Abstract
Background
There have been few systematic studies regarding clearance of uric acid (UA) in patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis (PD). This study investigated peritoneal UA removal and its influencing factors in patients undergoing PD.
Methods
This cross-sectional study enrolled patients who underwent peritoneal equilibration test and assessment of Kt/V from April 1, 2018 to August 31, 2019. Demographic data and clinical and laboratory parameters were collected, including UA levels in dialysate, blood, and urine.
Results
In total, 180 prevalent patients undergoing PD (52.8% men) were included. Compared with the normal serum UA (SUA) group, the hyperuricemia group showed significantly lower peritoneal UA clearance (39.1 ± 6.2 vs. 42.0 ± 8.0 L/week/1.73m2; P = 0.008). Furthermore, higher transporters (high or high-average) exhibited greater peritoneal UA clearance, compared with lower transporters (low or low-average) (42.0 ± 7.0 vs. 36.4 ± 5.6 L/week/1.73 m2; P < 0.001). Among widely used solute removal indicators, peritoneal creatinine clearance showed the best performance for prediction of higher peritoneal UA clearance in receiver operating characteristic curve analysis [area under curve (AUC) 0.96; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.93–0.99]. Peritoneal UA clearance was independently associated with continuous SUA [standardized coefficient (β), − 0.32; 95% CI, − 6.42 to − 0.75] and hyperuricemia [odds ratio (OR), 0.86; 95% CI, 0.76–0.98] status, only in patients with lower (≤2.74 mL/min/1.73 m2) measured glomerular filtration rate (mGFR). In those patients with lower mGFR, lower albumin level (β − 0.24; 95%CI − 7.26 to − 0.99), lower body mass index (β − 0.29; 95%CI − 0.98 to − 0.24), higher transporter status (β 0.24; 95%CI 0.72–5.88) and greater dialysis dose (β 0.24; 95%CI 0.26–3.12) were independently associated with continuous peritoneal UA clearance. Furthermore, each 1 kg/m2 decrease in body mass index (OR 0.79; 95% CI 0.63–0.99), each 1 g/dL decrease in albumin level (OR 0.08; 95%CI 0.01–0.47), and each 0.1% increase in average glucose concentration in dialysate (OR 1.56; 95%CI 1.11–2.19) were associated with greater peritoneal UA clearance (> 39.8 L/week/1.73m2).
Conclusions
For patients undergoing PD who exhibited worse residual kidney function, peritoneal clearance dominated in SUA balance. Increasing dialysis dose or average glucose concentration may aid in controlling hyperuricemia in lower transporters.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Uric acid (UA, 2,6,8-trihydroxypurine; C5H4N4O3), as the end-products of endogenous and dietary purine metabolism, is a weak diprotic acid that possesses two dissociable protons with a pKa1 of 5.4 and pKa2 of 10.3, respectively [1]. At a physiology PH of 7.4, 98% of UA exists as monosodium urate in the extracellular milieu [2]. UA is poorly soluble in aqueous media and cannot freely move through the cytomembrane; therefore, it is excreted mainly by means of UA transporters, generally located in the kidney and intestines. Reportedly, approximately 70% of UA is excreted by the kidney, while 30% is excreted by the gastrointestinal tract [3, 4]. Because of the important role of the kidney in excreting UA and maintaining UA balance in the internal environment, nearly 90% hyperuricemia is caused by impairment of renal UA excretion [5]. Similarly, hyperuricemia is common in patients with chronic kidney disease; these patients exhibit fivefold greater prevalence of hyperuricemia than patients with normal renal function [6].
Peritoneal dialysis (PD), a widely used dialysis modality, is becoming increasingly important in renal replacement therapy for patients with end-stage renal disease for its cost-effectiveness and related improvements in techniques and patient survival [7]. The prevalence of hyperuricemia increases with decline in renal function, these prevalences range from 40 to 70% in patients with chronic kidney disease stages 1–5 [8,9,10]. In patients receiving dialysis, the prevalence reportedly increased with increasing dialysis vintage, and are similar in patients undergoing hemodialysis and those undergoing PD [9, 11]. The effect of SUA on prognosis among patients undergoing dialysis is controversial. Most of studies of patients undergoing hemodialysis showed that the lower SUA level was a risk factor for mortality [12,13,14]. However, the higher SUA level was shown to be independently associated with mortality in patients undergoing PD [15,16,17], though some studies revealed no association [13, 18]; notably, one study recently showed an inverse association [19]. These inconsistent results between hemodialysis and PD therapies were reportedly partially related to the kinetics of UA clearance in each dialysis regimen [2]. To the best of our knowledge, there have been relatively few studies regarding UA clearance, especially in patients undergoing PD. In addition to the effects of UA-lowering agents and optimizing dietary and lifestyle factors [20], dialysis therapy itself plays a role in SUA control in patients undergoing PD [21]. However, the relative role of peritoneal UA clearance and residual renal removal in achievement of adequate SUA homeostasis have not been studied. Here, we systematically investigated the contributions of peritoneal UA clearance with respect to residual kidney function and identified its relevant modifiable factors of dialysis prescription in patients undergoing PD.
Methods
Study population
This single-center cross-sectional study enrolled patients who had undergone peritoneal equilibration test (PET) and assessment of Kt/V in our PD center from April 1, 2018 to August 31, 2019. The inclusion criteria included prevalent patients aged ≥18 years who had initiated PD therapy at least 1 month prior to PET and Kt/V tests. Patients were excluded if they had taken UA-lowering agents within 1 month before PET and Kt/V tests, had transferred from long-term hemodialysis (i.e., longer than 3 months), had undergone failed renal transplantation, or exhibited malignant tumors. All enrolled patients used standard lactate-glucose peritoneal dialysate (1.5, 2.5%, or 4.25% dextrose; Baxter, Guangzhou, China). Relevant clinical parameters were tested in the clinical laboratory of the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University using standard methods. All patients provided written informed consent to participate. The study was performed in accordance with the ethical principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University.
Data collection
Demographic data were collected, included age, sex, body mass index (BMI), diabetes status, cardiovascular disease status, and primary kidney disease. Data of the first PET and Kt/V tests during the study period were collected. The PD-related data that were collected included dialysis vintage, dialysis dose, average glucose concentration in dialysate, measured glomerular filtration rate (mGFR), Kt/V, weekly total creatinine clearance (CCL), 24 h residual urine volume, normalized protein catabolic rate and standard PET data. The standard PET data described the urea, creatinine, and UA levels in dialysate, blood, and urine samples with 2 L of 2.5% dextrose dialysate dwelling for 0, 2 or 4 h; 0 h was the time point in the PET test when all of the 2 L dialysate flowed into abdominal cavity, and the duration of this process was recorded. Patients undergoing PD were classified into high, high average, low average, or low transporters, in accordance with Twardowski’s criterion [22]. Clinical parameters included blood pressure, hemoglobin, neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio, high sensitivity C-reactive protein, serum albumin, prealbumin, corrected calcium, phosphorus, total cholesterol, triglyceride, serum urea nitrogen, creatinine, SUA and intact parathyroid hormone. Medication history was also collected, using follow-up records of patients who regularly visited our PD center for assessment and therapeutic regimen adjustment at 1–3-month intervals. Cardiovascular disease was defined as current or prior angina, myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, cerebrovascular events, or peripheral vascular disease [23]. The charlson comorbidity score was used to evaluate the comorbidities of enrolled patients [24]. Men with SUA > 420 μmol/L or women with SUA > 360 μmol/L were regarded as hyperuricemic. The data of mGFR, Kt/V, CCL and normalized protein catabolic rate were obtained using PD Adequest software 2.0 (Baxter, Deerfield, IL, USA). Body surface area (BSA) was calculated using the well-known DuBois & DuBois formula [25]. UA clearance was calculated using the following formulae:
Statistical analysis
Enrolled patients were divided into two groups according to median peritoneal UA clearance. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation for normally distributed continuous variables, medians (interquartile range) for non-normally distributed continuous variables, and frequencies and percentages for categorical variables. Differences between the lower and higher peritoneal UA clearance groups were analyzed using independent samples t-tests for normally distributed continuous variables, the Mann–Whitney U test for non-normally distributed continuous variables, and chi-squared tests for categorical variables. Pearson correlation or Spearman rank correlation test were used to evaluate correlations between variables of normal or skewed distribution, respectively. Multiple linear regression and binary logistic regression were performed to explore the independent influencing factors of continuous and categorical SUA and peritoneal UA clearance in total, lower (≤2.74 mL/min/1.73m2) and higher (> 2.74 mL/min/1.73m2) mGFR group, respectively. Following exclusion of the potential effects of multicollinearity, variables that were significant in univariate analysis (P < 0.05) and those that exhibited clinical correlations were entered into the final model. The performances of small solute removal indicators for prediction of higher peritoneal UA clearance were tested using area under the receiver operating characteristic curve analysis. Two-sided P values < 0.05 were regarded as statistically significant. All statistical analyses were conducted in SPSS Statistics software (version 20.0; IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).
Results
Patient characteristics
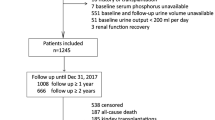
As shown in Fig. 1, 180 patients were included in this study (mean age, 45.0 ± 13.4 years; 52.8% men; 13.3% with diabetes). Primary kidney diseases included chronic glomerulonephritis (67.2%), diabetic nephropathy (8.9%), hypertensive lesions (7.8%), and others (16.1%). The mean SUA level was 410 ± 72 μmol/L; 15.0% of patients used diuretics within 1 month before PET and Kt/V tests performed at enrollment. Patients with higher peritoneal UA clearance were older, had a greater proportion of women, and lower level of BMI, serum albumin, and SUA (Table 1). PD-related data are shown in Table 2. Overall, the patients had a median dialysis vintage of 1.6(1.4–19.8) months and a mean peritoneal UA clearance of 40.2 ± 7.1 L/week/1.73m2. Patients with higher peritoneal UA clearance had longer PD vintage, as well as higher average glucose concentration in dialysate, dialysis dose, total Kt/V, peritoneal Kt/V, and peritoneal CCL; they also had lower residual renal Kt/V, renal CCL, residual urine volume, and mGFR. Notably, there was a larger proportion of high transporters and a smaller proportion of low average transporters.
Relationships between peritoneal UA clearance and peritoneal transport characteristics
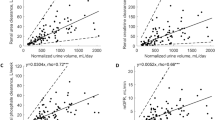
Distributions of peritoneal UA clearance according to peritoneal transport characteristics are shown in Fig. 2a; in particular, there was a progressive increase in peritoneal UA clearance with increasing peritoneal transport rate. Notably, higher transporters (high or high average) exhibited significantly greater peritoneal UA clearance, compared with lower transporters (low average or low) (42.0 ± 7.0 vs. 36.4 ± 5.6 L/week/1.73 m2; P < 0.001). As shown in Fig. 2b, 4h dialysate to plasma (D/P) UA was strongly correlated with 4 h D/P creatinine (r = 0.97; P < 0.001). Moreover, correlations were similar between 4 h D/P UA and peritoneal UA clearance (r = 0.47; P < 0.001) and between 4 h D/P creatinine and peritoneal UA clearance (r = 0.46; P < 0.001) (Fig. 2c and d). Among widely used small solute removal indicators, peritoneal CCL showed the best performance in receiver operating characteristic curve analysis [area under curve (AUC), 0.96; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.93–0.99; P < 0.001] for prediction of higher peritoneal UA clearance (Fig. 3).
The effects of peritoneal transport characteristics on peritoneal UA clearance. a Distribution of peritoneal UA clearance according to peritoneal transport characteristics. b Correlation between the 4 h D/P creatinine and 4 h D/P UA. c Correlation between 4 h D/P UA and peritoneal UA clearance. d Correlation between 4 h D/P creatinine and peritoneal UA clearance. D/P, dialysate to plasm; UA, uric acid
Relationships of peritoneal UA removal with SUA in patients undergoing PD
The distribution of SUA in patients undergoing PD is shown in Fig. 4a. The average mass transfers of urea, creatinine or UA with 2 L of 2.5% dextrose dialysate for dwell times of 0 and 4 h among all patients undergoing PD are described in Fig. 4b. Similar to the mass transfer of the small molecules of urea and creatinine, the peritoneal mass transfer of UA declined remarkably as dwell time increased. Whereas the average UA mass transfer for 4 h dwell time was positively correlated with SUA (r = 0.55; P < 0.001), peritoneal UA clearance was negatively correlated with SUA (r = − 0.25; P = 0.001) (Fig. 4c and d). In comparison with the normal SUA group, the hyperuricemia group showed significantly lower peritoneal UA clearance (39.1 ± 6.2 vs. 42.0 ± 8.0 L/week/1.73 m2; P = 0.008). The further analysis of multiple linear regression and binary logistic regression shown in Table 3 revealed that peritoneal UA clearance was independently associated with continuous SUA (β − 0.32; 95%CI − 6.42 to − 0.75; P = 0.01) and hyperuricemia status (OR 0.86; 95%CI 0.76–0.98; P = 0.02), only in patients undergoing PD who had lower mGFR.
The correlation between peritoneal UA clearance and SUA. a Distribution of SUA in PD patients enrolled. b Average dialytic mass transfer of urea, creatinine and UA with 2 L of 2.5% glucose-based dialysate for dwell times of 0 and 4 h. c Correlation between the 4 h UA mass transfer and SUA. d Correlation between peritoneal UA clearance and SUA. ***P < 0.001, 0 h vs 4 h. SUA, serum uric acid; UA, uric acid
Independent factors influencing peritoneal UA clearance
As shown in Table 4, after adjusting for relevant demographic and PD-related variables in the multiple linear regression model, serum albumin level (β − 0.24; 95%CI − 7.26 to − 0.99; P = 0.01) and BMI (β − 0.29; 95%CI − 0.98 to − 0.24; P = 0.001) were both negatively associated with peritoneal UA clearance, while the higher transporter status (β 0.24; 95%CI 0.72–5.88; P = 0.01) and dialysis dose (β 0.24; 95%CI 0.26–3.12; P = 0.02) were positively associated with peritoneal UA clearance in the lower mGFR group. Similarly, binary logistic regression analysis revealed that each 0.1% increase in average glucose concentration in dialysate (OR 1.56; 95%CI 1.11–2.19; P = 0.01), each 1 g/dL decrease in albumin level (OR 0.08; 95%CI 0.01–0.47; P = 0.006), and each 1 kg/m2 decrease in BMI (OR 0.79; 95%CI 0.63–0.99; P = 0.04) were independently associated with greater peritoneal UA clearance (> 39.8 L/week/1.73m2) (Table 5).
Discussion
The results of this study showed that peritoneal UA removal played a significant role in SUA control. Moreover, lower albumin and BMI, higher peritoneal transporter status, greater dialysis dose, and higher glucose concentration in dialysate were independently associated with greater peritoneal UA clearance in patients undergoing PD who had worse residual kidney function.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first systematic analysis of UA clearance and factors that independently influenced UA clearance in patients undergoing PD. As a small molecular solute, the vast majority of UA is present in the ionized form; ≤5% of circulating UA is bound to albumin [4]. Because UA exhibits high hydrophilicity and has a sieving coefficient of 1.01, which allows it to easily diffuse through the dialysis membrane, it is presumed to be sufficiently cleared by PD therapy [2, 9]. A previous study showed that UA clearance was inversely proportional to the PD dwell time; specifically, the average UA mass transfer for dwell times of 0-1 h, 1-4 h and 4-8 h with 2 L of 1.5% dialysate were 49.8 ± 3.9, 16.1 ± 1.0, 8.3 ± 0.6 mg/h/1.73m2, respectively [26]. Similarly, we found remarkable reductions of UA mass transfer of 72.9 ± 41.1 and 23.9 ± 5.6 mg/h/1.73 m2 in PD with 2 L 2.5% dialysate for dwell times of 0 h and 4 h. In addition, we revealed an average peritoneal UA clearance of 40.2 ± 7.1 L/week/1.73m2 in patients undergoing PD.
In the present study, peritoneal UA clearance was significantly greater in higher transporters than in lower transporters, when measured in terms of 4 h D/P creatinine; moreover, 4 h D/P UA was strongly correlated with 4 h D/P creatinine. Further analysis revealed similar correlations between 4 h D/P UA and peritoneal UA clearance, as well as between 4 h D/P creatinine and peritoneal UA clearance. Moreover, receiver operating characteristic curve analysis revealed that, among widely used solute removal indicators, peritoneal CCL showed the best performance for prediction of higher peritoneal UA clearance. These results illustrated that membrane characteristics, assessed in terms of creatinine transport, can be used to determine UA transport status. This similarity is presumably because the molecular weight of UA (168 Da) is near that of creatinine (113 Da); in addition, few circulating UA molecules are bound to albumin or affected by electrochemical gradient, whereas serum phosphorus molecules are affected in this manner [27]. The present study revealed that evaluation of peritoneal UA clearance solely in terms of the most frequently used indicator for peritoneal adequacy (i.e., Kt/V) may not exhibit sufficient accuracy. Peritoneal CCL may be a more reliable index for assessing UA clearance adequacy. Adjustment of dialysis prescription for better PD-related UA removal, based on peritoneal CCL rather than the widely used Kt/V, is presumably more appropriate, particularly for lower transporters with hyperuricemia.
A negative correlation was observed between peritoneal UA clearance and SUA in the present study; further multiple linear and logistic regression analyses suggested that greater peritoneal UA clearance was significantly associated with lower SUA only in patients undergoing PD who had relatively low mGFR. This suggests that the kidney still plays an indispensable role in removing excessive SUA in patients with residual kidney function; and the importance of peritoneal UA clearance gradually became evident with the decline of residual kidney removal. Therefore, the high SUA in patients undergoing PD who had unsatisfying renal function may have been partially caused by inadequate UA removal during PD. In the present study, we found that lower BMI and albumin level, higher transporter status, greater dialysis dose, and higher glucose concentration in dialysate were significantly associated with greater peritoneal UA clearance in the lower mGFR group. BMI is a body composition parameter, which was strongly correlated with BSA in this study (data not shown); accordingly, patients undergoing PD who had lower BMI may exhibit greater peritoneal UA removal, after adjustment for their relatively lower BSA. In addition, the serum albumin level was revealed to be associated with both continuous peritoneal UA clearance and higher peritoneal UA clearance category in patients with worse renal function. Previous studies have shown negative correlations between peritoneal albumin loss and serum albumin level in patients undergoing PD [26, 28]. Furthermore, peritoneal albumin loss was demonstrated to be positively associated with peritoneal CCL in a cross-sectional study including 351 patients undergoing PD [29]. Therefore, a potential mechanism underlying the negative association between peritoneal UA clearance and serum albumin level is as follows: greater peritoneal UA clearance itself indicates greater removal of albumin from peritoneum, which causes lower circulating albumin reserves, primarily because of inadequate albumin synthesis to compensate peritoneal albumin loss [26]. Therefore, peritoneal albumin loss should be considered when optimizing dialysis prescription for efficient solute removal. However, it remains unclear whether there is a causal relationship between lower albumin level and greater peritoneal UA clearance.
Notably, few studies have explored PD-related factors associated with greater peritoneal UA clearance, particularly in terms of residual kidney function; average UA clearance in PD was revealed to be positively proportional to the exchange volume and flow rate [21]. In the present study, patients who were higher transporters exhibited greater peritoneal UA removal, compared with patients who were lower transporters. With the exception of non-modifiable peritoneal membrane characteristics, the modifiable dialysis dose factors significantly increase the PD-related UA removal as well. In patients with worse residual kidney function, average glucose concentration in dialysate tended to be associated with greater peritoneal UA removal, although this was not statistically significant (β 0.19; 95%CI − 0.004 to 0.88; P = 0.052); however, the effect was shown to be statistically significant in logistic regression (OR1.56; 95%CI 1.11–2.19; P = 0.01). Therefore, the positive effect of the glucose concentration in dialysate may have been masked by the relatively small sample size after grouping based on residual kidney function.
There were some limitations in our study. First, the cross-sectional observational study itself only assessed associations rather than causal relationships. Second, this study did not explore the effects of different PD modalities (e.g., continuous cyclic peritoneal dialysis, automated peritoneal dialysis) or different exchange flow rate on peritoneal UA clearance. Third, the dialysis vintages of enrolled patients were relatively short, which may have led to bias involving inadequate and unstable dialysis. Fourth, this study used a small sample size of patients without residual kidney function; therefore, classification of residual kidney function was grouped on the basis of median mGFR, rather than the clinical standards of oliguria or anuria. Despite the above limitations, to the best of our knowledge, this was the first study to systematically explore the contributions of peritoneal UA clearance and residual kidney removal, and to identify independent factors that influence peritoneal UA clearance. In this study, we concurrently collected common small solute removal indicators for further comparison and analysis, which provides important guidance in optimizing prescription for achievement of better SUA control in patients undergoing PD, especially those with worse residual kidney function. Moreover, we excluded patients undergoing PD who had a history of taking UA-lowering agents, which enabled us to more specifically study UA clearance in PD regimen.
Conclusions
In summary, UA removal in patients undergoing PD was found to be more rely on peritoneal clearance, especially in patients with relatively worse residual kidney function. Peritoneal CCL may be an optimal indicator for assessment of UA removal during PD because of its similar removal characteristics through the dialysis membrane. For patients with unsatisfactory residual kidney function, increasing the dialysis dose or average glucose concentration in dialysate may aid in controlling hyperuricemia, particularly in patients who are lower transporters.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- BSA:
-
Body surface area
- CCL:
-
Creatinine clearance
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- D/P:
-
Dialysate to plasm
- mGFR:
-
measured glomerular filtration rate
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- PD:
-
Peritoneal dialysis
- PET:
-
Peritoneal equilibration test
- SUA:
-
Serum uric acid
- UA:
-
Uric acid
References
Ndrepepa G. Uric acid and cardiovascular disease. Clin Chim Acta. 2018;484:150–63.
Murea M, Tucker BM. The physiology of uric acid and the impact of end-stage kidney disease and dialysis. Semin Dial. 2019;32(1):47–57.
Dalbeth N, Merriman TR, Stamp LK. Gout. Lancet. 2016;388(10055):2039–52.
Richette P, Bardin T. Gout. Lancet. 2010;375(9711):318–28.
Terkeltaub R, Bushinsky DA, Becker MA. Recent developments in our understanding of the renal basis of hyperuricemia and the development of novel antihyperuricemic therapeutics. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8(Suppl 1):S4.
Krishnan E. Reduced glomerular function and prevalence of gout: NHANES 2009–10. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e50046.
Li PK, Chow KM, Van de Luijtgaarden MW, Johnson DW, Jager KJ, Mehrotra R, et al. Changes in the worldwide epidemiology of peritoneal dialysis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017;13(2):90–103.
Dousdampanis P, Trigka K, Musso CG, Fourtounas C. Hyperuricemia and chronic kidney disease: an enigma yet to be solved. Ren Fail. 2014;36(9):1351–9.
Murea M. Advanced kidney failure and hyperuricemia. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2012;19(6):419–24.
Chonchol M, Shlipak MG, Katz R, Sarnak MJ, Newman AB, Siscovick DS, et al. Relationship of uric acid with progression of kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007;50(2):239–47.
Silverstein DM, Srivaths PR, Mattison P, Upadhyay K, Midgley L, Moudgil A, et al. Serum uric acid is associated with high blood pressure in pediatric hemodialysis patients. Pediatr Nephrol. 2011;26(7):1123–8.
Park C, Obi Y, Streja E, Rhee CM, Catabay CJ, Vaziri ND, et al. Serum uric acid, protein intake and mortality in hemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2017;32(10):1750–7.
Bae E, Cho HJ, Shin N, Kim SM, Yang SH, Kim DK, et al. Lower serum uric acid level predicts mortality in dialysis patients. Medicine. 2016;95(24):e3701.
Latif W, Karaboyas A, Tong L, Winchester JF, Arrington CJ, Pisoni RL, et al. Uric acid levels and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in the hemodialysis population. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;6(10):2470–7.
Feng S, Jiang L, Shi Y, Shen H, Shi X, Jin D, et al. Uric acid levels and all-cause mortality in peritoneal dialysis patients. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2013;37(2–3):181–9.
Xia X, Zhao C, Peng FF, Luo QM, Zhou Q, Lin ZC, et al. Serum uric acid predicts cardiovascular mortality in male peritoneal dialysis patients with diabetes. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2016;26(1):20–6.
Xia X, He F, Wu X, Peng F, Huang F, Yu X. Relationship between serum uric acid and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients treated with peritoneal dialysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014;64(2):257–64.
Dong J, Han QF, Zhu TY, Ren YP, Chen JH, Zhao HP, et al. The associations of uric acid, cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in peritoneal dialysis patients. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e82342.
Lai KJ, Kor CT, Hsieh YP. An Inverse Relationship between Hyperuricemia and Mortality in Patients Undergoing Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis. J Clin Med. 2018;7(11):E416.
Vargas-Santos AB, Neogi T. Management of Gout and Hyperuricemia in CKD. Am J Kidney Dis. 2017;70(3):422–39.
Robson M, Oreopoulos DG, Izatt S, Ogilvie R, Rapoport A, de Veber GA. Influence of exchange volume and dialysate flow rate on solute clearance in peritoneal dialysis. Kidney Int. 1978;14(5):486–90.
Twardowski ZJ, Nolph KO, Khanna R, Prowant BF, Ryan LP, Moore HL, et al. Peritoneal equilibration test. Perit Dial Int. 1987;7:138–48.
Huang R, Liu Y, Wu H, Guo Q, Yi C, Lin J, et al. Lower plasma visceral protein concentrations are independently associated with higher mortality in patients on peritoneal dialysis. Br J Nutr. 2015;113(4):627–33.
Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis. 1987;40(5):373–83.
Du Bois D, Du Bois EF. A formula to estimate the approximate surface area if height and weight be known. 1916. Nutrition. 1989;5(5):303–11.
Kagan A, Bar-Khayim Y, Schafer Z, Fainaru M. Kinetics of peritoneal protein loss during CAPD: I. different characteristics for low and high molecular weight proteins. Kidney Int. 1990;37(3):971–9.
Graff J, Fugleberg S, Brahm J, Fogh-Andersen N. The transport of phosphate between the plasma and dialysate compartments in peritoneal dialysis is influenced by an electric potential difference. Clin Physiol. 1996;16(3):291–300.
Kaysen GA, Schoenfeld PY. Albumin homeostasis in patients undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Kidney Int. 1984;25(1):107–14.
Fan J, Ye H, Zhang X, Cao P, Guo Q, Mao H, et al. Association of Lean Body Mass Index and Peritoneal Protein Clearance in peritoneal Dialysis patients. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2019;44(1):94–102.
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to the doctors and nurses in our PD centers for their earnest work of clinical evaluation and data collecting. We thank Ryan Chastain-Gross, Ph.D., from Liwen Bianji, Edanz Group China (www.liwenbianji.cn/ac), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 81774069, 81570614), National Key Research and Development Program (Grant no. 2016YFC0906101), Program of the Ministry of Health of China (201502023), the Guangdong Science Foundation of China (Grant 2017A050503003, 2017B020227006), Foundation of Guangdong Key Laboratory of Nephrology (Grant no. 2017B030314019), and the Guangzhou Committee of Science and Technology, China (201704020167). These funding supported the data collection, management, and analysis, as well as the charges of manuscript editing and processing for paper publishing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XY1 and XY2 designed the research, HY and XX conducted the research, CY, JL and YP collected data, XH, MW and HW analyzed the data, HM and XY1 interpreted the findings, XX and XY2 wrote the paper, XY2 had the primary responsibility for the whole content and final approval of the version to be published. And all authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study has conformed to the ethical principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University. And all patients had signed informed consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, X., Ye, H., Yi, C. et al. Roles of peritoneal clearance and residual kidney removal in control of uric acid in patients on peritoneal dialysis. BMC Nephrol 21, 148 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-020-01800-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-020-01800-1