Abstract
Background
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (FBP) is a key enzyme in the plant sucrose synthesis pathway, in the Calvin cycle, and plays an important role in photosynthesis regulation in green plants. However, no systemic analysis of FBPs has been reported in Gossypium species.
Results
A total of 41 FBP genes from four Gossypium species were identified and analyzed. These FBP genes were sorted into two groups and seven subgroups. Results revealed that FBP family genes were under purifying selection pressure that rendered FBP family members as being conserved evolutionarily, and there was no tandem or fragmental DNA duplication in FBP family genes. Collinearity analysis revealed that a FBP gene was located in a translocated DNA fragment and the whole FBP gene family was under disequilibrium evolution that led to a faster evolutionary progress of the members in G. barbadense and in At subgenome than those in other Gossypium species and in the Dt subgenome, respectively, in this study. Through RNA-seq analyses and qRT-PCR verification, different FBP genes had diversified biological functions in cotton fiber development (two genes in 0 DPA and 1DPA ovules and four genes in 20–25 DPA fibers), in plant responses to Verticillium wilt onset (two genes) and to salt stress (eight genes).
Conclusion
The FBP gene family displayed a disequilibrium evolution pattern in Gossypium species, which led to diversified functions affecting not only fiber development, but also responses to Verticillium wilt and salt stress. All of these findings provide the foundation for further study of the function of FBP genes in cotton fiber development and in environmental adaptability.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (FBP, EC 3.1.3.11) catalyzes the decomposition of fructose 1,6-diphosphate (F-1,6-P2) into 6-phosphate fructose (F-6-P) and inorganic phosphorus (Pi) [1, 2]. It is ubiquitous across organisms and is a key enzyme in the Calvin cycle and the gluconeogenesis pathway [3, 4]. These reactions are involved in carbon fixation and sucrose metabolism and are present in the chloroplast stroma and the cytosol of green plants [5]. In most higher plants, FBP exists in three possible forms including a monomer, dimer, and tetramer, among which only the tetramer has catalytic activity [6].
In higher plants, based on their different catalytic mechanisms and independent evolutionary phylogensis, FBPs can be classified into two groups, cytosolic FBPs (cyFBPs) and chloroplast FBPs (cpFBPs). cyFBP plays an important regulatory role in the gluconeogenesis pathway and the synthesis of sucrose, while cpFBP is involved in the reduction of the pentose phosphate pathway [3, 4, 7]. cyFBP and sucrose phosphate synthase (SPS) are the main rate-limiting enzymes in the sucrose synthesis pathway [8]. 6-phosphate fructose is an essential monosaccharide for sucrose synthesis, and cyFBP and 6-phosphate fructokinase (PFK), pyrophosphate, and 1,6-diphosphate fructose transferase (PFP) jointly regulate the formation of fructose-6-phosphate. cyFBP can be inhibited by the metabolic product AMP, 2,6-diphosphoric fructose (F-2,6-P2), and also by Mg2+ and Ca2+, while cpFBP is not sensitive to either AMP or fructose-1,6-diphosphate [2]. Studies of FBP over expressions show that it can increase photosynthetic capacity, sucrose synthesis, and promote sugar accumulation, thereby accelerating plant growth.
Recently, some FBP genes have been cloned in several species such as Beta vulgaris, Spinaciaoleracea, Glycine max, Arabidopsis thaliana, Pisumsativum, G. hirsutum and Pyropia haitanensis, and other plants [5, 9,10,11,12,13,14]. The main research activities on these FBP genes have included identifying their functions in plant photosynthesis and glucose metabolism through molecular bioinformatic analysis and over-expression [11, 13,14,15,16,17,18]. In a transgenic study in A. thaliana, antisense transcripts were applied to inhibit the expression of a cyFBP gene. The decreased expression of the FBP gene resulted in decreased sucrose synthesis, accumulated intermediate metabolites, and eventually blocked photosynthesis [11]. In another study in A. thaliana, over-expression of a cyFBP gene caused an increase in sucrose synthesis and promoted plant growth in transgenic plants [15]. Inhibiting the expression of this gene in Solanum tuberosum could also reduce sucrose synthesis during the photosynthetic process [16]. In rice, loss of cyFBP reduced photosynthetic sucrose synthesis and delayed plant growth [17]. When cpFBP was inhibited in tomato, only small changes in carbohydrate metabolism were observed, but this inhibition caused a significant decrease in fruit size [18]. The different response modes of PhcpFBP mRNA levels in Pyropia haitanensis indicated that cpFBP also plays an important role in response to abiotic stresses such as high temperature and drought [14]. The different expression level of GhFBP at different times during cotton fiber development indicated that it plays a key role in the early stage of fiber secondary cell wall development [13].
Cotton is an important economic crop in the world, and cotton fiber is an important raw natural material for the textile industry. Cotton fiber is developed from the differentiation of a single ectodermic epidermal cell, and the fiber formation process can be divided into four distinct but partially overlapping periods: initiation, elongation (primary wall formation), secondary wall thickening, and dehydration maturity [19]. Many methods, including QTL identification [20,21,22], GWAS analysis [23,24,25,26], and functional gene identification [27,28,29], have been used to tackle the problems of fiber development and fiber quality formation. Studies have revealed that fiber development is a very complex process, with a large number of metabolic pathways providing material support, and thousands of specific genes being involved in expression regulation. At the same time, Verticillium wilt, which has the nickname “cotton cancer,” is currently one of the most serious diseases that restricts cotton production and affects fiber quality [30]. A high concentration of saline stress also negatively [31] affects the growth, development, and fiber quality of cotton [32, 33].
Although a few functional studies of FBP genes in some plant species have revealed that FBP genes could have certain impacts on various biological activities, FBP behavior is still poorly understood. Specifically, how FBP genes function at the whole genome level, especially in Gossypium species, remains unclear. The completion of whole genome sequencing databases for two important diploid cotton species G. raimondii [34, 35] and G. arboreum [36], and two domesticated tetraploid species G. hirsutum [37,38,39,40] and G. barbadense [39,40,41], provides brand-new platforms for functional genomic studies. In this study, we identified 41 FBP family members in the genomes of these four cotton species and 73 FBP members in nine other species. Intensive bioinformatic analyses, including physicochemical properties, chromosomal localization, evolutionary relationships and gene structure, conserved motifs and FBP domain features, and functional expression analyses including transcriptomic and quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) were performed. The results indicated that FBP genes were involved in plant responses to biotic and abiotic stresses, as well as cotton fiber formation. This study provides a foundation for functional verification of the FBP genes of cotton in the future and useful information for the improvement of cultivars with excellent fiber quality and broad environmental adaptability.
Results
Identification of FBP family members
A total of 41 FBP genes from four Gossypium species, including 14 in G. hirsutum (GhFBP), 15 in G. barbadense (GbFBP), 6 in G. arboreum (GaFBP), and 7 in G. raimondii (GrFBP), were identified in this report (Supplementary file 1). The number of FBP genes in the tetraploid genomes of G. hirsutum and G. barbadense (AD genome) was almost double those in the diploid genomes of G. raimondii (D genome) and G. arboreum (A genome). These two tetraploid Gossypium genomes arose from a natural hybridization between two ancestors of diploid G. raimondii and G. arboreum [38, 40, 42].
In addition, in order to elucidate the evolutionary and phylogenetic relationship of these FBP genes, we identified 73 FBP family genes in nine other species, including 4 in Arabidopsis thaliana, 5 in Theobroma cacao, 12 in populus trichocarpa, 12 in Glycine max, 11 in Zea mays, 5 in Vitis vinifera, 6 in Selaginella moellendorffii, 11 in Physcomitrella patens, and 7 in Oryza sativa (Supplementary file 1).
Phylogenetic analysis of the FBP gene family
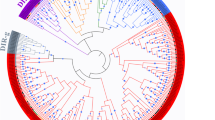
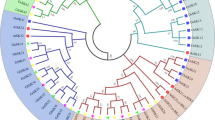
To elucidate the evolutionary relationship of the identified FBP proteins between Gossypium and other species, the amino acid sequences of all the FBP proteins were aligned to identify their phylogenetic similarities with orthologs using the neighbor-joining model from MEGA 7, and a phylogenetic tree was thus constructed as shown in Fig. 1a. According to their evolutionary relationships, 114 FBP proteins were divided into 2 groups: cytosolic FBPs, (cyFBPs) which included 40 members; and chloroplast FBPs, (cpFBPs) which included 74 members [7, 14]. The result of phylogenetic analysis indicated that FBPs had a closer evolutionary relationship between the four Gossypium species as compared with other species. The phylogenetic results also indicated that between all the other species, cocoa had the closest evolutionary relationship to the examined cotton species [38, 40]. Further phylogenetic analysis of FBPs from the four cotton species indicated that the cyFBPs were assorted into three subgroups, while the sorted into cpFBPs four subgroups (Fig. 1b). Each subgroup of Gossypium FBPs consisted of six members, including one from the A genome (G. arboreum) and one from the D genome (G. raimondii), two from G. hirsutum, and two from G. barbadense. As both of G. hirsutum and G. barbadense are comprised of At and Dt subgenomes, each subgenome provided one member in each sub-group of the FBP family. There is only one subgroup in cpFBPs that had 5 FBPs, but there was no FBP from G. arboreum identified in these analyses (Fig. 1b).
Phylogenetic trees of FBPs. a Phylogenetic tree of 114 FBPs from 13 species, including G. hirsutum, G. barbadense, G. arboreum, G. raimondii, A. thaliana, T. cacao, P. trichocarpa, G. max, Z. mays, V. vinifera, S. moellendorffii, P. patens and O. sativa; b Phylogenetic tree of 41 FBPs from four Gossypium species. I represent cyFBPs and II represent cpFBPs
Gene structure and protein domain of FBP family members
The length of amino acid (aa) sequences of FBP proteins ranged from 341 to 608, 341 to 412, 341 to 428, and 341 to 606 in G. arboreum, G. raimondii, G. hirsutum, and G. barbadense, respectively. The cyFBP group had 18 members (42.87%), which had a uniform length of 341 aa with only two exceptions, namely Gorai.005G080300.1 and GB_A02G1288.1. The cpFBP group had 23 members (57.13%), which had a varied length of aa sequences (Fig. 1, Supplementary file 2). The PI values of the four cotton FBPs ranged from 5.00 to 7.68.
In total, 10 motifs were identified in the FBP family in the four Gossypium species, with each FBP containing 7 to 9 motifs in general (Fig. 2a, Figure S1). The significant difference between cyFBPs and cpFBPs was that motif 5 was identified exclusively in cyFBPs, while motif 9 was exclusively present in cpFBPs. Each phylogenetic subgroup had a similar composition and arrangement of motifs, which was highly consistent with the results of phylogenetic analysis. The results also showed some minor variance in motif composition and arrangement between the subgroups (Fig. 2a).
Gene structure analysis also showed consistent results to our phylogenetic and protein motif analyses (Fig. 2b). The exon number of FBP genes ranged from 3 to 12. cyFBPs had 11 to 12 exons, while cpFBPs only had 3–5 exons. The gene structure of each subgroup was almost the same, which indicated conserved evolution patterns for FBP family members. The cyFBP gene structures could be further divided into three types (Fig. 2). Both subgroups cyFBP 1 and cyFBP 2 had 12 exons and 11 introns, with a varied distribution between them. Subgroup cyFBP 3 had 11 exons and 10 introns. In contrast to cyFBPs, cpFBPs had much fewer exons. The cpFBP genes could be sorted into four subgroups. Subgroups cpFBP 1 and cpFBP 2 had 4 exons and 3 introns, with different distributions between them. Subgroup cpFBP 4 had 8 exons and 7 introns, while subgroup cpFBP 3 had a varied number of exons and introns, and the exon number of this subgroup ranged from 3 to 8. The results also indicated that only FBP genes from G. raimondii had UTR structures. This indicated that cyFBPs had more complicated gene structures than cpFBPs had.
Analysis of cis-acting elements in the promoter regions of homologous FBP genes
To further understand how FBP genes function, the composition and distribution of cis-regulatory elements (CRE) were identified in the 5′ untranslated regions 2000 bp upstream of each gene from the PlantCare website (Fig. 3). The results indicated that the composition and distribution of CREs varied significantly across the whole FBP gene family. It also could be seen that the CREs had a high congruency with the results of gene structure, protein domain, and phylogenetic analyses. Each subcategory of FBP genes had identical or similar compositions and distributions of CREs in their 5′ upstream regions (Fig. 3).
Further analysis indicated that the 5′ up-stream regions of FBP genes contained almost all of the following categories of CREs: constitutive, inducible and tissue-specific. The constitutive CREs include typical basic components such as TATA-Boxes and CAAT-Boxes. Inducible CREs included photo-responsive elements, ATCC-motifs, Box 4, I-Boxes, Sp1, TCCC-motifs, GAG-motifs, gibberellin response elements (GARE-motifs), P-Boxes, abscisic acid responsive elements (ABREs), salicylic acid reaction elements, TCA-elements, anaerobic induction elements (AREs), stress-responsive elements, TC-rich repeats, and MYB binding site (MBS). In addition, the GARE-motif was exclusively identified in the promoter region of one subcategory of genes including GH_A02G0701.1, GH_D02G0715.1, GB_A02G0693.1, GB_D02G0741.1, GH_A02G1268.1, and GB_A02G1288.1.
Distribution and collinearity analysis of the FBP gene family Gossypium species
In the genome of G. arboreum, FBP genes were identified on chromosomes A02, A03, A04, A10, A11, and A12, while in the genome of G. raimondii, FBP genes were identified on chromosomes D02, D05, D07, D08, D11, and D12. In the tetraploid genomes of G. hirsutum and G. barbadense, FBP genes had similar distribution on chromosomes At02, At04, At10, At11, At12, Dt02, Dt03, Dt04, Dt10, Dt11, and Dt12. Homologous analysis indicated that a homologous gene identified on A03 of G. arboreum was identified on chromosome At02 in G. hirsutum and G. barbadense.
Tandem and fragmental DNA duplication provides major forces that drive the formation of gene families [43, 44] as well as whole genome evolution. In the current study, the duplication events of cotton FBP genes were analyzed. Although the results did not support any tandem repeat events occurring during the evolution of the cotton FBP gene family, collinearity analysis showed that in these two diploid species the FBP genes were perfectly chromosome-pair-wise homologous (Fig. 4a). Meanwhile, in the two tetraploid species, each FBP gene from one species (hirsutum or barbadense) had two homologous genes in both the At and Dt subgenomes in its counterpart species (barbadense or hirsutum) (Fig. 4d). Collinearity analysis between diploid and tetraploid species indicated that in G. hirsutum each gene had two homologous genes in the two diploid species (Fig. 4b), while in G. barbadense, two FBP genes on GbAt02 did not have homologous genes in raimondii and one FBP gene at GbDt12 did not have a homologous gene in arboreum (Fig. 4c).
Analysis of selection pressure of FBP genes in four cotton species
Calculating non-synonymous (Ka) and synonymous (Ks) substitution rates is a useful method for assessing sequence variation of protein orthologous in different species or taxa with unknown evolutionary states [45]. The value of Ka/Ks represents the ratio between Ka and Ks of two homologous protein-coding genes. Ka/Ks > 1 indicates that a gene has been positively selected, while a Ka/Ks = 1 indicates that a gene has been neutrally selected, and a Ka/Ks < 1 indicates that a gene has been selectively purified [45]. The Ka/Ks values of homologous FBP genes between G. arboreum and G. raimondii ranged from 0.05 to 0.62, while those between G. hirsutum and G. arboretum or G. raimondii ranged from 0 to 0.8. Those between G. barbadense and G. arboreum or G. raimondii ranged from 0 to 0.6, and the values between At and Dt paralogous genes in G. hirsutum and G. barbadense ranged 0.07 to 0.76 and 0.02 to 0.52, respectively (Fig. 5, supplementary file 3). These results indicated that the FBP genes in these four Gossypium species were under purifying selection.
FBP gene expression in fiber development and in response to biotic and abiotic stresses
To explore the potential function of FBP genes in the growth and development of cotton fibers, we downloaded cotton fiber transcriptome data from the NCBI SRA database and reanalyzed the expression profiling of FBP genes. The results of FBP gene expression analysis showed that the homologous genes GH_A02G0701.1 and GH_D02G0715.1 from G. hirsutum, and GB_A02G0693.1 and GB_D02G0741.1 from G. barbadense had higher FPKM values in developing fibers at 20 days post-anthesis (DPA) and 25 DPA (supplementary file 4). The homologous genes GH_A02G1268.1 and GB_A02G1288.1 had high expression FPKM values in the early stage of the fiber development (0 DPA and 1 DPA ovule) (Fig. 6a, b). The expression of GH_D02G0715.1 and GH_A02G0701.1 in the secondary cell wall synthesis stage of fiber development through qRT-PCR validation assays were consistent with in silico transcriptome analysis (Fig. 6c, d).
Expression levels of FBP genes in different stages of cotton fiber development. a Transcriptome analysis of FBP genes expression levels during fiber development in G. hirsutum; b Transcriptome analysis of FBP genes expression levels during fiber development in G. barbadense; c qRT-PCR validation of GH_D02G0715.1; d qRT-PCR validation of GH_A02G0701.1
In plant response to Verticillium wilt stress, the FPKM values of the FBP gene family members that were extracted from the previously mentioned transcriptome data showed that the homologous genes GH_A04G1526.1 and GH_D04G1869.1 had much higher expression values at 24 and 48 h after inoculation (HAI) with Verticillium dahliae, with their highest peaks being reached at 24 HAI (Fig. 7a, supplementary file 4). These results suggested a certain biological function of FBP genes in plant responses to Verticillium wilt stress.
Expression profiling of FBP genes in response to Verticillium wilt stress. a Result of transcriptome analysis, Z represents the susceptible line CCRI36, C represents the resistant line MBI8255 and 0, 24 and 48 represent hours after inoculation with V. dahliae; b qRT-PCR results from GH_A04G1526.1; c qRT-PCR results from GH_D04G1869.1. The red bars represent Jimian 11 (J11) and the blue bars represent ZZM
The results of qRT-PCR analysis showed that both GH_A04G1526.1 and GH_D04G1869.1 had different expression behaviors in root tissues between susceptible and resistant cultivars at different developmental stages of V. dahliae after inoculation. In the VW tolerant cultivar Jimian 11(J11), both GH_A04G1526.1 and GH_D04G1869.1 had immediate responses to inoculation with V. dahliae and their expression levels reached a maximum at 12 HAI. The levels then dropped rapidly and maintained fairly low expression levels (Fig. 7b and c). In the VW susceptible cultivar ZZM, GH_A04G1526.1 and GH_D04G1869.1 acted differently, with GH_A04G1526.1 slightly increasing its expression after inoculation up to 48 HAI, followed by its expression increasing rapidly and reaching a peak at 72 HAI (Fig. 7b), while GH_D04G1869.1 maintained low expression throughout the entire experimental procedure (Fig. 7c). These different responses suggested that GH_A04G1526.1 might take part in resistant reactions, while GH_D04G1869.1 participated in susceptible reactions to Verticillium wilt in cotton.
The responses of FBP genes to salt stress were also evaluated using RNA transcriptome data analysis [46] under salt stress (Fig. 8, supplementary file 4). Our transcriptome analysis indicated that six members of the FBP family, GH_A10G2530.1, GH_D10G2661.1, GH_A11G3741.1, GH_D11G3768.1, GH_A02G1268.1, and GH_D03G0740.1, had significantly higher responsive expression to salt stress treatments in foliage and two members, GH_A04G1526.1 and GH_D04G1869.1, had significantly higher responsive expression in roots (Fig. 8). In the salt susceptible cultivar CCRI12, the tested genes that had expressions in foliage had similar expression tendencies in responses to salt pressure. Their expressions were significantly inhibited within 3 h after salt stress was imposed. This inhibition continued and reached its highest at 12 h after the initiation of stress. After this time, as time proceeded, the plant began to develop some sorts of “adaption” mechanisms, and their expression recovered to a certain level. In the salt tolerant semi-wild species MAR85, the inhibition of these genes was to a much smaller extent. It could be seen from our results that the expression levels of these genes at 12 h from salt resistant material were almost double those from the salt sensitive materials. These expression differences between two cultivars reached significant level at least in one treatment stage (Fig. 8). Both GH_A04G1526.1 and GH_D04G1869.1 had significant higher responsive expressions in root tissues of CCRI12 than in root tissues of MAR85 (Fig. 8).
Discussion
Cotton FBP genes identification
FBPase decomposes fructose 1,6-diphosphate to 6-phosphate fructose and inorganic phosphate. It provides a key substrate for sucrose synthesis in the cytoplasm, participates in the regulation of the sucrose synthesis pathway, and affects the distribution of carbohydrates. cpFBP is mainly involved in the Calvin cycle and the synthesis of starch [47], and cyFBP is mainly involved in the synthesis of sucrose [3]. Studies have revealed that two reactions with FBP isozymes are in the branching points from which their metabolites flow from the Calvin cycle into the process of either starch or sucrose synthesis. In A. thaliana, an FBP mutant resulted in the decrease in soluble sugar content and starch accumulation, and a significant increase in SOD activity [48]. The mutant also led to developmental changes including an increase in the number of root vascular bundles [48]. The cloning of the FBP gene has also been reported in several plant species including cotton, but there has been no further report in cotton regarding FBP genes or gene family.
Our study suggested that the FBP gene family maintained a certain stability in different diploid species including A. thaliana (in which four FBP genes were identified), T. cacao (five FBP genes), G. arboretum (seven FBP genes), and G. raimondii (seven FBP genes). There were no identified tandem repeats or segmental duplications in FBP family across these species (Figs. 1 and 4). The fluctuation of the environment forces organisms living in it to continuously evolve to adapt to changes [49]. Gene duplication is a basic process in genome evolution [50]. A duplicated gene may face several evolutionary fates, either becoming degraded by loss of function mutations, shared due to gene dosage effects or becoming sub−/neo-functionalized [50]. Yet the exact evolutionary events functioning on a gene are always episodic [49]. Polyploidization is one major episodic evolutionary event that can provide whole genome level genetic variation for plant adaptive evolution [51]. Even though the mechanisms of how polyploidy genomes establish their genetic structure are still unclear, such duplicated genes in polyploidy species may face the same evolutionary fates [50]. Our FBP collinearity analysis suggested that there was no tandem or segmental duplications in this FBP gene family in Gossypium species, despite the whole genome replication event due to polyploidization, which gave rise to the allotetraploid AD genome species (G. hirsutum and G. barbadense) from a natural hybridization between ancestors of G. arboreum or G. herbaceum (A group) and G. raimondii (D group) 1.7 to 1.9 million years ago [38, 40, 52, 53]. Afterwards, these species, which were involved in this hybridization event, independently evolved and were domesticated in different geographical areas [40]. Taken the findings in the current study that this FBP gene family was subject to purifying selection pressure based on their lower Ka/Ks values and that the high similarities in gene structures and cis regulatory elements in the 5′ upstream regions of each subgroup of the FBP gene family, we concluded that the FBP gene family in Gossypium genomes was evolutionarily conserved.
A noticeable fact of the collinearity analysis in our study was that some potential collinearity of FBP gene pairs between G. barbadense and G. raimondii, between G. barbadense and G. arboreum and between G. hirsutum and G. raimondii, were lost (Fig. 4c). These findings were supported by their independent evolutions after phylogenesis of each species. These results also implied that the FBP gene members in G. barbadense may have undergone a faster evolution than those on the rest of the Gossypium species in this study. This result was highly consistent with previous findings [54,55,56]. Moreover, we also demonstrated additional structural rearrangements in the At subgenome rather than in the Dt subgenome of G. hirsutum [55]. Evidence showed asymmetric subgenome domestication for directional selection towards fiber length [56]. NAC family genes in the At and Dt subgenomes displayed asymmetric molecular evolution in terms of gene loss rates, evolutionary rates, and expression levels [54]. Recent evidence has demonstrated a faster evolution rate in allotetraploid cotton than in diploid cotton, in the At subgenome rather than in the Dt subgenome, and in G. barbadense than in G. hirsutum [40].
Evidence has demonstrated that both G. hirsutum and G. barbadense were from one transoceanic hybridization event between two ancestors of diploid species G. arboreum or G. herbaceum and G. raimondii [52, 53]. Through evolutionary analysis of the genomic sequence, we also domonstrated that after diploid cotton differentiated from a common ancestor of cocoa, and five or more genome-wide replication events occurred [38]. Actually, although this allotetraploid cotton species had conserved gene order and collinearity between the A and D subgenomes [24], there were at least 9 translocations and 28 inversions identified in G. hirsutum draft genome [38]. A recent study confirmed these translocations between the A genome and the D genome in diploid cotton [40]. Previous comparative studies demonstrated that, in Gossypium, chromosomes D03 of G. raimondii, A02 of G. arboreum, GhAt03 of G. hirsutum, and GbAt03 of G. barbadense were homologous [40]. A reciprocal translocation event between chromosome A01 and A02 in diploid G. arboretum was estimated before the ancestor of the extent domesticated tetraploid cotton was formed [38, 40]. Our results revealed that the genes Gorai.002G055400.1 in D02, Ga02G0778.1 in A02, GH_A02G1268.1 in GhAt02, GH_D03G0740.1 in GhDt03, GB_A02G1288.1 in GbAt02, and GB_D03G0699.1 in GbDt03 were homologous genes (Fig. 4). This fact demonstrated that the gene Ga02G0778.1 in A02 was located on a DNA fragment that was translocated from A01 to A02 (Fig. 6a, b). How these translocations affect the genes expression patterns is theretofore still unknown. We did, however, demonstrate a significant expression profiling difference between these orthologous genes regardless of whether they were on the translocated fragment.
Functional biodiversity of FBP genes in Gossypium species
FBPs in our study were mainly sorted into two groups based on their subcellular compartmentalization, which conditioned their respective functions and regulatory mechanisms [7]. cpFBP is a key carbon-metabolizing enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to fructose-6-phosphate in the Calvin cycle and eventually to starch, while cyFBP a key enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of triose phosphates to sucrose in the sucrose-biosynthesis pathway [7]. In the animal kingdom, FBP was found to be involved in various disease reactions, while in plants, it has been demonstrated to be involved in sugar partitioning [7], and thus, participates in plant growth [15, 17], as well as plant responses to biotic and abiotic stresses [14]. In the current study, we identified elevated expression of FBP genes during Gossypium fiber development (Fig. 6), in response to salt treatment (Fig. 8), and in response to V. dahliae inoculation (Fig. 7).
Cotton fibers are formed by a single ovule outer bead epidermal cell through a specialized process of initial differentiation, elongation, thickening, and dehydration to form mature epidermal fibers [19, 52, 57, 58]. The onset of cotton fiber differentiation usually occurs near the day of flowering (0 DPA). These initially differentiated fibrocytes develop into fiber cells. The secondary expansion of epidemic cells is initiated after 7 to 10 DPA, and these cells gradually develop into fuzz that is attached to the surface of a seed [57,58,59]. Factors that influence the initiation, differentiation, and development of fibers include phytohormones, such as IAA and GA, and brassinolactone, as well as transcription factors [60,61,62,63]. The arrangement of cellulose deposition plays an important role in the formation of fiber strength and fineness [64, 65]. It has been demonstrated that the sucrose content in the developing fibers of immature-fiber-mutants are significantly lower than that of TM-1 [66]. This could be explained by the finding that sucrose, which is imported into developing fiber cells, is the major carbon source for cellulose synthesis and energy production there. Sucrose, together with K+ and malate, also provides the major active osmotic solutes required to maintain cell turgor for fiber elongation [30]. It has also been demonstrated that suppressing GhSCP2D expression in cotton fiber eventually activates sucrose transporter genes such as SUTs and SWEETs in early fiber developmental stages [67]. The transcription factor GhMYB212 was also demonstrated to be involved in sucrose transport into elongating fiber cells [26]. A sufficient and sustainable supply of this sugar is essential for fiber development. Here we demonstrated high expression of some cyFBP genes, including GH_A02G0701.1, GH_D02G0715.1, and GH_A02G1268.1, in developing cotton fibers, which hinted that these cyFBP genes probably assumed the responsibility of maintaining the supply of sucrose in developing fiber cells, especially during late secondary cell wall thickness stages.
Verticillium wilt is the most important disease restricting cotton production due to its serious impacts on cotton yield and fiber quality [68]. Bioinformatic analysis revealed that the 5′-upstream regulatory regions of cyFBP genes in the current study, in particular in GH_A04G1526.1 and GH_D04G1869.1 (Fig. 3), harbor pathogen-induced, cis-acting elements, including W-boxes, GCC-motifs, TC-rich repeats, JERE-motifs, Gstl-motifs and D-motif components, G boxes, GT-1, GCC boxes and S boxes [69,70,71,72]. These findings hinted that these cyFBP genes affect a certain impact on plant responses to the onset of Verticillium wilt. It is generally recognized that the responses of cotton plant to Verticillium wilt are mainly accomplished by thickening the cell wall and blocking the catheter, which includes gel formation, epidermal lignification, and internal tissue cork modification to form an invasion plugging body, which prevents the spread of the pathogen in the plant and confines the invading V. daliae to a restricted local area [73]. After infection with V. daliae, corresponding changes in cotton plant metabolism also include the biosynthetic enhancement of lignin, phytoalexin, tannin, polysaccharide, gossypol, and lipids [70, 74]. Lignification of the cell wall enhances its mechanical resistance to the penetration of fungal appressoria [75]. The lignin-based disease resistance mechanisms are very important in the processes of plant pathogenic microorganism interactions [75]. Lignification has been extensively studied in cotton resistance [76,77,78], and tolerance to salt stress [79]. Actually, evidence suggests that increasing metabolizable sugar content should positively influence the abundance of lignins. Researchers have speculated that there also may be a mechanism in plants that senses changes in sugar content and regulates lignin biosynthesis [80].
In the current study, we identified significant differences in the inhibition of both cpFBP and cyFBP gene expression levels between CRI12, an upland cotton cultivar, and MAR85, a semi-wild relative of upland cotton (Fig. 8). Previous studies revealed that a cpFBP gene from Oriza sativa was more sensitive to salt stress treatments than that from its close halophytic relative, Porteresia coarctata [81, 82]. The cpFBP genes from the two plants were determined to have five amino acid residue differences [83]. Xiao et al. [14] detected a significant inhibition of PhcpFBP gene expression at the early stages of high temperature stress, while with persistent high temperature stress, the expression of PhcpFBP gradually resumed a normal level. Hark et al. [84] determined that the cyFBP gene was not expressed continuously in severe water stress, although a low level of enzyme activity was still present (33% of control). These studies indicated that both the cpFBP and cyFBP genes might be involved in plant responses to salt stress in one way or another. At the same time, the genes that have elevated expressions in response to inoculation with V. daliae also showed responsive expression to salt treatment (Fig. 8). This implies that the pathways these genes catalyze might be correlated to plant responses to both salt stress and V. daliae inoculation.
Conclusions
In this study, a total of 41 FBP genes were identified in four cotton species, distributed to six chromosomes in diploid cotton and 11 chromosomes in tetraploid cotton, and could be classified into two classes. There were large translocations between A02 and A03 chromosomes in tetraploid cotton and there was an inversion translocation on the A02 and D02 homologous chromosomes in diploid cotton, meaning the collinearity of the FBP genes changed. Through our results from RNA-seq and qRT-PCR, we know that the different FBP genes had different functions, not only affecting fiber development, but also the response to Verticillium wilt and salt stress. Additionally, GARE-motif may affect gene expression during the fiber development. Genes of the same subclass have the same motif, gene structure, and similar cis-acting elements, meaning they have similar functions. All of these results provide a foundation for further study on the function of the FBP genes in cotton fiber development and environmental adaptability.
Methods
Plant growth and tissue sampling
Fiber samples
The G. hirsutum cultivars ZR014121 (The National Cotton Germplasm Medium-term Bank of China, accession number ZM115357) and EZ60 (The National Cotton Germplasm Medium-term Bank of China, accession number M116025) were grown in the experimental farm of the Institute of Cotton Research, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences in Anyang, Henan, China. The experimental cultivars were planted in a scale of ten rows with row-length of 5 m, row-spacing of 0.8 m and plant-spacing of 0.2 m. Three repeats for each cultivar were planted. The flowers were tagged on the day of anthesis and that day was regarded as 0 DPA. Flowers and developing bolls were sampled on 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, and 28 DPA from the tagged flowers and the ovules and developing fibers were harvested from the developing bolls and samples were immediately dipped in liquid nitrogen and stored at − 80 °C for future use.
Root samples after Verticillium dahliae inoculation
The G. hirsutum cultivars Jimian 11 (J11) (The National Cotton Germplasm Medium-term Bank of China, accession number M110861), which is tolerant to V. dahliae, and ZZM (The National Cotton Germplasm Medium-term Bank of China, accession number M115705), which is susceptible to V. dahlia, were used in the study. The plant materials were grown in the green house in the Institute laboratory in three repeats. For each repeat, five uniform seedlings were maintained in each treatment. At the two-leaf stage, the cotton plants were inoculated with strain vd080 of V. dahliae by root-dips. Roots were sampled at 0 h (0 H), 6 H, 12 H, 24 H, 36 H, 48 H, 72 H, and 96 H after inoculation. Three replicates were collected and immediately stored at − 80 °C.
Transcriptome analyses and quantitative real-time PCR
Transcriptome data of cotton fiber development of G. hirsutum TM-1 and G. barbadense Hai7124 were downloaded (accession number PRJNA490626, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/ PRJNA490626) from the Sequence Read Archive (SRA) of the NCBI database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) [40]. Raw read data (Sra) were converted to Fastq data using Fastq-dump, and Fastq data were filtered using Trimmomatic-0.36 to remove residues and low quality reads. The filtered data were then assembled from scratch using Trinity, the transcripts were assembled, and the reads were then posted back to the reference genome to calculate expression. After FPKM values were obtained, a heat map was generated using MEV 4.0 software [85].
The expression levels of the members of the G. hirsutum FBP gene family were extracted and re-analyzed from the transcriptome data of MBI8255 and CCRI36 after Verticillium dahliae inoculation using high-throughput sequencing methods described in a previous study [86]. The transcriptome data from CRI12 and MAR85 in salt stress were kindly provided by Dr. Liu’s Lab [46]. The expression heat map of each member of the G. hirsutum FBP gene family was created using MEV 4.0 software [85].
Total RNA samples of cotton fiber and roots were extracted using an RNAprep Pure Plant Kit from Tiangen Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China) and were visualized on 1% agarose gels. cDNA was synthesized using a FastQuant RT Kit (Tiangen Biotech (Beijing) Co., Ltd.). Primer premier 5.0 software was used to design gene specific primers (Supplementary file 5) for fluorescent quantitative PCR based on full-length gene cDNA. The GhHistone3 gene used as an internal reference gene was downloaded from the NCBI Nucleotide database (accession number AF024716). qRT-PCR was performed using a LightCycler® 480 II Real-Time PCR Instrument (Basel Roche, Switzerland). The expression levels of the genes were calculated using the 2-ΔΔCT method, with three independent PCR amplifications [87].
Identification of cotton FBP genes
The latest versions of the genomes of four cotton species were downloaded from CottonFGD (https://cottonfgd.org/) [88], including G. hirsutum (https://cottonfgd.org/about/download/assembly/genome.Ghir.ZJU.fa.gz), G. barbadense (https://cottonfgd.org/about/download/assembly/genome.Gbar.ZJU.fa.gz), G. arboreum (https://cottonfgd.org/about/download/assembly/genome.Garb.CRI.fa.gz), G. raimondii (https://cottonfgd.org/about/download/assembly/genome.Grai.JGI.fa.gz). Some of the genomes for comparative analysis, including T. cacao (Tcacao/v2.1, https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/portal/pages/dynamicOrganismDownload.jsf?organism=Tcacao#) [89], Oryza sativa (Osativa/v7.0, https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/portal/pages/dynamicOrganismDownload.jsf?organism=Osativa#) [90], A. thaliana (Athaliana/TAIR10, https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/portal/pages/dynamicOrganismDownload.jsf?organism=Athaliana#) [91], P. trichocarpa (Ppatens/v3.3, https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/portal/pages/dynamicOrganismDownload.jsf?organism=Ptrichocarpa#) [92], V. vinifera (Vvinifera/v2.1, https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/portal/pages/dynamicOrganismDownload.jsf?organism=Vvinifera#) [93], S. moellendorffii (Smoellendorffii/v1.0, https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/portal/pages/dynamicOrganismDownload.jsf?organism=Smoellendorffii#) [94], Z. mays (ZmaysPH207/v1.1, https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/portal/pages/dynamicOrganismDownload.jsf?organism=ZmaysPH207#) [95], G. max (Gmax/Wm82.a4.v1, https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/portal/pages/dynamicOrganismDownload.jsf?organism=Gmax#) [96], and P. patens (Ppatens/v3.3, https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/portal/pages/dynamicOrganismDownload.jsf?organism=Ppatens#) [97], were downloaded from the ePhytozome V12.1 database (http://www.phytozome.net). A hidden Markov model (HMM) profile (PF00316) was downloaded from EMBL-EBI (http://pfam.xfam.org/family/PF00316/hmm). The hmmsearch program in HMMER 3.0 software [98] was then used to search for protein sequences of these four Gossypium species using Ces.hmm as a model and --cut_ga as a parameter. The relative molecular weight and the theoretical isoelectric point prediction of the obtained amino acid sequences of FBP proteins were performed using the ExPASy (http://expasy.org/) online database.
FBP gene family system evolution, gene structure, and chromosomal distribution analysis
Multi-sequence alignments of all FBP protein sequences were performed using Clustal X [99], and phylogenetic trees of related proteins were constructed using the MEGA software proximity method (version 6.06) (Neighbor-Joining, NJ) [100], with the calibration parameter Bootstrap being set to 1000. The structure of the candidate genes was analyzed using the online software GSDS 2.0 (http://gsds.cbi.pku.edu.cn/) [101]. The MEME online tool (http://meme-suite.org/) was used to analyze the conserved motifs of the amino acid sequences (Motif), in which the parameter settings were as follows: the minimum length of the conserved motif was six, the maximum length was fifty, and the maximum motif number was ten.
Collinearity and selection pressure analysis
To determine whether the FBP gene family expanded through segmental duplication or tandemduplication events, a collinear analysis was completed with an all-to-all BLAST array (E-value of 1e-5) in the MCScan program [102]. Selection pressure analysis was performed by calculation of the Ka (non-synonymous substitution rate) and Ks (synonymous substitution rate) values of homologous genes using KaKs_Calculator 2.0 software [103].
Prediction of cis-acting elements in cotton FBP gene promoters
Two thousand bp upstream sequences of the candidate genes were extracted from the genome sequences of the four Gossypium species. Cis-acting elements were predicted using online software PLANT CARE (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/Html/) [104].
Availability of data and materials
The latest versions of the genome of four cotton species were downloaded from CottonFGD (https://cottonfgd.org/), including G. hirsutum (https://cottonfgd.org/about/download/assembly/genome.Ghir.ZJU.fa.gz), G. barbadense (https://cottonfgd.org/about/download/assembly/genome.Gbar.ZJU.fa.gz), G. arboreum (https://cottonfgd.org/about/download/assembly/genome.Garb.CRI.fa.gz), G. raimondii (https://cottonfgd.org/about/download/assembly/genome.Grai.JGI.fa.gz). Some of the genomes for comparison analysis, including T. cacao (Tcacao/v2.1, https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/portal/pages/dynamicOrganismDownload.jsf?organism=Tcacao#), O. sativa (Osativa/v7.0, https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/portal/pages/dynamicOrganismDownload.jsf?organism=Osativa#), A. thaliana (Athaliana/TAIR10, https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/portal/pages/dynamicOrganismDownload.jsf?organism=Athaliana#), P. trichocarpa (Ptrichocarpa/v3.1, https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/portal/pages/dynamicOrganismDownload.jsf?organism=Ptrichocarpa#), V. vinifera (Vvinifera/v2.1, https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/portal/pages/dynamicOrganismDownload.jsf?organism=Vvinifera#), S. moellendorffii (Smoellendorffii/v1.0, https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/portal/pages/dynamicOrganismDownload.jsf?organism=Smoellendorffii#), Z. mays (ZmaysPH207/v1.1, https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/portal/pages/dynamicOrganismDownload.jsf?organism=ZmaysPH207#), G. max (Gmax/Wm82.a4.v1, https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/portal/pages/dynamicOrganismDownload.jsf?organism=Gmax#) and P. patens (Ppatens/v3.3, https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/portal/pages/dynamicOrganismDownload.jsf?organism=Ppatens#) were downloaded from the ePhytozome V12.1 database (http://www.phytozome.net).Transcriptome data of cotton fiber development of G. hirsutum TM-1 and G. barbadense Hai7124 was downloaded (accession number PRJNA490626, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/PRJNA490626) from the NCBI BioProject database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/)”. The GhHistone3 gene dataset was downloaded from the NCBI Nucleotide database (accession number AF024716,https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/AF024716).
All extra data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- aa:
-
Amino acid
- DPA:
-
Day post anthesis
- Ga:
-
Gossypium arboreum
- Gb:
-
Gossypium barbadense
- Gh:
-
Gossypium hirsutum
- Gr:
-
Gossypium raimondii
- Ka:
-
Nonsynonymous substitution rate
- Ks:
-
Synonymous substitution rate
- FBP:
-
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
- SPS:
-
Sucrose phosphate synthase
References
Al-Robaiy S, Eschrich K. Rat muscle fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase: cloning of the cDNA, expression of the recombinant enzyme, and expression analysis in different tissues. Biol Chem. 1999;380(9):1079–85.
Zimmermann G, Kelly GJ, Latzko E. Efficient purification and molecular properties of spinach chloroplast fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase. Eur J Biochem. 1976;70(2):361–7.
Daie J. Cytosolic fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase: a key enzyme in the sucrose biosynthetic pathway. Photosynth Res. 1993;38(1):5–14.
Nel WT. S. E., Plant fructose-1,6-bisphosphatases: characteristics and properties. Int J BioChemiPhysics. 1992;24(8):1267–83.
Anderson LE, Yousefzai R, Ringenberg MR, Carol AA. Both chloroplastic and cytosolic fructose bisphosphatase isozymes are present in the pea leaf nucleus. Plant Sci. 2004;166(3):721–30.
Schnarrenberger C, Martin W. The Calvin cycle-a historical perspective. Photosynthetica. 1997;33:331–45..
Serrato AJ, de Dios Barajas-Lopez J, Chueca A, Sahrawy M. Changing sugar partitioning in FBPase-manipulated plants. J Exp Bot. 2009;60(10):2923–31.
Huber SC, Huber JL. Role of sucrose-phosphate synthase in sucrose metabolism in leaves. Plant Physiol. 1992;99(4):1275–8.
Hur Y, Unger EA, Vasconcelos AC. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding cytosolic fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase from spinach. Plant Mol Biol. 1992;18(4):799–802.
Khayat E, Harn C, Daie J. Purification and light-dependent molecular modulation of the cytosolic Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphatase in Sugarbeet leaves. Plant Physiol. 1993;101(1):57–64.
Strand A, Zrenner R, Trevanion S, Stitt M, Gustafsson P, Gardestrom P. Decreased expression of two key enzymes in the sucrose biosynthesis pathway, cytosolic fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase and sucrose phosphate synthase, has remarkably different consequences for photosynthetic carbon metabolism in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2000;23(6):759–70.
Jang HK, Lee SW, Lee YH, Hahn TR. Purification and characterization of a recombinant pea cytoplasmic fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. Protein Expr Purif. 2003;28(1):42–8.
Xu W, Wang C, Xu X, Cai C, Guo W. Cloning and expression analysis of a novel gene encoding fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase in cotton. Cotton Sci. 2013;25:549–56..
Xiao H, Chen C, Xu Y, Ji D, Xie C. Cloning and expression analysis of the chloroplast fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase gene from Pyropia haitanensis. Acta Oceanol Sin. 2014;33(4):92–100.
Cho MH, Jang A, Bhoo SH, Jeon JS, Hahn TR. Manipulation of triose phosphate/phosphate translocator and cytosolic fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase, the key components in photosynthetic sucrose synthesis, enhances the source capacity of transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Photosynth Res. 2012;111(3):261–8.
Zrenner R, Krause KP, Apel P, Sonnewald U. Reduction of the cytosolic fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase in transgenic potato plants limits photosynthetic sucrose biosynthesis with no impact on plant growth and tuber yield. Plant J. 1996;9(5):671–81.
Lee SK, Jeon JS, Bornke F, Voll L, Cho JI, Goh CH, Jeong SW, Park YI, Kim SJ, Choi SB, Miyao A, Hirochika H, An G, Cho MH, Bhoo SH, Sonnewald U, Hahn TR. Loss of cytosolic fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase limits photosynthetic sucrose synthesis and causes severe growth retardations in rice (Oryza sativa). Plant Cell Environ. 2008;31(12):1851–63.
Obiadalla-Ali H, Fernie AR, Lytovchenko A, Kossmann J, Lloyd JR. Inhibition of chloroplastic fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase in tomato fruits leads to decreased fruit size, but only small changes in carbohydrate metabolism. Planta. 2004;219(3):533–40.
BASRA A S, M.C.P. Development of cotton fiber[M]. Int Rev Cytol. 1984;89:65–113.
Zhang Z, Li J, Jamshed Y M, Shi A, Liu J, Gong S, Wang J, Zhang F, Sun F, Jia Q, Ge L, Fan Z, Zhang J, Pan S, Fan Y, Wang Q, Lu R, Liu X, Deng X, Zou X, Jiang P, Liu P, Li MS, Iqbal C, Zhang J, Zou H, Chen Q, Tian X, Jia B, Wang N, Ai G, Feng Y, Wang M, Hong S, Li W, Lian B, Wu J, Hua C, Zhang J, Huang A, Xu H, Gong SW, Yuan Y. Genome-wide quantitative trait loci reveal the genetic basis of cotton fibre quality and yield-related traits in a Gossypium hirsutum recombinant inbred line population. Plant Biotechnol J. 2020;18(1):239–53.
Wang F, Zhang J, Chen Y, Zhang C, Gong J, Song Z, Zhou J, Wang J, Zhao C, Jiao M, Liu A, Du Z, Yuan Y, Fan S, Zhang J. Identification of candidate genes for key fibre-related QTLs and derivation of favourable alleles in Gossypium hirsutum recombinant inbred lines with G. barbadense introgressions. Plant Biotechnol J. 2020;18(3):707–20.
Deng X, Gong J, Liu A, Shi Y, Gong W, Ge Q, Li J, Shang H, Wu Y, Yuan Y. QTL mapping for fiber quality and yield-related traits across multiple generations in segregating population of CCRI 70. J Cotton Res. 2019;2:13.
Du X, Huang G, He S, Yang Z, Sun G, Ma X, Li N, Zhang X, Sun J, Liu M, Jia Y, Pan Z, Gong W, Liu Z, Zhu H, Ma L, Liu F, Yang D, Wang F, Fan W, Gong Q, Peng Z, Wang L, Wang X, Xu S, Shang H, Lu C, Zheng H, Huang S, Lin T, Zhu Y, Li F. Resequencing of 243 diploid cotton accessions based on an updated a genome identifies the genetic basis of key agronomic traits. Nat Genet. 2018;50(6):796–802.
Ma Z, He S, Wang X, Sun J, Zhang Y, Zhang G, Wu L, Li Z, Liu Z, Sun G, Yan Y, Jia Y, Yang J, Pan Z, Gu Q, Li X, Sun Z, Dai P, Liu Z, Gong W, Wu J, Wang M, Liu H, Feng K, Ke H, Wang J, Lan H, Wang G, Peng J, Wang N, Wang L, Pang B, Peng Z, Li R, Tian S, Du X. Resequencing a core collection of upland cotton identifies genomic variation and loci influencing fiber quality and yield. Nat Genet. 2018;50(6):803–13.
Su J, Li L, Zhang C, Wang C, Gu L, Wang H, Wei H, Liu Q, Huang L, Yu S. Genome-wide association study identified genetic variations and candidate genes for plant architecture component traits in Chinese upland cotton. Theor Appl Genet. 2018;131(6):1299–314.
Sun Z, Wang X, Liu Z, Gu Q, Zhang Y, Li Z, Ke H, Yang J, Wu J, Wu L, Zhang G, Zhang C, Ma Z. A genome-wide association study uncovers novel genomic regions and candidate genes of yield-related traits in upland cotton. Theor Appl Genet. 2018;131(11):2413–25.
Li Y, Wang NN, Wang Y, Liu D, Gao Y, Li L, Li XB. The cotton XLIM protein (GhXLIM6) is required for fiber development via maintaining dynamic F-actin cytoskeleton and modulating cellulose biosynthesis. Plant J. 2018;96(6):1269–82.
Zhang J, Huang GQ, Zou D, Yan JQ, Li Y, Hu S, Li XB. The cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) NAC transcription factor (FSN1) as a positive regulator participates in controlling secondary cell wall biosynthesis and modification of fibers. New Phytol. 2018;217(2):625–40.
Zhao B, Cao JF, Hu GJ, Chen ZW, Wang LY, Shangguan XX, Wang LJ, Mao YB, Zhang TZ, Wendel JF, Chen XY. Core cis-element variation confers subgenome-biased expression of a transcription factor that functions in cotton fiber elongation. New Phytol. 2018;218(3):1061–75.
Wang L, Ruan YL. Unraveling mechanisms of cell expansion linking solute transport, metabolism, plasmodesmtal gating and cell wall dynamics. Plant Signal Behav. 2010;5(12):1561–4.
Cai Y, He X, Mo J, Sun Q, Yang J, Liu J, Molecular research and genetic engineering of resistance to Verticillium wilt in cotton: A review. African Journal of Biotechnology. 2009;8(25):7363–7372.
Ashraf M, Ahmad S. Infuence of sodium chloride on ion accumulation, yield components and fiber characteristics in salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive lines of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Field Crop Res. 2000;66:115–27.
Abdelraheem A, Esmaeili N, O’Connell M, Zhang J. Progress and perspective on drought and salt stress tolerance in cotton. Ind Crop Prod. 2019;130:118–29.
Paterson AH, Wendel JF, Gundlach H, Guo H, Jenkins J, Jin D, Llewellyn D, Showmaker KC, Shu S, Udall J, Yoo MJ, Byers R, Chen W, Doron-Faigenboim A, Duke MV, Gong L, Grimwood J, Grover C, Grupp K, Hu G, Lee TH, Li J, Lin L, Liu T, Marler BS, Page JT, Roberts AW, Romanel E, Sanders WS, Szadkowski E, Tan X, Tang H, Xu C, Wang J, Wang Z, Zhang D, Zhang L, Ashrafi H, Bedon F, Bowers JE, Brubaker CL, Chee PW, Das S, Gingle AR, Haigler CH, Harker D, Hoffmann LV, Hovav R, Jones DC, Lemke C, Mansoor S, Rahman M, Rainville LN, Rambani A, Reddy UK, Rong JK, Saranga Y, Scheffler BE, Scheffler JA, Stelly DM, Triplett BA, Van Deynze A, Vaslin MF, Waghmare VN, Walford SA, Wright RJ, Zaki EA, Zhang T, Dennis ES, Mayer KF, Peterson DG, Rokhsar DS, Wang X, Schmutz J. Repeated polyploidization of Gossypium genomes and the evolution of spinnable cotton fibres. Nature. 2012;492(7429):423–7.
Wang K, Wang Z, Li F, Ye W, Wang J, Song G, Yue Z, Cong L, Shang H, Zhu S, Zou C, Li Q, Yuan Y, Lu C, Wei H, Gou C, Zheng Z, Yin Y, Zhang X, Liu K, Wang B, Song C, Shi N, Kohel RJ, Percy RG, Yu JZ, Zhu YX, Wang J, Yu S. The draft genome of a diploid cotton Gossypium raimondii. Nat Genet. 2012;44(10):1098–103.
Li F, Fan G, Wang K, Sun F, Yuan Y, Song G, Li Q, Ma Z, Lu C, Zou C, Chen W, Liang X, Shang H, Liu W, Shi C, Xiao G, Gou C, Ye W, Xu X, Zhang X, Wei H, Li Z, Zhang G, Wang J, Liu K, Kohel RJ, Percy RG, Yu JZ, Zhu YX, Wang J, Yu S. Genome sequence of the cultivated cotton Gossypium arboreum. Nat Genet. 2014;46(6):567–72.
Li F, Fan G, Lu C, Xiao G, Zou C, Kohel RJ, Ma Z, Shang H, Ma X, Wu J, Liang X, Huang G, Percy RG, Liu K, Yang W, Chen W, Du X, Shi C, Yuan Y, Ye W, Liu X, Zhang X, Liu W, Wei H, Wei S, Huang G, Zhang X, Zhu S, Zhang H, Sun F, Wang X, Liang J, Wang J, He Q, Huang L, Wang J, Cui J, Song G, Wang K, Xu X, Yu JZ, Zhu Y, Yu S. Genome sequence of cultivated Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum TM-1) provides insights into genome evolution. Nat Biotechnol. 2015;33(5):524–30.
Zhang T, Yhu W, Jiang L, Fang X, Guan J, Chen J, Zhang CA, Saski BE, Scheffler DM, Stelly AM, Hulse-Kemp Q, Wan B, Liu C, Liu S, Wang M, Pan Y, Wang D, Wang W, Ye L, Chang W, Zhang Q, Song RC, Kirkbride X, Chen E, Dennis DJ, Llewellyn DG, Peterson P, Thaxton DC, Jones Q, Wang X, Xu H, Zhang H, Wu L, Zhou G, Mei S, Chen Y, Tian D, Xiang X, Li J, Ding Q, Zuo L, Tao Y, Liu J, Li Y, Lin Y, Hui Z, Cao C, Cai X, Zhu Z, Jiang B, Zhou W, Li GR, Chen ZJ. Sequencing of allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. acc. TM-1) provides a resource for fiber improvement. Nat Biotechnol. 2015;33(5):531–7.
Wang M, Wang P, Lin M, Ye Z, Li G, Tu L, Shen C, Li J, Yang Q, Zhang X. Evolutionary dynamics of 3D genome architecture following polyploidization in cotton. Nat Plants. 2018;4(2):90–7.
Hu Y, Chen J, Fang L, Zhang Z, Ma W, Niu Y, Ju L, Deng J, Zhao T, Lian J, Baruch K, Fang D, Liu X, Ruan YL, Rahman MU, Han J, Wang K, Wang Q, Wu H, Mei G, Zang Y, Han Z, Xu C, Shen W, Yang D, Si Z, Dai F, Zou L, Huang F, Bai Y, Zhang Y, Brodt A, Ben-Hamo H, Zhu X, Zhou B, Guan X, Zhu S, Chen X, Zhang T. Gossypium barbadense and Gossypium hirsutum genomes provide insights into the origin and evolution of allotetraploid cotton. Nat Genet. 2019;51(4):739–48.
Liu X, Zhao B, Zheng HJ, Hu Y, Lu G, Yang CQ, Chen JD, Chen JJ, Chen DY, Zhang L, Zhou Y, Wang LJ, Guo WZ, Bai YL, Ruan JX, Shangguan XX, Mao YB, Shan CM, Jiang JP, Zhu YQ, Jin L, Kang H, Chen ST, He XL, Wang R, Wang YZ, Chen J, Wang LJ, Yu ST, Wang BY, Wei J, Song SC, Lu XY, Gao ZC, Gu WY, Deng X, Ma D, Wang S, Liang WH, Fang L, Cai CP, Zhu XF, Zhou BL, Chen ZJ, Xu SH, Zhang YG, Wang SY, Zhang TZ, Zhao GP, Chen XY. Gossypium barbadense genome sequence provides insight into the evolution of extra-long staple fiber and specialized metabolites. Sci Rep. 2015;5:14139.
WENDEL JF. New World tetraploid cottons contain Old World cytoplasm. Proc Nati Acad Sci. 1989;86:4132–6.
Cannon SB, Mitra A, Baumgarten A, Young ND, May G. The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2004;4:10.
Schaper E, Anisimova M. The evolution and function of protein tandem repeats in plants. New Phytol. 2015;206(1):397–410.
Hurst D. The Ka_Ks ratio_diagnosing the form of sequence evolution. Trends Genet. 2002;18(9):486–7.
Xu Y, Magwanga RO, Cai X, Zhou Z, Wang X, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Jin D, Guo X, Wei Y, Li Z, Wang K, Liu F. Deep Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Network Evolution, Response to Abiotic Stress, and Regulation of Fiber Development in Cotton. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:1863.
Chueca A, Sahrawy M, Pagano EA, Lopez Gorge J. Chloroplast fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase: structure and function. Photosynth Res. 2002;74(3):235–49.
Rojas-Gonzalez JA, Soto-Suarez M, Garcia-Diaz A, Romero-Puertas MC, Sandalio LM, Merida A, Thormahlen I, Geigenberger P, Serrato AJ, Sahrawy M. Disruption of both chloroplastic and cytosolic FBPase genes results in a dwarf phenotype and important starch and metabolite changes in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot. 2015;66(9):2673–89.
Guo H, Jiao Y, Tan X, Wang X, Huang X, Jin H, Paterson AH. Gene duplication and genetic innovation in cereal genomes. Genome Res. 2019;29(2):261–9.
Lan X, Pritchard JK. Coregulation of tandem duplicate genes slows evolution of subfunctionalization in mammals. Science. 2016;352(6288):1009–13.
Liu S, Y Liu X, Yang C, Tong D, Edwards IA, Parkin M, Zhao J, Ma J, Yu S, Huang X, Wang J, Wang K, Lu Z, Fang I, Bancroft TJ, Yang Q, Hu X, Wang Z, Yue H, Li L, Yang J, Wu Q, Zhou W, Wang GJ, King JC, Pires C, Lu Z, Wu P, Sampath Z, Wang H, Guo S, Pan L, Yang J, Min D, Zhang D, Jin W, Li H, Belcram J, Tu M, Guan C, Qi D, Du J, Li L, Jiang J, Batley AG, Sharpe BS, Park P, Ruperao F, Cheng NE, Waminal Y, Huang C, Dong L, Wang J, Li Z, Hu M, Huang ZY, Huang J, Shi J, Mei D, Jliu TH, Lee J, Wang H, Jin Z, Li X, Li J, Zhang L, Xiao Y, Zhou Z, Liu X, Liu R, Qin X, Tang W, Liu Y, Wang Y, Zhang J, Lee HH, Kim F, Denoeud X, Xu X, Liang W, Hua X, Wang J, Wang B, Chalhoub B, Paterson AH. The Brassica oleracea genome reveals the asymmetrical evolution of polyploid genomes. Nat Commun. 2014;5:3930.
Wendel JF, Schnabel A, Seelanan T. An Unusual Ribosomal DNA Sequence from Gossypium gossypioides Reveals Ancient, Cryptic, Intergenomic Introgression. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 1995;4(3):298–313..
Wendel JF. New World tetraploid cottons contain Old World cytoplasm. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1989;86:4132–6..
Fan K, Li F, Chen J, Li Z, Lin W, Cai S, Liu J, Lin W. Asymmetric evolution and expansion of the NAC transcription factor in Polyploidized cotton. Front Plant Sci. 2018;9:47.
Fang L, Guan X, Zhang T. Asymmetric evolution and domestication in allotetraploid cotton ( Gossypium hirsutum L.). The Crop Journal. 2017;5(2):159–65.
Wang X, Guo H, Wang J, Lei T, Liu T, Wang Z, Li Y, Lee TH, Li J, Tang H, Jin D, Paterson AH. Comparative genomic de-convolution of the cotton genome revealed a decaploid ancestor and widespread chromosomal fractionation. New Phytol. 2016;209(3):1252–63.
Kim HJ, Triplett BA. Cotton Fiber growth in Planta and in vitro. Models for plant cell elongation and Cell Wall biogenesis. Plant Physiol. 2001;127(4):1361–6.
Lee JJ, Woodward AW, Chen ZJ. Gene expression changes and early events in cotton fibre development. Ann Bot. 2007;100(7):1391–401.
Guan X, Song Q, Chen ZJ. Polyploidy and small RNA regulation of cotton fiber development. Trends Plant Sci. 2014;19(8):516–28.
Beasley CA. Hormonal regulation of growth in unfertilized cotton ovules. Science. 1973;179(4077):1003–5.
Suo JF, Liang XO, Pu L, Zhang YS, Xue YB. Identification of GhMYB109 encoding a R2R3 MYB transcription factor that expressed specifically in fiber initials and elongating fibers of cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.). Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta-Gene Structure Expression. 2003;1630(1):25–34.
Luo M, Xiao YH, Li XB, Lu XF, Deng W, Li D, Hou L, Hu MY, Li Y, Pei Y. GhDET2, a steroid 5 alpha-reductase, plays an important role in cotton fiber cell initiation and elongation. Plant J. 2007;51(3):419–30.
Sun W, Gao Z, Wang J, Huang Y, Chen Y, Li J, Lv M, Wang J, Luo M, Zuo K. Cotton fiber elongation requires the transcription factor GhMYB212 to regulate sucrose transportation into expanding fibers. New Phytol. 2019;222(2):864–81.
Xu WL, Zhang DJ, Wu YF, Qin LX, Huang GQ, Li J, Li L, Li XB. Cotton PRP5 gene encoding a proline-rich protein is involved in fiber development. Plant Mol Biol. 2013;82(4–5):353–65.
Wang JA, Wang HY, Zhao PM, Han LB, Jiao GL, Zheng YY, Huang SJ, Xia GX. Overexpression of a profilin (GhPFN2) promotes the progression of developmental phases in cotton fibers. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010;51(8):1276–90.
Cheng Wang YL. Wentin Xu, Tianzhen Zhang and Wangzhen Guo, Aberrant phenotype and transcriptome expression during fiber cell wall thickening caused by the mutation of the Im gene in immature fiber (im) mutant in Gossypium hirsutum L. BMC Genomics. 2014;15.
Zhang Z, Ruan YL, Zhou N, Wang F, Guan X, Fang L, Shang X, Guo W, Zhu S, Zhang T. Suppressing a putative sterol carrier gene reduces Plasmodesmal permeability and activates sucrose transporter genes during cotton Fiber elongation. Plant Cell. 2017;29(8):2027–46.
Zhang J, Sanogo S, Flynn R, Baral JB, Bajaj S, Hughs SE, Percy RG. Germplasm evaluation and transfer of Verticillium wilt resistance from Pima (Gossypium barbadense) to upland cotton (G. hirsutum). Euphytica. 2011;187(2):147–60.
Ouriel Faktor GL, Richard A. Dixon, Chris J. lamb, The G-box and H-box in a 39 bp region of a French bean. Plant J. 1997;11:1105–13.
Rushton PJ, Reinstadler A, Lipka V, Lippok B, Somssich IE. Synthetic plant promoters containing defined regulatory elements provide novel insights into pathogen- and wound-induced signaling. Plant Cell. 2002;14(4):749–62.
Brown RL, Kazan K, McGrath KC, Maclean DJ, Manners JM. A role for the GCC-box in jasmonate-mediated activation of the PDF1.2 gene of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2003;132(2):1020–32.
Park HC, Kim ML, Kang YH, Jeon JM, Yoo JH, Kim MC, Park CY, Jeong JC, Moon BC, Lee JH, Yoon HW, Lee SH, Chung WS, Lim CO, Lee SY, Hong JC, Cho MJ. Pathogen- and NaCl-induced expression of the SCaM-4 promoter is mediated in part by a GT-1 box that interacts with a GT-1-like transcription factor. Plant Physiol. 2004;135(4):2150–61.
DeVay JE, Weir BL, Wakeman RJ, Stapleton JJ. Effects of Verticillium dahliae infection of cotton plants (Gossypium hirsutum) on potassium levels in leaf petioles. Plant Dis. 1997;81:1089–92.
Fang W, Jin ZS, Ji D. Studies on the Inheritance of Verticillium dahliae Resistance in G. hisutum and G.barbadense. Cotton Sci. 2003;15:3–7..
Huckelhoven R. Cell wall-associated mechanisms of disease resistance and susceptibility. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2007;45:101–27.
Zhang Y, Wu L, Wang X, Chen B, Zhao J, Cui J, Li Z, Yang J, Wu L, Wu J, Zhang G, Ma Z. The cotton laccase gene GhLAC15 enhances Verticillium wilt resistance via an increase in defence-induced lignification and lignin components in the cell walls of plants. Mol Plant Pathol. 2019;20(3):309–22.
Xu L, Zhu L, Tu L, Liu L, Yuan D, Jin L, Long L, Zhang X. Lignin metabolism has a central role in the resistance of cotton to the wilt fungus Verticillium dahliae as revealed by RNA-Seq-dependent transcriptional analysis and histochemistry. J Exp Bot. 2011;62(15):5607–21.
Guo J, Wang MH. Characterization of the phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene (SlPAL5) from tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Mol Biol Rep. 2009;36(6):1579–85.
Hu Q, Min L, Yang X, Jin S, Zhang L, Li Y, Ma Y, Qi X, Li D, Liu H, Lindsey K, Zhu L, Zhang X. Laccase GhLac1 modulates broad-Spectrum biotic stress tolerance via manipulating Phenylpropanoid pathway and Jasmonic acid synthesis. Plant Physiol. 2018;176(2):1808–23.
Rogers LA, Dubos C, Cullis IF, Surman C, Poole M, Willment J, Mansfield SD, Campbell MM. Light, the circadian clock, and sugar perception in the control of lignin biosynthesis. J Exp Bot. 2005;56(416):1651–563.
Bose J, Munns R, Shabala S, Gilliham M, Pogson B, Tyerman SD. Chloroplast function and ion regulation in plants growing on saline soils: lessons from halophytes. J Exp Bot. 2017;68(12):3129–43.
Ghosh S, Bagchi S, Lahiri Majumder A. Chloroplast fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase from Oryza differs in salt tolerance property from the Porteresia enzyme and is protected by osmolytes. Plant Sci. 2001;160(6):1171–81.
Chatterjee J, Patra B, Mukherjee R, Basak P, Mukherjee S, Ray S, Bhattacharyya S, Maitra S, GhoshDastidar K, Ghosh S, Sengupta S, Majumder AL. Cloning, characterization and expression of a chloroplastic fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase from Porteresia coarctata conferring salt-tolerance in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture (PCTOC). 2013;114(3):395–409.
Harn CH. Jaleh Daie I and Jang Ryol Liu, Regulation of Cytosolic Fructose-l,6-Bisphosphatase Under Water-Stressed Leaves of Sugar Beet: Protein Modification is not a Mechanism for Coarse Control. J Plant Biol. 1997;40(4):261–6.
Saeed AI, Sharov V, White J. TM4_ A Free, Open-Source System for Microarray Data Management and Analysis. BioTechniques. 2003;34:374–8..
Li PT, Rashid MHO, Chen TT, Lu QW, Ge Q, Gong WK, Liu AY, Gong JW, Shang HH, Deng XY, Li JW, Li SQ, Xiao XH, Liu RX, Zhang Q, Duan L, Zou XY, Zhang Z, Jiang X, Zhang Y, Peng RH, Shi YZ, Yuan YL. Transcriptomic and biochemical analysis of upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) and a chromosome segment substitution line from G. hirsutum x G. barbadense in response to Verticillium dahliae infection. BMC Plant Biol. 2019;19(1):19.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402–8.
Zhu T, Liang C, Meng Z, Sun G, Meng Z, Guo S, Zhang R. CottonFGD: an integrated functional genomics database for cotton. BMC Plant Biol. 2017;17(1):101.
Argout X, Salse J, Aury JM, Guiltinan MJ, Droc G, Gouzy J, Allegre M, Chaparro C, Legavre T, Maximova SN, Abrouk M, Murat F, Fouet O, Poulain J, Ruiz M, Roguet Y, Rodier-Goud M, Barbosa-Neto JF, Sabot F, Kudrna D, Ammiraju JS, Schuster SC, Carlson JE, Sallet E, Schiex T, Dievart A, Kramer M, Gelley L, Shi Z, Berard A, Viot C, Boccara M, Risterucci AM, Guignon V, Sabau X, Axtell MJ, Ma Z, Zhang Y, Brown S, Bourge M, Golser W, Song X, Clement D, Rivallan R, Tahi M, Akaza JM, Pitollat B, Gramacho K, D'Hont A, Brunel D, Infante D, Kebe I, Costet P, Wing R, McCombie WR, Guiderdoni E, Quetier F, Panaud O, Wincker P, Bocs S, Lanaud C. The genome of Theobroma cacao. Nat Genet. 2011;43(2):101–8.
Ouyang S, Zhu W, Hamilton J, Lin H, Campbell M, Childs K, Thibaud-Nissen F, Malek RL, Lee Y, Zheng L, Orvis J, Haas B, Wortman J, Buell CR. The TIGR Rice Genome annotation resource: improvements and new features. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(Database issue):D883–7.
Cao J, Schneeberger K, Ossowski S, Gunther T, Bender S, Fitz J, Koenig D, Lanz C, Stegle O, Lippert C, Wang X, Ott F, Muller J, Alonso-Blanco C, Borgwardt K, Schmid KJ, Weigel D. Whole-genome sequencing of multiple Arabidopsis thaliana populations. Nat Genet. 2011;43(10):956–63.
Tuskan GA, Difazio S, Jansson S, Bohlmann J, Grigoriev I, Hellsten U, Putnam N, Ralph S, Rombauts S, Salamov A, Schein J, Sterck L, Aerts A, Bhalerao RR, Bhalerao RP, Blaudez D, Boerjan W, Brun A, Brunner A, Busov V, Campbell M, Carlson J, Chalot M, Chapman J, Chen GL, Cooper D, Coutinho PM, Couturier J, Covert S, Cronk Q, Cunningham R, Davis J, Degroeve S, Dejardin A, Depamphilis C, Detter J, Dirks B, Dubchak I, Duplessis S, Ehlting J, Ellis B, Gendler K, Goodstein D, Gribskov M, Grimwood J, Groover A, Gunter L, Hamberger B, Heinze B, Helariutta Y, Henrissat B, Holligan D, Holt R, Huang W, Islam-Faridi N, Jones S, Jones-Rhoades M, Jorgensen R, Joshi C, Kangasjarvi J, Karlsson J, Kelleher C, Kirkpatrick R, Kirst M, Kohler A, Kalluri U, Larimer F, Leebens-Mack J, Leple JC, Locascio P, Lou Y, Lucas S, Martin F, Montanini B, Napoli C, Nelson DR, Nelson C, Nieminen K, Nilsson O, Pereda V, Peter G, Philippe R, Pilate G, Poliakov A, Razumovskaya J, Richardson P, Rinaldi C, Ritland K, Rouze P, Ryaboy D, Schmutz J, Schrader J, Segerman B, Shin H, Siddiqui A, Sterky F, Terry A, Tsai CJ, Uberbacher E, Unneberg P, Vahala J, Wall K, Wessler S, Yang G, Yin T, Douglas C, Marra M, Sandberg G, Van de Peer Y, Rokhsar D. The genome of black cottonwood, Populus trichocarpa (Torr. & Gray). Science. 2006;313(5793):1596–604.
Jaillon, O., J.M. Aury, B. Noel, A. Policriti, C. Clepet, A. Casagrande, N. Choisne, S. Aubourg, N. Vitulo, C. Jubin, A. Vezzi, F. Legeai, P. Hugueney, C. Dasilva, D. Horner, E. Mica, D. Jublot, J. Poulain, C. Bruyere, A. Billault, B. Segurens, M. Gouyvenoux, E. Ugarte, F. Cattonaro, V. Anthouard, V. Vico, C. Del Fabbro, M. Alaux, G. Di Gaspero, V. Dumas, N. Felice, S. Paillard, I. Juman, M. Moroldo, S. Scalabrin, A. Canaguier, I. Le Clainche, G. Malacrida, E. Durand, G. Pesole, V. Laucou, P. Chatelet, D. Merdinoglu, M. Delledonne, M. Pezzotti, A. Lecharny, C. Scarpelli, F. Artiguenave, M.E. Pe, G. Valle, M. Morgante, M. Caboche, A.F. Adam-Blondon, J. Weissenbach, F. Quetier, P. Wincker, and . French-Italian Public Consortium for Grapevine Genome, The gra0070evine genome sequence suggests ancestral hexaploidization in major angiosperm phyla. Nature, 2007. 449(7161): p. 463-467..
Banks JA, Nishiyama T, Hasebe M, Bowman JL, Gribskov M, dePamphilis C, Albert VA, Aono N, Aoyama T, Ambrose BA, Ashton NW, Axtell MJ, Barker E, Barker MS, Bennetzen JL, Bonawitz ND, Chapple C, Cheng C, Correa LG, Dacre M, DeBarry J, Dreyer I, Elias M, Engstrom EM, Estelle M, Feng L, Finet C, Floyd SK, Frommer WB, Fujita T, Gramzow L, Gutensohn M, Harholt J, Hattori M, Heyl A, Hirai T, Hiwatashi Y, Ishikawa M, Iwata M, Karol KG, Koehler B, Kolukisaoglu U, Kubo M, Kurata T, Lalonde S, Li K, Li Y, Litt A, Lyons E, Manning G, Maruyama T, Michael TP, Mikami K, Miyazaki S, Morinaga S, Murata T, Mueller-Roeber B, Nelson DR, Obara M, Oguri Y, Olmstead RG, Onodera N, Petersen BL, Pils B, Prigge M, Rensing SA, Riano-Pachon DM, Roberts AW, Sato Y, Scheller HV, Schulz B, Schulz C, Shakirov EV, Shibagaki N, Shinohara N, Shippen DE, Sorensen I, Sotooka R, Sugimoto N, Sugita M, Sumikawa N, Tanurdzic M, Theissen G, Ulvskov P, Wakazuki S, Weng JK, Willats WW, Wipf D, Wolf PG, Yang L, Zimmer AD, Zhu Q, Mitros T, Hellsten U, Loque D, Otillar R, Salamov A, Schmutz J, Shapiro H, Lindquist E, Lucas S, Rokhsar D, Grigoriev IV. The Selaginella genome identifies genetic changes associated with the evolution of vascular plants. Science. 2011;332(6032):960–3.
Hirsch CN, Hirsch CD, Brohammer AB, Bowman MJ, Soifer I, Barad O, Shem-Tov D, Baruch K, Lu F, Hernandez AG, Fields CJ, Wright CL, Koehler K, Springer NM, Buckler E, Buell CR, de Leon N, Kaeppler SM, Childs KL, Mikel MA. Draft assembly of elite inbred line PH207 provides insights into genomic and Transcriptome diversity in maize. Plant Cell. 2016;28(11):2700–14.
Schmutz J, Cannon SB, Schlueter J, Ma J, Mitros T, Nelson W, Hyten DL, Song Q, Thelen JJ, Cheng J, Xu D, Hellsten U, May GD, Yu Y, Sakurai T, Umezawa T, Bhattacharyya MK, Sandhu D, Valliyodan B, Lindquist E, Peto M, Grant D, Shu S, Goodstein D, Barry K, Futrell-Griggs M, Abernathy B, Du J, Tian Z, Zhu L, Gill N, Joshi T, Libault M, Sethuraman A, Zhang XC, Shinozaki K, Nguyen HT, Wing RA, Cregan P, Specht J, Grimwood J, Rokhsar D, Stacey G, Shoemaker RC, Jackson SA. Genome sequence of the palaeopolyploid soybean. Nature. 2010;463(7278):178–83.
Lang D, Ullrich KK, Murat F, Fuchs J, Jenkins J, Haas FB, Piednoel M, Gundlach H, Van Bel M, Meyberg R, Vives C, Morata J, Symeonidi A, Hiss M, Muchero W, Kamisugi Y, Saleh O, Blanc G, Decker EL, van Gessel N, Grimwood J, Hayes RD, Graham SW, Gunter LE, McDaniel SF, Hoernstein SNW, Larsson A, Li FW, Perroud PF, Phillips J, Ranjan P, Rokshar DS, Rothfels CJ, Schneider L, Shu S, Stevenson DW, Thummler F, Tillich M, Villarreal Aguilar JC, Widiez T, Wong GK, Wymore A, Zhang Y, Zimmer AD, Quatrano RS, Mayer KFX, Goodstein D, Casacuberta JM, Vandepoele K, Reski R, Cuming AC, Tuskan GA, Maumus F, Salse J, Schmutz J, Rensing SA. The Physcomitrella patens chromosome-scale assembly reveals moss genome structure and evolution. Plant J. 2018;93(3):515–33..
Finn RD, Clements J, Eddy SR. HMMER web server: interactive sequence similarity searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39(Web Server issue):29–37.
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Des G. Higgins, Multiple Sequence Alignment Using ClustalW and ClustalX. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2003;2:1–22.
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30(12):2725–9.
Hu B, Jin J, Guo AY, Zhang H, Luo J, Gao G. GSDS 2.0: an upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics. 2015;31(8):1296–7.
Wang Y, Tang H, Debarry JD, Tan X, Li J, Wang X, Lee TH, Jin H, Marler B, Guo H, Kissinger JC, Paterson AH. MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(7):e49.
Wang D, Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Zhu J, Yu J. KaKs_Calculator 2.0: a toolkit incorporating gamma-series methods and sliding window strategies. Genomics, Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2010;8(1):77–80.
Lescot M, Dehais P, Thijs G, Marchal K, Moreau Y, Van de Peer Y, Rouze P, Rombauts S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002;30(1):325–7.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was supported in part by grants from the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFD0101603, 2016YFD0100500, and 2016YFD0101401), the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program for CAAS (CAAS-ASTIP-ICRCAAS), and the Natural Science Foundation of China (31801404).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QC, YY and WG initiated the research. QG, JL, JG, and QL designed the analysis and experiments. QG, YC, and JP performed the functional analysis and molecular experiments. YS, HS, AL, XD, and PL performed genomic analyses. QG and WG drafted the manuscript. QC, YY, and WG finalized the manuscript. All authors contributed in the interpretation of results and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1
Multiple sequence alignment involving 114 sequences from the genomes of the following eight species: G. hirsutum, G. arboreum, G. barbadense, G. raimondii, A. thaliana, T. cacao, P. trichocarpa, G. max, Z. mays, V. vinifera, S. moellendorffii, P. patens, and O. sativa.
Additional file 2.
Amino acid compositions of FBP genes.
Additional file 3
Ka/Ks ratio of FBP homologous genes.
Additional file 4
The FPKM value of FBP genes in tetraploid cotton species.
Additional file 5.
The primer sequences used for qRT-PCR.
Additional file 6 Figure S1.
Logos of 10 motifs for four cotton species according to the MEME suite.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Gě, Q., Cūi, Y., Lǐ, J. et al. Disequilibrium evolution of the Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase gene family leads to their functional biodiversity in Gossypium species. BMC Genomics 21, 379 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-020-6773-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-020-6773-z