Abstract
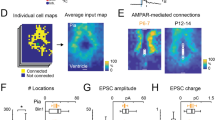
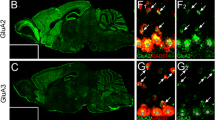
Anatomical and electrophysiological experiments1,2,3,4,5,6 show that central excitatory synapses initially display NMDA (N-methyl-d-aspartate) receptors (NMDARs) and subsequently mature by acquiring AMPA (α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid) receptors (AMPARs). NMDAR activation can lead to rapid synaptic delivery of AMPARs ('AMPAfication')7,8, but the view that AMPAfication during development requires NMDAR activation has been challenged by studies showing that chronic removal of NMDAR function (either genetically9,10 or pharmacologically11,12,13,14) has no apparent effect on acquisition of AMPAR-mediated synaptic transmission. Here we show that NMDARs are crucial in the developmental acquisition of AMPAR-mediated synaptic transmission, and that chronic disabling of NMDAR function triggers compensatory mechanisms for NMDAR-independent AMPAfication.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Durand, G.M., Kovalchuk, Y. & Konnerth, A. Nature 381, 71–75 (1996).
Wu, G., Malinow, R. & Cline, H.T. Science 274, 972–976 (1996).
Isaac, J.T., Crair, M.C., Nicoll, R.A. & Malenka, R.C. Neuron 18, 269–280 (1997).
Nusser, Z. et al. Neuron 21, 545–559 (1998).
Petralia, R.S. et al. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 31–36 (1999).
Zhu, J.J., Esteban, J.A., Hayashi, Y. & Malinow, R. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 1098–1106 (2000).
Hayashi, Y. et al. Science 287, 2262–2267 (2000).
Liao, D., Scannevin, R.H. & Huganir, R. J. Neurosci 21, 6008–6017 (2001).
Li, Y., Erzurumlu, R.S., Chen, C., Jhaveri, S. & Tonegawa, S. Cell 76, 427–437 (1994).
Kutsuwada, T. et al. Neuron 16, 333–344 (1996).
Rao, A. & Craig, A.M. Neuron 19, 801–812 (1997).
O'Brien, R.J. et al. Neuron 21, 1067–1078 (1998).
Gomperts, S.N., Carroll, R., Malenka, R.C. & Nicoll, R.A. J. Neurosci. 20, 2229–2237 (2000).
Luthi, A., Schwyzer, L., Mateos, J.M., Gahwiler, B.H. & McKinney, R.A. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 1102–1107 (2001).
Hsia, A.Y., Malenka, R.C. & Nicoll, R.A. J. Neurophysiol. 79, 2013–2024 (1998).
Acknowledgements
We thank N. Dawkins-Pisani for technical assistance, and H. Cline and members of the Malinow laboratory for helpful comments and discussions. This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health (R.M.), the Alle Davis and Maxine Harrison Endowment (R.M.), the Alzheimer's Association (J.J.Z.) and the Fraxa Medical Research Foundation (J.J.Z.). J.J.Z. is a Naples Investigator of the NARSAD (National Alliance for Research on Schizophrenia and Depression) Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, J., Malinow, R. Acute versus chronic NMDA receptor blockade and synaptic AMPA receptor delivery. Nat Neurosci 5, 513–514 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn0602-850
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn0602-850
- Springer Nature America, Inc.
This article is cited by
-
A critical role for VEGF and VEGFR2 in NMDA receptor synaptic function and fear-related behavior
Molecular Psychiatry (2016)
-
AMPA-silent synapses in brain development and pathology
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2013)
-
Up-regulation of Ras/Raf/ERK1/2 signaling impairs cultured neuronal cell migration, neurogenesis, synapse formation, and dendritic spine development
Brain Structure and Function (2013)
-
Increased midgestational IFN-γ, IL-4 and IL-5 in women bearing a child with autism: A case-control study
Molecular Autism (2011)
-
Abnormal Glutamate Receptor Expression in the Medial Temporal Lobe in Schizophrenia and Mood Disorders
Neuropsychopharmacology (2007)