Abstract
Background
To detect the right atrial (RA) functions in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) patients by using volume-derived values and two-dimensional strain.
Methods
Thirty-two HCM patients and 34 age and gender matched normal controls were enrolled for this study. RA volume-derived values were measured by using 2D ultrasonic images. RA strain (S-reservoir, S-conduit, S-booster pump) and strain rate (SR-reservoir, SR-conduit, SR-booster pump), representing the reservoir, conduit and booster pump functions, respectively, were measured by EchoPAC.
Results
Total RA emptying fraction (RAEF) and RA expansion index in HCM patients were significantly lower than normal controls (p < 0.05). The values of S-reservoir, S-conduit, Sr-reservoir and Sr-conduit in HCM patients were significantly lower than normal controls (p < 0.001). Although there were no significant differences in S-booster pump and Sr-booster pump between HCM patients and normal controls, the absolute values in HCM patients were lower than normal controls.
Conclusions
In this study, we concluded that RA dysfunctions, including the reservoir and conduit functions were impaired in HCM patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a genetic disease which is often diagnosed in the clinic. It is characterized by asymmetric left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy and involves the interventricular septum [1, 2]. With the development of imaging technology, such as echocardiography, cardiac radionuclide imaging and magnetic resonance imaging (Cardiac MRI), the discovery and diagnosis of HCM become more and more easy [3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. However, Echocardiography is considered one of the most useful technique in screening for HCM patients.
Right atrial (RA) functions play a key role in the cardiac also like left atrial (LA): as a reservoir during right ventricular (RV) systole, a conduit from vena cave veins and coronary sinus to the RV during early diastole and a booster pump in late diastole [10]. Traditional two-dimensional echocardiography detected the RA diameter, containing the middle, longitudinal diameter, however, it is simple and can’t assess RA functions comprehensive.
Recently, two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography (2D-STE) for detecting the strain and strain rate in RA functions were mainly focused on patients with pulmonary artery hypertension, acute pulmonary embolism and tricuspid regurgitation severity [11,12,13]. These studies were necessary to demonstrate that the technique could detect the RA functions flexibility and accuracy.
The mechanism of the association between RA function and HCM is unknown. Biagini et al. [14] found complex genotypes with double or triple mutations in end-stage HCM patients. Progressive diastolic dysfunction and atrial fibrillation may represent adequate substrates for RA remodeling [15]. A progressive “atrial myopathy” has been also suggested in patients with HCM [16].
Doesch C, et al. [17] found that RA and RV involvement could predict atrial fibrillation (AF) in patients with HCM evaluated by cardiac MRI, reduced tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE) and RA dilatation could serve as determinable markers of AF in patients with HCM. McCullough SA, et al. [18] also elevated RA pressure in HCM patients was associated with left-sided heart failure and was an independent predictor of all-cause mortality and new-onset AF. Limongelli G, et al. [15] demonstrated that RA enlargement may serve as a very useful marker of disease progression and adverse outcome in patients with sarcomeric hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. From these previous studies, we conclude that RA dysfunctions detection in HCM patients are very important.
In the study, we combined volume-derived values and two-dimensional strain, strain rate to assess RA functions in HCM patients. To our knowledge, this is the first research to detect the RA functions by volume- and strain-derived values in HCM patients.
Methods
All HCM patients and normal controls had completed the consent forms for participation in the study. This study was subjected to approval by the ethics committee of “the Affiliated Changzhou No.2 People′s Hospital with Nanjing Medical University”.
Study samples
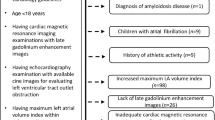
Thirty-two HCM patients and 34 age and gender matched normal controls were enrolled for the research. The inclusion criteria for HCM patients were: ① M-mode and 2D echocardiographic evidence of wall thickness ≥ 15 mm in one or more LV myocardial segments and non-dilated LV. ② Absence of another cardiac or systemic disease capable of producing the magnitude of hypertrophy evident in patients with HCM, such as valvular heart disease, hypertension, hyperthyroidism heart disease, uremic cardiomyopathy and coronary heart disease. ③ All enrolled HCM patients were non-obstructive, excluded the apical HCM, there was no obstruction at rest or provocation (peak gradient < 30 mmHg) based on the degree of LV outflow tract obstruction by continuous wave Doppler.
The normal controls had no evidence of hypertension and any other cardiovascular diseases. All of the physical examination, electrocardiogram, and echocardiography were showed normal.
Two-dimensional doppler echocardiography
All HCM patients and normal controls underwent conventional 2D echocardiography (Vivid E9, GE Healthcare, Horten, Norway), and left atrial diameter (LAd), interventricular septal thickness at the end-diastolic period (IVSd) and LV posterior wall thickness at the end-diastolic period (LVPWd) were measured in the parasternal long-axis view of the LV using M-mode. RV diameter at the middle level (RVd middle), RV diameter at the longitudinal (RVd longitudinal), RV diameter at the base level (RVd basal), RA diameter at the middle level (RAd middle), RA diameter at the longitudinal (RAd longitudinal), and tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE) were measured in the apical four-chamber view. Systolic pulmonary arterial pressure (sPAP) was measured in the parasternal 4-chamber view, if the tricuspid valve regurgitation was absence, sPAP was measured by the regurgitation of pulmonary valve in the parasternal short-axis view at the level of aortic valve or right ventricular outflow view. RV free wall thickness (RVWd) was measured in the subcostal 4-chamber view.
LV end-diastole volume (LVEDV), LV end-systole volume (LVESV) and LV ejection fraction (LVEF) were calculated by bi-plane Simpson′s method.
Peak early and late diastolic velocities of tricuspid valve (E and A, respectively) were measured by pulsed-wave Doppler, and the ratio of E/A was then calculated.
The peak systolic (S′), early (E′) and late (A′) diastolic tricuspid annular velocities were obtained at the RV lateral wall using TDI, and the ratio of E′/A′ was then calculated.
The maximum RA volume (RAVmax), the precontraction RA volume (RAVpre) and the minimum RA volume (RAVmin) were measured in the 2D images using Simpson′s method in the apical four and two chamber views, then total RA emptying volume (RAEV), passive RAEV, active RAEV, total RA emptying fraction (RAEF), passive RAEF, active RAEF and RA expansion index were calculated as following methods: Total RAEV = RAVmax-RAVmin, Passive RAEV = RAVmax-RAVpre, Active RAEV = RAVpre-RAVmin, Total RAEF = Total RAEV / RAVmax * 100, Passive RAEF = Passive RAEV / RAVmax * 100, Active RAEF = Active RAEV / RAVpre * 100, RA expansion index = Total RAEV / RAVmin * 100.
ECG leads were connected to all the participants. The standard high frame rate (40–90 /s) of the apical 4-chamber views (all contained the RA) of three consecutive cycles were stored for off-line analysis.
Data analysis for RA function
The apical 4-chamber views were analysed using the EchoPAC software (EchoPAC Version: 203, GE Vingmed Ultrasound, Norway). Using the button A4C to sketch the endocardial of the RA. The software automatically created a region of interest (ROI) that matched the RA walls. Once the ROI was approved, The RA strain (S-reservoir, S-conduit and S-booster pump) and strain rate (Sr-reservoir, Sr-conduit and Sr-booster pump) were measured (Fig. 1).
Statistical analysis
All data analyses were performed using SPSS 24.0 software (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA). Shapiro-Wilk′s test was used to detect the normality of all the values. Differences between HCM patients and normal controls were compared with independent Student′s t-test for the data distribution was normal. For variables with a non-normal distribution, the nonparametric Mann-Whitney test was used. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (mean ± SD). Difference was considered statistically significant in all tests when the p-value was < 0.05.
Intra- and interobserver variability
Twenty patients were randomly selected for intra- and interobserver variability. RA strain and strain rate were measured by two experienced cardiologists who were blinded to patients′ clinical data results. Intraobserver variability was measured at different time. Interobserver variability was determined by repeating measurements from the same off-line images. Intra- and interobserver variability was calculated using intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs).
Results
Clinical baseline parameters and 2D echocardiographic characteristics between HCM patients and normal controls were shown in the Table 1.
There were significant differences in LAd, IVSd, LVPWd and RAd longitudinal, E, E/A, E′ and E′/A′ between HCM patients and normal controls (p < 0.05). LAd, IVSd, LVPWd and RAd longitudinal were significantly larger than normal controls, while E, E/A, E′ and E′/A′ were significantly lower than normal controls. No significant differences were found in LVEF, RVWd, RVd middle, RVd basal, RAd middle, TAPSE, A, S′ and A′ (p > 0.05).
2D echocardiographic RA volume and volume-derived values between HCM patients and normal controls were shown in Table 2, Fig. 2a.
There were significant differences in Total RASV, Passive RASV, Total RAEF and RA expansion index (p < 0.05), and all the values were significantly lower than normal controls. Although there were no significant differences in RAVmax, RAVpre, RAVmin, Active RASV, Passive RASV and Active RAEF (p > 0.05), the absolute values of Active RASV, Passive RASV and Active RAEF were lower than normal controls.
RA reservoir, conduit and booster pump functions between HCM patients and normal controls by detecting the RA Strain and strain rate were shown in Table 3, Fig. 2b, c
There were significant differences in S-reservoir, S-conduit, Sr-reservoir and Sr-conduit between HCM patients and normal controls (p < 0.001). All the values were significantly lower than normal controls. Although there were no significant differences in S-booster pump and Sr-booster pump between HCM patients and normal controls, the absolute values in HCM patients were lower than normal controls.
Intra- and interobserver variability
The results for the intraobserver and interobserver variability for the RA strain and strain rate upon repeated measurements in 20 random patients were shown in Table 4. ICC values were higher for intraobserver and interobserver variability when the same images were analyzed by the two different cardiologists. What′s more, the results also demonstrated that the analysis of the software had the well repeatability and reliability in this study.
Discussion
The main findings of the research were: RA reservoir and conduit functions were impaired in HCM patients when compared with normal controls.
2D-STE is a new echocardiographic technique that has been validated for the assessment of LV, LA, RV and RA functions in HCM patients by previous studies [19]. Also, our group had been done some researches in LA and LV function of HCM. Huang J, et al. [20, 21] detected the longitudinal and circumferential strain of different myocardium layers, radial strain, and longitudinal rotation by using 2D-STE, and demonstrated that the long-axis and short-axis LV functions in HCM patients were impaired. Huang J, et al. [22] also detected the LA dysfunction in HCM patients by 2D-STE and volume-derived values. Fujimoto K et al. [23] elucidated the impact of LA function by 2D-STE and cardiac MRI, and found loss of LA active function was associated with increased cardiac events in patients with HCM.
RA functions play an important role in the cardiac and 2D-STE is a feasible, angle-independent method for the evaluation of RA function [24]. Researchers mainly focused RA functions on pulmonary artery hypertension, acute pulmonary embolism, hypertension, the influence of severity tricuspid regurgitation, right ventricular myocardial infarction, tetralogy of Fallot, and so on [11, 12, 25,26,27]. However, till now, we have not found a research about RA functions in HCM patients by using 2D-STE and RA volume-derived values.
Recently, some researchers have found RV functions were impaired in HCM patients by 2D-STE. Cincin A, et al. [28] explored RV mechanical function in HCM patients by demonstrated 2D-STE-derived RV systolic function was impaired in HCM patients when compared with healthy subjects. D’Andrea A, et al. [29] analyzed RV systolic function in patients with HCM at rest and during exercise, and found that RV contractile reserve for HCM was impaired. This study demonstrates for the first time that 2D-STE algorithm applied to routine grey-scale 2D images represents a promising and feasible non-invasive technique to assess RA functions in HCM patients.
From basic 2D echocardiographic characteristics between HCM patients and normal controls, we found RA and LA diameters were dilated in HCM patients. From the volume-derived values, total RAEV, total RAEF and RA expansion index represented the reservoir function, passive RAEV represented the conduit function were significantly lower than normal subjects, the results indicated that RA reservoir and conduit functions were impaired. Strain and strain rate analysis also demonstrated that reservoir and conduit functions were impaired. Although the booster pump function of volume and strain derived-values had no significant differences between HCM patients and normal controls, the absolute values in HCM patients were lower than normal controls. HCM is a progressive disease characterized by LV hypertrophy and fibrosis. LA, LV and RV dysfunctions were observed and demonstrated that the functions were damaged. Our findings may stress the significance of the evaluation of RA dysfunction because it permits us to evaluate RV function on the other hand.
Conclusion
From the study, we concluded that RA dysfunctions, including the reservoir and conduit functions were impaired in HCM patients.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- HCM:
-
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- 2D-STE:
-
Two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- RA:
-
Right atrial
- RV:
-
Right ventricular
- LA:
-
Left atrial
- LV:
-
Left ventricular
- LAd:
-
Left atrial diameter
- IVSd:
-
Interventricular septal thickness at the end-diastolic period
- LVPWd:
-
LV posterior wall thickness at the end-diastolic period
- RVWd:
-
RV free wall diameter
- RVd middle:
-
RV diameter at the middle level
- RVd longitudinal:
-
RV diameter at the longitudinal
- RVd basal:
-
RV diameter at the base level
- RAd middle:
-
RA diameter at the middle level
- RAd longitudinal:
-
RA diameter at the longitudinal
- TAPSE:
-
Tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion
- sPAP:
-
Systolic pulmonary arterial pressure
- LVEDV:
-
LV end-diastole volume
- LVESV:
-
LV end-systole volume
- LVEF:
-
LV ejection fraction
- RAEV:
-
RA emptying volume
- RAEF:
-
RA emptying fraction
- ROI:
-
Region of interest
- ICCs:
-
Intraclass correlation coefficients
References
Badano LP, Kolias TJ, Muraru D, Abraham TP, Aurigemma G, Edvardsen T, D'Hooge J, Donal E, Fraser AG, Marwick T, et al. Standardization of left atrial, right ventricular, and right atrial deformation imaging using two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography: a consensus document of the EACVI/ASE/industry task force to standardize deformation imaging. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018;19(6):591–600.
Bai Y, Yang J, Liu J, Ning H, Zhang R. Right atrial function for the prediction of prognosis in connective tissue disease-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension: a study with two-dimensional speckle tracking. Int J Card Imaging. 2019;35(9):1637–49.
Cai M, Tian YQ, He ZX. Myocardial radionuclide imaging in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Nucl Med Commun. 2013;34(4):298–305.
Cincin A, Tigen K, Karaahmet T, Dundar C, Gurel E, Bulut M, Sunbul M, Basaran Y. Right ventricular function in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a speckle tracking echocardiography study. Anatolian J Cardiol. 2015;15(7):536–41.
D'Andrea A, Limongelli G, Baldini L, Verrengia M, Carbone A, Di Palma E, Vastarella R, Masarone D, Tagliamonte G, Riegler L, et al. Exercise speckle-tracking strain imaging demonstrates impaired right ventricular contractile reserve in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Int J Cardiol. 2017;227(1):209–16.
Dominguez F, Gonzalez-Lopez E, Padron-Barthe L, Cavero MA, Garcia-Pavia P. Role of echocardiography in the diagnosis and management of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Heart. 2018;104(3):261–73.
Elliott PM, Anastasakis A, Borger MA, Borggrefe M, Cecchi F, Charron P, Hagege AA, Lafont A, Limongelli G, Mahrholdt H, et al. 2014 ESC guidelines on diagnosis and management of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: the task force for the diagnosis and Management of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2014;35(39):2733–79.
Fujimoto K, Inoue K, Saito M, Higashi H, Kono T, Uetani T, Aono J, Nagai T, Nishimura K, Suzuki J, et al. Incremental value of left atrial active function measured by speckle tracking echocardiography in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Echocardiography (Mount Kisco, NY). 2018;35(8):1138–48.
Grover S, Lloyd R, Perry R, Lou PW, Haan E, Yeates L, Woodman R, Atherton JJ, Semsarian C, Selvanayagam JB. Assessment of myocardial oxygenation, strain, and diastology in MYBPC3-related hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a cardiovascular magnetic resonance and echocardiography study. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019;20(8):932–8.
Hensley N, Dietrich J, Nyhan D, Mitter N, Yee MS, Brady M. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a review. Anesth Analg. 2015;120(3):554–69.
Huang J, Yan ZN, Fan L, Rui YF, Song XT. Left ventricular systolic function changes in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy patients detected by the strain of different myocardium layers and longitudinal rotation. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2017;17(1):214.
Huang J, Yan ZN, Rui YF, Fan L, Liu C, Li J. Left ventricular short-axis systolic function changes in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy detected by two-dimensional speckle tracking imaging. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2018;18(1):13.
Huang J, Yan ZN, Rui YF, Fan L, Shen D, Chen DL. Assessment of left atrial function in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy using two-dimensional strain: a comparison with volume-derived values. Minerva Cardioangiol. 2018;66(1):26–37.
Biagini E, Olivotto I, Iascone M, Parodi MI, Girolami F, Frisso G, Autore C, Limongelli G, Cecconi M, Maron BJ, Maron MS, Rosmini S, Formisano F, Musumeci B, Cecchi F, Iacovoni A, Haas TS, Bacchi Reggiani ML, Ferrazzi P, Salvatore F, Spirito P, Rapezzi C. Significance of sarcomere gene mutations analysis in the end-stage phase of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol. 2014;114(5):769–76.
Limongelli G, Masarone D, Frisso G, Iacomino M, Ferrara I, Rea A, Gravino R, Bossone E, Salvatore F, Calabro R, Elliott P, Pacileo G. Clinical and genetic characterization of patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and right atrial enlargement. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2017;18(4):249–54.
Olivotto I, Girolami F, Nistri S, Rossi A, Rega L, Garbini F, Grifoni C, Cecchi F, Yacoub MH. The many faces of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: from developmental biology to clinical practice. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2009;2(4):349–67.
Doesch C, Lossnitzer D, Rudic B, Tueluemen E, Budjan J, Haubenreisser H, Henzler T, Schoenberg SO, Borggrefe M, Papavassiliu T. Right ventricular and right atrial involvement can predict atrial fibrillation in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy? Int J Med Sci. 2016;13(1):1–7.
McCullough SA, Fifer MA, Mohajer P, Lowry PA, Reen CO, Baggish AL, Vlahakes GJ, Shimada YJ. Clinical correlates and prognostic value of elevated right atrial pressure in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Circ J. 2018;82(5):1405–11.
Moody WE, Schmitt M, Arumugam P. Coronary microvascular dysfunction in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy detected by Rubidium-82 positron emission tomography and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. J Nucl Cardiol. 2019;26(2):666–70.
Mor-Avi V, Lang RM, Badano LP, Belohlavek M, Cardim NM, Derumeaux G, Galderisi M, Marwick T, Nagueh SF, Sengupta PP, et al. Current and evolving echocardiographic techniques for the quantitative evaluation of cardiac mechanics: ASE/EAE consensus statement on methodology and indications endorsed by the Japanese Society of Echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2011;24(3):277–313.
Nourian S, Hosseinsabet A, Jalali A, Mohseni-Badalabadi R. Evaluation of right atrial function by two-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography in patients with right ventricular myocardial infarction. Int J Card Imaging. 2017;33(1):47–56.
Quarta G, Aquaro GD, Pedrotti P, Pontone G, Dellegrottaglie S, Iacovoni A, Brambilla P, Pradella S, Todiere G, Rigo F, et al. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: the importance of clinical context. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018;19(6):601–10.
Rai AB, Lima E, Munir F, Faisal Khan A, Waqas A, Bughio S, ul Haq E, Attique HB, Rahman ZU: Speckle tracking echocardiography of the right atrium: the neglected chamber. Clin Cardiol 2015, 38(11):692–697.
Rakowski H, Hoss S, Williams LK. Echocardiography in the diagnosis and Management of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Cardiol Clin. 2019;37(1):11–26.
Ramberg E, Olausson M, Jorgensen TB, Nepper ML, Bhardwaj P, Binko TS, Petersen JR, Fornitz GG. Right atrial and ventricular function evaluated with speckle tracking in patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Am J Emerg Med. 2017;35(1):136–43.
Sciagra R, Calabretta R, Cipollini F, Passeri A, Castello A, Cecchi F, Olivotto I, Pupi A. Myocardial blood flow and left ventricular functional reserve in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a 13NH3 gated PET study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2017;44(5):866–75.
Tadic M, Cuspidi C, Kocijancic V, Celic V, Vukomanovic V. Does Left Ventricular Geometric Patterns Impact Right Atrial Phasic Function? Findings from the Hypertensive Population. Echocardiography (Mount Kisco, NY). 2016;33(8):1186–94.
Teixeira R, Monteiro R, Garcia J, Baptista R, Ribeiro M, Cardim N, Goncalves L. The relationship between tricuspid regurgitation severity and right atrial mechanics: a speckle tracking echocardiography study. Int J Card Imaging. 2015;31(6):1125–35.
Timoteo AT, Branco LM, Rosa SA, Ramos R, Agapito AF, Sousa L, Galrinho A, Oliveira JA, Oliveira MM, Ferreira RC. Usefulness of right ventricular and right atrial two-dimensional speckle tracking strain to predict late arrhythmic events in adult patients with repaired tetralogy of Fallot. Rev Port Cardiol. 2017;36(1):21–9.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the department of Echocardiography, the Affiliated Changzhou No.2 People’s Hospital with Nanjing Medical University and the department of Interventional Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University.
Funding
This study was funded by Changzhou Science and Technique Program (Grant No.: CJ20190098), and Changzhou “Qingmiao talents” Project. Among the included findings, Changzhou Science and Technique Program major helps in the design of the study and collection of patients; Changzhou “Qingmiao talents” Project major helps in the analysis and interpretation of the data, revision of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HJ designed the study and carried out the study, data collection, analysis and wrote the manuscript, YC and NCF revised the manuscript. YZN and FL designed part of the experiments, and collected the HCM patients and normal controls. SXT performed the statistical analysis. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study complied with the Declaration of Helsinki and was reviewed and approved by the Human Subjects Committee of Changzhou No.2 People’s Hospital approved this study. Written informed consent was obtained from each couple enrolled in the study.
Consent for publication
This manuscript does not include any individual person’s data.
Competing interests
The authors declare there were no Competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, J., Yang, C., Ni, CF. et al. Right atrial function assessed by volume-derived values and speckle tracking echocardiography in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 20, 335 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-020-01610-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-020-01610-1