Abstract
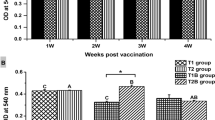
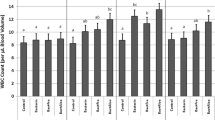
Seawater fishes are affected by a pathology commonly called ‘myxobacteriosis’, caused by Tenacibaculum maritimum (formerly Flexibacter maritimus). The disease is characterized by fin erosion and necrotic ulcers of skin and muscle, and by low but constant mortality in cultured marine fish; in Italy is one of the most important and widely spread diseases affecting sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax, gilthead seabream Sparus aurata, sharp-snouted bream Diplodus puntazzo, white bream Diplodus sargus, and six-tooted bream Dentex dentex. In order to obtain an effective vaccine against the disease, formalin killed cells (FKC), extracellular products (ECPs) and crude lipopolysaccharide (LPS) preparations were obtained from the T. maritimum strain SPVId and injected intraperi-toneally twice into the sea bass. The fish immune response to the preparations was studied: agglutinating antibody titer and in vitro phagocytosis were determined after the first and second injection in order to evaluate whether the preparations are immunogenic or not and if the booster effect took place. The results show that FKC and LPS preparations increased the antibody titer after the first injection when compared to the control sea bass. Moreover, all the preparations stimulated a secondary (booster) response. In vitro phagocytosis of the total blood was significantly higher for all the preparations when compared to the controls, but the crude LPS immunized sea bass showed the highest activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wakabayashi H, Hikida M, Masumura K. Flexibacter maritimus sp. nov., a pathogens of marine fishes. Int. J. Sys. Bac. 1986;; 36: 396–398.
Hikida M, Wakabayashi H, Egusa S, Masumura K. Flexibacter sp., a gliding bacterium pathogenic to some marine fishes in Japan. Bull. Jpn Soc. Sci. Fish. 1979; 45: 421–428.
Wakabayashi H, Hikida M, Masumura K. Flexibacter infection in cultured marine fish in Japan. Helgolander Meeresunters 1984; 37; 587–593.
Baxa DV, Kawai K, Kusuda R. Characteristics of gliding bacteria isolated from diseased cultured flounder. Paralich thys oliveceous. Fish Pathol. 1986; 21: 251–258.
Bernardet J-F, Kerouault B, Michel C. Comparative study on Flexibacter maritimus strains isolated from farmed sea bass (Dicenttrarchus labrax) in France. Fish Pathol. 1994; 29: 105–111.
Kusuda R, Salati F. Principali malattie batteriche dell’acquacoltura in Giappone. Atti delle Giornate Scientifiche ‘70mo dalla Fondazione’. Quaderni dell’Istituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale della Sardegna 1994; 173–186 (in Italian).
Bernardet J-F, Campbell AC, Buswell JF. Flexibacter maritimus is the agent of ‘black patch necrosis’ in dover sole in Scotland. Dis. Aqua. Organ. 1990; 8: 233–237.
Alsina M, Blanch AR. First isolation of Flexibacter maritimus from cultivated turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Bull. Eur. Ass. Fish Pathol. 1993; 13: 157–160.
Pepin JF, Emery E. Marine Cytophaga-Like Bacteria (CLB) isolated from diseased reared sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) from french mediterranean coast. Bull. Eur. Ass. Fish Pathol. 1993; 13: 165–167.
Pazos R, Santos Y, Nunez JS, Toranzo AE. Increasing occurence of Flexibacter maritimus in the marine aquaculture of Spain. FHS Newsletter 1993; 21: 1–2.
Salati F, Viale I, Meloni A. Lacquacoltura e lo stato sanitario dei pesci allevati in Sardegna. Boll. Soc. It. Pat. Ittica 1999; 27: 3–9 (in Italian).
Salati F, Meloni A, Cubadda C, Viale I. Prove di allevamento e patologie del dentice (Dentex dentex L.) in Sardegna. Boll. Soc. It. Pat. Ittica 2003; 38: 12–26 (in Italian).
Ellis AE. Immunization with bacterial antigen. Dev Biol. Standard 1997; 90: 107–116.
Westphal O, Jann K. Bacterial Lipopolysaccharides. Extraction with phenol-water and further applications of the procedure. In: Whistler RL, BeMiller JN, Wolfrom MI (eds). Methods in carbohydrate chemistry. Academic Press, New York. 1965; 5: 83–91.
Salati F, Kusuda R. Vaccine preparation used for immunization of eel Anguilla japonica against Edwardsiella tarda infection. Bull. Jpn Soc. Sci. Fish. 1985; 51: 1233–1237.
Takatsy G. Antigen-antibody reactions. In: Nowotny A (ed). Basic Exercices in Immunochemistry. Springer-Verlag New York Inc., New York, USA. 1969; 139–143.
Baxa D, Kawai K, Kusuda R. In vitro and in vivo activities of Flexibacter maritimus toxins. Rep. USA Mar. Biol. Inst. 1988; 10: 1–8.
Magarinos B, Pazos F, Santos Y, Romalde JL, Toranzo AE. Response of Pasteurella piscicida and Flexibacter maritimus to skin mucus of marine fish. Dis. Aqua. Organ. 1995; 21: 103–108.
Al-Harbi AH, Austin B, Purification of macroglobulins from the serum, and skin and gut mucus of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) immunized with Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from a fish-pathogenic Cytophaga-Like Bacterium (CLB). Bull. Eur. Ass. Fish Pathol. 1993; 13: 40–44.
Rahman MH, Ootake M, Lida Y, Yokomizo Y, Nakanishi T. Efficacy of Oil-Adjuvanted vaccine for coldwater disease in Ayu Plecoglossus altivelis. Fish Pathol. 2000; 35: 199–203.
Salati F, Kawai K, Kusuda R. Immune response of eel against Edwardsiella tarda antigens. Fish Pathol. 1983; 18: 135–141.
Salati F, Hamaguchi M, Kusuda R. Immune response of sea bream to Edwardsiella tarda antigens. Fish Pathol. 1987; 22: 93–98.
Salati F, Ikeda Y, Kusuda R. Effect of Edwardsiella tarda lipopolysaccharide immunization on phagocytosis in the eel. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1987; 53: 201–204.
Salati F, Kusuda R. Immune response of eel (Anguilla japonica) to lipopolysaccharides from serologically different strains of Edwardsiella tarda. Riv. It. Acquacolt 1991; 26: 111–117.
Salati F. Vaccination against Edwardsiella tarda. In: Ellis AE (ed). Fish Vaccination. Academic Press, London, 1988; 135–151.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salati, F., Cubadda, C., Viale, I. et al. Immune response of sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax to Tenacibaculum maritimum antigens. Fish Sci 71, 563–567 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1444-2906.2005.01000.x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1444-2906.2005.01000.x