Abstract
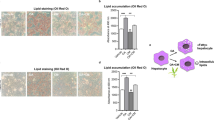
Phytanic acid is a derivative of the phytol side-chain of chlorophyll. It appears in humans following the ingestion of fat-containing foods and is present in human blood at a low micromolar concentration. It may activate retinoid X receptors (RXR) or peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) α in vitro. Phytanic acid induced the adipocyte differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells in culture as assessed by accumulation of lipid droplets and induction of the aP2 mRNA marker. This effect was mimicked by a synthetic activator of RXR but not by a PPARα agonist or by palmitic acid. In human pre-adipocytes in primary culture, phytanic acid also induced adipocyte differentiation. These findings indicate that phytanic acid may act as a natural rexinoid in adipose cells and suggest a potential use in the treatment of human type 2 diabetes and obesity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Verhoeven NM, Wanders RJ, Poll-The BT, Saudubray JM, Jakobs C . The metabolism of phytanic acid and pristanic acid in man: a review J Inherit Metab Dis 1998 21: 697–728.
Kitareewan S, Burka LT, Tomer KB, Parker CE, Deterding LJ, Stevens RD, Forman BM, Mais DE, Heyman RA, McMorris T, Weinberger C . Phytol metabolites are circulating dietary factors that activate the nuclear receptor RXR Mol Biol Cell 1996 7: 1153–1166.
Ellinghaus P, Wolfrum C, Assmann G, Spener F, Seedorf U . Phytanic acid activates the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) in sterol carrier protein 2-/sterol carrier protein x-deficient mice J Biol Chem 1999 274: 2766–2772.
Avigan J . The presence of phytanic acid in normal human and animal plasma Biochim Biophys Acta 1966 116: 391–394.
Mukherjee R, Davies PJ, Crombie DL, Bischoff ED, Cesario RM, Jow L, Hamann LG, Boehm MF, Mondon CE, Nadzan AM, Paterniti JR Jr, Heyman RA . Sensitization of diabetic and obese mice to insulin by retinoid X receptor agonists Nature 1997 386: 407–410.
Neve BP, Fruchart JC, Staels B . Role of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR) in atherosclerosis Biochem Pharmac 2000 60: 1245–1250.
Schlüter A, Barberá MJ, Iglesias R, Giralt M, Villarroya F . Phytanic acid, a novel activator of uncoupling protein-1 gene transcription and brown adipocyte differentiation Biochem J 2001 362: 61–69.
Laughton C . Measurement of the specific lipid content of attached cells in microtiter cultures Anal Biochem 1986 156: 307–314.
Tontonoz P, Singer S, Forman BM, Sarraf P, Fletcher JA, Fletcher CD, Brun RP, Mueller E, Altiok S, Oppenheim H, Evans RM, Spiegelman BM . Terminal differentiation of human liposarcoma cells induced by ligands for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and the retinoid X receptor Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999 94: 237–241.
Brun RP, Tontonoz P, Forman BM, Ellis R, Chen J, Evans RM, Spiegelman BM . Differential activation of adipogenesis by multiple PPAR isoforms Genes Devl 1996 10: 974–984.
Liu YL, Sennitt MV, Hislop DC, Crombie DL, Heyman RA, Cawthorne MA . Retinoid X receptor agonists have anti-obesity effects and improve insulin sensitivity in Zucker fa/fa rats Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2000 24: 997–1004.
McCarty MF . The chlorophyll metabolite phytanic acid is a natural rexinoid-potential for treatment and prevention of diabetes Med Hypoth 2001 56: 217–219.
Acknowledgements
Thanks are given to B Spiegelman (Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, MA, USA) for the aP2 probe. This work was supported by grant PM98-0188 from Ministerio de Educación y Cultura (Spain) and SGR99-38 from Generalitat de Catalunya.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schlüter, A., Yubero, P., Iglesias, R. et al. The chlorophyll-derived metabolite phytanic acid induces white adipocyte differentiation. Int J Obes 26, 1277–1280 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802068
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802068
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Chemical characterization of the lipophilic extract of Hydrilla verticillata: a widely spread aquatic weed
Journal of Plant Biochemistry and Biotechnology (2013)
-
Effect of vitamin A content in cafeteria diet on the expression of nuclear receptors in rat subcutaneous adipose tissue
Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry (2005)