Abstract
Background
Adenocarcinomas or combined adeno-neuroendocrine carcinomas (MANEC) of small bowel usually have a dismal prognosis with limited systemic therapy options. This is the first description of a patient showing a germline-related BRCA1 mutated MANEC of his ileum. The tumor presented a susceptibility to a combined chemotherapy and the PARP1-inhibitor olaparib.
Case presentation
A 74-year old male patient presented with a metastasized MANEC of his ileum. Due to clinical symptoms his ileum-tumor and the single brain metastasis were removed. We verified the same pathogenic (class 5) BRCA1 mutation in different tumor locations. There was no known personal history of a previous malignant tumor. Nevertheless we identified his BRCA1 mutation as germline-related. A systemic treatment was started including Gemcitabine followed by selective internal radiotherapy (SIRT) to treat liver metastases and in the further course Capecitabine but this treatment finally failed after 9 months and all liver metastases showed progression. The treatment failure was the reason to induce an individualized therapeutic approach using combined chemotherapy of carboplatin, paclitaxel and the Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase- (PARP)-inhibitor olaparib analogous to the treatment protocol of Oza et al.
All liver metastases demonstrated with significant tumor regression after 3 months and could be removed. In his most current follow up from December 2017 (25 months after his primary diagnosis) the patient is in a very good general condition without evidence for further metastases.
Conclusion
We present first evidence of a therapy susceptible germline-related BRCA1 mutation in small bowel adeno-neuroendocrine carcinoma (MANEC). Our findings offer a personalized treatment option. The germline background was unexpected in a 74-year old man with no previously known tumor burden. We should be aware of the familiar background in tumors of older patients as well.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Small bowel carcinomas are rare and account only for 0.5% of all cancers. The 5 year overall survival rates for patients with small-bowel adenocarcinoma is 34.9%. To best of our knowledge no valid prognostic or survival data exist to the mixed adeno-neuroendocrine carcinoma (MANEC)-subtype of the small bowel. There is a strong need for a more effective and personalized systemic treatment option in carcinoma of the small bowel. Most recently Schrock, A et al. [1] described molecular alterations in a very large cohort of 317 small bowel carcinomas. According to this study microsatellite-instability (MSI) was present in 7,6% and are characterized by the following mutations like KRAS (53,6%), APC (26,8%), CDKN2A (14,5%), SMAD4 (17,4%) and BRAF (9,1% but only 10% of these have the typical V600E mutation) as well as ERBB2 mutation in 8,2% of the analysable tumors.
The most important pathway in DNA double strand break (DNA-dbs.) repair is homologous recombination (HR). The HR pathway is dependent on different proteins including BRCA1 and BRCA2 and others (e.g. MNR complex, CtIP, MRE11, RAD51, ATM, H2AX, PALB2, RPA, RAD52) [2, 3].
Effective DNA repair is essential to maintain DNA integrity – so BRCA1/2 deficient cells show a high degree of chromosomal instability which increases the risk of malignant transformation [4, 5]. Germline mutations of BRCA1/2 (gBRCA-mut) were described in carcinoma of the ovary in 5–18% and in some other solid malignant tumors including breast carcinoma, pancreatic carcinoma and less frequent in prostate carcinoma. It became apparent that BRCA mutations also occur in sporadic carcinomas and these tumors respond to Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase- (PARP) inhibition. The full significance of somatic BRCA mutations as a biomarker for the prediction of therapeutic response to PARP inhibition is not entirely clear but ovarian cancer patients with a somatic BRCA mutation are equally likely to benefit from treatment with PARP inhibitors as those with a germline mutation of BRCA. Some authors suggest to perform somatic BRCA testing in routine clinical diagnostics of all advanced tumors, which are potentially amenable to PARP inhibitors [3, 6,7,8,9,10,11].
Each BRCA variant was classified according to the established IARC classification. This classification ranges from class 1 variants (not pathogenic or of no clinical significance) via class 2 (likely not pathogenic or of no clinical significance), class 3 (uncertain), class 4 (likely pathogenic) to class 5 variants (definitively pathogenic) according to different databases (compare: BRCA mutation database: http://arup.utah.edu/database/BRCA/orClinVardatabase:http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar/ or Universal mutation database BRCA share: http://www.umd.be/BRCA1/).
Parallel sequencing
Tumor areas were marked on H&E-stained tissue slides by a pathologist (AQ) and DNA was extracted from corresponding unstained 10 μm thick slides by manual macrodissection. After proteinase K treatment, the DNA was automatically purified using the Maxwell 16 FFPE Tissue LEV DNA Purification Kit (Promega, Madison, USA) on the Maxwell 16 Instrument (Promega) following the manufacturers’ protocol. The DNA concentration was measured using a real-time qPCR-based method.
By parallel sequencing, all tumor manifestations were analyzed for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation and were further analyzed using a panel of 12 other genes resulting altogether in a total of 452 amplicons. Additionally, in these tumor manifestations microsatellite status was checked using five different mononucleotide markers: BAT25, BAT26, NR-21, NR-22 and NR-27 [12].
Isolated DNA (10 ng each) was amplified with the Human BRCA1 and BRCA2 GeneRead DNAseq Targeted Panel V2 (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) or with a customized GeneRead DNAseq Alignment and annotation was done using a modified version of a previously described method [13]. Resulting BAM files were visualized using the Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV; http://www.broadinstitute.org/igv/, Cambridge; USA). A 5% cutoff for variant calls was used and results were only interpreted if the coverage was > 200×.
Histopathological findings
The primary MANEC of the ileum showed two different tumor components: One gland-forming adenocarcinoma-component including PAS-positive mucins in the tumor cell cytoplasm or gland lumina as well as a solid tumor forming neuroendocrine carcinoma-component showing a strong and diffuse immunohistochemical positivity for synatophysin and to a lesser content chromogranin A as well (Fig. 1). The tumor infiltrated the subserosal tissue of the ileum and presented with vessel invasion including a single regional lymph node metastasis. Both, the brain and liver metastasis showed the adenocarcinoma-component.
a Primary MANEC of the ileum (HE, 2,5×) showing the gland-forming adenocarcinoma-component (left side) as well as the solid forming neuroendocrine carcinoma component (right side); b the gland forming adenocarcinoma showing PAS-positive mucins in gland lumina (PAS, 20×); c the solid growth-pattern of the neuroendocrine carcinoma component (HE, 20×); d Immunohistochemistry using an antibody against synaptophysin – diffuse and strong positivity of all tumor cells in the neuroendocrine-carcinoma component (synaptophysin, 5×); e Immunohisto-chemistry using an antibody against chromogranin A – more patchy positivity in the neuroendocrine-carcinoma component (chromogranin A, 5×) f1 Metastasis in liver and f2 in the brain, both formed by the adenocarcinoma component (HE, 10× and 20×)
Case presentation
We describe the case of a 74-year old man presented to our hospital due to a liver tumor in the segments II and III as well as satellite metastatic lesions in the right liver lobe. After taken a liver biopsy from the tumor the diagnosis of an adenocarcinoma was established and interpreted as an unresectable cholangiocarcinoma, initially lacking the information of the primary tumor in the small intestine. The patient was treated with a mono-chemotherapy of Gemcitabine ((1000 mg/qm d1–8) 12/2015–03/2016) followed by selective internal radiotherapy (SIRT) analogous to the SIRCCA study protocol (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02807181). Because of anemia and poor general condition the administration of cisplatin was withheld. In the further course of treatment an additional tumor site in the ileum was detected and progression with cerebral metastasis occurred. The ileum tumor and one brain metastasis were removed. The ileum tumor was classified as a mixed adeno-neuroendocrine carcinoma (MANEC). Tumor manifestations in the liver and in the brain could be characterized as metastases from the adenocarcinoma component (Fig. 1).
In the further course we patient was treated with capecitabine (500 mg 2–0-2, 5d/week) 05–09/2016). This treatment finally failed 4 months later and all liver metastases showed progression. The treatment failure was the reason to analyze the tumor-DNA for molecular alterations using two panels of 14 genes including BRCA 1 and BRCA 2 (452 amplicons in total; compare versions below). We verified the same BRCA1 mutation (c.3700_3704delGTAAA p.V1234Qfs*8) with a very high allele frequency up to 96% in all locations using ultra deep sequencing in the formalin-fixed paraffin embedded material (Fig. 2). According to different databases (UMD, ARUP, ClinVar) this BRCA1 mutation was classified as pathogenic (class 5). The MANEC was microsatellite stable. The mutational hot spots of all other analyzed genes (KRAS, NRAS, HRAS, BRAF, DDR2, ERBB2, KEAP1, NFE2L2, PIK3CA, PTEN, RHOA and BRCA2) were wild type.
BRCA deletion (BRCA1: c.3700_3704delGTAAA; p.V1234Qfs*8) as visualized by the IGV (integrative genomics viewer; www.broadinstitute.org/igv/)
According to the encouraging experiences using combined platin-based chemotherapy and PARP-inhibitors in BRCA-mutated ovarian carcinomas the molecular results have been the trigger for the personalized therapeutic approach using combined chemotherapy of carboplatin, paclitaxel and the PARP1-inhibitor olaparib analogous to the treatment protocol of Oza et al. [14] following a bridging therapy with capecitabine (olaparib 200 mg capsules twice daily, administered orally on days 1–10 of each 21-day cycle) plus paclitaxel (175 mg/m2, administered intravenously on day 1) and carboplatin (4 mg/mL per min) in total five cycles for the following 4 months.
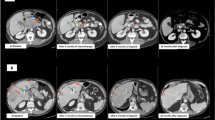
All tumor manifestations demonstrated with a significant tumor regression in the MINT analysis and Ga-68-Dotatate PET-CT after 3 months of treatment (mind analysis Table 1 and Ga-68-Dotatate PET-CT Fig. 3) – and the persistent highly necrotic liver metastasis of 6 cm could be removed. In his most current follow up from December 2017 (25 months after his primary diagnosis) the patient is in a very good general condition without evidence for further metastases (compare time table, Table 2).
Response to personalized treatment (including olaparib): Ga-68 Dotatate PET/CT. Upper row (May 2016) demonstrating an 8 cm tumor in the left liver lobe below physiologic liver uptake and a SRS-positive brain metastasis. Lower row: (Nov 2016): Follow-up PET/CT with tumor shrinkage to 6 cm and disappearance of the brain metastasis
Discussion and conclusion
To the best of our knowledge this is the first description of pathogenic and treatable germline-related BRCA1 mutation in mixed adeno-neuroendocrine carcinoma (MANEC) of the small bowel. There was no known personal history of a previous malignant tumor. Nevertheless, the high allele frequency of the BRCA1 mutation in all tumor manifestations suggested a germline background. Consequently, we tested histologically tumor-free ileum mucosa and were able to detect the same BRCA1 mutation with an allele frequency of 48%. This finding clearly identifies the mutation as germline and a deletion of the wild type BRCA1 allele in the tumor. The homogeneous distribution of BRCA1 mutated tumor cells in the primary tumor and in the different metastasis analyzed here suggests a clonal origin and a causative role of this second hit. Even though a gBRCA1 mutation could be a marker for prostate cancer we did not find any indications for prostate cancer [7].
According to treatment protocols established in BRCA mutated ovarian carcinomas we successfully applied combined chemotherapy of carboplatin, paclitaxel and the PARP1-inhibitor olaparib. Initially, we assumed a somatic background of the BRCA1 mutation in our treated patient, because there was no known personal history of a prior malignant tumor in the 74 year-old man. The germline background of the BRCA1 mutated small bowel carcinoma (like in ovarian adenocarcinoma) is especially promising for a successful combination therapy using platinum-based chemotherapy and a PARP inhibitor (e.g. Olaparib). It has to be questioned whether the somatic pathogenic BRCA mutation itself is the main predictor of an effective PARP inhibition [3].
Beyond BRCA1/2 somatic mutations or the promoter methylation of BRCA some other alterations are potential markers of an effective PARP inhibition (like microsatellite-instable cancers with MRE11-dominant negative mutations, PTEN deficiency, ATM mutation and FANCF promoter methylation) [15].
Additionally, first evidence came up that gBRCA mutated ovarian carcinoma are sensitive to therapies using immune-checkpoint inhibition most likely due to its higher mutational load compared to wild type ovarian carcinoma [16]. It remains to be shown whether our BRCA mutated MANEC also benefit from immune-checkpoint inhibition as an additional future treatment option.
Our findings are remarkable in many ways: Here we provide first evidence of a therapy susceptible BRCA1 mutation in a metastasized mixed adeno-neuroendocrine carcinoma (MANEC) of small bowel.
The germline background of our patient was unexpected because he is a 74-year old man with no previously known tumor burden. Currently, there is increasing evidence that the first germline associated tumor manifestation (e.g. endometrial carcinoma in Lynch syndrome) may occur beyond the sixth decade of living which means that we should be aware of the familiar background in tumors of older patients as well [17].
Abbreviations
- BRCA1:
-
Breast cancer gene 1
- MANEC:
-
Mixed adeno-neuroendocrine carcinoma
- PARP:
-
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase
References
Schrock AB, Devoe CE, McWilliams R, Sun J, Aparicio T, Stephens PJ, Ross JS, Wilson R, Miller VA, Ali SM, et al. Genomic profiling of small-bowel adenocarcinoma. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3(11):1546–53.
Lupo B, Trusolino L. Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation in cancer: old and new paradigms revisited. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1846(1):201–15.
Moschetta M, George A, Kaye SB, Banerjee S. BRCA somatic mutations and epigenetic BRCA modifications in serous ovarian cancer. Ann Oncol. 2016;27(8):1449–55.
Hoeijmakers JH. Genome maintenance mechanisms for preventing cancer. Nature. 2001;411(6835):366–74.
Levy-Lahad E, Friedman E. Cancer risks among BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers. Br J Cancer. 2007;96(1):11–5.
Yuan W, Zhang Z, Dai B, Wei Q, Liu J, Liu Y, Liu Y, He L, Zhou D. Whole-exome sequencing of duodenal adenocarcinoma identifies recurrent Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway mutations. Cancer. 2016;122(11):1689–96.
O'Sullivan CC, Moon DH, Kohn EC, Lee JM. Beyond breast and ovarian cancers: PARP inhibitors for BRCA mutation-associated and BRCA-like solid tumors. Front Oncol. 2014;4:42.
Ledermann J, Harter P, Gourley C, Friedlander M, Vergote I, Rustin G, Scott CL, Meier W, Shapira-Frommer R, Safra T, et al. Olaparib maintenance therapy in patients with platinum-sensitive relapsed serous ovarian cancer: a preplanned retrospective analysis of outcomes by BRCA status in a randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(8):852–61.
Hennessy BT, Timms KM, Carey MS, Gutin A, Meyer LA, Flake DD 2nd, Abkevich V, Potter J, Pruss D, Glenn P, et al. Somatic mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2 could expand the number of patients that benefit from poly (ADP ribose) polymerase inhibitors in ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(22):3570–6.
Pennington KP, Walsh T, Harrell MI, Lee MK, Pennil CC, Rendi MH, Thornton A, Norquist BM, Casadei S, Nord AS, et al. Germline and somatic mutations in homologous recombination genes predict platinum response and survival in ovarian, fallopian tube, and peritoneal carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20(3):764–75.
Ashworth A. A synthetic lethal therapeutic approach: poly(ADP) ribose polymerase inhibitors for the treatment of cancers deficient in DNA double-strand break repair. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(22):3785–90.
Nardon E, Glavac D, Benhattar J, Groenen PJ, Hofler G, Hofler H, Jung A, Keller G, Kirchner T, Lessi F, et al. A multicenter study to validate the reproducibility of MSI testing with a panel of 5 quasimonomorphic mononucleotide repeats.
Peifer M, Fernandez-Cuesta L, Sos ML, George J, Seidel D, Kasper LH, Plenker D, Leenders F, Sun R, Zander T, et al. Integrative genome analyses identify key somatic driver mutations of small-cell lung cancer. Nat Genet. 2012;44(10):1104–10.
Oza AM, Cibula D, Benzaquen AO, Poole C, Mathijssen RH, Sonke GS, Colombo N, Spacek J, Vuylsteke P, Hirte H, et al. Olaparib combined with chemotherapy for recurrent platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer: a randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(1):87–97.
Murai J, Huang SY, Das BB, Renaud A, Zhang Y, Doroshow JH, Ji J, Takeda S, Pommier Y. Trapping of PARP1 and PARP2 by clinical PARP inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2012;72(21):5588–99.
Higuchi T, Flies DB, Marjon NA, Mantia-Smaldone G, Ronner L, Gimotty PA, Adams SF. CTLA-4 blockade synergizes therapeutically with PARP inhibition in BRCA1-deficient ovarian Cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. 2015;3(11):1257–68.
Mills AM, Liou S, Ford JM, Berek JS, Pai RK, Longacre TA. Lynch syndrome screening should be considered for all patients with newly diagnosed endometrial cancer. Am J Surg Pathol. 2014;38(11):1501–9.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AQ, DW and CB were responsible for study concept and design. AQ, DW, TG, MD, CB, AB, WR, NH, MS and LT were responsible for acquisition of data. AQ, AB, CH and MS were responsible for analyses and interpretation of data. AQ and SM were responsible for writing of the manuscript. TZ was responsible for critical revision of the manuscript. HA, TZ, CH, PK, PP, HG, LT and SB were responsible technical or material support. CH, RB and SM were responsible for study supervision. All authors have fully read the manuscript and have approved the accuracy and completeness of the content of all parts of the manuscript and assume responsibility for it.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Procedures were followed as outlined in accordance with ethical standards formulated in the Helsinki Declaration 1975 (and revised in 1983). Informed consent was obtained prior to participation in this study with approval by the Ethics Committee at the University Hospital, Cologne (reference number: 13–091). This approval was necessary due to gene analysis made in this study.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images, and is available on request.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Quaas, A., Waldschmidt, D., Alakus, H. et al. Therapy susceptible germline-related BRCA 1-mutation in a case of metastasized mixed adeno-neuroendocrine carcinoma (MANEC) of the small bowel. BMC Gastroenterol 18, 75 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-018-0803-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-018-0803-1