Abstract
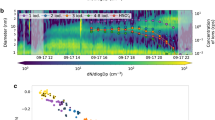
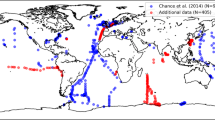
O'Dowd et al. reply - McFiggans1 raises some interesting, but partly speculative, issues about the possibility of additional condensable-iodine-vapour (CIV) precursors being involved in marine aerosol formation from biogenic iodine emissions, and about the relative roles of iodine oxide and sulphuric acid in the marine new-particle formation process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McFiggans, G. Nature doi:10.1038/nature03372 (2005).
O'Dowd, C. et al. Nature 417, 632–636 (2002).
Yoon, Y. J. et al. Proc. 16th Intl Conf. Nucleation and Atmospheric Aerosols, Kyoto (eds Kasahara, M. & Kulmala, M.) 674–677 (Kyoto University Press, 2004).
McFiggans, G. et al. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 4, 1–13 (2004).
Pirjola, L., O'Dowd, C. D., Brooks, I. M. & Kulmala, M. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 26531–26546 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O'Dowd, C., Jimenez, J., Bahreini, R. et al. Marine aerosols and iodine emissions (Reply). Nature 433, E13–E14 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03373
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03373
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Characterization of iodine species in the marine aerosol: To understand their roles in particle formation processes
Frontiers of Chemistry in China (2006)