Abstract
Background
Hyperhomocysteinemia may be a risk factor for endothelial dysfunction. Folate and vitamin B12 regulate the homocysteine metabolic process. This study aimed to evaluate the associations between subsequent events of adverse pregnancy outcome and early variables of homocysteine, folate, and vitamin B12 in pregnant women.
Methods
This multicenter, retrospective, case–control study involved 563 pregnant women with adverse pregnancy outcome and 600 controls. Adverse pregnancy outcomes included one or more of the following events: preeclampsia, preterm birth, low birth weight, and stillbirth. The associations between subsequent events of adverse pregnancy outcome and early variables of homocysteine, folate, and vitamin B12; metabolic parameters; inflammatory markers; anthropometrics; and lifestyle habits at 11–12 weeks of gestation were analyzed using the logistic regression model.
Results
Compared to the lower quartile homocysteine concentrations, the upper quartile homocysteine concentrations were associated with preeclampsia, preterm birth and low birth weight. On the contrary, the lower quartile folate concentrations were associated with preeclampsia, preterm birth and low birth weight compared with the upper quartile folate concentrations. The incidence of adverse pregnancy outcome increased progressively from the first to fourth homocysteine quartiles but decreased progressively from the first to fourth folate quartiles. After adjusting for confounding factors, multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that besides systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, body mass index and age, homocysteine (IV vs I quartile, aOR 5.89, 95% CI 4.08–8.51, P < 0.001), folate (IV vs I quartile, aOR 0.35, 95% CI 0.25–0.50, P < 0.001), folate supplementation (yes vs no, aOR 0.55, 95% CI 0.35–0.86, P = 0.010) during early pregnancy were independently associated with subsequent events of adverse pregnancy outcome, and vitamin B12 was rejected. Of these, the homocysteine revealed the highest odds ratio in all risk variables, and folate showed the lowest odds ratio in all protective variables.
Conclusions
Higher homocysteine concentration and lower folate level during early pregnancy were associated with adverse pregnancy outcome. However, no association was found between vitamin B12 and adverse pregnancy outcome. Supplementation with folate in early pregnancy may reduce adverse pregnancy outcome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Adverse pregnancy outcome (APO) is defined as an event that reduces the opportunity of having a healthy newborn, including preeclampsia, preterm birth, low birth weight, stillbirth, and so on. APOs may lead to severe complications, such as massive postpartum hemorrhage and neonatal death [1, 2]. Preeclampsia is a serious, pregnancy-specific syndrome that affects multiple organs. It continues to afflict 5–8% of pregnancies worldwide and is one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality among pregnant women and fetuses [3]. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), low birth weight is defined as a birth weight less than 2500 g regardless of gestational age, which may be due to either preterm birth or intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), or a combination of both [4]. The burden of APO is substantial in both developed and developing countries. It is not only the primary cause of infant morbidity and mortality but also the critical determinant of child survival, disabilities, stunting, and long-term adverse consequences [5, 6].
Previous studies demonstrated that elevated levels of homocysteine (Hcy) were associated with an increased risk of vascular diseases and may cause direct damage to endothelial cells both in vitro and in vivo [7, 8]. Maternal hyperhomocysteinemia (HHcy) exhibited a wide range of effects, including maternal and placental vascular endothelial dysfunction, DNA dysfunction, and proliferation of smooth muscle cells through oxidative stress. It increased the levels of asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA), promoted artery calcification, and was involved in inflammation, leading to APO [9, 10]. Folate and vitamin B12 (VB12) deficiency was significantly associated with HHcy and endothelial dysfunction owing to folate and VB12 serving as co-substrates, co-factors, and vital regulators in the metabolism of Hcy [11, 12]. Supplementation of folate and VB12 could decrease serum Hcy levels in patients with HHcy [13] and also reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in pregnant rats with pregnancy-related complications [14].
Despite the harmful effects of Hcy on pregnancy outcomes, numerous related issues remain unknown. This study aimed to analyze retrospectively the relationship between subsequent events of APO and early variables of metabolic parameters, inflammatory markers, anthropometrics, and lifestyle habits in pregnant women at 11–12 weeks of gestation. It also explored the associations of subsequent events of APO with early maternal serum Hcy and folate concentrations and the VB12 status in pregnant women.
Methods
Study participants
This multicenter retrospective case–control study was conducted between October 2016 and March 2017 in Chengdu Women’s and Children’s Central Hospital, School of Medicine, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences and Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, School of Medicine, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, and Mianyang Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine. It included 563 pregnant women with APO, aged 19.33–48.25 (29.78 ± 5.97) years, and 600 non-APO pregnant women aged 21.25–46.68 (28.02 ± 4.38) years matched for age and lifestyle habits (controls).
A total of 563 APOs in this study included the following events: 234 preeclampsia without other APOs, 118 preterm birth without other APOs, 92 low birth weight without other APOs, 16 stillbirth without other APOs, 30 preeclampsia with preterm birth, 16 preeclampsia with low birth weight, 2 preeclampsia with stillbirth, 12 preeclampsia with preterm birth and low birth weight, 43 preterm birth with low birth weight.
-
(1) Preeclampsia, which is defined as a new onset of hypertension and proteinuria after the 20th gestational week, or a new onset of hypertension in the absence of proteinuria but combined with hematological complications, renal insufficiency, impaired liver function, neurological symptoms, or uteroplacental dysfunction, diagnosed based on the International Society for the Study of Hypertension in Pregnancy criteria [15];
-
(2) Preterm birth, which is defined as babies born alive before 37 completed weeks of gestation;
-
(3) Low birth weight, which is defined by the WHO as a birth weight less than 2500 g, regardless of gestational age, caused by either preterm birth or IUGR, or a combination of both;
-
(4) Stillbirth, which is defined as in utero fetal death at 20 weeks of gestation or greater, unexplained by chromosomal abnormality, anatomic malformation, or congenital infection.
While selecting 600 controls, their information of these controls was matched with that of pregnant women with APO as follows:
-
(1) Similar age: The age difference between the controls and pregnant women with APO was ≤1 year, and the closest one was selected first.
-
(2) Similar habits: The controls were close to pregnant women with APO in terms of smoking, drinking, and supplementation with folate and VB12.
-
(3) Close delivery time: The delivery time of the controls was less than 1 week from that for pregnant women with APO, and the closest was preferred.
Women with the following causes and diseases were excluded from this study: missing data on some basic information, family history of hereditary diseases, congenital diseases, thyroid dysfunction, cancer, leukemia, or autoimmune diseases, or recent infection of TORCH, abortion, or multiple pregnancies.
Sample collection and measurement
Fasting blood was sampled with a vacuum blood collection tube in the morning, and the blood was transferred, making it flow down the wall of the tube to minimize the mechanical disruption or turbulence that might result in hemolysis or activation. The sampled blood was vertically placed; the plasma was separated within 30 min, and the serum was separated within 60 min after blood collection. If the serum could not be separated within 60 min, the blood was vertically placed in the refrigerator at 4 °C but separated within 4 hs.
The blood was centrifuged for 10 min at 3000 rpm to separate plasma or serum. Fresh plasma was used for measuring the fasting plasma glucose (FPG) level. An aliquot of fresh serum was used for determining the levels of Hcy, folate, VB12, total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), uric acid (UA), and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP). Another aliquot of serum was frozen and stored at − 80 °C. When the sample collection was completed, the frozen serum was brought up to room temperature by gradual thawing and centrifuged for 10 min at 3000 rpm. The serum supernatant fluid was used for determining the interleukin-6 (IL-6) level.
Quality control
The Sichuan Homocysteine Study was conducted by the Chengdu Women’s and Children’s Central Hospital, School of Medicine, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, the Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences and Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, School of Medicine, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, and the Mianyang Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Standard operating procedures were developed, including inclusion/exclusion criteria, project implementation, biological sample collection, storage, testing, and data collection. Moreover, the main inspection projects of all laboratories participated in the External Quality Assessment (EQA) of the National Center for Clinical Laboratories and achieved good results.
Collection of data
The data were retrospectively collected from early pregnant women at 11–12 weeks of gestation. Complete laboratory and clinical data measured by the medical staff (doctors, technicians, nurses, and medical assistants) included serum concentrations of Hcy, folate, VB12, TC, TG, LDL-C, HDL-C, FPG, UA, IL-6, and hs-CRP; height; body weight; and blood pressure. Basic information filled in by pregnant women included ethnicity, age, gestational age, reproductive history, history of illness, family history of disease, vitamin (folate and VB12) supplementation (yes or no), and lifestyle habits such as smoking and drinking (yes or no). Non-smoking is defined as never smoked or quit smoking for more than a year, while excessive drinking is defined as drinking more than 200 mL of over 45% alcohol once a week. Information related to pregnancy, labor, birth, and maternal, fetal, and neonatal out comes was also collected. Pregnant women underwent a comprehensive examination (including some free items) when they had a health care data card in early pregnancy, benefiting from the government’s provision of free pregnancy eugenic tests for every couple of childbearing age. The data were completed, and the collection was not so difficult.
Metabolic parameters
The concentration of Hcy was determined by the enzymatic cycling assay using a Hitachi 7600 Automatic Biochemistry Analyzer (Hitachi High-Tech Instruments Co., Ltd., Japan; reagent and calibrator, Beijing Strong Biotechnologies, Inc., China; quality control material of Liquichek Hcy, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., USA). The levels of TC, TG, LDL-C, HDL-C, FPG, and UA were measured by commercial test kits using the aforementioned analyzer. The concentrations of folate and VB12 were detected by chemiluminescent immunoassay using an ADVIA Centaur XP and matched reagent, calibrator, and quality control materials (Siemens Industry, Inc., USA).
Hypercholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia, low HDL-C level, and high LDL-C level were defined as TC ≥ 6.22 mmol/L and TG ≥ 2.26 mmol/L, HDL-C < 1.04 mmol/L, and LDL-C ≥ 4.14 mmol/L, respectively, according to the Chinese guidelines on the prevention and treatment of dyslipidemia in adults [16]. Gestational diabetes was diagnosed when patients’ FPG was ≥5.1 mmol/L, and/or 1-h plasma glucose (1hPG) during an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) ≥ 10.0 mmol/L, and/or 2-h plasma glucose (2hPG) during an OGTT ≥8.5 mmol/L, according to the 2010 International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups recommendations on the diagnosis and classification of hyperglycemia in pregnancy [17].
The cutoff values for quartile distribution of each metabolic parameters considered in the study were Hcy (μmol/L): I < 7.03, II 7.03–7.98, III 7.99–12.60, IV > 12.60; folate (nmol/L): I < 18.31, II 18.31–21.43, III 21.44–29.25, IV > 29.25; VB12 (pmol/L): I < 255.81, II 255.81–401.28, III 401.29–546.90, IV > 546.90; TC (mmol/L): I < 4.43, II 4.43–5.29, III 5.30–5.87, IV > 5.87; TG (mmol/L): I < 1.35, II 1.35–1.57, III 1.58–1.88, IV > 1.88; LDL-C (mmol/L): I < 2.27, II 2.27–2.89, III 2.90–3.65, IV > 3.65; HDL-C (mmol/L): I < 1.22, II 1.22–1.37, III 1.38–1.62, IV > 1.62; FPG (mmol/L): I < 4.25, II 4.25–4.57, III 4.58–4.83, IV > 4.83; and UA (μmol/L): I < 271.63, II 271.63–299.09, III 299.10–372.09, IV > 372.09.
Inflammatory markers and anthropometrics
The level of hs-CRP was measured by the noncompetitive near-infrared particle immunoassay with a matched high-sensitivity CRP Kit (IMMAGE 800 Immunochemistry System, Beckman Coulter, Inc., USA). The concentration of IL-6 was quantified by the step sandwich method with an ACCESS 2 Immunoassay System and matched a reagent and calibrator (Beckman Coulter, Inc.). Systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), body weight, and height were measured with standard techniques. The body mass index (BMI) was calculated as body weight (kg) divided by the square of height (m).
Hypertension was diagnosed when patients’ SBP was ≥140 mmHg and/or DBP ≥ 90 mmHg. Underweight, overweight, and obesity were defined as BMI < 18.5 kg/m2, 24.0 to < 28.0 kg/m2, and ≥ 28 kg/m2, respectively, according to the guidelines for the prevention and control of overweight and obesity in Chinese adults [18, 19]. The cutoff values for the quartile distribution of each of the inflammatory markers and anthropometrics considered in the study were hs-CRP (mg/L): I < 1.68, II 1.68–3.74, III 3.75–9.21, IV > 9.21; IL-6 (pg/mL) I < 23.64, II 23.64–37.28, III 37.29–74.57, IV > 74.57; age (year): I < 25.71, II 25.71–27.08; III 27.09–29.37, IV > 29.37; SBP (mmHg): I < 119, II 119–124, III 125–129, IV > 129; DBP (mmHg): I < 76, II 76–80, III 81–86, IV > 86; and BMI (kg/m2) I < 19.03, II 19.03–21.60, III 21.61–23.40, IV > 23.40.
Statistical analysis
Data were statistically analyzed using the Statistical Package for Social Science version 19.0 (SPSS Inc., IL, USA). Continuous variables with a normal distribution were expressed as mean ± standard deviation, and the difference in data between the two groups was analyzed using the independent-samples t test. Continuous variables with skewed distribution were presented as median (25th to 75th percentiles), and the difference in data between the two groups was analyzed using the Mann–Whitney U rank-sum test. Categorical variables were presented as a percentage and analyzed using the chi-square test.
The associations of APO with each of the metabolic parameters, inflammatory markers, anthropometrics, and lifestyle habits (quantitative data expressed as quartiles and qualitative variables expressed as “yes” or “no”) were evaluated by the univariate logistic regression analysis. They were expressed as the odds ratio (OR) and its 95% confidence interval (95% CI). Variables with a P value < 0.25 in the univariate analysis were retained for further multivariate logistic regression analysis. The adjusted odds ratio (aOR) and its 95% CI were calculated by the multivariate logistic regression analysis (stepwise forward Wald method) to select the variables independently associated with APO. All P values were two-tailed, and a P value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Comparison of principal characteristics between pregnant women with APO and controls in early pregnancy
Compared with controls, pregnant women with APO were characterized by increased serum concentrations of Hcy, TC, TG, LDL-C, and FPG; higher value of SBP, DBP, and BMI; older age; and decreased serum levels of folate, VB12, and HDL-C (P < 0.05). No significant differences were found in hs-CRP, IL-6, and UA concentrations (P > 0.05). Moreover, pregnant women with APO had higher rates of age > 35 years, hypercholesterolemia, low HDL-C, high LDL-C, gestational diabetes, hypertension, overweight, and obesity, and lower rates of folate and VB12 supplementation compared with controls (P < 0.05). No significant difference was observed in the rates of smoking, excessive drinking, hypertriglyceridemia, and underweight between the two groups (P > 0.05). The principal characteristics of 1163 early pregnant women at 11–12 weeks of gestation according to subsequent events of APO and non-APO are reported in Table 1.
Relative risks of APO categories by quartiles of Hcy, folate, and VB12 in pregnant women
The relative risks of APO categories by quartiles of Hcy, folate, and VB12 in pregnant women are shown in Table 2. Compared with the lower-quartile Hcy levels, the upper-quartile Hcy levels were associated with preeclampsia (P < 0.001), preterm birth (P < 0.001), and low birth weight (P < 0.001). On the contrary, the lower-quartile folate concentrations were associated with preeclampsia (P < 0.001), preterm birth (P < 0.001), and low birth weight (P = 0.001) compared with the upper-quartile folate concentrations. However, compared with the upper-quartile VB12 levels, the lower-quartile VB12 concentrations were associated with only preterm birth (P = 0.008) and not with preeclampsia (P = 0.087) and low birth weight (P = 0.292). No association was observed between the upper-quartile and lower-quartile Hcy, folate, and VB12 for stillbirth.
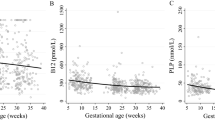
The incidence of APO by quartiles of Hcy, folate, and VB12 distribution in 1163 pregnant women are shown in Fig. 1. The incidence of APO increased progressively from 9.11% in quartile I to 9.29% in quartile II, to 10.58% in quartile III, and to 19.43% in quartile IV of the Hcy distribution (P < 0.001). On the contrary, the incidence of APO decreased progressively from 15.99% in quartile I to 13.41% in quartile II, to 10.32% in quartile III, and to 8.68% in quartile IV of the folate distribution (P < 0.001). Similarly, the incidence of APO progressively decreased from 13.93% in quartile I to 11.78% in quartile II, to 11.69% in quartile III, and to 11.01% in quartile IV of the VB12 distribution (P = 0.032). Four APO categories, including preeclampsia, preterm birth, low birth weight, and stillbirth, by quartiles of Hcy, folate, and VB12 distribution in 1163 pregnant women are shown in Figs. 2, 3, and 4, respectively.
Associations of APO with each of the early variables in pregnant women as detected by the univariate logistic regression analysis
Among qualitative variables, APO was significantly associated with folate supplementation (yes vs no, OR 0.34, 95% CI 0.23–0.51, P < 0.001) and VB12 supplementation (yes vs no, OR 0.72, 95% CI 0.51–0.98, P = 0.034). However, it was not significantly associated with smoking (yes vs no, OR 1.51, 95% CI 0.66–3.42, P = 0.329) and excessive drinking (yes vs no, OR 0.89, 95% CI 0.49–1.61, P = 0.703). Among quantitative variables, Hcy (quartile IV vs I), folate (quartile IV vs I), VB12 (quartile IV vs I), TC (quartile IV vs I), HDL-C (quartile IV vs I), SBP (quartile IV vs I), DBP (quartile IV vs I), BMI (quartile IV vs I), and age (quartile IV vs I) were significantly associated with APO (P < 0.05). However, hs-CRP (quartile IV vs I), IL-6 (quartile IV vs I), TG (quartile IV vs I), LDL-C (quartile IV vs I), FPG (quartile IV vs I), and UA (quartile IV vs I) were not significantly associated with APO (P > 0.05). The associations of APO with each of the early variables of metabolic parameters, inflammatory markers, and anthropometric variables in 1163 pregnant women, as detected by the univariate logistic regression analysis, are shown in Table 3.
Independent associations of subsequent events of APO with each of the early variables in pregnant women as detected by multivariate logistic regression analysis
After adjusting for confounding factors, the multivariate logistic regression analysis (stepwise forward Wald method) showed that Hcy (quartile IV vs I), folate (quartile IV vs I), SBP (quartile IV vs I), DBP (quartile IV vs I), BMI (quartile IV vs I), age (quartile IV vs I), and folate supplementation (yes vs no) during early pregnancy were independently associated with subsequent events of APO (P < 0.05); VB12 was rejected. Of these, Hcy revealed the highest OR in all risk variables (quartile IV vs I, aOR 5.89, 95% CI 4.08–8.51), and folate showed the lowest OR in all protective variables (quartile IV vs I, aOR 0.35, 95% CI 0.25–0.50). The results of the multivariate logistic regression analysis are shown in Table 4.
Discussion
A number of factors before and during pregnancy may affect the events of APO, including maternal age [20], smoking, excessive drinking [21, 22], overweight or obesity, metabolic disorders (such as diabetes) [23, 24], and some chronic diseases such as chronic kidney disease [25], systemic lupus erythematosus [26], cardiovascular diseases [27], and so on. The results indicated that pregnant women with APO were characterized by higher Hcy, TC, TG, LDL-C, FPG, age, SBP, DBP, and BMI, and lower folate, VB12, and HDL-C concentrations, compared with controls (P < 0.05). In addition, pregnant women with APO had higher age (> 35 years), hypercholesterolemia, low HDL-C, high LDL-C, gestational diabetes, hypertension, overweight, and obesity compared with controls (P < 0.05). However, pregnant women with APO had lower folate level and VB12 supplementation compared with controls (P < 0.05). No significant difference was found in the rates of smoking, excessive drinking, hypertriglyceridemia, and underweight between the two groups (P > 0.05).
The vascular endothelium plays a pivotal role in regulating vasoconstriction and vasodilatation, coagulation and thrombosis, inflammation, and so on [28]. Endothelial dysfunction can be described as an imbalance between vasoconstrictors and vasodilators produced by the endothelium, which has significant effects on the development of placenta-mediated vascular-related diseases [7]. Hcy, as a sulfur-containing amino acid, derives from the demethylation of methionine during DNA or/and RNA methylation. It is associated with endothelial dysfunction. HHcy, as a metabolic disorder parameter, has been considered an independent risk factor for vascular-related diseases [29, 30]. Available evidence shows that HHcy may be a cause of the endothelial dysfunction provoked by oxidative stress, and elevated Hcy levels are significantly associated with preeclampsia [31], preterm birth [32], low birth weight [33], fetal death [34], IUGR [35], and so on.
In the present study, the upper-quartile Hcy concentrations were associated with preeclampsia (P < 0.001), preterm birth (P < 0.001), and low birth weight (P < 0.001) compared with the lower-quartile Hcy levels. The incidence of APO increased progressively from quartile I to IV of Hcy levels. After adjusting for confounding factors, the multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that, besides SBP, DBP, BMI, and age, Hcy (quartile IV vs I) was independently associated with APO. Of these, Hcy revealed the highest OR in all risk variables. The present study provided valuable evidence that higher serum Hcy concentrations during early pregnancy were independently associated with subsequent events of APO.
Maternal HHcy can increase oxidative stress, and augmented oxidative stress exerts an adverse effect on pregnancy outcome. Oxidative stress in uteroplacental tissues plays an important role in the development of placental-related diseases because of induced cellular and DNA damage and partly generated superoxide [36,37,38,39]. In women with chronic oxidative stress in the placenta, the development of the placento–decidual interface is severely impaired, leading to the early and widespread onset of maternal blood flow and major oxidative degeneration [40]. Jacobsen et al. [41] reported that more than 98% of Hcy existed in an oxidized state due to a highly reactive sulfhydryl group in Hcy, which readily self-oxidized to form a disulfide linkage with other free thiols, along with the generation of superoxide radicals as a byproduct. Maternal HHcy also increases the ADMA level, which causes the uncoupling of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), decreased production and bioavailability of nitric oxide, and increased production of superoxide, leading to further endothelial dysfunction [42].
Folate and VB12 are two vital regulators of the metabolism of Hcy [43]. A significant association is observed between maternal lower folate concentrations and higher Hcy levels as well as an increase in the risk of preeclampsia [44]. Furness et al. [45] found that pregnant women with decreased red blood cell folate concentration and increased plasma concentrations of Hcy at 18–20 weeks of gestation had a higher risk of developing IUGR compared with controls (P < 0.001). They concluded that low red blood cell folate levels and high Hcy concentrations in women with the second trimester were associated with subsequent reduced fetal growth. A case–control study by Serrano et al. [46] confirmed that lower concentrations of folate were significantly associated with higher levels of Hcy in pregnant women, increasing the risk of preeclampsia.
However, folate adequacy during pregnancy was associated with a decreased risk of pregnancy-related complications, such as preterm birth, low birth weight, and fetal growth restriction [47]. A birth cohort study in a multiethnic Asian population showed that higher levels of folate in pregnant woman were associated with a lower risk of all preterm birth (OR 0.79, 95% CI 0.63–1.00) and spontaneous preterm birth (OR 0.76, 95% CI 0.56–1.04) [48]. Another birth cohort study also found that maternal higher folate concentrations were associated with a lower risk of preterm birth (aOR 0.74,95% CI 0.56–0.97) [49].
The lower-quartile folate concentrations were associated with preeclampsia, preterm birth, and low birth weight compared with the upper-quartile folate concentrations. The incidence of APO decreased progressively from quartile I to quartile IV of folate concentrations. The univariate logistic regression analysis showed that APO was significantly associated with folate (quartile IV vs I, P < 0.001) and VB12 levels (quartile IV vs I, P = 0.006), folate supplementation (yes vs no, P < 0.001), and VB12 supplementation (yes vs no, P = 0.034). After adjusting for confounding factors, the multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that the folate level (quartile IV vs I) and folate supplementation (yes vs no) were independently associated with APO, while the VB12 level and VB12 supplementation were rejected. These findings suggested that lower serum folate concentrations during early pregnancy were independently associated with subsequent events of APO.
Increasing evidence supports that folate supplementation during pre-pregnancy and early pregnancy can reduce Hcy concentration in the bloodstream of pregnant women, thus decreasing the risk of APO. A prospective cohort study revealed that the supplementation of multivitamins containing folate in pregnant women at 12–20 weeks of gestation increased the serum folate concentration, decreased the serum Hcy level, and reduced the risk of preeclampsia (aOR 0.37; 95% CI 0.18–0.75) [50]. Another prospective cohort study also showed that the incidence of preeclampsia was lower in pregnant women with folate supplementation than in pregnant women with folate non-supplementation [51].
More recently, a large cohort study, including 240,954 pregnant women, demonstrated that folate supplementation before pregnancy was associated with 8% lower risk of preterm birth (RR 0.92, 95% CI 0.85–1.00, P = 0.04) and 19% lower risk of small for gestational age (SGA) birth (RR 0.81, 95% CI 0.70–0.95, P = 0.008) compared with controls [52]. Another large cohort study, including 200,589 singleton live birth mothers, showed that women with folate supplementation had a lower incidence of low birth weight (2.09% vs 2.27%) and SGA (5.73% vs 5.90%) compared with women without folate supplementation. It concluded that maternal daily folate supplementation significantly reduced the risks of infant low birth weight and SGA [53].
In addition, a systematic review and meta-analysis based on the UK regional population database analyzed the significance of folate supplementation in pregnancy. It revealed that the pre-pregnancy commencement of folate supplementation was associated with the reduced risk of SGA < 10th percentile (OR 0.80, 95% CI 0.71–0.90, P < 0.01) and SGA < 5th percentile (OR 0.78, 95% CI 0.66–0.91, P < 0.01). It concluded that supplementation with folate significantly reduced the risk of SGA at birth [54]. Another systematic review and meta-analysis of eight observational studies showed significantly lower odds of preeclampsia in pregnant women with folate supplementation compared with those without folate supplementation (OR 0.78, 95% CI 0.63–0.98) [55].
In a multicenter study by Wen et al. [56], which was a randomized and double–blind study, including 2301 pregnant women with at least one high risk factor for preeclampsia (1144 to the folate group and 1157 to the placebo group), preeclampsia occurred in 169/1144 (14.8%) women in the folate group and 156/1157 (13.5%) in the placebo group. No differences were found between the two groups (RR = 1.10, 95% CI 0.90–1.34, P = 0.37). This study also showed that supplementation with 4.0 mg/day folate beyond the first trimester did not prevent preeclampsia in women at high risk of this condition. It indicated that more evidence is needed to explore the relationship between folate and APO.
The present study had several limitations. First, it did not evaluate the efficacy and safety of the use of high doses of folate supplementation during early pregnancy for APO prevention because it was a retrospective case–control study. In addition, it only measured the concentration of VB12, but not its activity. It is necessary to further determine the activity of VB12 so as to provide a more reliable assessment of VB12 status in early pregnancy. Second, the quantitative parameters were expressed as the quartiles during data analysis in this study, leading to significant bias (versus tertiles, quintiles, etc.). Third, the BMI threshold for overweight and obesity in this study was defined as 24.0–27.9 kg/m2 and ≥ 28 kg/m2, respectively, because the participants were all Chinese, which differed from the usual cutoff of 25–29.9 kg/m2 and 30 kg/m2, respectively, in the general Western population. The prevalence of overweight and obesity, as shown in Table 1, might have slightly changed if the cutoff value appropriate for the Western population was used. However, the result that APO was independently associated with BMI (quartile IV vs I, aOR 1.83, 95% CI 1.30–2.58, P = 0.001) did not change because BMI quartiles without threshold were used in the logistic regression analysis. Furthermore, APO and control groups had a very low percentage of smoking (2.49% vs 1.67%) and excessive drinking (3.73% vs 4.17%), leading to distorted results of the logistic regression analysis due to sampling bias.
Conclusions
This study demonstrated that higher Hcy concentration as a risk factor and lower folate level as a protective factor during early pregnancy were associated with subsequent events of preeclampsia, preterm birth, and low birth weight. The incidence of APO increased progressively from quartile I to IV of Hcy levels, but decreased progressively from quartile I to IV of folate concentrations. Hcy (quartile IV vs I) and folate levels (quartile IV vs I) and folate supplementation (yes vs no) during early pregnancy were independently associated with subsequent events of APO. However, no association was found between VB12 and APO. Supplementation with folate in early pregnancy may reduce APO.
Availability of data and materials
The data sets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- 1hPG:
-
1-h plasma glucose
- 2hPG:
-
2-h plasma glucose
- 95% CI:
-
95% confidence interval
- ADMA:
-
Asymmetric dimethylarginine
- aOR:
-
adjusted odds ratio
- APO:
-
Adverse pregnancy outcome
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- DBP:
-
Diastolic blood pressure
- eNOS:
-
endothelial nitric oxide synthase
- EQA:
-
External Quality Assessment
- FPG:
-
Fasting plasma glucose
- Hcy:
-
Homocysteine
- HDL-C:
-
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- HHcy:
-
Hyperhomocysteinemia
- hs-CRP:
-
high-sensitivity C-reactive protein
- IADPSG:
-
International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- ISSHP:
-
International Society for the Study of Hypertension in Pregnancy
- IUGR:
-
Intrauterine growth restriction
- LDL-C:
-
Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- OGTT:
-
Oral glucose tolerance test
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- SBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- SGA:
-
Small for gestational age
- TC:
-
Total cholesterol
- TG:
-
Triglyceride
- UA:
-
Uric acid
- VB12:
-
Vitamin B12
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
Leijnse JEW, de Heus R, de Jager W, Rodenburg W, Peeters LLH, Franx A, et al. First trimester placental vascularization and angiogenetic factors are associated with adverse pregnancy outcome. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2018;13:87–94.
Lean SC, Derricott H, Jones RL, Heazell AEP. Advanced maternal age and adverse pregnancy outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2017;12(10):e0186287.
Jim B, Karumanchi SA. Preeclampsia: pathogenesis, prevention, and long-term complications. Semin Nephrol. 2017;37(4):386–97.
Blencowe H, Krasevec J, de Onis M, Black RE, An X, Stevens GA, et al. National, regional, and worldwide estimates of low birthweight in 2015, with trends from 2000: a systematic analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2019;7(7):e849–60.
Lee AC, Katz J, Blencowe H, Cousens S, Kozuki N, Vogel JP, et al. National and regional estimates of term and preterm babies born small for gestational age in 138 low-income and middle-income countries in 2010. Lancet Glob Health. 2013;1(1):e26–36.
Beck S, Wojdyla D, Say L, Betran AP, Merialdi M, Requejo JH, et al. The worldwide incidence of preterm birth: a systematic review of maternal mortality and morbidity. Bull World Health Organ. 2010;88(1):31–8.
Pushpakumar S, Kundu S, Sen U. Endothelial dysfunction: the link between homocysteine and hydrogen sulfide. Curr Med Chem. 2014;21(32):3662–72.
Cheng Z, Yang X, Wang H. Hyperhomocysteinemia and endothelial dysfunction. Curr Hypertens Rev. 2009;5(2):158–65.
Demir B, Demir S, Pasa S, Guven S, Atamer Y, Atamer A, et al. The role of homocysteine, asymmetric dimethylarginine and nitric oxide in pre-eclampsia. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2012;32(6):525–8.
Lentz SR. Mechanisms of homocysteine-induced atherothrombosis. J Thromb Haemost. 2005;3(8):1646–54.
Herrmann M, Peter Schmidt J, Umanskaya N, Wagner A, Taban-Shomal O, Widmann T, et al. The role of hyperhomocysteinemia as well as folate, vitamin B (6) and B (12) deficiencies in osteoporosis: a systematic review. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2007;45(12):1621–32.
Beletić A, Mirković D, Dudvarski-Ilić A, Milenković B, Nagorni-Obradović L, Đorđević V, et al. Questionable reliability of Homocysteine as the metabolic marker for Folate and vitamin B12 deficiency in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Med Biochem. 2015;34(4):467–72.
Shidfar F, Homayounfar R, Fereshtehnejad SM, Kalani A. Effect of folate supplementation on serum homocysteine and plasma total antioxidant capacity in hypercholesterolemic adults under lovastatin treatment: a double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial. Arch Med Res. 2009;40(5):380–6.
Kemse NG, Kale AA, Joshi SR. A combined supplementation of omega-3 fatty acids and micronutrients (folic acid, vitamin B12) reduces oxidative stress markers in a rat model of pregnancy induced hypertension. PLoS One. 2014;9(11):e111902.
Tranquilli AL, Dekker G, Magee L, Roberts J, Sibai BM, Steyn W, et al. The classification, diagnosis and management of the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy: a revised statement from the ISSHP. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2014;4(2):97–104.
Joint Committee for Developing Chinese guidelines on Prevention and Treatment of Dyslipidemia in Adults. Chinese guidelines on prevention and treatment of dyslipidemia in adults. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2007;35(5):390–419.
Sibartie P, Quinlivan J. Implementation of the International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups Criteria: Not Always a Cause for Concern. J Pregnancy. 2015;2015:754085.
Lv YB, Yuan JQ, Mao C, Gao X, Yin ZX, Kraus VB, et al. Association of Body Mass Index with Disability in activities of daily living among Chinese adults 80 years of age or older. JAMA Netw Open. 2018;1(5):e181915.
Chen C, Lu FC, Department of Disease Control Ministry of Health, PR China. The guidelines for prevention and control of overweight and obesity in Chinese adults. Biomed Environ Sci. 2004;17:1–36.
Londero AP, Rossetti E, Pittini C, Cagnacci A, Driul L. Maternal age and the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2019;19(1):261.
Maccani JZ, Maccani MA. Altered placental DNA methylation patterns associated with maternal smoking: current perspectives. Adv Genomics Genet. 2015;2015(5):205–14.
Firns S, Cruzat VF, Keane KN, Joesbury KA, Lee AH, Newsholme P, et al. The effect of cigarette smoking, alcohol consumption and fruit and vegetable consumption on IVF outcomes: a review and presentation of original data. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2015;13:134.
Martin KE, Grivell RM, Yelland LN, Dodd JM. The influence of maternal BMI and gestational diabetes on pregnancy outcome. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2015;108(3):508–13.
Lowe WL Jr, Lowe LP, Kuang A, Catalano PM, Nodzenski M, Talbot O, et al. Maternal glucose levels during pregnancy and childhood adiposity in the hyperglycemia and adverse pregnancy outcome follow-up study. Diabetologia. 2019;62(4):598–610.
Leaños-Miranda A, Campos-Galicia I, Ramírez-Valenzuela KL, Berumen-Lechuga MG, Isordia-Salas I, Molina-Pérez CJ. Urinary IgM excretion: a reliable marker for adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with chronic kidney disease. J Nephrol. 2019;32(2):241–51.
Dalal DS, Patel KA, Patel MA. Systemic lupus Erythematosus and pregnancy: a brief review. Obstet Gynaecol India. 2019;69(2):104–9.
Stryuk RI, Burns CA, Filippov MP, Brytkova YV, Borisov IV, Barkova EL, et al. Cardiovascular disease and associated comorbid conditions as determinants of adverse perinatal outcomes in pregnancy - an analysis of the results of the register of pregnant BEREG. Ter Arkh. 2018;90(1):9–16.
Eren E, Ellidag HY, Aydin O, Yılmaz N. Homocysteine, Paraoxonase-1 and vascular endothelial dysfunction: omnibus viis Romam Pervenitur. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014;8(9):CE01–4.
Wang H, Liu J, Wang Q, Zhao H, Shi H, Yu X, et al. Descriptive study of possible link between cardioankle vascular index and homocysteine in vascular-related diseases. BMJ Open. 2013;3(3):e002483.
Klai S, Fekih-Mrissa N, El Housaini S, Kaabechi N, Nsiri B, Rachdi R, et al. Association of MTHFR A1298C polymorphism (but not of MTHFR C677T) with elevated homocysteine levels and placental vasculopathies. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2011;22(5):374–8.
Dymara-Konopka W, Laskowska M. The Role of Nitric Oxide, ADMA, and Homocysteine in The Etiopathogenesis of Preeclampsia-Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(11):E2757.
Ronnenberg AG, Goldman MB, Chen D, Aitken IW, Willett WC, Selhub J, et al. Preconception homocysteine and B vitamin status and birth outcomes in Chinese women. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002;76(6):1385–91.
Bergen NE, Schalekamp-Timmermans S, Jaddoe VW, Hofman A, Lindemans J, Russcher H, et al. Maternal and neonatal markers of the Homocysteine pathway and fetal growth: the generation R study. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2016;30(4):386–96.
Tiwari D, Das CR, Bose PD, Bose S. Associative role of TYMS6bpdel polymorphism and resulting hyperhomocysteinemia in the pathogenesis of preterm delivery and associated complications: a study from Northeast India. Gene. 2017;627:129–36.
Pandey K, Dubay P, Bhagoliwal A, Gupta N, Tyagi G. Hyperhomocysteinemia as a risk factor for IUGR. J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2012;62(4):406–8.
Ezashi T, Das P, Roberts RM. Low O2 tensions and the prevention of differentiation of hES cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(13):4783–8.
Micle O, Muresan M, Antal L, Bodog F, Bodog A. The influence of homocysteine and oxidative stress on pregnancy outcome. J Med Life. 2012;5(1):68–73.
Dutta EH, Behnia F, Boldogh I, Saade GR, Taylor BD, Kacerovský M, et al. Oxidative stress damage-associated molecular signaling pathways differentiate spontaneous preterm birth and preterm premature rupture of the membranes. Mol Hum Reprod. 2016;22(2):143–57.
Lai WK, Kan MY. Homocysteine-induced endothelial dysfunction. Ann Nutr Metab. 2015;67(1):1–12.
Jauniaux E, Poston L, Burton GJ. Placental-related diseases of pregnancy: involvement of oxidative stress and implications in human evolution. Hum Reprod Update. 2006;12(6):747–55.
Jacobsen DW. Hyperhomocysteinemia and oxidative stress: time for a reality check? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000;20(5):1182–4.
Emeksiz HC, Serdaroglu A, Biberoglu G, Gulbahar O, Arhan E, Cansu A, et al. Assessment of atherosclerosis risk due to the homocysteine-asymmetric dimethylarginine-nitric oxide cascade in children taking antiepileptic drugs. Seizure. 2013;22(2):124–7.
Liu C, Yang Y, Peng D, Chen L, Luo J. Hyperhomocysteinemia as a metabolic disorder parameter is independently associated with the severity of coronary heart disease. Saudi Med J. 2015;36(7):839–46.
Shahbazian N, Jafari RM, Haghnia S. The evaluation of serum homocysteine, folic acid, and vitamin B12 in patients complicated with preeclampsia. Electron Physician. 2016;8(10):3057–61.
Furness D, Fenech M, Dekker G, Khong TY, Roberts C, Hague W. Folate, vitamin B12, vitamin B6 and homocysteine: impact on pregnancy outcome. Matern Child Nutr. 2013;9(2):155–66.
Serrano NC, Quintero-Lesmes DC, Becerra-Bayona S, Guio E, Beltran M, Paez MC, et al. Association of pre-eclampsia risk with maternal levels of folate, homocysteine and vitamin B12 in Colombia: a case-control study. PLoS One. 2018;13(12):e0208137.
Tuenter A, Bautista Nino PK, Vitezova A, Pantavos A, Bramer WM, Franco OH, et al. Folate, vitamin B12, and homocysteine in smoking-exposed pregnant women: a systematic review. Matern Child Nutr. 2019;15(1):e12675.
Chen LW, Lim AL, Colega M, Tint MT, Aris IM, Tan CS, et al. Maternal folate status, but not that of vitamins B-12 or B-6, is associated with gestational age and preterm birth risk in a multiethnic Asian population. J Nutr. 2015;145(1):113–20.
Olapeju B, Saifuddin A, Wang G, Ji Y, Hong X, Raghavan R, et al. Maternal postpartum plasma folate status and preterm birth in a high-risk US population. Public Health Nutr. 2019;22(7):1281–91.
Wen SW, Chen XK, Rodger M, White RR, Yang Q, Smith GN, et al. Folic acid supplementation in early second trimester and the risk of preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;198(1):45.e1–7.
Wen SW, Guo Y, Rodger M, White RR, Yang Q, Smith GN, et al. Folic acid supplementation in pregnancy and the risk of pre-Eclampsia-a cohort study. PLoS One. 2016;11(2):e0149818.
Zheng JS, Guan Y, Zhao Y, Zhao W, Tang X, Chen H, et al. Pre-conceptional intake of folic acid supplements is inversely associated with risk of preterm birth and small-for-gestational-age birth: a prospective cohort study. Br J Nutr. 2016;115(3):509–16.
Li N, Li Z, Ye R, Liu J, Ren A. Impact of Periconceptional folic acid supplementation on low birth weight and small-for-gestational-age infants in China: a large prospective cohort study. J Pediatr. 2017;187:105–10.
Hodgetts VA, Morris RK, Francis A, Gardosi J, Ismail KM. Effectiveness of folic acid supplementation in pregnancy on reducing the risk of small-for-gestational age neonates: a population study, systematic review and meta-analysis. BJOG. 2015;122(4):478–90.
Bulloch RE, Lovell AL, Jordan VMB, McCowan LME, Thompson JMD, Wall CR. Maternal folic acid supplementation for the prevention of preeclampsia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2018;32(4):346–57.
Wen SW, White RR, Rybak N, Gaudet LM, Robson S, Hague W, et al. Effect of high dose folic acid supplementation in pregnancy on pre-eclampsia (FACT): double blind, phase III, randomised controlled, international, multicentre trial. BMJ. 2018;362:k3478.
Acknowledgements
The Sichuan Homocysteine Study was conducted by the Chengdu Women’s and Children’s Central Hospital, School of Medicine, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, the Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences and Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, School of Medicine, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, and the Mianyang Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine. We would like to thank all pregnant women for their assistance with obtaining the data used in this study as well as to appreciate the staff in these hospital for their support and guidance. We also thank all funds supporting the experiment and all coauthors devoting their time to the manuscript.
Funding
The clinical case screening and data collection were supported by the Sichuan Provincial Science and Technology Department Research Foundation of China (2013FZ0080). The experiment works and statistical analysis were supported by the Sichuan Provincial Science and Technology Department Research Foundation of China (2013FZ0080) and the Chengdu Science and Technology Bureau Research Foundation of China (2015-HM01–00623-SF), respectively. The professional language editing work and other works were supported by the Chengdu Science and Technology Bureau Research Foundation of China (2015-HM01–00623-SF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CL, DL, YM, TW and PZ carried out the clinical case screening, data collection. QW, LP, JT and DP carried out the sample measurements, information classification and performed the statistical analysis.CL, DL, YM and LP carried out the design of the study and coordination, and drafted the manuscript. All authors read the manuscript critically and gave final approval of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was carried out in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration andwas approved by the Medical Ethics Committee at Chengdu Women’s and Children’s Central Hospital, Chengdu, China [(2013)2, Medical Ethics Committee, CWCCH]. The consent from each participant was waived because the present study is a retrospective case-control study. However, the private information in the study has been well protected.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Luo, D., Wang, Q. et al. Serum homocysteine and folate concentrations in early pregnancy and subsequent events of adverse pregnancy outcome: the Sichuan Homocysteine study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 20, 176 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-020-02860-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-020-02860-9