurai G, Vijayalingam S, Rashmi R. BIK, the founding member of the BH3-only family proteins: mechanisms of cell death and role in cancer and pathogenic processes. Oncogene. 2008;27 Suppl 1:S20–9.
Buonamici S, Trimarchi T, Ruocco MG, Reavie L, Cathelin S, Mar BG, et al. CCR7 signalling as an essential regulator of CNS infiltration in T-cell leukaemia. Nature. 2009;459(7249):1000–4.
Hoggatt J, Pelus LM. Eicosanoid regulation of hematopoiesis and hematopoietic stem and progenitor trafficking. Leukemia. 2010;24(12):1993–2002.
Kawaguchi A, Orba Y, Kimura T, Iha H, Ogata M, Tsuji T, et al. Inhibition of the SDF-1alpha-CXCR4 axis by the CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 suppresses the migration of cultured cells from ATL patients and murine lymphoblastoid cells from HTLV-I Tax transgenic mice. Blood. 2009;114(14):2961–8.
Saraiva N, Prole DL, Carrara G, Johnson BF, Taylor CW, Parsons M, et al. hGAAP promotes cell adhesion and migration via the stimulation of store-operated Ca2+ entry and calpain 2. J Cell Biol. 2013;202(4):699–713.
Sabatier L, Djokic J, Fagotto-Kaufmann C, Chen M, Annis DS, Mosher DF, et al. Complex contributions of fibronectin to initiation and maturation of microfibrils. Biochem J. 2013;456(2):283–95.
Abaeva AA, Canault M, Kotova YN, Obydennyy SI, Yakimenko AO, Podoplelova NA, et al. Procoagulant platelets form an alpha-granule protein-covered “cap” on their surface that promotes their attachment to aggregates. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(41):29621–32.
Patel B, Kang Y, Cui K, Litt M, Riberio MS, Deng C, et al. Aberrant TAL1 activation is mediated by an interchromosomal interaction in human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 2014;28(2):349–61.
Liu P, Keller JR, Ortiz M, Tessarollo L, Rachel RA, Nakamura T, et al. Bcl11a is essential for normal lymphoid development. Nat Immunol. 2003;4(6):525–32.
Cain DW, O’Koren EG, Kan MJ, Womble M, Sempowski GD, Hopper K, et al. Identification of a tissue-specific, C/EBPbeta-dependent pathway of differentiation for murine peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 2013;191(9):4665–75.
Johnson KD, Hsu AP, Ryu MJ, Wang J, Gao X, Boyer ME, et al. Cis-element mutated in GATA2-dependent immunodeficiency governs hematopoiesis and vascular integrity. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(10):3692–704.
Chen X, Xu H, Yuan P, Fang F, Huss M, Vega VB, et al. Integration of external signaling pathways with the core transcriptional network in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2008;133(6):1106–17.
Tiwari N, Meyer-Schaller N, Arnold P, Antoniadis H, Pachkov M, van Nimwegen E, et al. Klf4 is a transcriptional regulator of genes critical for EMT, including Jnk1 (Mapk8). PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57329.
Han Y, Amin HM, Frantz C, Franko B, Lee J, Lin Q, et al. Restoration of shp1 expression by 5-AZA-2′-deoxycytidine is associated with downregulation of JAK3/STAT3 signaling in ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Leukemia. 2006;20(9):1602–9.
Nishikawa Y, Miyazaki T, Nakashiro K, Yamagata H, Isokane M, Goda H, et al. Human FAT1 cadherin controls cell migration and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma through the localization of beta-catenin. Oncol Rep. 2011;26(3):587–92.
Real PJ, Ferrando AA. NOTCH inhibition and glucocorticoid therapy in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 2009;23(8):1374–7.
Hale AT, Tian H, Anih E, Recio 3rd FO, Shatat MA, Johnson T, et al. Endothelial Kruppel-like factor 4 regulates angiogenesis and the Notch signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(17):12016–28.
Nagel S, Kaufmann M, Drexler HG, MacLeod RA. The cardiac homeobox gene NKX2-5 is deregulated by juxtaposition with BCL11B in pediatric T-ALL cell lines via a novel t(5;14)(q35.1;q32.2). Cancer Res. 2003;63(17):5329–34.
Grabarczyk P, Przybylski GK, Depke M, Volker U, Bahr J, Assmus K, et al. Inhibition of BCL11B expression leads to apoptosis of malignant but not normal mature T cells. Oncogene. 2007;26(26):3797–810.
Huang X, Chen S, Shen Q, Chen S, Yang L, Grabarczyk P, et al. Down regulation of BCL11B expression inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in malignant T cells by BCL11B-935-siRNA. Hematology. 2011;16(4):236–42.
Trapnell C, Pachter L, Salzberg SL. TopHat: discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics. 2009;25(9):1105–11.
Trapnell C, Williams BA, Pertea G, Mortazavi A, Kwan G, van Baren MJ, et al. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28(5):511–5.
Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods. 2008;5(7):621–8.
Wang L, Feng Z, Wang X, Wang X, Zhang X. DEGseq: an R package for identifying differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq data. Bioinformatics. 2010;26(1):136–8.
Qing G, Li B, Vu A, Skuli N, Walton ZE, Liu X, et al. ATF4 regulates MYC-mediated neuroblastoma cell death upon glutamine deprivation. Cancer Cell. 2012;22(5):631–44.
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank Dr. Xiaoping Chen and Dr. Jiekai Chen for generously providing the lentiviral vectors. We thank Dr. Piotr Grabarczyk for providing help to revise this manuscript. This study was supported in part by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. XDA01020310), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81272329, 81200255 to P. L., 81327801 to D. W., 81272211, and 81200381 to H. L.), the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (2011CB504004 and 2010CB945500), and the Equipment Function Development & Technology Innovation Project of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. yg2010080, yg2011082, and yg2012049).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
Contribution: WL, YY, and PL conceived the study and designed the experiments; WL, ZJ, and TL designed the constructs used in this study and performed most of the studies related to leukemia; ZJTL and performed the in vivo studies; JJ, YH, and HL performed ChIP assays and western blots; YL, SC, SG, JW, XD, and LY provided T-ALL samples; BX provided adult BM samples; MZ provided cord blood samples; HX and YZ helped to perform FACS analysis; HL, MZ, XL, XH, and YC contributed the discussion part of the manuscript; PL and DW provided vital new reagents and revised the manuscript; and PL and YY discussed and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Wei Li and Zhiwu Jiang contributed equally to this work.
Additional files
Additional file 1:
Supplementary Figures.
Additional file 2:
Supplementary Figure Legends.
Additional file 3: Table S2.
RNA-sequencing results.
Additional file 4: Table S1.
Primers used in this study.
Additional file 5:
Supplementary Methods.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Jiang, Z., Li, T. et al. Genome-wide analyses identify KLF4 as an important negative regulator in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia through directly inhibiting T-cell associated genes. Mol Cancer 14, 26 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-014-0285-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-014-0285-x