Abstract
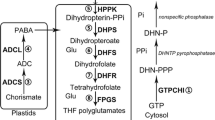
Rice, the world's major staple crop, is a poor source of essential micronutrients, including folates (vitamin B9). We report folate biofortification of rice seeds achieved by overexpressing two Arabidopsis thaliana genes of the pterin and para-aminobenzoate branches of the folate biosynthetic pathway from a single locus. We obtained a maximal enhancement as high as 100 times above wild type, with 100 g of polished raw grains containing up to four times the adult daily folate requirement.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Geisel, J. J. Perinat. Neonatal Nurs. 17, 268–279 (2003).
Li, G.M., Presnell, S.R. & Gu, L.Y. J. Nutr. Biochem. 14, 568–575 (2003).
Berry, R.J. & Li, Z. Epidemiology 13, 114–116 (2002).
Storozhenko, S. et al. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 16, 271–281 (2005).
Diaz de la Garza, R.I., Gregory, J.F., III & Hanson, A.D. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 4218–4222 (2007).
de la Garza, R. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 13720–13725 (2004).
Sohta, Y., Ohta, T. & Masada, M. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 61, 1081–1085 (1997).
Nakase, M. et al. Gene 170, 223–226 (1996).
Takaiwa, F., Oono, K., Wing, D. & Kato, A. Plant Mol. Biol. 17, 875–885 (1991).
Zhang, G.F. et al. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 19, 963–969 (2005).
Patarca, R. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 22, 117–127 (2003).
Oakley, G.P. Teratology 66, 44–54 (2002).
Gutstein, S., Bernstein, L.H., Levy, L. & Wagner, G. Dig. Dis. 18, 142–146 (1973).
Melse-Boonstra, A. et al. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 79, 424–429 (2004).
Sauberlich, H.E. et al. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 46, 1016–1028 (1987).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from Ghent University (Bijzonder Onderzoeksfonds, GOA 1251204) to D.V.D.S. and W.L.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.S., experimental design, molecular cloning and analysis of transgenic lines; M.V., rice transformation, plant culture and genomic DNA isolation; O.N. and D.B., expression analysis; V.D.B., G.-F.Z. and W.L., development and application of chromatographic analyses; D.V.D.S., experimental design, initiation and coordination of the research project.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–3, Supplementary Tables 1–4, Supplementary Methods, Supplementary Note (PDF 760 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Storozhenko, S., De Brouwer, V., Volckaert, M. et al. Folate fortification of rice by metabolic engineering. Nat Biotechnol 25, 1277–1279 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1351
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1351
- Springer Nature America, Inc.