Abstract
Background
Education of healthcare workers is a core element of multicomponent delirium strategies to improve delirium care and, consequently, patient outcomes. However, traditional educational strategies are notoriously difficult to implement. E-learning is hypothesised to be easier and more cost effective, but research evaluating effectiveness of delirium education through e-learning is scarce at present. Aim is to determine the effect of a nursing e-learning tool for delirium on: (1) in-hospital prevalence, duration and severity of delirium or mortality in hospitalized geriatric patients, and (2) geriatric nurses’ knowledge and recognition regarding delirium.
Methods
A before-after study in a sample of patients enrolled pre-intervention (non-intervention cohort (NIC); n = 81) and post-intervention (intervention cohort (IC); n = 79), and nurses (n = 17) of a geriatric ward (university hospital). The intervention included an information session about using the e-learning tool, which consisted of 11 e-modules incorporating development of knowledge and skills in the prevention, detection and management of delirium, and the completion of a delirium e-learning tool during a three-month period. Key patient outcomes included in-hospital prevalence and duration of delirium (Confusion Assessment Method), delirium severity (Delirium Index) and mortality (in-hospital; 12 months post-admission); key nurse outcomes included delirium knowledge (Delirium Knowledge Questionnaire) and recognition (Case vignettes). Logistic regression and linear mixed models were used to analyse patient data; Wilcoxon Signed Rank tests, McNemar’s or paired t-tests for nursing data.
Results
No significant difference was found between the IC and NIC for in-hospital prevalence (21.5% versus 25.9%; p = 0.51) and duration of delirium (mean 4.2 ± SD 4.8 days versus 4.9 ± SD 4.8 days; p = 0.38). A trend towards a statistically significant lower delirium severity (IC versus NIC: difference estimate − 1.59; p = 0.08) was noted for delirious IC patients in a linear mixed model. No effect on patient mortality and on nurses’ delirium knowledge (p = 0.43) and recognition (p = 1.0) was found.
Conclusion
Our study, the first in its area to investigate effects of delirium e-learning on patient outcomes, demonstrated no benefits on both geriatric patients and nurses. Further research is needed to determine whether delirium e-learning nested within a larger educational approach inclusive of enabling and reinforcing strategies, would be effective.
Trial registration
ISRCTN (82,293,702, 27/06/2017).
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Delirium, defined as an acute and fluctuating disturbance in attention and awareness together with a disturbance in cognition or perception, is the most common hospital complication in older patients [1, 2]. Nurses in particular play a key role in the prevention and early detection of delirium. However, lack of knowledge and competencies required to prevent or manage delirium effectively and negative attitudes towards delirium care, result in adverse patient outcomes, including an increased risk of functional decline, mortality, institutionalisation or dementia [3,4,5,6,7].
Evidence suggests that multicomponent delirium strategies, including educational approaches, improve delirium-related knowledge and recognition of healthcare staff as well as prevent in-hospital delirium [8,9,10,11]. Education of nurses and physicians about delirium, with packages including formal presentations or structured courses followed by case-based discussions, feedback, reminders and/or expert local specialist input, are a key element of those multicomponent strategies. Studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of delirium education in improving delirium-related knowledge and recognition skills of nurses and other healthcare staff [10, 11]. Yet, evidence determining its impact on the incidence or in-hospital prevalence of delirium is rather scarce [10, 12, 13].
Moreover, within routine care outside a research environment, these educational initiatives are difficult to implement. Specific challenges include to be time-consuming and labour-intensive to implement and to maintain compliance within systems of care that do not align to good delirium practice [14,15,16].
E-learning has been identified as an alternative and cost-effective method of delivering education to large groups of hospital staff, and may overcome the challenges of traditional educational approaches [17, 18]. It is proposed that its accessibility, availability, and the use of interactive feedback mechanisms and real care situations make e-learning easier to implement. Arguably, therefore, e-learning at a theoretical level can improve the integration of acquired knowledge into clinical practice, thereby, improving patient outcomes [19, 20].
Two large systematic reviews already evaluated the effect of e-learning education on knowledge, skills and behaviour change in healthcare workers working in the medical (e.g. on management of osteoporosis), psychiatric (e.g. on management of depression), surgical (e.g. on prevention of skin lesion) and nursing (e.g. on prevention of medication errors) field [21, 22]. Though the findings were positive, only one study evaluated the effectiveness of e-learning on patient outcomes [21,22,23,24]. Moreover, despite the fact that e-learning gains growing attention in hospital settings and has direct relevance for day-to-day delirium care, no studies exist on the effects of delirium education through e-learning on patient outcomes, and only four studies investigated its effectiveness on nursing outcomes [25,26,27,28].
The aim of our study was to explore the effect of a delirium e-learning tool for nurses on in-hospital prevalence, duration and severity of delirium in older patients. The effect on patients’ mortality, and geriatric nurses’ delirium knowledge and their ability to recognize delirium were included as secondary outcomes.
Methods
Design, setting and participants
A before-after study (sequential design) was conducted on a geriatric ward of a university hospital in Belgium. The e-learning intervention was implemented over 3 months between 2 periods of data collection i.e. the non-intervention patient cohort (before group, consisting of usual care; enrolled during 4 months) and the intervention patient cohort (after group; enrolled during 4 months). Both cohorts had a follow-up of 12 months from time of admission to the geriatric ward. Dutch speaking patients who were 70 years or older and consecutively admitted to the geriatric ward, were eligible for inclusion. Patients with severe hearing or visual problems, very poor health condition (e.g. palliative patients, patients with unstable cardiac or respiratory problems), isolation because of infectious disease, or those unable to hold a conversation were excluded. Patients who were readmitted during the study period, or had an expected discharge within 24 h after admission were also excluded. Furthermore, all nurses of the geriatric ward were eligible for inclusion. The study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the University Hospitals Leuven, and written informed/proxy consent was obtained in each patient before inclusion.
Intervention
An on-line self-directed nursing staff educational program on delirium was developed by the research team (ED, FD, EJ, KM). This e-learning tool consists of 11 modules including information about delirium specifics, prevention and treatment strategies for delirium (e.g. including a checklist of 12 risk factors), and information about screening tools for the detection of delirium (with possibility to download the instruments). To help translate new knowledge into practice, the tool incorporates textual information in combination with audio-visual materials, case studies and tests for self-assessment with feedback. The e-learning tool is freely accessible at www.deliriummodule.be. Details about the content, development and feasibility testing of the tool have been described elsewhere [25, 29].
The intervention included (1) a live information session (one hour at the geriatric ward) to offer nurses oral and written information about navigation through the e-learning program, and (2) the completion of six compulsory modules (e.g. ‘occurrence and consequences’, ‘clinical presentation’, ‘exercises in delirium recognition’, ‘predisposing and precipitating risk factors’, ‘screening for delirium, and ‘prevention of delirium’) during a 3-month learning period. The five other modules could be completed on a voluntary basis. The e-learning tool remained available until the end of the study. Participants could access the modules at any time using their personal log-in code. It takes between 5 and 15 min to complete one module. Nurses who did not complete the six compulsory modules within two months were encouraged by the head nurse to complete the course. Additionally, a poster was displayed at the geriatric ward to act as a prompt and further enable knowledge translation.
Variables and measurements
Baseline data
Patient baseline data collected included age, gender, social living circumstances, education level, main diagnosis, number of medications prescribed, number of comorbidities, premorbid functional status, cognitive functioning, confirmed diagnosis of dementia and history of delirium. The number of comorbidities was retained from the modified Charlson Comorbidity Index, and varies between 0 and 13 [30]. The premorbid functional status was evaluated using the Katz Index of activities of daily living (ADL) [31], indicating the level of independence in performing the following six activities scored on a 3-point scale (0 = independent; 1 = partly dependent; 2 = dependent): bathing, dressing, feeding, continence, transfer and toileting. Total score ranges between 0 and 12, with higher scores indicating more dependency. Cognitive functioning was evaluated with the 12-item Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) [32]. Total scores vary between 0 and 12, with higher scores indicating better cognitive functioning. Patient baseline data were collected through patient interview, requested from a family member, or based on the medical or nursing records.
Nurse characteristics were collected at the start of the intervention implementation period and included age, gender, work experience as a nurse, percentage employment, day- or night work, highest level of education and delirium education attended in the 5 years prior to the start of the study.
Primary outcomes
In-hospital prevalence of delirium was measured with the Confusion Assessment Method (CAM) [33, 34], which was scored after a structured interview including the 12-item Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) [32]. Accordingly, delirium was diagnosed when the criteria “(acute onset OR fluctuation), inattention, AND (disorganized thinking OR altered level of consciousness)” were rated as positive on at least one of the measurement points (see procedure).
Duration of delirium was defined as the number of days on which a positive CAM score was obtained.
Severity of delirium was assessed with the 7-item Delirium Index (DI) [35], including inattention, disorganized thinking, altered level of consciousness, disorientation, memory impairment, perceptual disturbance, and disorder of psychomotor activity. Each item was scored on a scale from 0 (absent) to 3 (present and severe) resulting in a total score varying between 0 and 21, with higher scores indicating greater severity.
Secondary outcomes
Patients’ in-hospital mortality is defined as the number of deaths occurring while being hospitalized at the geriatric unit. Twelve-month mortality includes all patients that died within 12 months after admission, including cases of in-hospital mortality.
Delirium recognition in nurses was assessed with standardized ‘cases vignettes’ [36], including validated cases about hospitalized patients with dementia, hypoactive delirium, hyperactive delirium, hypoactive delirium superimposed on dementia (DSD) or hyperactive DSD. Before as well as after the e-learning intervention, four slightly different case vignettes were used to avoid recall bias (i.e. dementia, hypoactive delirium, hyperactive delirium and, hyperactive DSD or hypoactive DSD). The behavioral symptoms described in each case had to be scored as dementia, delirium, DSD, normal ageing, depression or none of the options, with each case having only one correct answer. Total delirium recognition (DR) was defined as the number of case vignettes answered correctly (range 0 to 4).
Delirium knowledge in nurses was assessed with the 35-item true-false Delirium Knowledge Questionnaire (DKQ) [25, 37]. Ten items are related to the presentation, symptoms and consequences of delirium, 11 items to the causes and risk factors of delirium, and 14 items to the prevention and management strategies of delirium. The total DKQ score was defined as the number of questions answered correctly and ranged from 0 to 35.
Completion of the e-learning tool in nurses
The number of e-learning modules finalized by each nurse was recorded and ranged from 0 to 11.
Procedure
Patient baseline data, premorbid functional status, number of comorbidities, cognitive functioning, delirium and delirium severity were assessed on the first day after admission to the geriatric ward. In addition, delirium and delirium severity were evaluated on the third, fifth and seventh day after admission to the geriatric ward, and on the day before discharge. From the seventh day after admission, delirium and delirium severity were assessed weekly (e.g. 14th, 21th, day) until hospital discharge. If the patient had delirium on one of the measurement points, the patient was followed up daily until a negative CAM score was obtained. Mortality was recorded during hospitalisation and twelve-month mortality was checked by telephone contact with the patient or his proxy. Procedures for patient assessments in the non-intervention and intervention cohorts were identical. There were no service changes or changes to protocol during the entire study period.
Six study nurses with a master degree performed all assessments. They were trained (i.e. theoretical training of 4 h) by two experts in delirium (ED and KM) according to criteria set in the manuals of MMSE and CAM [33, 34], including evaluation of four clinical cases at the bedside and follow-up discussions. Inter-rater reliability for CAM was κ = 1.00, indicating perfect agreement (inter-rater reliability refers to the agreement of CAM scoring for each study nurse compared with CAM scoring of one of the investigators (ED), and calculated two by two in a random sample of 18 paired observations of enrolled patients).
At the beginning of the one-hour live information session before implementation of the intervention and at the end of the study, nurses received the three questionnaires to assess their baseline data, their knowledge about delirium (DKQ) and their ability to recognize delirium (case vignettes), as described above. Returning a completed questionnaire was considered as informed consent.
Sample size
According to a power analysis for two cohorts using a two-tailed test of significance with an alpha of 0.10, a beta of 0.30 and an estimated proportion of delirium of 30% for the control cohort [38,39,40], a sample size of 71 participants was required in each cohort to detect a difference of 50% in prevalence of delirium.
Blinding
Although patients were blinded to the intervention, nurses and research nurses (data collectors) could not be blinded because of the nature of this study.
Analysis
Descriptive analysis (i.e. means/median, standard deviations/interquartile ranges, or absolute numbers and percentages) for patients in the control and intervention cohorts, as well as for all included nurses were calculated as appropriate.
A chi square test was used to compare in-hospital prevalence of delirium in the control and intervention cohort. This difference was further explored using a logistic regression model in which a random effect for patient was modelled to account for clustering. Duration of delirium (in days) was compared with the Mann-Whitney U-test. Severity of delirium in the two cohorts was compared using a linear mixed model with a random effect accounting for clustering. The mortality risk was explored with a logistic regression model in all patients and in the subgroup of delirious patients. To correct for baseline differences between both cohorts, baseline functional status score and gender were included in all logistic regression and linear mixed models.
Both in the logistic regression and linear mixed models, a time by group interaction was tested first, and a main effect is estimated in case of a non-significant interaction effect. Non-linear trends of time are considered using quadratic and cubic splines-based trends. The models are likelihood-based and therefore provide valid results in case of a random drop-out pattern, this is when the drop-out chance may be associated with previous observations or covariates in the model [41]. Linear mixed models were performed by using the measurement data on the first, third, fifth, seventh, fourteenth, twenty-first days after admission and those of the day before discharge.
In nurses, delirium recognition scores and delirium knowledge scores before and after introduction of the e-learning intervention were compared using paired t-tests for normally distributed data and the Wilcoxon Signed Rank test for non-normally distributed data. McNemar’s tests were used to test differences in proportions of correct answers on the four ‘case vignettes’.
All tests were two-sided, with p-values < 0.05 considered as significant. All analysis were performed on intention-to-treat principle using SPSS, version 21 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL) and SAS System for Windows version 9.2 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA).
Results
Study participants
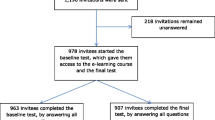
During the before and after study, 153 and 143 patients were consecutively admitted to the geriatric ward, of whom 81 consenting patients were included in the non-intervention and 79 in the intervention cohort (Fig. 1). There were no significant differences in the baseline characteristics of both cohorts, except for gender and premorbid functional status (Table 1).
A total of 22 nurses were eligible for inclusion. Five of them dropped-out because of inability to follow the e-learning course during the study period (i.e. no time or long-term sick leave; n = 2) or because they were transferred to another unit (n = 3). Characteristics of the 17 included nurses are shown in Table 2.
Completion of the e-learning tool in nurses
Out of the 17 nurses participating, 15 completed the 6 compulsory modules during the implementation period. The remaining 2 completed the 6 modules one month after the implementation period. Moreover, 3 nurses recompleted the 6 compulsory modules plus 2 (n = 1) or 5 additional modules (n = 2).
Primary outcomes
In-hospital prevalence, duration and severity of delirium
There was no significant difference in the overall proportion of delirious patients in the control (25.9%, n = 21) and intervention cohort (21.5%, n = 17; p = 0.51; Odds Ratio (OR) = 0.47, Confidence Interval (CI) = 0.16–1.42; p = 0.18).
The mean duration of delirium was 4.9 (SD 4.8) days in the control and 4.2 (SD 4.8) days in the intervention cohort (p = 0.38).
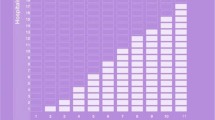
Although the mean DI scores for delirious patients in the intervention cohort were lower than for those in the control cohort on all measurement points, except for day 1 (Fig. 2), linear mixed model analysis noted a trend towards a lower severity score in the intervention cohort (intervention cohort (IC) versus control cohort (CC): Difference Estimate (DE) = − 1.59; 95% CI -3.37 – 0.19; p = 0.08).
Severity of Delirium. Abbreviations: DI = Delirium Index (range 0–21). a number of delirious patients in intervention/non-intervention cohorts day 1, n = 10/n = 9. b number of delirious patients in intervention/non-intervention cohorts day 3, n = 6/n = 7. c number of delirious patients in intervention/non-intervention cohorts day 5, n = 4/n = 9. d number of delirious patients in intervention/non-intervention cohorts day 7, n = 6/n = 10. e number of delirious patients in intervention/non-intervention cohorts day 14, n = 3/n = 4. f number of delirious patients in intervention/non-intervention cohorts day 21, n = 2/n = 6. g number of delirious patients in intervention/non-intervention cohorts day before discharge, n = 1/n = 2
Secondary outcomes
Patients’ mortality
The mortality risk was calculated for all patients and for delirious patients only. The odds ratios for in-hospital mortality and twelve-month mortality between the non-intervention and intervention cohorts was 0.85 (95% CI 0.20–3.66; p = 0.80) and 0.75 (95% CI 0.33–1.71; p = 0.50), respectively. For delirious patients, multivariable analysis showed no significant difference in the risk for in-hospital mortality (OR = 3.28; 95% CI 0.40–27.26; p = 0.27) and twelve-month mortality (OR = 1.00; 95% CI 0.23–4.37; p = 0.99) between both cohorts.
Nurses’ delirium recognition (DR)
There were no significant differences in the proportions of nurses who were able to correctly identify dementia (76.5% vs. 94.1%; p = 0.37), hyperactive delirium (82.4% vs. 88.8%; p = 0.62), hypoactive delirium (52.9% vs. 64.7%; p = 1.0) and delirium superimposed on dementia (94.1% vs. 58.8%; p = 0.07) before and after the introduction of the e-learning intervention, respectively. No significant improvement in the mean total DR score (3.1 (SD 0.83) vs. 3.1 (SD 0.75), p = 1.0, respectively) was noted.
Nurses’ delirium knowledge
The mean total DKQ score of nurses before introduction was not significantly different from the score after introduction of the e-learning intervention (29.3 (SD 2.6) vs. 29.9 (SD 3.2); p = 0.43, respectively).
Discussion
To the authors’ knowledge, this is the first study to report effects of delirium education for nurses through e-learning on patient outcomes. Nevertheless, we found no impact of the delirium e-learning tool on the in-hospital prevalence, duration and severity of delirium or mortality in patients, nor on nurses’ knowledge about delirium or on their ability to recognize delirium using case vignettes. Hence, our findings do not support the assumption that e-learning facilitates knowledge acquisition and its integration into clinical practice.
In understanding the findings, important considerations should be taken into account. First, in contrast with previous research [25, 26, 36, 37], our geriatric nurses’ baseline recognition and knowledge levels regarding delirium were already high, likely because of their specific experience with delirious patients and the prevention and management strategies not present in nurses working on non-geriatric wards. As a consequence, one could hypothesise that the effect of e-learning education on nursing and patient outcomes is potentially more favourable when implemented on wards where the clinical experience with delirium is rather limited. Second, the majority of nurses were only exposed to the 6 compulsory modules which exclusively focussed on the prevention and recognition of delirium. Although the state of the science on delirium management is not strong and prevention remains the most important strategy to address delirium [42,43,44], a lack of completion of all modules available within the tool might in part explain why our e-learning tool failed to affect particularly delirium severity and duration. Third, our findings are in line with a previous study in the broader e-learning literature regarding fall prevention, who did not find an effect of e-learning on patient outcomes either [23]. Overall, studies testing the effectiveness of e-learning in clinical practice is relatively scarce at present, hence, the real value of e-learning has yet to be demonstrated.
Further studies might consider approaches to improve uptake and effect of e-learning. More specifically, educational interventions embedding enabling and reinforcing strategies (guidelines, pocket cards, reminders or feedback) appear to be effective in improving patient outcomes [10, 45]. Therefore, future studies should investigate the efficacy of delirium e-learning integrated within a larger approach of blended-learning education extended with enabling and reinforcing strategies. Moreover, future research should also evaluate the extent to which delirium e-learning can influence behaviour change and positive delirium practice. Examples of clinicians’ behaviour that might optimize patient outcomes are assessing risk factors of delirium, use of screening tools, delirium detection rates, documentation of delirium in notes, or implementation of preventive/management strategies. The fact that most of our nurses did not complete all available e-learning modules indicates that there might be additional factors, such as attitudes and motivation, that could potentially hinder a successful change in clinical practice [46].
Some methodological limitations need to be considered. First, a before/after design was used. More rigorous designs (e.g. cluster randomized trial) might potentially yield different results, although one should realize that education is a social process heavily influenced by contextual factors which cannot be controlled for completely [47]. Second, unlike previous data where post-intervention nursing outcomes were evaluated immediately after exposure to the e-learning education [25,26,27,28], we evaluated nurses’ delirium-related knowledge and recognition levels only 4 months after the education implementation period. This four-month interval between the exposure to e-learning education and the measurement of nursing outcomes might have been too long to identify statistically significant improvements in those outcomes. Nevertheless, a clinically significant 12% to 18% higher proportion of correctly identified hypoactive delirium and dementia cases were found, respectively. A lack of statistical significance in those latter nursing findings could be due to the small sample size of nurses. Last, we are aware that we have a high refusal rate in patients. However, it is inherent to this patient population that the drop out is high and the cooperation is limited.
Despite these caveats, this study has several strengths including its prospective design; the repeated assessments during hospitalisation; the use of validated instruments to assess patients’ delirium prevalence and duration, and nurses’ level of recognition; the detailed statistical analysis; the implementation of a well-designed self-directed e-learning tool, and its development via a robust process and feasibility testing.
Conclusion
Despite the delivery of a well-designed delirium educational e-learning tool, e-learning as an educational approach had neither a direct impact on the in-hospital delirium prevalence, duration and severity or mortality, nor did it improve nurses’ delirium knowledge and their recognition skills. Future studies should therefore focus on evaluating patient outcomes as well as on healthcare workers’ delirium knowledge, behaviour and practices using e-learning within a larger educational approach or quality improvement project with enabling and reinforcing strategies both on geriatric and non-geriatric wards.
Abbreviations
- ADL:
-
Activities of daily living
- CAM:
-
Confusion Assessment Method
- CC:
-
Control cohort
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- DE:
-
Difference estimate
- DI:
-
Delirium Index
- DKQ:
-
Delirium Knowledge Questionnaire
- DR:
-
Delirium recognition
- DSD:
-
Delirium superimposed on dementia
- IC:
-
Intervention cohort
- MMSE:
-
Mini-Mental State Examination
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
References
American Psychiatric Association. Neurocognitive disorders. In: Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2013. p. 591–643.
Siddiqi N, House AO, Holmes JD. Occurrence and outcome of delirium in medical in-patients: a systematic literature review. Age Ageing. 2006;35:350–64.
Inouye S, Foreman M, Mion L, Katz KH, Cooney LM. Nurses’ recognition of delirium and its symptoms: comparison of nurse and researcher ratings. Arch Intern Med. 2001;12:2467–73.
Steis MR, Fick DM. Are nurses recognizing delirium? A systematic review. J Gerontol Nurs. 2008;34:40–8.
Teodorczuk A, Mukaetova-Ladinska E, Corbett S, Welfare M. Reconceptualising models of delirium education: findings of a grounded theory study. Int Psychogeriatr. 2013;254:645–55.
Witlox J, Eurelings LSM, de Jonghe JFM, Kalisvaart KJ, Eikelenboom P, van Gool WA. Delirium in elderly patients and the risk of postdischarge mortality, institutionalization, and dementia. J Am Med Assoc. 2010;304:443–51.
Young J, Murthy L, Westby M, Akunne A, O'Mahony R. Diagnosis, prevention, and management of delirium: summary of NICE guidance. Brit Med J. 2010;341:c3704.
Hshieh TT, Yue J, Oh E, Puelle M, Dowal S, Travison T, Inouye SK. Effectiveness of multicomponent nonpharmacological delirium interventions: a meta-analysis. J Am Med Assoc Intern Med. 2015;175:512–20.
Martinez F, Tobar C, Hill N. Preventing delirium: should non-pharmacological, multicomponent interventions be used? A systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. Age Ageing. 2015;44:196–204.
Wand APF. Evaluating the effectiveness of educational interventions to prevent delirium. Aust J Ageing. 2011;30:175–85.
Yanamadala M, Wieland D, Heflin MT. Educational interventions to improve recognition of delirium: a systematic review. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2013;61:1983–93.
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence: Delirium: prevention, diagnosis and management. 2015. https://www.nice.org.uk/Guidance/CG103. Accessed 5 Dec 2016.
Tabet N, Hudson S, Sweeney V, Sauer J, Bryant C, Macdonald A, Howard R. An educational intervention can prevent delirium on acute medical wards. Age Ageing. 2005;34:152–6.
Greysen SR. Delirium and the “know-do” gap in acute Care for Elders. J Am Med Assoc Intern Med. 2015;175:521–2.
Irving K, Detroyer E, Foreman M, Milisen K. The virtual gateway: opening doors in delirium teaching and learning. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2009;21:15–9.
Teodorczuk A, Reynish E, Milisen K. Improving recognition of delirium in clinical practice: a call for action. BMC Geriatr. 2012;12:55.
Curran VR, Fleet LJ, Kirby F. A comparative evaluation of the effect of internet-based CME delivery format on satisfaction, knowledge and confidence. BMC Med Educ. 2010;10:10–7.
Walsh K, Rutherford A, Richardson J, Moore P. NICE medical education modules: an analysis of cost-effectiveness. Educ Prim Care. 2010;21:396–8.
Bélanger L, Ducharme F. Narrative-based educational nursing intervention for managing hospitalized older adults at risk for delirium: field testing and qualitative evaluation. Geriatr Nurs. 2015;36:40–6.
Cook DA, Levinson AJ, Garside S, Dupras DM, Erwin JP, Montori VM. Instructional design variations in internet-based learning for health professions education: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acad Med. 2010;85:909–22.
Cook DA, Levinson AJ, Garside S, Dupras DM, Erwin PJ, Montori VM. Internet-based learning in the health professions: a meta-analysis. J Am Med Assoc. 2008;300:1181–96.
Curran VR, Fleet L. A review of evaluation outcomes of web-based continuing medical education. Med Educ. 2005;39:561–7.
Johnson M, Kelly L, Siric K, Tran DT, Overset B. Improving falls risk screening and prevention using an e-learning approach. J Nurs Manag. 2015;23:910–9.
Sinclair PM, Kable A, Levett-Jones T, Booth D. The effectiveness of internet-based e-learning on clinician behaviour and patient outcomes: a systematic review. Int J Nurs Stud. 2016;57:70–81.
Detroyer E, Dobbels F, Debonnaire D, Irving K, Teodorczuk A, Fick DM, Joosten E, Milisen K. The effect of an interactive delirium e-learning tool on healthcare workers' delirium recognition, knowledge and strain in caring for delirious patients: a pilot pre-test/post-test study. BMC Med Educ. 2016;16:17.
McCrow J, Sullivan KA, Beattie ER. Delirium knowledge and recognition: a randomized controlled trial of web-based educational intervention for acute care nurses. Nurse Educ Today. 2014;34:912–7.
van de Steeg L, Ijkema R, Langelaan M, Wagner C. Can an e-learning course improve nursing care for older people at risk of delirum: a stepped wedge cluster randomised trial. BMC Geriatr. 2014;14:69.
van de Steeg L, Ijkema R, Wagner C, Langelaan M. The effect of an e-learning course on nursing staff's knowledge of delirium: a before-and-after study. BMC Med Educ. 2015;15:12.
Detroyer E, Joosten E, Milisen K. An interactive e-learning tool about delirium for healthcare providers: development and testing of feasibility. Ann Delirium Care. 2014;13:2–7.
Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis. 1997;40:373–83.
Katz S, Akpom CA. Index of ADL. Med Care. 1976;14:116–8.
Braekhus A, Laake K, Engedal K. The mini-mental state examination: identifying the most efficient variables for detecting cognitive impairment in the elderly. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1992;40:1139–45.
Inouye SK, van Dyck CH, Alessi CA, Balkin S, Siegal AP, Horwitz RI. Clarifying confusion: the confusion assessment method. A new method for detection of delirium. Ann Intern Med. 1990;113:941–8.
Inouye SK. The confusion assessment method (CAM): training manual and coding guide. New Haven: Yale University School of Medicine; 2003.
McCusker J, Cole MG, Dendukuri N. The delirium index, a measure of the severity of delirium: new findings on reliability, validity, and responsiveness. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004;52:1744–9.
Fick DM, Hodo DM, Lawrence F, Inouye SK. Recognizing delirium superimposed on dementia: assessing nurses’ knowledge using case vignettes. J Gerontol Nurs. 2007;33:40–9.
Hare M, Wynaden D, McGowan S. A questionnaire to determine nurses’ knowledge of delirium and its risk factors. Contemp Nurse. 2008;29:23–31.
Detroyer E, Dobbels F, Verfaillie E, Meyfroidt G, Sergeant P, Milisen K. Is preoperative anxiety and depression associated with onset of delirium after cardiac surgery in older patients? A prospective cohort study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008;56:2278–84.
Lemiengre J, Nelis T, Joosten E, Braes T, Foreman M, Gastmans C, Milisen K. Detection of delirium by bedside nurses using the confusion assessment method. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54:685–9.
Milisen K, Foreman MD, Abraham IL, De Geest S, Godderis J, Vandermeulen E, Fischler B, Delooz HH, Spiessens B, Broos PL. A nurse-led interdisciplinary intervention program for delirium in elderly hip-fracture patients. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2001;49:523–32.
Kenward M, Molenberghs G. Missing data in clinical studies. Chichester: John Wiley and Sons; 2007.
Inouye SK, Westendorp RGJ, Saczynski JS. Delirium in elderly people. Lancet. 2014;383:911–22.
MacLullich A, Anand A, Davis DHJ, Jackson T, Barugh AJ, Hall RJ, Ferguson KJ, Meagher DJ, Cunningham C. New horizons in the pathogenesis, assessment and management of delirium. Age Ageing. 2013;42:667–74.
Milisen K, Lemiengre J, Braes T, Foreman M. Multicomponent intervention strategies for managing delirium in hospitalized older people: systematic review. J Adv Nurs. 2005;52:79–90.
Davis DA, Thomson MA, Oxman AD, Haynes RB. Changing physician performance: a systematic review of the effect of continuing medical education strategies. J Am Med Assoc. 1995;274:700–5.
Damschroder LJ, Aron DC, Keith RE, Kirsh SR, Alexander JA, Lowery JC. Fostering implementation of health services research findings into practice: a consolidated framework for advancing implementation science. Implement Sci. 2009;4:50.
Eva KW. Broadening the debate about quality in medical education research. Med Educ. 2009;43:294–6.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the staff of the participating geriatric ward and all consenting patients for their cooperation. We also thank study nurses Herman Baerten, Natasja Jennekens, Marjoly Sintobin and Jochen Fonteyn, and Annouschka Laenen from the Leuven Biostatisics and Statistical Bioinformatics Center.
Funding
This work was supported by PWO Flanders, Belgium. They had no role in the design, data collection, analysis, study results interpretation, article writing or article submission.
Availability of data and materials
This study is part of a larger doctoral study on delirium in hospitalized older patients. Since this study has not been finished yet, we currently prefer not to make the raw data available to others. At the final end of this doctoral study, data can be made available upon request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ED, FD, EJ, KM contributed to the study concept and design. ED and YD contributed to the acquisition of data. ED, FD, AT, MD, YD, EJ and KM contributed in the analysis or interpretation of data. ED, FD, AT, MD, YD, EJ, KM contributed to drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content. All authors have read and approved the final draft of the paper. KM supervised the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the University Hospitals Leuven, and written informed/proxy consent was obtained in each patient before inclusion. For nurses, returning a completed questionnaire was considered as informed consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Koen Milisen is member of the BMC Geriatrics editorial board. Mieke Deschodt was associated editor of BMC Geriatrics until November 2017.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Detroyer, E., Dobbels, F., Teodorczuk, A. et al. Effect of an interactive E-learning tool for delirium on patient and nursing outcomes in a geriatric hospital setting: findings of a before-after study. BMC Geriatr 18, 19 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-018-0715-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-018-0715-5