Abstract
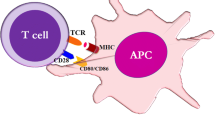
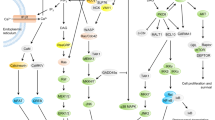
Ligation of T cell receptor (TCR) alone is insufficient to induce full activation of T lymphocytes. Additional ligand-receptor interactions (costimulation) on antigen presenting cells (APCs) and T cells are required. T cell costimulation has been shown to be essential for eliciting efficient T cell responses, involving all phases during T cell development. However, the mechanisms by which costimulation affects the function of T cells still need to be elucidated. In recent years, advances have been made in studies of costimulation as potential therapies in cancer, infectious disease as well as autoimmune disease. In this review, we discussed intracellular costimulation signals that regulate T cell proliferation, cell cycle progression, cytokine production, survival, and memory development. In general, the pathway of phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (PKB, also known as Akt)/nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) might be central to many costimulatory effects. Through these pathways, costimulation controls T-cell expansion and proliferation by maintenance of survivin and aurora B expression, and sustains long-term T-cell survival and memory development by regulating the expression of bcl-2 family members.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, J., Lei, F., Xiong, X. et al. Intracellular Signals of T Cell Costimulation. Cell Mol Immunol 5, 239–247 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2008.30
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2008.30
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Survivin but not Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 ligand is up-regulated before the onset of rheumatoid arthritis: a pilot study
Arthritis Research & Therapy (2014)
-
Vitamin C supplementation reconstitutes polyfunctional T cells in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
European Journal of Nutrition (2012)
-
Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the promoter region of the IL1B gene influence outcome in multiple myeloma patients treated with high-dose chemotherapy independently of relapse treatment with thalidomide and bortezomib
Annals of Hematology (2011)
-
T Cells Expressing Constitutively Active Akt Resist Multiple Tumor-associated Inhibitory Mechanisms
Molecular Therapy (2010)
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor signalling selectively regulates murine lymphocyte proliferation and maintenance of peripheral regulatory T cells
Diabetologia (2010)