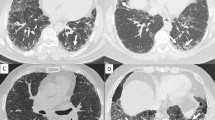
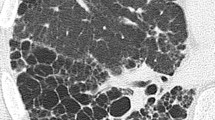
Abstract
Background
Usual interstitial pneumonia can present with a probable pattern on high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT), but the probability of identifying usual interstitial pneumonia by surgical lung biopsy in such cases remains controversial. We aimed to determine the final clinical diagnosis in patients with a probable usual interstitial pneumonia pattern on HRCT who were subjected to surgical lung biopsy.
Methods
HRCT images were assessed and categorized by three radiologists, and tissue slides were evaluated by two pathologists, all of whom were blinded to the clinical findings. The final clinical diagnosis was accomplished via a multidisciplinary discussion. Patients with a single layer of honeycombing located outside of the lower lobes on HRCT were not excluded.
Results
A total of 50 patients were evaluated. The most common final clinical diagnosis was fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis (38.0%) followed by idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (24.0%), interstitial lung disease ascribed to gastroesophageal reflux disease (12.0%) and familial interstitial lung disease (10.0%). In the group without environmental exposure (n = 22), 10 patients had a final clinical diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (45.5%). Irrespective of the final clinical diagnosis, by multivariate Cox analysis, patients with honeycombing, dyspnoea and fibroblastic foci on surgical lung biopsy had a high risk of death.
Conclusions
The most common disease associated with a probable usual interstitial pneumonia pattern on HRCT is fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis followed by idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and interstitial lung disease ascribed to gastroesophageal reflux disease. In patients without environmental exposure, the frequencies of usual interstitial pneumonia and a final clinical diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis are not sufficiently high to obviate the indications for surgical lung biopsy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a fibrosing interstitial lung disease (ILD) of unknown aetiology defined by the presence of usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) pattern on surgical lung biopsy (SLB) [1]. On high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT), the UIP pattern is characterized by predominant basal reticular abnormalities with honeycombing cysts and the absence of inconsistent features and is considered sufficient for diagnosis in the proper clinical context [1]. However, many patients with IPF do not have a UIP pattern on HRCT. Patients with the same findings of the UIP pattern except for honeycombing were classified by the American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society/Japanese Respiratory Society/Latin American Thoracic Association (ATS/ERS/JTS/ALAT) in 2011 as having possible UIP [1].
Some studies found a high positive predictive value of a possible UIP pattern on HRCT for the diagnosis of UIP on lung biopsy [2,3,4,5,6]. However, these studies included patients with a high prevalence of UIP, which introduced a selection bias and inflated the diagnosis of IPF. A study of individuals with possible UIP patterns on HRCT showed that the positive predictive value is highly dependent on the underlying prevalence [5]. In that study, the second most common diagnosis was hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP). In Brazil, HP is a common cause of ILD [7].
More recently, the Fleischner Society and ATS/ERS/JTS/ALAT guidelines suggested four categories for classifying HRCT patterns of UIP [8, 9]. In the absence of honeycombing and in the appropriate clinical context, a reticular pattern with lower lobe predominance and traction bronchiectasis should not be considered a possible UIP pattern but rather a probable UIP pattern. According to the Fleischner Society, SLB can be avoided in such cases, but the ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT made a conditional recommendation for SLB in these cases [8, 9].
The objective of the present study was to evaluate the frequency of IPF and other ILDs in patients with a probable UIP pattern on HRCT.
Methods
This study was approved by the Ethics and Research Committee of the Federal University of Sao Paulo (register number 2.180.594). Informed consent was not required as the data were collected retrospectively and anonymously analysed.
Study population
Patients were selected retrospectively from ILD reference centres in Brazil. The period of the study was from 2002 to 2018. For inclusion in the study, HRCT, histological samples, and clinical data were available for central review and a multidisciplinary discussion (MDD). All HRCT images were obtained within 1 year of the biopsy. Consecutive patients were evaluated until 50 filled the criteria for analysis.
Inclusion criteria
The inclusion criterion was the presence of a probable UIP pattern on HRCT according ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT 2018 guidelines [9].
Exclusion criteria
Patients with any one of the following HRCT UIP patterns were excluded: UIP or indeterminate or alternative diagnosis of UIP, including predominant bronchovascular abnormalities [9]; furthermore, those with inadequate HRCT image quality; emphysema with extension greater than 10% on HRCT; diagnosis of connective tissue disease prior to SLB; and a probable UIP pattern on HRCT with exposure to HP and lymphocytosis (> 20%) on bronchoalveolar lavage were also excluded. Patients with a single layer of honeycombing cysts located outside of the lower lobes on HRCT were not excluded.
Clinical data
Demographic data were recorded. Dyspnoea was scored as absent, major, moderate, small effort or at rest, according Mahler’s scale for magnitude of task [10]. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) symptoms investigated included heartburn, regurgitation and dyspepsia. GERD was evaluated by endoscopy, oesophageal manometry and pH monitoring [11, 12].
Familial ILD was defined as the diagnosis of an ILD in two or more relatives who shared common ancestry [13].
The predicted values for forced vital capacity (FVC) were those derived from the Brazilian population [14].
HRCT evaluation
All HRCT scans were reviewed through a protocol by three thoracic radiologists (GSPM, IM and KN) with experience in ILD (18, 22 and 8 years, respectively) without knowledge of the clinical data and final clinical diagnosis. The presence of a probable UIP pattern in each patient was established by a consensus. Patients in whom no consensus was reached among radiologists for probable UIP were excluded.
Histologic evaluation
All samples were reviewed independent of each other by two pathologists (RGF and ENAMC) with experience in ILD (35 and 27 years, respectively).
The histological pattern of UIP was characterized according to the criteria proposed for definitive and probable UIP in 2011 by the ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT [1].
Bronchiolocentric fibrosis (BF) was defined by predominant involvement centred on the airways associated with inflammation or peribronchiolar metaplasia [15]. The presence of giant cells and granuloma, fibroblastic foci (FF) and microscopic honeycombing was noted. The number of FF was considered relevant if greater than occasional [16].
Histological findings suggestive of autoimmune disease were characterized by the presence of lymphocytic pleuritis, bronchiolitis, vascular sclerosis, several lymphoid follicles, and intense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate [17].
Unclassifiable ILD was defined as the presence of overlapping patterns found in a single lobe or multiple lobes or when it was not possible to include the patient in any of the categories proposed for the classification of interstitial pneumonias [18].
Final clinical diagnosis
The patients were reassessed, and the final clinical diagnosis was established by an MDD with the same pathologists and three pulmonologists experienced in ILD (RCCT, MRS, and CACP). IPF was defined as definitive or probable histological patterns of UIP in the absence of other potential aetiologies [1]. In the presence of environmental exposure, the diagnosis was still defined as IPF in the presence of a UIP pattern in more than one lobe, without any other histological findings suggestive of HP. [19] Fibrotic HP (FHP) was defined as the presence of environmental exposure before the onset of symptoms and by the presence of one of the following histological findings: 1) BF and/or lymphomononuclear infiltrate, bronchiolar poorly defined nonnecrotizing granulomas, and/or giant cells and bronchiolitis or 2) BF with or without giant cells or granulomas in the absence of GERD [20].
For the diagnosis of ILD ascribed to GERD, the patients had to fulfil the following criteria [15] in the presence or absence of symptoms of GERD: histological patterns of BF in the absence of environmental exposure to HP and GERD confirmed through one or more of the following: oesophagitis on upper gastrointestinal endoscopy or abnormal oesophageal pH monitoring characterized by a DeMeester score greater than 14.7 or proximal reflux characterized by 1% or more of the total time with a pH less than 4 at the proximal sensor [11, 12].
The clinical diagnosis of familial ILD was maintained irrespective of the histopathologic findings [21]. Interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features was characterized as suggested by the ATS/ERS task force [22].
Statistical analysis
Continuous data are expressed as the mean and standard deviation or as the median and interquartile range. Categorical variables are described as absolute numbers and percentages. The values for the most common final clinical diagnosis and histologic patterns are expressed as the mean percentage and 95% confidence interval of proportions. The comparison between categorical variables was performed using Fisher’s exact chi-square test.
The test characteristics of the probable UIP pattern (sensitivity, specificity and positive predictive value) for histopathological UIP were calculated using the prevalence of IPF observed in Brazil (10%) and in other countries with the highest prevalence [7, 23, 24].
Survival time was calculated from the date of biopsy to death, lung transplantation (n = 1) or loss to follow-up. The survival status was obtained from telephone interviews and/or medical records. The follow-up time was censored on April 30, 2019. All-cause mortality was evaluated.
Univariate Cox analysis was performed to select variables related to survival, and those with p values < 0.20 were entered into a multivariate forward Wald Cox model to select variables predictive of survival. Kaplan-Meier curves were generated to calculate the median survival time and to compare survival between patients with and without the variables of interest.
A p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS software version 21 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA).
Results
One hundred seventy-seven patients with HRCT images available for re-reading and an SLB sample available for review were selected. After review, 127 patients were excluded (Supplementary Fig. S1). Ultimately, 50 patients were included. The general characteristics are described in Table 1.
Environmental exposure to HP was reported in 28 patients (56%): mould (n = 10), birds/feathers (n = 11), mould and birds (n = 4), and wood dust (n = 3).
GERD symptoms were also common and were reported in 22 (44%) patients.
Honeycombing located outside of the lower lobes was recorded in eight patients (16.0%).
The histological patterns are described in Table 2. BF was the most commonly observed histological pattern in 26 (52.0%) patients. The classical histological triad of HP was found in seven (14%) patients, and BF with giant cells and/or granulomas was found in five (10%) patients, two of whom had histological findings of FF and/or microscopic honeycombing. Bridging fibrosis were observed in four patients with BF. The second most prevalent pattern was UIP (26%). Unclassifiable ILD and interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features were found in two (4%) patients each.
The final clinical diagnoses are described in Table 3. The most frequent diagnosis was FHP followed by IPF and ILD ascribed to GERD. After excluding patients with environmental exposure (n = 22), 10 (45%) patients were diagnosed with IPF. One patient without apparent exposure but with typical findings on SLB received a final clinical diagnosis of FHP.
The final diagnosis established among the 28 patients with environmental exposure were: 18 FHP; three patients with familial ILD; two unclassifiable ILD; two IPF; one IPAF; in two patients, the final clinical diagnosis was FHP and/or ILD ascribed to GERD due to the presence of BF on histology, relevant environmental exposure and confirmed GERD.
In two patients with histological findings of BF, no cause was apparent (idiopathic BF).
After the MDD, the two patients with histological patterns of unclassifiable ILD remained without a final clinical diagnosis.
In five patients, there was a familial history of ILD, which was the final clinical diagnosis. These patients presented with the following histological patterns: BF (n = 3), UIP (n = 1) and classical histological triad of HP (n = 1).
Groups of patients with FHP, IPF and the other diagnoses were compared. As expected, the presence of environmental exposure was different between the groups: 20 cases (95.2%) in the FHP group, two cases (16.7%) in the IPF group and 11 cases (64.7%) in the other diagnoses group (χ2 = 21.8; p < 0.001). Confirmed GERD was more frequent in the group with other diagnoses: 11 cases (64.7%) compared to three cases (15%) in the FHP group and two cases (16.7%) in the IPF group (χ2 = 13.7; p = 0.002). The presence of Velcro crackles, forced vital capacity (FVC%), and peripheral oxygen saturation at rest and at the end of exercise were similar in the three groups (Supplementary Table S1).
In the present study, no patient died in the first month after SLB. The median general survival time was 72.0 (95% CI = 57.5–96.5) months. According to Kaplan-Meier curves, the median survival time was similar when patients with IPF, FHP and other diagnoses were compared (Supplementary Fig. S2).
Honeycombing outside of the lower lobes was present in four patients with FHP, one with IPF, and three with other diagnoses. Fibroblastic foci was observed in all 12 patients with IPF, eight patients with FHP and 12 patients with others diagnosis: five familial ILD; three ILD ascribed to GERD; two idiopathic BF; one IPAF and one case that was classified as HP plus ILD ascribed to GERD. In the univariate Cox analysis, age, dyspnoea score, FVC%, FF and honeycombing on HRCT were selected. In the multivariate Cox analysis, honeycombing outside of the lower lobes, dyspnoea score and FF on SLB remained significant (Table 4). When the FVC% was entered in the model instead of dyspnoea, it became significant, with lower values associated with poorer survival (p = 0.01).
Antifibrotic agents were prescribed for 13 patients, including seven with IPF.
After excluding environmental exposure (n = 28) as a possible cause of the number of FHP cases diagnosed, a probable UIP pattern on HRCT demonstrated a sensitivity and specificity of 83.3% (95% CI 51.6 to 97.9%) and 68.4% (95% CI 51.3 to 82.5%), respectively. The positive predictive value was 22.7% (95% CI 14.7 to 33.3%) when considering the prevalence of IPF as 10 and 63.7% (95% CI 50.8 to 74.9%) when considering the prevalence of IPF as 40%.
Discussion
In the present study, FHP was the most frequent cause of a probable UIP pattern on HRCT. Considering only the patients without a history of environmental exposure, IPF was observed in less than 50% of the sample, with several ILDs diagnosed in the remaining subjects.
In 2011, the ATS proposed a tomographic classification for UIP in three categories [1]. In 2017, the Fleischner Society suggested splitting the possible group from the ATS 2011 guidelines into the probable and indeterminate groups [8]. Probable UIP was characterized by the presence of a reticular pattern with peripheral traction bronchiectasis or bronchiolectasis in the absence of honeycombing. A diagnosis of IPF could confidently be made in a patient with a typical clinical context of IPF, with an HRCT pattern of probable UIP [8]. This statement was based on two papers: one had a recognized selection bias [3], and the other included patients with an undefined location of honeycombing on HRCT as a probable UIP pattern [4].
Similar to the Fleischner Society, in 2018, the ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT suggested a pattern of “probable UIP”, but the panel emphasized that the decision to perform SLB should be made in the context of an MDD by experienced clinicians [9].
Criteria for the diagnosis of IPF have been discussed for a long time. Criteria for the diagnosis of FHP have been suggested more recently, but many differences persist [25,26,27]. Relevant environmental exposure, suggestive HRCT findings, and increased lymphocytes in bronchoalveolar lavage are important for diagnosis but are not helpful in many cases. Histopathologic findings can be typical, but these are absent in many cases of FHP.
In Brazil, HP is more common than IPF as a cause of ILD (24 vs 10%), as shown in a recent multicentre study [7]. However, 53% of all patients with ILD had potential exposure to HP, raising the question of whether other diagnoses can be excluded simply by the presence of environmental antigens. In the present study, only one patient without apparent exposure had a diagnosis of FHP established by typical findings on biopsy. According to the 2020 Guideline for diagnosis of HP, this case would be classified as “high confidence diagnosis” (HRCT with indetermined findings plus typical histopathologic findings) [28].
In contrast, in many studies, the causal agent for HP has not been identified [26]. Indeed, the prevalence of HP can be underestimated. In a study from Spain, almost half of the patients diagnosed with IPF based on the 2011 criteria were subsequently diagnosed with FHP [29].
HP can present with several histopathologic patterns [19]. In FHP, a typical pattern is characterized by chronic fibrosing pneumonia, airway-centred fibrosis and poorly formed nonnecrotizing granulomas. Fibrosing interstitial pneumonia is characterized by architectural distortion; FF and subpleural honeycombing can be present. In airway-centred fibrosis or BF, there is also extensive peribronchiolar metaplasia and, in many cases, bridging fibrosis. In FHP, the presence of granulomas and giant cells is uncommon. Another possible presentation for FHP is a pattern of nonspecific interstitial pneumonia.
In the present study, six patients were diagnosed with ILD ascribed to GERD. In these patients, the histological pattern was BF, there was no environmental exposure to HP, and GERD was substantiated. In our opinion, the role of GERD as an aetiological factor of fibrosing ILD, not UIP, has been neglected [15].
In two patients in the present series with BF, FHP and ILD ascribed to GERD were possible causes. In our opinion, these patients cannot be discriminated by biopsy. In the other two patients, a possible cause for BF was not determined.
Patients with nonspecific interstitial pneumonia were not observed in the present series, probably due to a high frequency of findings inconsistent with UIP on HRCT.
In the present study, five patients had familial ILD. On SLB, three displayed BF with FF and/or microscopic honeycombing, one had a typical PH pattern, and one had an isolated UIP pattern. In a study of 30 patients with familial ILD, diagnostic features of UIP were observed in less than 50% of the samples, but FF were observed in 87%, and multifocal BF was observed in 37% [21]. Familial ILD presents in many different ways on HRCT and in lung biopsies [13, 30]. Genetic factors can predispose patients to several ILDs, and diverse pathologic expressions can be found in the same family [13, 31]. The indications for SLB in familial ILD remain controversial [32, 33].
The likelihood of a histopathological UIP pattern in patients with a probable UIP pattern on HRCT remains undefined.
In a recent paper from Japan, the prevalence of a histopathological UIP pattern was 83% (90 of 109) in patients with a probable UIP pattern on HRCT, but the diagnosis of IPF after the MDD was made in only 66% [32]. The median survival time was 72.1 months for patients with the probable UIP pattern, which was very similar to that found in our series. This survival time was longer than that found in patients with IPF, suggesting that a heterogeneous number of diagnoses were included in the group with a probable UIP pattern. In this study, different clinical diagnoses were not the objective and were not explored [34].
In the present study, the degree of dyspnoea, the presence of honeycombing not in the lower lobes irrespective of diagnosis, and the presence of FF on SLB were predictive of poor survival. The presence of honeycombing on HRCT in an ILD other than IPF is a predictor of a poor prognosis, but in most cases, honeycombing is present in the lower lobes [35]. Even with a limited sample, we found that honeycombing outside of the lower lobes was associated with poor survival, irrespective of the final diagnosis.
FF are a major histological feature of UIP in SLB but can be present in other conditions. It has been recognized for a long time that the presence and extent of FF predict poor survival in patients with IPF as well as in those with FHP [16, 20, 36, 37].
In the INPULSIS trial, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of nintedanib in the treatment of IPF, subjects enrolled with the possible UIP pattern and traction bronchiectasis showed similar disease progression and treatment responsiveness to subjects enrolled with the IPF HRCT pattern [38]. This was used as an argument supporting these cases as IPF.
The INBUILD trial was a randomized, double-blind, multicentre, parallel group trial performed in 663 patients with a progressive fibrosing ILD other than IPF [39, 40]. Chronic HP was diagnosed in 173 patients (26%). Participants were randomly assigned to receive 150 mg of nintedanib twice daily or placebo for at least 52 weeks. Nintedanib reduced the rate of ILD progression, as measured by a decline in the FVC, irrespective of the underlying ILD diagnosis. In patients with a UIP-like fibrotic pattern, the adjusted rate of decline in the FVC over the 52-week period was more conspicuous [40].
These studies raise the question of whether the diagnosis of fibrosing ILD truly matters. In FHP, if the antigen is not identified, the prognosis is worse [41]. Otherwise, identification and antigen avoidance, even in FHP, can result in a prolonged survival time [42]. A subset of patients with FHP experience a progressive disease course, even after antigen avoidance, and these patients can be treated with pharmacologic agents, including antifibrotic drugs if necessary.
In patients with fibrotic ILD of indeterminate aetiology, we currently recommend transbronchial lung cryobiopsy before entertaining SLB [43].
Some authors suggest that older age, male sex and smoking could increase the positive predictive value for IPF diagnostics in patients with a possible UIP pattern on HRCT [2]. In the present study, these data were not helpful.
Several limitations to our study should be noted. The sample size was relatively small. This was a retrospective study, and selection bias should be considered. All the patients were reviewed by two expert pathologists in ILD, but the concordance was not evaluated. HRCT during expiration was not performed in all patients; thus, air trapping was not evaluated; however, this finding has a lower predictive value for separating FHP from IPF compared to that for the mosaic pattern [44]. Treatment was not standardized, making it difficult to evaluate its effect on survival.
Conclusions
Different ILDs are observed in patients with a probable UIP pattern on HRCT. Even in patients without relevant environmental exposure, IPF should not be presumed as the most common diagnosis. After considering the risks, a biopsy approach should be entertained.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article and its additional supplemental files.
Abbreviations
- ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT:
-
American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society/Japanese Respiratory Society/Latin American Thoracic Association
- BF:
-
Bronchiolocentric fibrosis
- FF:
-
Fibroblastic foci
- FHP:
-
Fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- FVC:
-
Forced vital capacity
- GERD:
-
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- HP:
-
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- HRCT:
-
High-resolution computed tomography
- ILD:
-
Interstitial lung disease
- IPF:
-
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- MDD:
-
Multidisciplinary discussion
- SLB:
-
Surgical lung biopsy
- UIP:
-
Usual interstitial pneumonia
- 95% CI:
-
95% confidence interval
References
Raghu G, Collard HR, Egan JJ, Martinez FJ, Behr J, Brown KK, et al. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;183(6):788–824..
Fell CD, Martinez FJ, Liu LX, Murray S, Han MK, Kazerooni EA, et al. Clinical predictors of a diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;181(8):832–7.
Raghu G, Lynch D, Godwin JD, Webb R, Colby TV, Leslie KO, et al. Diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with high-resolution CT in patients with little or no radiological evidence of honeycombing: secondary analysis of a randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2014;2(4):277–84.
Chung JH, Chawla A, Peljto AL, Cool CD, Groshong SD, Talbert JL, et al. CT scan findings of probable usual interstitial pneumonitis have a high predictive value for histologic usual interstitial pneumonitis. Chest. 2015;147(2):450–9.
Brownell R, Moua T, Henry TS, Elicker BM, White D, Vittinghoff E, et al. The use of pretest probability increases the value of high-resolution CT in diagnosing usual interstitial pneumonia. Thorax. 2017;72(5):424–9.
Salisbury ML, Xia M, Murray S, Bartholmai BJ, Kazerooni EA, Meldrum CA, et al. Predictors of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in absence of radiologic honeycombing: a cross sectional analysis in ILD patients undergoing lung tissue sampling. Respir Med. 2016;118:88–95.
Pereira CAC, Soares MR, Botelho A, Gimenez A, Beraldo B, Fukuda C, et al. Multicenter Registry of interstitial lung diseases in adults in Brazil. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;201:A3352.
Lynch DA, Sverzellati N, Travis WD, Brown KK, Colby TV, Galvin JR, et al. Diagnostic criteria for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a Fleischner society White paper. Lancet Respir Med. 2018;6(2):138–53.
Raghu G, Remy-Jardin M, Myers JL, Richeldi L, Ryerson CJ, Lederer DJ, et al. Diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;198(5):e44–68.
Mahler DA, Weinberg DH, Wells CK, Feinstein AR. The measurement of dyspnea. Contents, interobserver agreement, and physiologic correlates of two new clinical indexes. Chest. 1984;85(6):751–8.
Jamieson JR, Stein HJ, DeMeester TR, Bonavina L, Schwizer W, Hinder RA, et al. Ambulatory 24-h esophageal pH monitoring: normal values, optimal thresholds, specificity, sensitivity, and reproducibility. Am J Gastroenterol. 1992;87(9):1102–11.
Dobhan R, Castell DO. Normal and abnormal proximal esophageal acid exposure: results of ambulatory dual-probe pH monitoring. Am J Gastroenterol. 1993;88(1):25–9.
Steele MP, Speer MC, Loyd JE, Brown KK, Herron A, Slifer SH, et al. Clinical and pathologic features of familial interstitial pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;172(9):1146–52.
Pereira CA, Sato T, Rodrigues SC. New reference values for forced spirometry in white adults in Brazil. J Bras Pneumol. 2007;33(4):397–406.
Kuranishi LT, Leslie KO, Ferreira RG, Coletta EA, Storrer KM, Soares MR, et al. Airway-centered interstitial fibrosis: etiology, clinical findings and prognosis. Respir Res. 2015;16:55.
Coletta ENAM, Pereira CAC, Ferreira RG, Rubin AS, Vilela LS, Malheiros T, et al. Achados Histopatológicos e sobrevida na fibrose pulmonar idiopática. J Bras Pneumol. 2003;29(6):371–8.
Adegunsoye A, Oldham JM, Valenzi E, Lee C, Witt LJ, Chen L, et al. Interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features: value of histopathology. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2017;141(7):960–9.
Travis WD, Costabel U, Hansell DM, King TE, Lynch DA, Nicholson AG, et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: update of the international multidisciplinary classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;188(6):733–48.
Takemura T, Akashi T, Kamiya H, Ikushima S, Ando T, Oritsu M, et al. Pathological differentiation of chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis/usual interstitial pneumonia. Histopathology. 2012;61(6):1026–35.
Churg A, Bilawich A, Wright JL. Pathology of chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis what is it? What are the diagnostic criteria? Why do we care? Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2018;142(1):109–19.
Leslie KO, Cool CD, Sporn TA, Curran-Everett D, Steele MP, Brown KK, et al. Familial idiopathic interstitial pneumonia: histopathology and survival in 30 patients. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2012;136(11):1366–76.
Fischer A, Antoniou KM, Brown KK, Cadranel J, Corte TJ, du Bois RM, et al. An official European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society research statement: interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features. Eur Respir J. 2015;46(4):976–87.
Fisher JH, Kolb M, Algamdi M, Morisset J, Johannson KA, Shapera S, et al. Baseline Characteristics and Comorbidities in the CAnadian REgistry for Pulmonary Fibrosis. BMC Pulm Med. 2019;19(1):223.
Singh S, Collins BF, Sharma BB, Joshi JM, Talwar D, Katiyar S, et al. Interstitial Lung Disease in India. Results of a Prospective Registry. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;195(6):801–813.
Salisbury ML, Myers JL, Belloli EA, Kazerooni EA, Martinez FJ, Flaherty KR. Diagnosis and treatment of fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonia. Where we stand and where we need to go. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;196(6):690–9.
Vasakova M, Morell F, Walsh S, Leslie K, Raghu G. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: perspectives in diagnosis and management. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;196(6):680–9.
Morisset J, Johannson KA, Jones KD, Wolters PJ, Collard HR, Walsh SLF, et al. Identification of diagnostic criteria for chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis: an international modified Delphi survey. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;197(8):1036–44.
Raghu G, Remy-Jardin M, Ryerson CJ, Myers JL, Kreuter M, Vasakova M, et al. Diagnosis of hypersensitivity pneumonitis in adults. An official ATS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;202(3):e36–69.
Morell F, Villar A, Montero M, Muñoz X, Colby TV, Pipvath S, et al. Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis in patients diagnosed with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a prospective case-cohort study. Lancet Respir Med. 2013;1(9):685–94.
Lee HY, Seo JB, Steele MP, Schwarz MI, Brown KK, Loyd JE, et al. High-resolution CT scan findings in familial interstitial pneumonia do not conform to those of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. Chest. 2012;142(6):1577–83.
Adegunsoye A, Vij R, Noth I. Integrating genomics into Management of Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Disease. Chest. 2019;155(5):1026–40.
Borie R, Kannengiesser C, Sicre de Fontbrune F, Gouya L, Nathan N, Crestani B. Management of suspected monogenic lung fibrosis in a specialised centre. Eur Respir Rev. 2017;26(144):160122.
Newton CA, Batra K, Torrealba J, Kozlitina J, Glazer CS, Aravena C, et al. Telomere-related lung fibrosis is diagnostically heterogeneous but uniformly progressive. Eur Respir J. 2016;48(6):1710–20.
Fukihara J, Kondoh Y, Brown KK, Kimura T, Kataoka K, Matsuda T, et al. Probable usual interstitial pneumonia pattern on chest CT: is it sufficient for a diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Eur Respir J. 2020;55(4):1802465.
Adegunsoye A, Oldham JM, Bellam SK, Montner S, Churpek MM, Noth I, et al. Computed tomography honeycombing identifies a progressive fibrotic phenotype with increased mortality across diverse interstitial lung diseases. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019;16(5):580–8.
King TE, Schwarz MI, Brown K, Tooze JA, Colby TV, Waldron JA, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: relationship between histopathologic features and mortality. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164(6):1025–32.
Wang P, Jones KD, Urisman A, Elicker BM, Urbania T, Johannson KA, et al. Pathologic findings and prognosis in a large prospective cohort of chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest. 2017;152(3):502–9.
Raghu G, Wells AU, Nicholson AG, Richeldi L, Flaherty KR, Le Maulf F, et al. Effect of Nintedanib in subgroups of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by diagnostic criteria. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;195(1):78–85.
Flaherty KR, Wells AU, Cottin V, Devaraj A, Walsh SLF, Inoue Y, et al. Nintedanib in progressive Fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(18):1718–27.
Wells AU, Flaherty KR, Brown KK, Inoue Y, Devaraj A, Richeldi L, et al. Nintedanib in patients with progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases-subgroup analyses by interstitial lung disease diagnosis in the INBUILD trial: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(5):453–60.
Fernández Pérez ER, Swigris JJ, Forssén AV, Tourin O, Solomon JJ, Huie TJ, et al. Identifying an inciting antigen is associated with improved survival in patients with chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest. 2013;144(5):1644–51.
Gimenez A, Storrer K, Kuranishi L, Soares MR, Ferreira RG, Pereira CAC. Change in FVC and survival in chronic fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Thorax. 2018;73(4):391–2.
Troy LK, Grainge C, Corte TJ, Williamson JP, Vallely MP, Cooper WA, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of transbronchial lung cryobiopsy for interstitial lung disease diagnosis (COLDICE): a prospective, comparative study. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(2):171–81.
Barnett J, Molyneaux PL, Rawal B, Abdullah R, Hare SS, Vancheeswaran R, et al. Variable utility of mosaic attenuation to distinguish fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J. 2019;54(1):1900531.
Acknowledgements
We thank the collaboration group of investigators: Eliana Viana Mancuzo, MD, PhD; Marcelo Palmeira Rodrigues, MD, PhD; Maria Auxiliadora Carmo Moreira, MD, PhD; Sergio Fernandes de Oliveira Jezler, MD, PhD; and Gediel Cordeiro Junior, MD.
Funding information
This study was funded by CAPES, Ministry of Education, Brazil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RCCT participated in the study design, had full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity and accuracy of the data. MRS participated in the multidisciplinary discussion and helped draft the manuscript. KMS participated in the study design. GSPM, KN and IM collaborated to perform the radiological analysis. ENAMC and RGF collaborated to perform the histological analysis. CACP is the guarantor of the paper and coordinated the study, performed the statistical analysis and helped draft the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ information
RCCT, MRS, KMS and CACP: Pulmonary Department, Federal University of Sao Paulo, Sao Paulo, Brazil. GSPM: Imaging Department, Fleury Group, Sao Paulo, Brazil. KN and IM: Radiology Department, Federal University of Sao Paulo, Sao Paulo, Brazil. ENAMC and RGF: Pathology Department, Federal University of Sao Paulo, Sao Paulo, Brazil.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Ethics and Research Committee of the Federal University of Sao Paulo (register number 2.180.594), and the requirement for informed consent was waived due to the retrospective nature of the analysis.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Fig. S1.
Inclusion criteria diagram. Fig. S2. Probable usual interstitial pneumonia pattern on high resolution chest tomography. Fig. S3. Fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Fig. S4. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Fig. S5. Interstitial lung disease ascribed to gastroesophageal reflux disease. Fig. S6. Survival in patients with a probable UP pattern on HRCT was analysed according to the main diagnostic groups. Table S1. Clinical characteristics, functional characteristics, and HRCT findings of 50 patients with fibrotic chronic hypersensitivity pneumonia, IPF, and other diagnoses and a probable UIP HRCT pattern.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Tibana, R.C.C., Soares, M.R., Storrer, K.M. et al. Clinical diagnosis of patients subjected to surgical lung biopsy with a probable usual interstitial pneumonia pattern on high-resolution computed tomography. BMC Pulm Med 20, 299 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-020-01339-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-020-01339-9