Abstract
Background
TNF-α plays a role in angiogenesis and collagen synthesis, both essential in the wound healing process. There are concerns that pre-operative anti-TNF-α treatment may influence the surgical stress response and increase the risk of surgical complications. The aim of this study was to describe the surgical stress response in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and to investigate whether the pre-operative administration of anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha (anti-TNF-α) agents modify the surgical stress response.
Methods
This was a prospective, multi-center cohort pilot study. The primary outcome was the change in concentration of immunological biomarkers of the surgical stress response (TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10). Secondary outcome measures were changes in IL-8, IL-17A, C-reactive protein, white blood cells, cortisol, transferrin, ferritin, and D-Dimer in addition to 30 days’ post-operative complications and length of post-operative stay in the hospital (LOS).
Results
Forty-six patients with IBD undergoing major abdominal surgery were included, and 18 received anti-TNF- α treatment pre-operatively. Peak increase of most of the immunological biomarkers occurred 6 hours after surgical incision. Then the concentration decreased after 24 h followed by a plateau at 48 h. After adjusting for confounders including detectable blood concentrations, no difference in the concentrations of immunological, endocrinological or haematological biomarkers of stress was found between anti-TNF-α treated and anti-TNF-α naïve patients. No increase in post-operative complications or LOS was noticed in patients who received anti-TNF-α treatment.
Conclusions
Anti-TNF-α did not affect surgical stress response in this pilot study. Withdrawal of anti-TNF-α drugs prior to surgical intervention in IBD patients might not be justified without measurement of drug concentration and drug antibodies.
Trial registration
Clinicaltrails.gov.: NCT01974869.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Surgical injury induces a stress response with activation of endocrine, metabolic, and immunologic mediators aiming to restore hemostasis and induce tissue repair. The immunologic and inflammatory response to stress is regulated by cytokines produced in activated macrophages, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and giant cells. Tissue injury and infection are sensed by a group of protein receptors called pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that can be activated by pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs). A wide range of PRRs have been described, including membrane bound Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and C-type lectin receptors (CLRs), or cytoplasmic receptors such as NOD (Nucleotide-binding oligomerisation domain)-like receptors (NLR). Following stimulation of these receptors, multiple downstream proteins will be activated leading to intracellular signaling pathways that culminate in activation (phosphorylation) of transcription factors such as NF-kB among others which in turn drive the production of a large array of both pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines [1, 2].
The cytokines of special interest include interleukins (IL) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α).
Anti-TNF-α agents (biologicals) are antibodies directed against this key cytokine acting in two ways: First, by scavenging soluble TNF-α, thereby preventing activation of immune cells via TNF-a-receptors; and second, by “reverse signaling” acting on membrane bound TNF-α -receptors on monocytes and T-cells inducing apoptosis and inhibition of further cytokine release [1].
Besides being an important component of the immune defense, TNF-α plays a role in angiogenesis [2], collagen synthesis [3,4,5] and wound healing. Inhibition of these pathways may impair wound healing after surgery. Several observational retrospective studies have been carried out to investigate the risk of post-operative complications in patients with IBD who received pre-operative anti- tumor necrosis factor-alpha (anti-TNF-α) treatment [6,7,8]. The results of these studies are conflicting but a common point is that at least 1/3 of patients received anti-TNF-α) treatment [8].
The aim of this study was to describe the surgical stress response in patients with IBD undergoing surgical intervention and to investigate whether anti-TNF-α agents modify the surgical stress response.
Methods
Study design
The null hypothesis was that pre-operative administration of anti-TNF-α agents within 12 weeks before surgery, have no significant effect on surgical stress response. To investigate this; a prospective, non-interventional multi-center pilot study was designed.
The primary outcome measure was the difference in the plasma concentrations of the main immunological biomarkers of surgical stress response (TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10) between anti-TNF-α treated patients and anti-TNF-α naive.
The secondary outcome measures were difference in the plasma concentrations of other biomarkers of surgical stress including IL-8, IL-17A, the ratio of TNF-α/ IL-10 and Il-6/IL10, cortisol, transferrin, ferritin, and D-Dimer in addition to 30-days, post-operative complications and length of hospital stay (LOS). Overall complication was defined as any deviation from the expected post-operative recovery. Intra-abdominal septic complications (IASC) were defined as overt anastomotic leakage, intra-abdominal abscess formation or enteric fistula. Superficial surgical site infection (SSI) was defined as clinically documented skin infection at the site of surgery with or without positive culture. Grade of complications were assessed using Clavian-Dindo classification of surgical complications.
The choice of sampling intervals at six, 24 and 48 h after surgical incision was based on previous investigations [9,10,11,12,13]. Biomarkers of surgical stress were selected according to the existing evidence [2, 5, 9, 11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24].
Inclusion criteria: adult patients with Crohn’s disease (CD) or ulcerative colitis (UC) who were scheduled to elective intestinal resection or terminal stoma closure in three Danish university hospitals during the study period (March 2014–May 2016). Open as well as laparoscopic approaches were included.
Exclusion criteria: patients with pre-operative sepsis, acute intestinal obstruction, patients operated in acute setting (within 48 h of admission) and patients who had loop ileostomy take down without laparotomy or laparoscopy.
Details of the procedures
Laboratory procedures
Peripheral blood samples were taken before the induction of anesthesia, and six, 24 and 48 h after surgical incision. EDTA plasma and serum was separated by centrifugation, aliquoted and stored at − 80 °C until analysis.
The concentration of anti-TNF-α biological compounds administered pre-operatively (drug concentration) was measured in peripheral blood at the day of surgery together with antibodies against the specific compound (anti-drug antibodies). Details of the method used explained in the laboratory homepage [25].
Cortisol was measured by ELISA (DRG International, Inc.; Catalog number: EIA 1887; Marburg, Germany). IL-6, IL-10, IL-17A, and TNF-α were measured by a human high sensitive magnetic ProCartaPlex luminex kit (eBioscience; Catalog number: EPX040–00000-801; Vienna, Austria). IL-8 and D-Dimer were measured using ProCartaPlex Human IL-8 simplex, ProCartaPlex Human D-Dimer simplex, and Human Basic kit (eBioscience; catalog numbers: EPX010–10204-901, EPX010–12149-901, and EPX010–10420-901; Vienna, Austria). All samples were measured in duplicates according to the manufactures instructions, using the mean for statistical analyses. Plasma levels of CRP, transferrin, ferritin and D-dimer were measured using standard methods by the Department of Clinical Biochemistry, Copenhagen University Hospital, Amager and Hvidovre, Denmark.
Anesthesia, surgery and post-operative care
All the operations took place between 08:00 a.m. - 04.00 p.m. to avoid circadian rhythm as a confounder. General anesthesia was administered according to the standard practice of the anesthesia department in the participating hospitals. All patients received single prophylactic pre-operative antibiotics at the induction of anesthesia. The type and dose was determined by local standard of pre-operative care in the participating hospitals. Laparoscopic surgery and enhanced post-operative recovery principles were the standard procedures in the participating centers.
Statistical analysis
Sample size
Reference values for the changes in the biomarkers for surgical stress in IBD patients were not available at the time of the study to allow precise sample size calculations. Chalhoub et al. showed that 28 patients were needed to demonstrate a significant change in TNF-α concentration after moderately stressful surgery [26]. Moreover, Dimopoulou et al. [14] found that 40 patients should be included to detect a significant correlation between the values in TNF-α concentration and post-operative complications. Based on these two studies (non-IBD patients) and a meta-analyses by the authors [8], this pilot study was a priori designed to recruit at least 40 patients of whom 1/3 had received anti-TNF-α treatment prior to surgery keeping in mind that repeated measures will reduce the expected variations in outcome
Statistical methods
Pre-operative and peri-operative characteristics were compared between anti-TNF-α treated and anti-TNF-α naïve patients with chi-squared tests. Median, inter-quartile range (IQR), minimum and maximum were used to visualize changes in the concentration of biomarkers from baseline (before operation) to one of the post-operative follow-up time-points (six, 24 and 48 h after surgical incision). The difference of the medians of the changes from baseline between anti-TNF-α treated and anti-TNF-α naïve patients was assessed using a bootstrap approach in which patients (retaining the up-to-four-measurements per patient) were sampled with replacement using 1000 bootstrap replicates. To reduce bias from confounding, the calculated medians were weighted by a propensity score, i.e. the inverse of the estimated probability of the received anti-TNF-α regimen conditional on potential confounders. These probabilities were estimated from a multivariable logistic regression model included: Harvey-Bradshaw index for disease severity, nutritional risk screening score, parenteral nutrition, previous IBD-related abdominal operations, steroid stress dose, pre-operative Dexamethasone, epidural analgesia, access to abdominal cavity (open versus laparoscopic), type of resection and disease classification in case of CD. These were pre-operative factors that were either significantly different between the two anti-TNF-α regimens, or deemed important determinants from clinical experience. Propensity scores were re-calculated within each bootstrap replicate.
A permutation test, in which the four measurements for each patient were randomly redistributed over the time points in 1000 replicates to assess the null hypothesis of no development, was used to assess the statistical significance of the changes in the median concentration of biomarkers over time.
Logistic regression was used to investigate post-operative outcome where adjustment for confounding was done by stepwise backwards elimination, starting with a model including all pre- and peri-operative characteristics deemed clinically and/or statistically significant different between the two treatment groups. Variables were then removed one by one until all variables had p < 0.10.
All analyses, except for the bootstrap analyses, were done using IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 19.0. Armonk, NY: IBM Corp.2010. The bootstrap analyses were performed in the R environment for statistical computing version 3.1.2. A significance level of 5% was chosen.
We used non-parametric, robust methods for inference, i.e. a non-parametric bootstrap on the difference of propensity score weighted medians. These methods are described in detail in the statistics section of the paper. The SAMPLE guidelines were not very applicable to the inferential methods we used. This has been referred to in the manuscript.
Results
Patients were identified using outpatient’s clinic records, operation lists and reports from IBD conferences. All patients who fulfilled the inclusion criteria accepted to participate in the project. One patient was excluded because blood samples were accidently discarded. This explorative study succeeded, thus, in recruiting 46 patients, of which 18 had one type or another of anti-TNF-α agent treatment within 3 months prior to surgery.
Background characteristics
Median age was (42.5, IQR 23) years, 25/46 of the patients were females (54.3%). Median body mass index was (23.5, IQR 6.3). In anti-TNF- α group, 4/18 (22.2%) had one or more co-morbidities compared to 7/28 (31.8%) in anti-TNF-α naïve. No difference in the mean duration of disease was found between anti-TNF-α treated patients (7.61 SD ± 7.82) years and anti-TNF-α naive (10.11 SD ± 9.15). Pre-and intra-operative patients’ characteristics are reported in Table 1.
Anti-TNF-α naïve patients had higher rate of previous IBD surgeries compared to anti-TNF- α treated patients (p = 0.003). Anti-TNF-α treated patients were more likely to receive pre-operative parenteral nutritional support (p = 0.028). Moreover, anti-TNF-α treated patients with CD had a longer ileocecal/ileo-colic resected segment (mean 31.11 SD ± 35.51) cm versus 27.43 SD ± 18.83 p = 0.036) and were more likely to suffer from a stricturing CD phenotype (10/76.9% versus 8/42.1% p = 0.01). But this did not affect the results in multivariate analyses. Type of surgical incision and type of bowel resections were similar in the two groups.
In the 18 patients who received anti-TNF-α pre-operatively, different type of anti-TNF-α drugs were administered using different doses with wide variations of the interval from last administered dose to surgery (Table 2). Thus, 44% of anti-TNF-α treated patients had undetectable drug concentration in peripheral blood and only three of these 18 patients had anti-drug antibodies at the time of surgery.
Pattern of change in surgical stress markers in IBD
Figures 1 & 2 depict the surgical stress response according to all 12 inflammatory biomarkers. Peak increase in TNF-α occurred 6 hours after surgical incision (median 0.596, IQR range 0.679) then the concentration decreased after 24 h (median 0.517, IQR range 0.969) followed by a plateau at 48 h (median 0.446, IQR range 0.655). The same pattern was observed for IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-17A, IL-6/IL-10 ratio, WBC, D-Dimer, ferritin and transferrin while CRP peaked at 48 h after surgical incision. The ratio of TNF- α/IL-10 and cortisol decreased at 6 hours then started to increase at 24 h reaching a plateau at 48 h. The stress response over time was significant in all biomarkers (p < 0.01) except TNF-α, IL-17A and cortisol.
Surgical stress response in 46 patients with inflammatory bowel disease who underwent surgical interventions as part of disease treatment. Immunological, endocrinological and hematological biomarkers of stress are shown. The box shows the median and inter-quartile while the numbers above show concentrations for the outliers
Difference in surgical stress response between the two groups
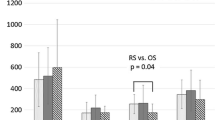
There was a tendency towards a higher concentration in most of the inflammatory biomarkers in patients treated with anti-TNF-α agents compared to the anti-TNF-α naive as shown in Fig. 3. This was more pronounced in patients with detectable drug concentration and no anti-drug antibodies. However, the differences were not statistically significant (Table 3).
Sub-group analyses
Sub-group analyses was done by selecting patients who underwent laparoscopic ileocecal/ileo-colic resections (12/46) to obtain a homogenous group of patients with same type of surgical procedure. Then by comparing anti-TNF-α treated and anti-TNF-α naïve in this sub-group showed no significant difference in surgical stress response (results not shown).
Post-operative outcome
No difference was found in adjusted analyses of overall complications between the two groups (27.8% versus 28.6%), superficial SSI (7.8% versus 7.1%), IASC (5.6% versus 7.1%) and re-admission rates (22.2% versus 25%). Mean LOS was 5.33 (± 2.57) for anti-TNF- α treated versus (6.25 ± 3.01) in the anti-TNF- α naive group. The difference was not statistically significant. The time interval between last dose of anti-TNF- α and the day of surgery did not affect the rate of complications. Nor did the type of anti-TNF- α agents used (Table 2).
Discussion
This explorative prospective multi-center pilot study described the pattern of surgical stress response in IBD patients as measured by evidence-based biomarkers of surgical stress response. The results showed that the administration of anti-TNF-α drugs in the pre-operative period did not have a significant effect on the immunological, hematological or endocrinological biomarkers of the surgical stress response. At first glance, this might be unexpected as the anti-TNF-α are potent drugs that affect the immune system and thus the inflammatory phase of wound healing. However, deeper insights reveal that this is not a stand-alone observation because the effect of anti-TNF- α drugs on surgical site infection and anastomotic leak was not significant in two nation-wide database studies [27, 28] and four experimental studies in which confounders were well controlled and measurements of effective drug concentration were available [29,30,31,32]. Moreover, Lau et al. showed a correlation between anti-TNF-α drugs concentration of more than 3 μg/mL and post-operative infectious complication but no wound healing related complications in CD patients [33]. The measurement of detectable blood concentration of anti-TNF-α might explain this because-as shown in this cohort- not all patients who received anti-TNF-α had a detectable drug concentration in their blood prior to surgery and some of them had neutralizing antibodies. This finding may also explain some of the controversies seen in observational studies [8].
However, having undetectable drug concentration do not rule out that anti-TNF-α drugs had an effect on immune system.
Anti-TNF-α drugs did not reduce the concentration of TNF-α in our study. A finding that is in line with two other studies [34, 35], in which serial measurements of 17 serum cytokines were conducted in 37 and 24 patients respectively. This can be related to a dose-dependent effect in which the anti-TNF-α drugs reduce the concentration of TNF-α in higher doses. Verification of such hypothesis as well as finding the cut-off concentration are to be investigated in experimental studies and/or in clinical studies where the interval between anti-TNF-α administration and surgery is not more than few days.
We did not find an association between anti-TNF-α treatment and post-operative outcomes. This did not appear to be explained by possible clinically and intra-operative factors that might influence the stress response to surgery or drug concentration and presence of anti-drug antibodies, as we adjusted for these. However, this might be due to small sample size [8] or due to a dose-dependent effect of anti-TNF-α on post-operative outcome [33].
Limitations of this study include the small sample size (pilot study) and the lack of measurements of other influential factors in wound healing, for instance vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), granulocytes-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and transforming growth factor (TGF-β). However, these factors are regulated by IL-6 [23] and other cytokines measured in this study. Another limitation might be heterogeneity of patients’ population (CD and UC) and surgical procedures. However, sub-group analysis did not change the results which were in line with a recently published prospective study where the authors included only CD patients undergoing ileo-caecal resections [36]. The choice of anesthetic agents was left to the routine practice in the participating departments. This might be a limitation in the study as different anesthetic agents may affect the surgical stress response differently [37].
Conclusion
This pilot study showed no difference in surgical stress response between anti-TNF-α treated and anti-TNF-α naïve patients. Withdrawal of anti-TNF-α drugs prior to surgical intervention in IBD patients might not be justified without measurement of drug concentration and drug antibodies. Further large sample prospective studies are needed.
References
Peake STC, Bernardo D, Mann ER, Al-Hassi HO, Knight SC, Hart AL. Mechanisms of action of anti-tumor necrosis factor α agents in Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013;19:1546–55.
Alazawi W, PhD M, Pirmadjid N, Lahiri R, MBBS M, Bhattacharya S, et al. Inflammatory and immune responses to surgery and their clinical impact. Ann Surg. 2016;264:73–80.
Mast B, Schultz GS. Interactions of cytokines, growth factors, and proteases in acute and chronic wounds. Wound Rep Reg. 1996;4:411-20.
Park JE, Barbul A. Understanding the role of immune regulation in wound healing. Am J Surg. 2004;187:11S–6S.
Tsirogianni AK, Moutsopoulos NM, Moutsopoulos HM. Wound healing: immunological aspects. Injury. 2006;37(Suppl 1):S5–12.
Holubar SD, Holder-Murray J, Flasar M, Lazarev M. Anti-tumor necrosis factor-α antibody therapy management before and after intestinal surgery for inflammatory bowel disease: a CCFA position paper. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015;21:2658–72.
El-Hussuna A, Theede K, Olaison G. Increased risk of post-operative complications in patients with Crohn’s disease treated with anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha agents - a systematic review. Dan Med J. 2014;61:A4975.
El-Hussuna A, Krag A, Olaison G, Bendtsen F, Gluud LL. The effect of anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha agents on postoperative anastomotic complications in Crohn’s disease: a systematic review. Dis Colon Rectum. 2013;56:1423–33.
Desborough JP. The stress response to trauma and surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2000;85:109–17.
Chachkhiani I, Gürlich R, Maruna P, Frasko R, Lindner J. The postoperative stress response and its reflection in cytokine network and leptin plasma levels. Physiol Res. 2005;54:279–85.
Jaffer U, Wade RG, Gourlay T. Cytokines in the systemic inflammatory response syndrome: a review. HSR Proc Intensive Care Cardiovasc Anesth. 2010;2:161–75.
Fink-Neuboeck N, Lindenmann J, Bajric S, Maier A, Riedl R, Weinberg AM, et al. Clinical impact of interleukin 6 as a predictive biomarker in the early diagnosis of postoperative systemic inflammatory response syndrome after major thoracic surgery: a prospective clinical trial. Surgery. 2016;160:443–53.
Bastian D, Tamburstuen MV, Lyngstadaas SP, Reikerås O. Systemic and local cytokine kinetics after total hip replacement surgery. Eur Surg Res. 2008;41:334–40.
Dimopoulou I, Armaganidis A, Douka E, Mavrou I, Augustatou C, Kopterides P, et al. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNFalpha) and interleukin-10 are crucial mediators in post-operative systemic inflammatory response and determine the occurrence of complications after major abdominal surgery. Cytokine. 2007;37:55–61.
Mannick J a, Rodrick ML, Lederer J a. The immunologic response to injury. J Am Coll Surg. 2001 Sep;193:237–44.
Nishimoto N, Kishimoto T. Interleukin 6: from bench to bedside. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2006;2:619–26.
Jawa RS, Anillo S, Huntoon K, Baumann H, Kulaylat M. Analytic review: Interleukin-6 in surgery, trauma, and critical care: part I: basic science. J Intensive Care Med. 2013;26:3–12.
Giannoudis PV, Dinopoulos H, Chalidis B, Hall GM. Surgical stress response. Injury. 2006;37(Suppl 5):S3–9.
Lin E, Lowry SF. Inflammatory cytokines in major surgery: a functional perspective. Intensive Care Med. 1999;25:255–7.
Naito Y. Response of plasma adrenocortictropic hormones, cortisol, and cytokines during and after upper abdominal surgery. Anesthesiology. 1992;77:426–31.
Mokart D, Merlin M, Sannini a BJP, Delpero JR, Houvenaeghel G, et al. Procalcitonin, interleukin 6 and systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS): early markers of postoperative sepsis after major surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2005;94:767–73.
Baigrie RJ, Lamont PM, Kwiatkowski D, Dallman MJ, Morris PJ. Systemic cytokine response after major surgery. Br J Surg. 1992;79:757–60.
Behm B, Babilas P, Landthaler M, Schreml S. Cytokines, chemokines and growth factors in wound healing. J Eur Acad Dermatology Venereol. 2012;26:812–20.
Werner S, Grose R. Regulation of wound healing by growth factors and cytokines. Physiol Rev. 2003;83:835–70.
Measuring the concentration of TNF blockers [cited 2017 May 29]. Available from: http://www.wieslab.com/diagnostic-services/index.php?headId=72&pageId=72&langId=1&productId=324
Chalhoub V, Pottecher J, Asehnoune K, Mazoit JX, Duranteau J, Benhamou D. Cytokine response and reactive oxygen species production after low- and intermediate-risk surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2011;55:549–57.
Nørgård BM, Nielsen J, Qvist N, Gradel KO, de Muckadell OBS, Kjeldsen J. Pre-operative use of anti-TNF-α agents and the risk of post-operative complications in patients with Crohn’s disease--a nationwide cohort study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013;37:214–24.
Nørgård BM, Nielsen J, Qvist N, Gradel KO, de Muckadell OBS, Kjeldsen J. Pre-operative use of anti-TNF-α agents and the risk of post-operative complications in patients with ulcerative colitis - a nationwide cohort study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012;35:1301–9.
Ågren MS, Andersen TL, Andersen L, Schiødt CB, Surve V, Andreassen TT, et al. Nonselective matrix metalloproteinase but not tumor necrosis factor-α inhibition effectively preserves the early critical colon anastomotic integrity. Int J Color Dis. 2011;26:329–37.
Myrelid P, Salim SY, Darby T, Almer S, Melgar S, Andersson P, et al. Effects of anti-inflammatory therapy on bursting pressure of colonic anastomosis in murine dextran sulfate sodium induced colitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2015;50:991–1001.
Ploug T, Andersen K, Hansen K, Hjelmborg J, Qvist N. Influence of adalimumab treatment on anastomotic strength, degree of inflammation, and collagen formation: an experimental study on the small intestine of rabbits. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013;19:254–8.
Strebel K, Nielsen SRH, Biagini M, Qvist N. Effect of Humira® on intestinal anastomotic response in rabbits. J Investig Surg Off J Acad Surg Res. 2015;28:167–72.
Lau C, Dubinsky M, Melmed G, Vasiliauskas E, Berel D, McGovern D, et al. The impact of preoperative serum anti-TNFα therapy levels on early postoperative outcomes in inflammatory bowel disease surgery. Ann Surg. 2015;261:487–96.
Mizutani T, Akasaka R, Tomita K, Chiba T. Serial changes of cytokines in Crohn’s disease treated with infliximab. Hepatogastroenterology. 2011;58:1523–6.
Abiko Y, Mizutani T, Chiba T. Serial changes of serum cytokines in Crohn’s disease following treatment with adalimumab. Hepatogastroenterology. 2014;61:357–62.
Fumery M, Seksik P, Auzolle C, et al. Postoperative complications after Ileocecal resection in Crohn’s disease: a prospective study from the REMIND group. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112:337–45.
Dang Y, Shi X, Xu W, Zuo M. The effect of anesthesia on the immune system in colorectal Cancer patients. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;7940603.
Aknowledgment
This work could not be achieved without the help of many colleagues in the departments of surgery, anesthesia, and biochemistry in Køge, Odense and Slagelse University Hospitals. In addition to the dedicated workers in the Clinical Research Centre at Hvidovre Hospital and Eurodiagostica lab in Malmö- Sweden (www.eurodiagnostica.com). The authors would especially like to thank Mrs. Linda Camilla Andersen, Clinical Research Centre at Hvidovre Hospital, who helped in planning and conducting the analyses of the blood samples.
The financial support received from different funds was essential to conduct the expensive blood investigations, pay the salaries of the staff who interviewed the patients, collected blood samples, registered and analyzed data. Special thanks to:
1. Research fund: The region of Zealand- Denmark
2. Research fund: Slagelse Hospital-Denmark
3. Aage og Johanne Louise Hansens Fond
4. Research fund: The region of north Jutland- Denmark
5. Crohn & Colitis organization research fund
6. King Christian the 10th fund
7. Desirée & Niels Yde fund
Funding
The region of Zealand fund- Denmark, Slagelse Hospital- Denmark, Aage og Johanne Louise Hansens Fond, The north Jutland region, Crohn & Colitis organization in Denmark, King Christian the 10th fund, Desirée & Niels Yde fund.
Declarations
The study was approved by Ethics Committee in the capital region (reference number H-2-2013-166) and the region of Zealand (SJ-399), Danish Data Protection Agency (Datatilsynet) in the capital region (reference number HVH-2013-046 / 02515) and in the region of Zealand (reference number REG-85-2013). The study was registered in clinicaltrails.gov (Identifier: NCT01974869) and Trial map on ESCP website (http://www.escp.eu.com/research/international-trials/trials-map).
This study adhered to the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) guidelines. Written informed consent was obtained from the participants in this study. No conflicts of interests to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have contributed to the manuscript as bellow: AE, IG, NQ: Conception and design, analysis and interpretation, data collection, writing the article, critical revision of the article and obtaining funding. MZ: Data collection, writing the article, critical revision of the article and obtaining funding. AL: Analysis and interpretation, writing the article, critical revision of the article and obtaining funding. VS: Analysis and interpretation, writing the article, critical revision of the article and obtaining funding. SL: Data collection. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
El-Hussuna, A., Qvist, N., Zangenberg, M.S. et al. No effect of anti-TNF-α agents on the surgical stress response in patients with inflammatory bowel disease undergoing bowel resections: a prospective multi-center pilot study. BMC Surg 18, 91 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12893-018-0425-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12893-018-0425-0