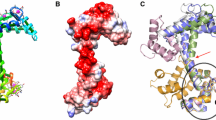
Abstract
The S100 calcium-binding proteins are implicated as effectors in calcium-mediated signal transduction pathways. The three-dimensional structure of the S100 protein calcyclin has been determined in solution in the apo state by NMR spectroscopy and a computational strategy that incorporates a systematic docking protocol. This structure reveals a symmetric homodimeric fold that is unique among calcium-binding proteins. Dimerization is mediated by hydrophobic contacts from several highly conserved residues, which suggests that the dimer fold identified for calcyclin will serve as a structural paradigm for the S100 subfamily of calcium-binding proteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Donato, R. Perspectives in S-100 protein biology. Cell Calc. 12, 713–726 (1991).
Hilt, D.C. & Kligman, D. in The S-100 protein family: a biochemical and functional overview. Novel calcium-binding proteins, (ed. C.W. Heizmann) 65–103 (Springer-Verlag, New York, 1991).
Engelkamp, D., Schafer, B.W., Mattei, M.G., Erne, P. & Heizmann, C.W. Six S100 genes are clustered on human chromosome 1q21: identification of two genes coding for the two previously unreported calcium-binding protein S100D and S100E. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90, 6547–6551 (1993).
Schafer, B.W., Wicki, R., Engelkamp, D., Mattei, M.G. & Heizmann, C.W. Isolation of a YAC clone covering a cluster of nine S100 genes on human chromosome 1q21: rationale for a new nomenclature of the S100 calcium-binding protein family. Genomics 25, 638–643 (1995).
Calabretta, B. et al. Cell-cycle-specific genes differentially expressed in human leukemias. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 4463–4467 (1985).
Calabretta, B. et al. Altered expression of G1 specific genes in human myeloid cells. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 1495–1498 (1986).
Murphy, L.C., Murphy, L.J., Tsuyuki, D., Duckworth, M.L. & Shiu, R.P.C. Cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding a highly conserved, putative calcium binding protein, identified by an anti-prolactin receptor antiserum. J. biol. Chem. 263, 2397–2401 (1988).
Hirschhorn, R.R., Aller, P., Yuan, Z., Gibson, C.W. & Baserga, R. Cell-cycle-specific cDNAs from mammalian cells temperature sensitive for growth. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 6004–6008 (1984).
Ferrari, S. et al. Structural and functional analysis of a growth-regulated gene, the human calcyclin. J. biol. Chem. 262, 8325–8332 (1987).
Tokumitsu, H., Mizutani, A., Minami, H., Kobayashi, R. & Hidaka, H. A calcyclin-associated protein is a newly identified member of the Ca2+/phospholipid-binding proteins, annexin family. J. biol. Chem. 267, 8919–8924 (1992).
Minami, H. et al. Specific binding of CAP-50 to calcyclin. FEBS Lett. 305, 217–219 (1992).
Tokumitsu, H., Mizutani, A. & Hidaka, H. Calcyclin-binding site located on the NH2-terminal domain of rabbit CAP-50 (annexin XI): functional expression of CAP-50 in Escherichia coli. Arch. biochem. Biophys. 303, 302–306 (1993).
Mizutani, A. et al., CAP-50, a newly identified annexin, localizes in nuclei of cultured fibroblast 3Y1 cells. J. biol. Chem. 267, 13498–13504 (1992).
Baudier, J. & Cole, R.D. Interactions between the microtubule-associated τ proteins and S100b regulate τ phosphorylation by the Ca2+/ calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. J. biol. Chem. 263, 5876–5883 (1988).
Gerke, V. & Weber, K. The regulatory chain in the p36-kd substrate complex of viral tyrosine-specific proteins is related in sequence to the S-100 protein of glial cells. EMBO J. 4, 2917–2920 (1985).
Glenney Jr., J.R. & Tack, B.F. Amino-terminal sequence of p36 and associated p10: identification of the site of tyrosine phosphorylation and homology with S-100. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 7884–7888 (1985).
McPhalen, C.A., Strynadka, N.C. & James, M.N. Calcium-binding sites in proteins: a structural perspective. Adv. Prot. Chem. 42, 77–144 (1991).
Szebenyi, D.M.E. & Moffat, K. The refined structure of vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein from bovine intestine. Molecular details, ion binding, and implications for the structure of other calcium-binding proteins. J. biol. Chem. 261, 8761–8777 (1986).
Svensson, L.A., Thulin, E. & Forsén, S., Proline cis-transisomers in calbindin D9k observed by X-ray crystallography. J. molec. Biol. 223, 601–606 (1992).
Kördel, J., Skelton, N.J., Akke, M. & Chazin, W.J. High-resolution solution structure of calcium-loaded calbindin D9k . J. molec. Biol. 231, 711–734 (1993).
Skelton, N.J., Kördel, J., & Chazin, W.J. Determination of the solution structure of apo calbindin D9k by NMR spectroscopy. J. molec. Biol. 249, 441–462 (1995).
Wüthrich, K. Protein structure determination in solution by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Science 243, 45–50 (1989).
Barger, S.W., Wolchok, S.R. & Van Eldik, L.J. Disulfide-linked S100β dimers and signal transduction. Biochim. biophys. Acta 1160, 105–112 (1992).
Teigelkamp, S. et al., Calcium-dependent complex assembly of the myeloic differentiation proteins MRP-8 and MRP-14. J. biol. Chem. 266, 13462–13467 (1991).
Gerke, V. & Weber, K. Calcium-dependent conformational changes in the 36-kDa subunit of intestinal protein I related to the cellular 36-kDa target of Rous sarcoma virus tyrosine kinase. J. biol. Chem. 260, 1688–1695 (1985).
Dell'Angelica, E.C., Schleicher, C.H. & Santome, J.A. Primary structure and binding properties of calgranulin C, a novel S100-like calcium-binding protein from pig granulocytes. J. biol. Chem. 269, 28929–28936 (1994).
Pedrocchi, M., Schafer, B.W., Durussel, I., Cox, J.A. & Heizmann, C.W. Purification and characterization of the recombinant human calcium-binding S100 proteins CAPL and CACY. Biochemistry 33, 6732–6738 (1994).
Skelton, N.J., Kordel, J., Forsen, S. & Chazin, W.J. Comparative structural analysis of the calcium free and bound states of the calcium regulatory protein calbindin D9k . J. molec. Biol. 213, 539–598 (1990).
Kilby, P.M., Van Eldik, L.J. & Roberts, G.C.K. Nuclear magnetic resonance assignments and secondary structure of bovine S100β protein. FEBS Lett. 363, 90–96 (1995).
Crivici, A. & Ikura, M. Molecular and structural basis of target recognition by calmodulin. A. Rev. Biophys. biomol. Struct. 24, 85–116 (1995).
Wojda, U. & Kuznicki, J. Calcyclin from mouse Ehrlich ascites tumor cells and rabbit lung form non-covalent dimers. Biochim. biophys. Acta 1209, 248–252 (1994).
Kuznicki, J., Filipek, A., Hunziker, P., Huber, S. & Heizmann, C.W. Calcium-binding protein from mouse Ehrlich ascites-tumour cells is homologous to human calcyclin. Biochem. J. 263, 951–956 (1989).
Ando, Y., Watanabe, M., Akatsuka, H., Tokumitsu, H. & Hidaka, H. Site-directed mutation makes rabbit calcyclin dimer. FEBS Lett. 314, 109–113 (1992).
Johnsson, N. & Weber, K. Alkylation of cysteine 82 of p11 abolishes the complex formation with the tyrosine-protein kinase substrate p36 (annexin 2, calpactin 1, lipocortin 2). J. biol. Chem. 265, 14464–14468 (1990).
Kube, E., Becker, T., Weber, K. & Gerke, V. Protein-protein interaction studied by site-directed mutagenesis. Characterization of the annexin ll-binding site on p11, a member of the S100 protein family. J. biol. Chem. 267, 14175–14182 (1992).
Tokumitsu, H., Kobayashi, R. & Hidaka, H. A calcium-binding protein from rabbit lung cytosol identified as the product of a growth-regulated gene (2A9) and its binding proteins. Arch. biochem. Biophys. 288, 202–207 (1991).
Ludvigsen, S. & Poulsen, F.M. Positive φ-angles in proteins by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. biomol. NMR 2, 227–233 (1992).
Pearlman, D.A., Case, D.A., Yip, P. SANDER/AMBER 4.0. San Francisco, University of California, 1991.
Weiner, S.J., Kollman, P.A., Nguyen, D.T., & Case, D.A. An all-atom force field for simulations of proteins and nucleic acids. J. comput. Chem. 7, 230–252 (1986).
Connolly, M.L. Solvent-accessible surfaces of proteins and nucleic acids. Science 221, 709–713 (1983).
Chothia, C., Levitt, M. & Richardson, D. Helix to helix packing in proteins. J. molec. Biol. 145, 215–250 (1981).
Duncan, B., Macke, T. & Olson, A. Biomolecular visualization using AVS. J. molec. Graphics, in the press.
Duncan, B., Pique, M. & Olson, A. AVS for molecular modeling. Proc. AVS Conf. (1993).
Strynadka, N.C.J. & James, M.N.G. Crystal structures of the helix-loop-helix calcium-binding proteins. A. Rev. Biochem. 58, 951–998 (1989).
Kawasaki, H. & Kretsinger, R.H. Calcium-binding proteins 1: EF-hands. Protein Profile 1, 343–517 (1994).
Carsen, M. Ribbons 2.0. J. appl. Crystallogr. 24, 958–961 (1991).
Sanner, M.F., Olson, A.J. & Spehner, J.C. Fast and robust computation of molecular surfaces. Proc. 11th ACM Symp. comp. Geom. C6–C7 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Potts, B., Smith, J., Akke, M. et al. The structure of calcyclin reveals a novel homodimeric fold for S100 Ca2+-binding proteins. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2, 790–796 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0995-790
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0995-790
- Springer Nature America, Inc.
This article is cited by
-
Proteomics reveals that quinoa bioester promotes replenishing effects in epidermal tissue
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Binding of transition metals to S100 proteins
Science China Life Sciences (2016)
-
Solution structure of human Ca2+-bound S100A12
Journal of Biomolecular NMR (2013)
-
Transgenic expression of S100A2 in hairless mouse skin enhances Cxcl13 mRNA in response to solar-simulated radiation
Archives of Dermatological Research (2009)
-
Observation of μs time-scale protein dynamics in the presence of Ln3+ ions: application to the N-terminal domain of cardiac troponin C
Journal of Biomolecular NMR (2007)