Abstract
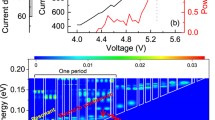
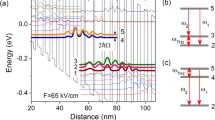
Semiconductor devices have become indispensable for generating electromagnetic radiation in everyday applications. Visible and infrared diode lasers are at the core of information technology, and at the other end of the spectrum, microwave and radio-frequency emitters enable wireless communications. But the terahertz region (1–10 THz; 1 THz = 1012 Hz) between these ranges has remained largely underdeveloped, despite the identification of various possible applications—for example, chemical detection, astronomy and medical imaging1,2,3,4. Progress in this area has been hampered by the lack of compact, low-consumption, solid-state terahertz sources5,6,7,8,9. Here we report a monolithic terahertz injection laser that is based on interminiband transitions in the conduction band of a semiconductor (GaAs/AlGaAs) heterostructure. The prototype demonstrated emits a single mode at 4.4 THz, and already shows high output powers of more than 2 mW with low threshold current densities of about a few hundred A cm-2 up to 50 K. These results are very promising for extending the present laser concept to continuous-wave and high-temperature operation, which would lead to implementation in practical photonic systems.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miles, R. E., Harrison, P. & Lippens, D. (eds) Terahertz Sources and Systems Vol. 27 (NATO Science Series II, Kluwer, Dordrecht, 2001)
Han, P. Y., Cho, G. C. & Zhang, X.-C. Time-domain transillumination of biological tissue with terahertz pulses. Opt. Lett. 25, 242–244 (2000)
Mittleman, D. M., Jacobsen, R. H. & Nuss, M. C. T-ray imaging. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. Electron. 2, 679–692 (1996)
Mittleman, D. M., Hunsche, S., Boivin, L. & Nuss, M. C. T-ray tomography. Opt. Lett. 22, 904–906 (1997)
Pavlov, S. G. et al. Stimulated emission from donor transitions in silicon. Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 5220–5223 (2000)
Matsuura, S., Tani, M. & Sakai, K. Generation of coherent terahertz radiation by photomixing in dipole photoconductive antennas. Appl. Phys. Lett. 70, 559–561 (1997)
Hu, B. B., Zhang, X.-C. & Auston, D. H. Terahertz radiation induced by subband-gap femtosecond optical excitation of GaAs. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 2709–2712 (1991)
Kersting, R., Unterrainer, K., Strasser, G., Kauffmann, H. F. & Gornik, E. Few-cycle THz emission from cold plasma oscillations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 79, 3038–3041 (1997)
Bründermann, E., Chamberlin, D. R. & Haller, E. E. High duty cycle and continuous terahertz emission from germanium. Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 2991–2993 (2000)
Faist, J. et al. Quantum cascade laser. Science 264, 553–556 (1994)
Rochat, M., Faist, J., Beck, M., Oesterle, U. & Ilegems, M. Far-infrared (λ = 88 µm) electroluminescence in a quantum cascade structure. Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 3724–3726 (1998)
Williams, B. S., Xu, B., Hu, Q. & Melloch, M. R. Narrow-linewidth terahertz intersubband emission from three-level systems. Appl. Phys. Lett. 75, 2927–2929 (1999)
Ulrich, J., Zobl, R., Schrenk, W., Strasser, G. & Unterrainer, K. Terahertz quantum cascade structures: Intra- versus interwell transition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 1928–1930 (2000)
Helm, M., England, P., Colas, E., De Rosa, F. & Allen, S. J. Intersubband emission from semiconductor superlattices excited by sequential resonant tunnelling. Phys. Rev. Lett. 63, 74–77 (1989)
Colombelli, R. et al. Far-infrared surface-plasmon quantum-cascade lasers at 21.5 µm and 24 µm wavelengths. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 2620–2622 (2001)
Hofstetter, D., Beck, M., Aellen, T. & Faist, J. High-temperature operation of distributed feedback quantum-cascade lasers at 5.3 µm. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 396–398 (2001)
Köhler, R., Iotti, R. C., Tredicucci, A. & Rossi, F. Design and simulation of terahertz quantum cascade lasers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 79, 3920–3922 (2001)
Tredicucci, A. et al. High performance interminiband quantum cascade lasers with graded superlattices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 2101–2103 (1998)
Iotti, R. C. & Rossi, F. Nature of charge transport in quantum-cascade lasers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 146603-1–146603-4 (2001)
Iotti, R. C. & Rossi, F. Carrier thermalization versus phonon-assisted relaxation in quantum-cascade lasers: A Monte Carlo approach. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 2902–2904 (2001)
Sirtori, C. et al. Long-wavelength (λ∼8–11.5 µm) semiconductor lasers with waveguides based on surface plasmons. Opt. Lett. 23, 1366–1368 (1998)
Rochat, M., Beck, M., Faist, J. & Oesterle, U. Measurement of far-infrared waveguide loss using a multisection single-pass technique. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 1967–1969 (2001)
Köhler, R. et al. High-intensity interminiband terahertz emission from chirped superlattices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 1867 (2002)
Acknowledgements
We thank S. Dhillon for discussions.This work was supported in part by the European Commission through the IST Framework V FET project WANTED. R.K. was supported by the C.N.R.; E.H.L. and A.G.D were supported by Toshiba Research Europe Ltd and The Royal Society, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Köhler, R., Tredicucci, A., Beltram, F. et al. Terahertz semiconductor-heterostructure laser. Nature 417, 156–159 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/417156a
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/417156a
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Effects of background doping, interdiffusion and layer thickness fluctuation on the transport characteristics of THz quantum cascade lasers
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Electrically-pumped compact topological bulk lasers driven by band-inverted bound states in the continuum
Light: Science & Applications (2023)
-
M-plane GaN terahertz quantum cascade laser structure design and doping effect for resonant-phonon and phonon-scattering-injection schemes
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Ultrasmall and tunable TeraHertz surface plasmon cavities at the ultimate plasmonic limit
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Enhanced Delivery and Detection of Terahertz Frequency Radiation from a Quantum Cascade Laser Within Dilution Refrigerator
Journal of Low Temperature Physics (2023)