Abstract
Background
Inherited palmoplantar keratodermas (PPKs) are clinically and genetically heterogeneous and phenotypically diverse group of genodermatoses characterized by hyperkeratosis of the palms and soles. More than 20 genes have been reported to be associated with PPKs including desmoglein 1 (DSG1) a key molecular component for epidermal adhesion and differentiation. Mal de Meleda (MDM) is a rare inherited autosomal recessive genodermatosis characterized by transgrediens PPK, associated with mutations in the secreted LY6/PLAUR domain containing 1 (SLURP1) gene.
Methods
This study describes clinical as well as genetic whole exome sequencing (WES) and di-deoxy sequencing investigations in two Pakistani families with a total of 12 individuals affected by PPK.
Results
WES identified a novel homozygous nonsense variant in SLURP1, and a novel heterozygous nonsense variant in DSG1, as likely causes of the conditions in each family.
Conclusions
This study expands knowledge regarding the molecular basis of PPK, providing important information to aid clinical management in families with PPK from Pakistan.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Palmoplantar keratoderma (PPK) is a heterogeneous entity of both genetics and acquired keratinization disorder, which is characterized by persistent marked epidermal thickening of palms and soles [1]. Hereditary PPKs comprising an increasing number of entities with different prognoses, which may be associate with cutaneous and extracutaneous manifestations [2].
Depending on different patterns of hyperkeratosis, PPKs are further classified into four distinct types: diffuse, striate, focal and punctate [3, 4]. So far, deleterious mutations in > 20 genes have been reported in pathogenesis of different forms of hereditary PPKs [3, 4]. In last few years, advent of cutting edge genetic techniques such as whole genome microarray scans and whole exome sequencing have incredibly accelerated the identification of disease causing variants in many genes involved in various inherited forms of PPKs, and thus significantly increasing understanding about intricate molecular mechanisms of heterogeneous disorders, consecutively aiding valuable genetic counselling and patient care [3].
Mal de Meleda (MDM), a type of transgradient palmoplantar keratoderma (PPK), is a rare autosomal recessive disorder. Luca Stulli, a Croatian born scientist in 1826 first described Mal de Meleda on the Adriatic Meleda island (now Mljet) [5]. The disease can feature other potentially disfiguring effects on the hands and feet that can severely impact function.
The disease onset is soon after birth and is clinically characterized by erythema, transgradients and progradients hyperkeratosis of palms and soles with well demarcated borders and hypohydrosis. Other associated features are brachydactyly, nail abnormalities and lichenoid plaques [6]. Rigorous keratoderma can lead to deformity in hands and feet and gradually this may results into severe impairment [7, 8].
Furthermore, previous reports have shown that MDM may be caused due to mutations in the SLURP1 gene (previously known as ARS-B gene) encoding a secreted toxin-like mammalian lymphocyte antigen 6/urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor-related protein 1(SLURP1). Expression of SLURP1 is reported in epithelium, stomach, sensory nerve cells, gums, esophagus and immune cells with highest level in keratinocytes especially in palms and soles [9,10,11].
Striate PPK type I is a rare type of PPK and shows the autosomal dominant mode of inheritance associated with DGS1 heterozygous mutation. Clinical features of this condition are linear hyperkeratotic lesions on the palms extending along the length of fingers and associated with thick patches of diffuse hyperkeratosis on the soles [12].
Heterozygous mutation in DSG1 gene in an autosomal dominant pattern have also been reported in focal PPK in a Libyan family, and in a Jewish Yemenite family with diffuse PPK [13, 14], a discovery which elucidates that different patterns of palmoplantar involvement may result from mutations in the DSG1 gene. Additionally, bi-allelic mutations in DSG1 gene have also been recently reported in the severe SAM syndrome, characterized by sinusitis, palmoplantar keratoderma, erythroderma, multiple allergies and metabolic defects, with heterozygous mutation carriers only presenting hyperkeratotic palmoplantar lesions [15].
Here we report findings regarding investigations of two families from Pakistan with clinically-defined PPK, for which the specific genetic basis was unclear.
Methods
Genetic studies
The research work presented in this manuscript was approved by the Ethical Review Boards Committee at International Islamic University, Islamabad, Pakistan (IIUI; Pakistan). Informed written consent was obtained for all participants for the collection of blood samples, with clinical evaluations and family histories performed by a dermatologist. Extraction of high quality genomic DNA from the whole blood was carried out by using the ReliaPrep™ kit (Blood gDNA Miniprep System, Promega) following the manufacturer’s protocol. Whole exome sequencing (WES) was undertaken on a NextSeq500 (Illumina, CA, San Diego, USA) with targeting using Agilent Sure select Whole Exome v6. The reads were aligned using BWA-MEM (v0.7.12), with mate-pairs fixed and duplicates removed using Picard (v1.129). InDel realignment and base quality recalibration were performed using GATK (v3.4–46). SNVs and InDels were detected using GATK Haplotype Caller or SnpEff tool (http://snpeff.sourceforge.net/SnpEff_manual.html), and annotated using Alamut batch (v1.4.4). Read depth was determined for the whole exome using GATK Depth of Coverage.
Primer3 web software was used to design the allele-specific primers (primer sequences are available upon request) to validate and verify the segregation of identified variants via Sanger sequencing. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was performed for all affected and healthy individuals of recruited families by using allele-specific primers following standard conditions, with products sequenced by Source Bio-Science Life Sciences (https://www.sourcebioscience.com/).
Results
Subjects
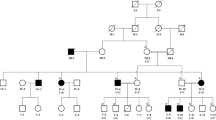
Pedigree analysis was indicative of an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern of family 1, and an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance of family 2 (Fig. 1). All 12 living affected individuals with PPK as well as 6 unaffected (healthy) individuals including parents and siblings from both families (Family 1 and 2) were investigated. The seven affected individuals from family 1:IV:7, IV:8, IV:12, V:2, V:4, V:8 and V:9 were 27, 22, 45, 16, 11, 15 and 13 years of age respectively at the time of examination, while the five affected individuals from family 2: III:2, III:5, III:6, IV:1 and IV:2 were 28, 36, 40, 12 and 8 years of age respectively. On the basis of basic clinical dermatological examination, PPK was the main finding exhibit in all patients (affected members) of the recruited families.
SLURP1 Chr8(GRCh37):g.143823760C > T; c.44C > T; p.Trp15 (Family 1). DSG1 Chr18(GRCh37):g.28906885C > T; c.133C > T; p.Arg45* (Family 2). a, e Simplified pedigrees of the extended Pakistani families investigated with genotypes of affected and unaffected ndividuals. b Electropherograms showing the DNA sequence at the position of SLURP1 c.44 C > T in a heterozygous healthy carrier and homozygous affected individual. c-d Palmoplantar keratoderma in an individual homozygous for SLURP1 c.44 C > T. f Electropherograms showing the DNA sequence at the position of DSG1 c.133C > T in a wild type control and heterozygous affected individual. g-h Palmoplantar Keratoderma in an individual heterozygous for DSG1 c.133C > T
Disease onset was from 3 months to 1 year. Affected individuals of family 1 show cuff-like pattern with well demarcated margins and waxy yellow tone on hands and feet. Diffuse hyperkeratosis of hand and feet was common in patients. Fingers were tapered towards the tips and flexion deformity due to contractures was observed in 2 (IV:7 and IV:8) patients. Knuckle pads were observed in interphalangeal joints and hyperhidrosis was also common in all patients. Patients in family 2 showed diffuse hyperkeratosis with cracks and fissuring of the volar surface of the digits of hands and soles, toes were observed in two siblings. All other patients have mild hyperkeratosis. Mild to severe deafness was observed in patients and one patient (III:5) was deaf as well as mute. Both families’ phenotypes are summarized in Table 1 and Fig. 1.
All patients of family 1 and 2 were intellectually normal and hair, nail, teeth and cardiac anomalies were not observed in any of the patient. Disease conditions worsened due to aging.
Genetic findings
To identify the causative gene mutation, single affected individual from each of the family was initially selected to perform WES (subject IV:12 of family 1 and III:2 of family 2, Fig. 1) to generate a profile of rare and novel sequence variants, with regard to mode of inheritance in each of the families. After that, exome data was first reviewed to identify pathogenic variants in disease associated genes, filtering for highly likely deleterious (nonsense, frame-shift, non-synonymous exonic or splice-site) variants for comparison with allele frequencies in online genome databases (including the Exome Aggregation Consortium; ExAC, the 1000 Genomes Project and the Genome Aggregation Database; gnomAD). This identified a single candidate novel homozygous nonsense variant [NM_020427.2:c.44G > A; Chr8:143823760C > T (GRCh37)] in the first coding exon of SLURP1 gene (Fig. 1) in family 1. This variant leads to substitution of tryptophan by a premature termination codon and is at the evolutionary conserved position 15 (p.Trp15*). In family 2, a heterozygous variant [NM_001942.3:c.133C > T; Chr18:28906885C > T (GRCh37)] was identified in coding exon 3 of the DSG1 gene (Fig. 1), which is predicted to result in a premature stop codon (p.Arg45*). The SLURP1 gene variant in family 1 is not listed in online genome databases and segregates as predicted for an autosomal recessive form in family 1. The DSG1 gene variant identified of family 2 is listed in the gnomAD browser database in 1 Latino individual in heterozygous form out of 31,370 genomes, corresponding to a minor allele frequency of 0.00003188; both variants are summarized in Additional file 1: Tables S1 and S2 alongside all other reported disease-associated SLURP1 and DSG1 variants.
Discussion
SLURP1 has been localized to the granular layer of epidermis [16], where it functions as part of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors found on keratinocyte cells as a pro-apoptotic protein [17]. Arredondo et al. [17] demonstrated that keratinocytes are stimulated by SLURP1 through nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, leading to decline in keratinocytes cell number, indicative of the inhibitory and regulatory nature of SLURP1. Therefore, when SLURP1 is non-functional, as seen in Mal de Meleda, severe hyperkeratosis results due to improper keratinocyte apoptosis regulation [8, 18].
We identified nonsense variant in family 1 which causes substitution of evolutionarily conserved tryptophan at 15th amino acid position in SLURP1 by a premature termination codon. Nonsense variant (c.129C > A; p.Cys43*) is also reported in exon 2 of SLURP1 gene in a Turkish family. Similarly another nonsense mutation (c.286C > T; p.Arg96*) is also found in exon 3 in Croatian family and is predicted to truncate protein synthesis via nonsense-mediated mRNA decay [19, 20]. Family reported in this study have same clinical features to previously reported Mal de Meleda families.
The SLURP1 gene mutation p.Gly86Arg is most often found in sporadic patients with MDM of Asian origin [21, 22].
So far 20 mutations in SLURP1 are reported to cause Mal de Meleda, a form of PPK (Additional file 1: Table S1,). c.44G > A; p.Trp15Term is the second variant identified in Pakistan apart from c.2 T > C, p.Met1Thr variant which was recently reported [23].
“Desmoglein” comprises of the two Greek words “desmos” for “tie” and “glein” for “glue-like.” Perturbations of desmoglein expression in the epidermis have been known to impact cell adhesion properties. DSG1 is distinctively located, just above the stratum germinativum, to be candidate of epidermis stratification and differentiation [24]. A study in which DSG1 was down regulated in skin culture confirmed the importance of DSG1 for directing those functions [25].
In all reported PPKs cases where DSG1 gene variants (frameshift or nonsense) have been reported, there is evidence that affected protein haploinsufficiency leads to the striate, focal PPK and striate PPK with wooly hair and cardiomyopathy. Haploinsufficiency is predicted to cause through nonsense mediated mRNA decay because of premature termination codons [26, 27]. Interestingly, a heterozygous DSG1 mutation has also been reported in focal PPK [13].
To date, 31 mutations (8 nonsense mutations, 14 frame-shift variants and 9 splice-site variants) in DSG1 have been reported to cause striate/focal PPK (Additional file 1: Table S2). In 2009, Dua-Awereh et al. reported five heterozygous variants (p.Arg26*; c.373-2A > G; c.515C > T; c.1266-3C > G and c.1399delA) in DSG1 gene in five families with autosomal dominant striate PPK [28]. Thus, c.133C > T; p.Arg45* variant identified in this study is the sixth mutation underlying dominantly inherited form of striate PPK in Pakistan.
MDM presented a consistently severe phenotype than Nagashima form of PPK. MDM shows progressive hyperkeratosis among all PPKs and causes flexion contracture and constricting band [29]. While, Nagashima PPK is characterized by non-progressive and mild hyperkeratosis and does not show flexion contracture and constricting band [30, 31]. Nagashima PPK is caused by biallelic loss of function mutation in SERPINB7 while, MDM is caused by SLURP1 gene mutation [20]. Therefore, MDM is genetically distinct from Nagashima PPK [32]. PPKs are diagnosed on the basis of differential diagnosis to find out the disease entity. Differential diagnosis of PPK is summarized in Table 2.
Conclusion
The identification of a novel homozygous nonsense variant in SLURP1, and a novel heterozygous nonsense variant in DSG1, as likely causes of PPK in the Pakistani families investigated alongside a review of previously reported variants adds to knowledge of the molecular causes of these conditions. Additionally, the data here provides important information regarding the nature, spectrum and molecular basis of PPK in Pakistan, enabling early clinical intervention, increased awareness regarding inherited disorders present in a community, and aiding diagnosis and counselling.
Availability of data and materials
The patient’s non-sensitive datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- ARS-B:
-
Arylsulfatase B
- DSG1 :
-
Desmoglein 1
- HGMD:
-
Human gene mutation data base
- MDM:
-
Mal de Meleda
- OMIM:
-
Online Mendelian inheritance in man
- PPK:
-
Palmoplantar Keratoderma
- SAM:
-
Sinobronchial allergic mycosis
- SERPIN7 :
-
Serpin Peptidase Inhibitor, Clade B (Ovalbumin), Member 7
- SLURP1 :
-
Secreted ly6/plaur domain-containing 1 gene
- WES:
-
Whole Exome Sequencing
References
Patel S, Zirwas M, English JC. Acquired palmoplantar keratoderma. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2007;8(1):1–1.
Has C, Technau-Hafsi K. Palmoplantar keratodermas, clinical and genetic aspects. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2016;149(2):3–142.
Guerra L, Castori M, Didona B, Castiglia D, Zambruno G. Hereditary palmoplantar keratodermas. Part I. non-syndromic palmoplantar keratodermas: classification, clinical and genetic features. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32(5):704–19.
Sakiyama T, Kubo A. Hereditary palmoplantar keratoderma “clinical and genetic differential diagnosis”. J Dermatol. 2016;43(3):264–74.
Fatović-Ferencić S, Holubar K. The portrait and paper of a forgotten hero--Luca Stulli (1772-1828) and the mal de Meleda of yesteryear: a 175-year anniversary. J Invest Dermatol. 2001;116(1):198.
Bergqvist C, Kadara H, Hamie L, Nemer G, Safi R, Karouni M, Marrouche N, Abbas O, Hasbani DJ, Kibbi AG, Nassar D. SLURP-1 is mutated in mal de Meleda, a potential molecular signature for melanoma and a putative squamous lineage tumor suppressor gene. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57(2):162–70.
Itin PH, Fistarol SK. Palmoplantar keratodermas. Clin Dermatol. 2005;23(1):15–22.
Perez C, Khachemoune A. Mal de Meleda: a focused review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2016;17(1):63–70.
Fischer J, Bouadjar B, Heilig R, Huber M, Lefèvre C, Jobard F, Macari F, Bakija-Konsuo A, Ait-Belkacem F, Weissenbach J, Lathrop M. Mutations in the gene encoding SLURP-1 in mal de Meleda. Hum Mol Genet. 2001;10(8):875–80.
Tjiu JW, Lin PJ, Wu WH, Cheng YP, Chiu HC, Thong HY, Chiang BL, Yang WS, Jee SH. SLURP1 mutation-impaired T-cell activation in a family with mal de Meleda. Br J Dermatol. 2011;164(1):47–53.
Lyukmanova EN, Shulepko MA, Kudryavtsev D, Bychkov ML, Kulbatskii DS, Kasheverov IE, Astapova MV, Feofanov AV, Thomsen MS, Mikkelsen JD, Shenkarev ZO. Human secreted Ly-6/uPAR related protein-1 (SLURP-1) is a selective allosteric antagonist of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. PLoS One. 2016;11(2):0149733.
Rickman L, Šimrak D, Stevens HP, Hunt DM, King IA, Bryant SP, Eady RA, Leigh IM, Arnemann J, Magee AI, Kelsell DP. N-terminal deletion in a desmosomal cadherin causes the autosomal dominant skin disease striate palmoplantar keratoderma. Hum Mol Genet. 1999;8(6):971–6.
Milingou M, Wood P, Masouye I, McLean WH, Borradori L. Focal palmoplantar keratoderma caused by an autosomal dominant inherited mutation in the desmoglein 1 gene. Dermatol. 2006;212(2):117–22.
Keren H, Bergman R, Mizrachi M, Kashi Y, Sprecher E. Diffuse nonepidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma caused by a recurrent nonsense mutation in DSG1. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141(5):625–8.
Samuelov L, Sarig O, Harmon RM, Rapaport D, Ishida-Yamamoto A, Isakov O, Koetsier JL, Gat A, Goldberg I, Bergman R, Spiegel R. Desmoglein 1 deficiency results in severe dermatitis, multiple allergies and metabolic wasting. Nat Genet. 2013;45(10):1244.
Favre B, Plantard L, Aeschbach L, Brakch N, Christen-Zaech S, de Viragh PA, Sergeant A, Huber M, Hohl D. SLURP1 is a late marker of epidermal differentiation and is absent in mal de Meleda. J Invest Dermatol. 2007;127(2):301–8.
Arredondo J, Chernyavsky AI, Webber RJ, Grando SA. Biological effects of SLURP-1 on human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;125(6):1236–41.
Grando SA, Pittelkow MR, Schallreuter KU. Adrenergic and cholinergic control in the biology of epidermis: physiological and clinical significance. J Invest Dermatol. 2006;126(9):1948–65.
Muslumanoglu MH, Saracoglu N, Cilingir O, et al. A novel mutation in the ARS (component B) gene encoding SLURP-1 in a Turkish family with mal de Meleda. Br J Dermatol. 2006;155(2):467–9.
Fischer J, Bouadjar B, Heilig R, Huber M, Lefèvre C, Jobard F, Macari F, Bakija-Konsuo A, Ait-Belkacem F, Weissenbach J, Lathrop M. Mutations in the gene encoding SLURP-1 in mal de Meleda. Hum Mol Gene. 2001;10(8):875–80.
Taylor JA, Bondavalli D, Monif M, Yap LM, Winship I. Mal de Meleda in Indonesia: mutations in the SLURP1 gene appear to be ubiquitous. Australas J Dermatol. 2014;57(1):11–3.
Zhang J, Cheng R, Ni C, Liang J, Yao Z. First mal de Meleda report in Chinese mainland: two families with a recurrent homozygous missense mutation in SLURP-1. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;30(5):871–3.
Shah K, Nasir A, Shahzad S, Khan S, Ahmad W. A novel homozygous mutation disrupting the initiation codon in the SLURP1 gene underlies mal de Meleda in a consanguineous family. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2016;41(6):675–9.
Hammers CM, Stanley JR. Desmoglein-1, differentiation, and disease. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(4):1419–22.
Getsios S, Simpson CL, Kojima SI, Harmon R, Sheu LJ, Dusek RL, Cornwell M, Green KJ. Desmoglein 1–dependent suppression of EGFR signaling promotes epidermal differentiation and morphogenesis. J Cell Biol. 2009;185(7):1243–58.
Lovgren ML, McAleer MA, Irvine AD, Wilson NJ, Tavadia S, Schwartz ME, Cole C, Sandilands A, Smith FJD, Zamiri M. Mutations in desmoglein1 cause diverse inherited palmoplantar keratoderma phenotypes:implications for genetic screening. Br J Dermatol. 2017;176(5):1345–50.
Vodo D, O’Toole EA, Malchin N, Lahav A, Adir N, Saring O, Green KJ, FJD, Sprecher E. Striate palmoplantar kerato-derma resulting from a missense mutation in DSG1. Br J Dermatol 2018;179(3):755–757.
Hovorka O. E. Ehlers Mal de Meleda. Arch Dermatol Res. 1897;40:251–6.
Mitsuhashi Y, Hashimato I. Keratosis palmoplantaris Nagashima. Dermatol. 1989;179:231.
Kabashima K, Sakabe JI, Yamada Y, Tokura Y. “Nagashima-type” keratosis as a novel entity in the palmoplantar keratoderma category. Arch Dermatol 2008;144(3):375–379.
Kubo A, Shiohama A, Sasaki T, Nakabayashi K, Kawasaki H, Atsugi T, Sato S, Shimizu A, Mikami S, Tanizaki H, Uchiyama M. Mutations in SERPINB7, encoding a member of the serine protease inhibitor superfamily, cause Nagashima-type palmoplantar keratosis. Am J Hum Genet. 2013;93(5):945–56.
Dua-Awereh MB, Shimomura Y, Kraemer L, Wajid M, Christiano AM. Mutations in the desmoglein 1 gene in five Pakistani families with striate palmoplantar keratoderma. J Dermatol Sci. 2009;53(3):192–7.
Acknowledgements
First and foremost, the authors would like to thank the affected individuals and their families for participation in this study. We also thank all of the clinicians and geneticists with whom we have collaborated for their input.
Funding
This study was partially supported by the Higher Education Commission (HEC) of Pakistan by awarding International Research Support Initiative Program (IRSIP) (Grant No: 1–8/HEC/HRD/2017/7949, PIN: IRSIP 37 BMS 39) to AA and RILD Wellcome Wolfson Centre (Level 4), Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust, UK. Exome/Sanger sequencing and analysis was carried out at RILD Wellcome Wolfson Center UK and was funded by HEC Pakistan and Wellcome Trust UK (to ELB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Clinical data was collected and collated by AA, while, WA and GVH provided the assistance in genomic DNA extraction. AA, CP1 (Claire Prince), CP2 (Chloe Payne), GVH, AHC, ELB, JF performed genetic testing, analyzed and interpreted the patient data. AA, AG and GVH drafted the manuscript. Study was supervised by ELB, AHC, and AG. All authors reviewed, read and approved the manuscript.
Authors information
Not applicable
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Ethical Review Boards Committee of International Islamic University Islamabad, Pakistan, and the study was carried out in accordance with the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki (1964). Informed written consent was obtained for all participants, including minors (< 16 years of age) with parental consent, for the collection of blood samples with clinical evaluations and family histories performed by a dermatologist.
Consent for publication
Written informed consents were obtained for publication of clinical and genetic data from individuals > 18 years, while consent for individuals < 18 years of age were given by their parents or legal guardians.
Competing interests
WA is a member of the editorial board (Associate Editor) of BMC Medical Genetics. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Additional file
Additional file 1:
Table S1. List of candidate pathogenic variants in SLURP1 gene previously reported in association with Mal de Meleda. Table S2. List of candidate pathogenic variants in DSG1 gene previously reported to be associated with Palmoplantar Keratoderma. (DOCX 66 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Akbar, A., Prince, C., Payne, C. et al. Novel nonsense variants in SLURP1 and DSG1 cause palmoplantar keratoderma in Pakistani families. BMC Med Genet 20, 145 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12881-019-0872-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12881-019-0872-1